前不久,刚学习了jms的简单入门,后面紧接着就做了一个关于jms的负载均衡的项目,做完之后颇有打通任督二脉的感觉,感觉很多之前不是很理解的东西,都有些理解了,比如服务器端的监听、具体的jms的使用等,收获有点大。
流程如下图所示:
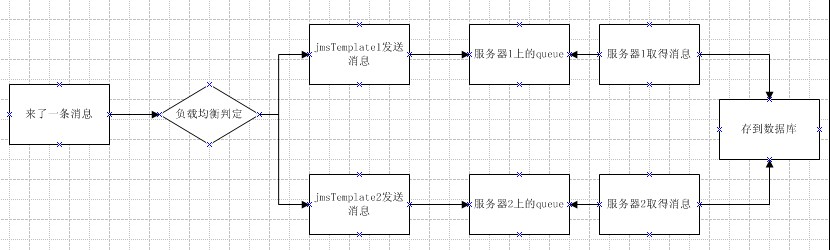
客户端:
xml配置,这里用到了两台服务器,connectionFactory便可以看出,因为传的是对象,用到了转换器
< beans xmlns ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-2.5.xsd" >
<!-- 配置JMS连接工厂 -->
<!-- <bean id="connectionFactory" class="org.apache.activemq.spring.ActiveMQConnectionFactory"> -->
<!-- <property name="brokerURL" value="tcp://localhost:61616" /> -->
<!-- </bean> -->
< bean id ="connectionFactory" class ="org.apache.activemq.pool.PooledConnectionFactory" destroy-method ="stop" >
< property name ="connectionFactory" >
< bean class ="org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnectionFactory" >
< property name ="brokerURL" >
< value >tcp://localhost:61616 </ value >
</ property >
< property name ="useAsyncSend" >
< value >true </ value >
</ property >
</ bean >
</ property >
</ bean >
< bean id ="connectionFactory_1" class ="org.apache.activemq.pool.PooledConnectionFactory" destroy-method ="stop" >
< property name ="connectionFactory" >
< bean class ="org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnectionFactory" >
< property name ="brokerURL" >
< value >tcp://192.168.130.13:61616 </ value >
</ property >
< property name ="useAsyncSend" >
< value >true </ value >
</ property >
</ bean >
</ property >
</ bean >
<!-- 发送消息的目的地(一个队列) -->
< bean id ="destination" class ="org.apache.activemq.command.ActiveMQQueue" >
<!-- 设置消息队列的名字 -->
< constructor-arg index ="0" value ="activeMQQueue" />
</ bean >
<!-- 消息转换 -->
< bean id ="messageConverter" class ="com.pis.activeMQ.ObjectMessageConverter" />
<!-- 配置JMS模版 -->
< bean id ="jmsTemplate_1" class ="org.springframework.jms.core.JmsTemplate" >
< property name ="connectionFactory" ref ="connectionFactory" />
< property name ="messageConverter" ref ="messageConverter" />
</ bean >
< bean id ="jmsTemplate_2" class ="org.springframework.jms.core.JmsTemplate" >
< property name ="connectionFactory" ref ="connectionFactory_1" />
< property name ="messageConverter" ref ="messageConverter" />
</ bean >
<!-- 生产消息配置 -->
< bean id ="queueProducer" class ="com.pis.activeMQ.client.MessageProducer" >
< property name ="destination" ref ="destination" />
< property name ="jmsTemplate" >
< list >
< ref bean ="jmsTemplate_1" />
< ref bean ="jmsTemplate_2" />
</ list >
</ property >
</ bean >
<!-- 生产消息action bean -->
< bean id ="jmsAction" class ="com.pis.action.JmsAction" >
< property name ="queueProducer" ref ="queueProducer" />
</ bean >
</ beans >
转换器如下所示: 转来转去有点恶心的代码 O(∩_∩)O~
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import javax.jms.JMSException;
import javax.jms.Message;
import javax.jms.ObjectMessage;
import javax.jms.Session;
import org.springframework.jms.support.converter.MessageConversionException;
import org.springframework.jms.support.converter.MessageConverter;
public class ObjectMessageConverter implements MessageConverter{
// 从消息中取出对象
@Override
public Object fromMessage(Message message) throws JMSException,MessageConversionException {
Object object = null;
if(message instanceof ObjectMessage) {
// 两次强转,获得消息中的主体对象字节数组流
byte[] obj = ( byte[])((ObjectMessage)message).getObject();
// 读取字节数组中为字节数组流
ByteArrayInputStream bis = new ByteArrayInputStream(obj);
try {
// 读字节数组流为对象输出流
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(bis);
// 从对象输出流中取出对象 并强转
object = ois.readObject();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return object;
}
// 将对象转换成消息
@Override
public Message toMessage(Object object, Session session) throws JMSException,MessageConversionException {
ObjectMessage objectMessage = session.createObjectMessage();
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); // 字节数组输出流
try {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos); // 对象输出流
oos.writeObject(object); // 写入对象
byte[] objMessage = bos.toByteArray(); // 字节数组输出流转成字节数组
objectMessage.setObject(objMessage); // 将字节数组填充到消息中作为消息主体
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return objectMessage;
}
}
生产者 这里用到了原子类来计数,避免使用线程同步,也是第一次接触,convertAndSend方法会调用转换器,把对象转换成消息类型
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
import org.apache.activemq.command.ActiveMQQueue;
import org.springframework.jms.core.JmsTemplate;
