Radar Installation
Time Limit: 1000MS
Memory Limit: 10000K
Total Submissions: 15638
Accepted: 3116
Description
Assume the coasting is an infinite straight line. Land is in one side of coasting, sea in the other. Each small island is a point locating in the sea side. And any radar installation, locating on the coasting, can only cover d distance, so an island in the sea can be covered by a radius installation, if the distance between them is at most d.
We use Cartesian coordinate system, defining the coasting is the x-axis. The sea side is above x-axis, and the land side below. Given the position of each island in the sea, and given the distance of the coverage of the radar installation, your task is to write a program to find the minimal number of radar installations to cover all the islands. Note that the position of an island is represented by its x-y coordinates.
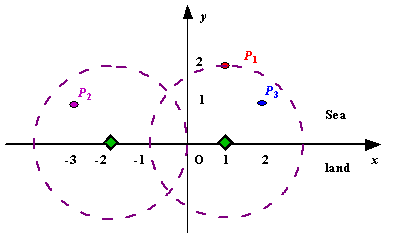
Figure A Sample Input of Radar Installations
Input
The input consists of several test cases. The first line of each case contains two integers n (1<=n<=1000) and d, where n is the number of islands in the sea and d is the distance of coverage of the radar installation. This is followed by n lines each containing two integers representing the coordinate of the position of each island. Then a blank line follows to separate the cases.
The input is terminated by a line containing pair of zeros
Output
For each test case output one line consisting of the test case number followed by the minimal number of radar installations needed. "-1" installation means no solution for that case.
Sample Input
3 2 1 2 -3 1 2 1 1 2 0 2 0 0
Sample Output
Case 1: 2 Case 2: 1
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Solution:
1. For each island, get the min and max value of x for the radar to cover it. Call this tuple (min, max) the radar-possible-area. RPA
2. Collapse any two RPA if they intersect with each other into their common area.
3. Now the remaining RPAs are independent to any other. The number of the RPAs are the minimal # radars we need to cover all the island.
Conclusion:
This problem is fairly easy using the greedy algorithm, but it is a good warm-up exercise.




 本文介绍了一种使用贪婪算法解决海岸线上雷达安装问题的方法。目标是最小化覆盖所有海上岛屿所需的雷达数量。通过计算每个岛屿对应的雷达可能区域,并将相交的区域合并,最后得到的独立区域数量即为所需雷达的最小数量。
本文介绍了一种使用贪婪算法解决海岸线上雷达安装问题的方法。目标是最小化覆盖所有海上岛屿所需的雷达数量。通过计算每个岛屿对应的雷达可能区域,并将相交的区域合并,最后得到的独立区域数量即为所需雷达的最小数量。
















 737
737

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








