Accept: 185 Submit: 679
Time Limit: 3000 mSec
Problem Description
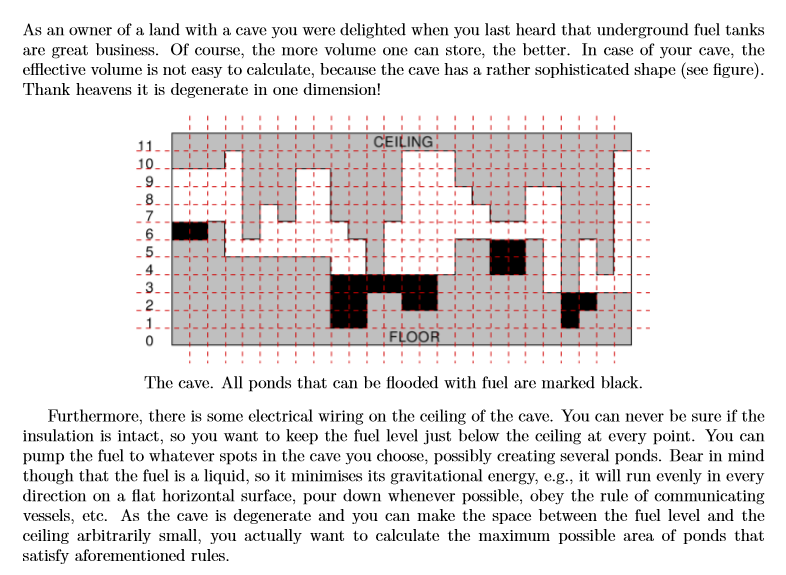
Input
The input contains several test cases. The first line of the input contains a positive integer Z ≤ 15, denoting the number of test cases. Then Z test cases follow, each conforming to the format described below. In the first line of an input instance, there is an integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 106) denoting the width of the cave. The second line of input consists of n integers p1,p2,...,pn and the third line consists of n integers s1,s2,...,sn, separated by single spaces. The numbers pi and si satisfy 0 ≤ pi < si ≤ 1000 and denote the floor and ceiling level at interval [i,i + 1), respectively.
Output
Sample Input
15
6 6 7 5 5 5 5 5 5 1 1 3 3 2 2
10 10 10 11 6 8 7 10 10 7 6 4 7 11 11
Sample Output
14
题解:扫描法。对于每一个单位小区间[i,i+1],它的最高高度应该满足,在这个高度向左右两边发出两条射线,这两条射线应穿出洞穴或者碰到下面的墙壁,这样一来,我们就可以用扫描法从左到右和从右到左分别进行扫描,从左到右扫描时只看左边的射线,右边同理。扫描的过程,其实就是在维护一个最高高度,由物理的连通器原理,当前单位小区间的高度不应高于左边的小区间,但是如果该区间和左边不连通,那就可以大于左边的高度,这种情况也就是该处墙壁最低点高于左边水位,如果当前高度大于上面的墙壁,那么肯定要降低到上面墙壁的高度,利用这样两条规则就可以扫描出合理的最高高度。
1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 3 using namespace std; 4 5 const int maxn = 1000000 + 100; 6 7 int n; 8 int low[maxn], high[maxn]; 9 int h[maxn]; 10 11 int main() 12 { 13 //freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin); 14 int iCase; 15 scanf("%d", &iCase); 16 while (iCase--) { 17 scanf("%d", &n); 18 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { 19 scanf("%d", &low[i]); 20 } 21 for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) { 22 scanf("%d", &high[j]); 23 } 24 25 int level = high[1]; 26 h[1] = level; 27 for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) { 28 if (level > high[i]) level = high[i]; 29 if (level < low[i]) level = low[i]; 30 h[i] = level; 31 } 32 33 h[n] = min(h[n], high[n]); 34 level = h[n]; 35 for (int i = n - 1; i >= 1; i--) { 36 if (level > high[i]) level = high[i]; 37 if (level < low[i]) level = low[i]; 38 h[i] = min(h[i], level); 39 } 40 41 int ans = 0; 42 43 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { 44 ans += h[i] - low[i]; 45 } 46 47 printf("%d\n", ans); 48 } 49 return 0; 50 }







 本文介绍了一种解决UVA1442-Cav问题的有效算法——扫描法。通过两次扫描(从左到右和从右到左),确定了洞穴中能够形成的最大面积的水塘。具体步骤包括初始化最高水平面、考虑墙壁限制条件等。
本文介绍了一种解决UVA1442-Cav问题的有效算法——扫描法。通过两次扫描(从左到右和从右到左),确定了洞穴中能够形成的最大面积的水塘。具体步骤包括初始化最高水平面、考虑墙壁限制条件等。
















 3804
3804

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