import com.pis.model.Product;
public class MessageProducer {
private ActiveMQQueue destination;
private List<JmsTemplate> jmsTemplate;
private Product product;
// 原子整型计数(CAS),可以不使用同步
private AtomicInteger current = new AtomicInteger(0);
// 轮询算法解决负载均衡
private JmsTemplate findJmsTemplate(){
int cur = current.getAndIncrement();
int index = cur%jmsTemplate.size();
return jmsTemplate.get(index);
}
// 发送消息
public void sendMessage(Product product){
this.findJmsTemplate().convertAndSend(destination, product);
}
public ActiveMQQueue getDestination() {
return destination;
}
public void setDestination(ActiveMQQueue destination) {
this.destination = destination;
}
public List<JmsTemplate> getJmsTemplate() {
return jmsTemplate;
}
public void setJmsTemplate(List<JmsTemplate> jmsTemplate) {
this.jmsTemplate = jmsTemplate;
}
public Product getProduct() {
return product;
}
public void setProduct(Product product) {
this.product = product;
}
}
服务器端:
xml配置如下:这里只是我本机的服务器配置,另外一台如法炮制,这里用到了监听器,见名知意,大概干嘛用的一看就知道,有消息是会触发监听器,监听器指定使用queueConsumer中的receive方法,这就很清楚了,来一条收一条,来两条收一双。
< beans xmlns ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-2.5.xsd" >
< bean id ="connectionFactory" class ="org.apache.activemq.pool.PooledConnectionFactory" destroy-method ="stop" >
< property name ="connectionFactory" >
< bean class ="org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnectionFactory" >
< property name ="brokerURL" >
< value >tcp://localhost:61616 </ value >
</ property >
< property name ="useAsyncSend" >
< value >true </ value >
</ property >
</ bean >
</ property >
</ bean >
<!-- 发送消息的目的地(一个队列) -->
< bean id ="destination" class ="org.apache.activemq.command.ActiveMQQueue" >
<!-- 设置消息队列的名字 -->
< constructor-arg index ="0" value ="activeMQQueue" />
</ bean >
<!-- 消息转换 -->
< bean id ="messageConverter" class ="com.pis.activeMQ.ObjectMessageConverter" />
<!-- 生产消息配置 -->
< bean id ="queueConsumer" class ="com.pis.activeMQ.server.MessageConsumer" />
< bean id ="queueListener" class ="org.springframework.jms.listener.adapter.MessageListenerAdapter" >
< constructor-arg ref ="queueConsumer" />
< property name ="defaultListenerMethod" value ="receive" />
< property name ="messageConverter" ref ="messageConverter" />
</ bean >
< bean id ="queueListenerContainer" class ="org.springframework.jms.listener.DefaultMessageListenerContainer" >
< property name ="connectionFactory" ref ="connectionFactory" />
< property name ="destination" ref ="destination" />
< property name ="messageListener" ref ="queueListener" />
</ bean >
</beans>
消费者 很简洁的代码
import com.pis.model.Product;
public class MessageConsumer {
public void receive(Product product) {
// 如果消费到了就会打印出来
System.out.println("server端收到消息:"+product.getName());
}
}
好了,我这是个struts2+spring的代码,有了第一个xml中的jmsAction的配置,下面就是action的代码
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
import com.pis.activeMQ.client.MessageProducer;
import com.pis.model.Product;
public class JmsAction extends ActionSupport {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 132132131312L;
private MessageProducer queueProducer;
private Product product;
@Override
public String execute() throws Exception {
System.out.println(product.getName());
queueProducer.sendMessage(product);
return null;
}
public MessageProducer getQueueProducer() {
return queueProducer;
}
public void setQueueProducer(MessageProducer queueProducer) {
this.queueProducer = queueProducer;
}
public Product getProduct() {
return product;
}
public void setProduct(Product product) {
this.product = product;
}
}
product类,记得要实现serializable方法!
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Product implements Serializable{
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
好吧,struts中的配置我就不给了,太简单了,直接访问 localhost:8060/pis/produceMessage.action?product.name=85252 顺便说下,由于懒,这里我就直接把product实体类当成参数传进去了,吼吼,没有界面……懒吧
期间测试可以看http://localhost:8161/admin/queues.jsp 和http://192.168.130.13:8161/admin/queues.jsp可以很明显的看出每次浏览器回车一下,只有其中的一个消息多列一条,完美实现了负载均衡,并且对object类型的message队列学习了一下,收获很大




 本文通过Struts2+Spring框架实现了一个JMS负载均衡的项目案例。详细介绍了客户端和服务端的XML配置,包括连接工厂、消息队列、消息转换器等组件的设置,并展示了如何通过轮询算法实现负载均衡。
本文通过Struts2+Spring框架实现了一个JMS负载均衡的项目案例。详细介绍了客户端和服务端的XML配置,包括连接工厂、消息队列、消息转换器等组件的设置,并展示了如何通过轮询算法实现负载均衡。
















 1092
1092

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








