test 1


package equals; import java.time.*; import java.util.Objects; public class Employee { private String name; private double salary; private LocalDate hireDay; public Employee(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day) { this.name = name; this.salary = salary; hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day); } public String getName() { return name; } public double getSalary() { return salary; } public LocalDate getHireDay() { return hireDay; } public void raiseSalary(double byPercent) { double raise = salary * byPercent / 100; salary += raise; } public boolean equals(Object otherObject) { // a quick test to see if the objects are identical if (this == otherObject) return true; // must return false if the explicit parameter is null if (otherObject == null) return false; // if the classes don't match, they can't be equal if (getClass() != otherObject.getClass()) return false; // now we know otherObject is a non-null Employee Employee other = (Employee) otherObject; // test whether the fields have identical values return Objects.equals(name, other.name) && salary == other.salary && Objects.equals(hireDay, other.hireDay); } public int hashCode() { return Objects.hash(name, salary, hireDay); } public String toString() { return getClass().getName() + "[name=" + name + ",salary=" + salary + ",hireDay=" + hireDay + "]"; } }


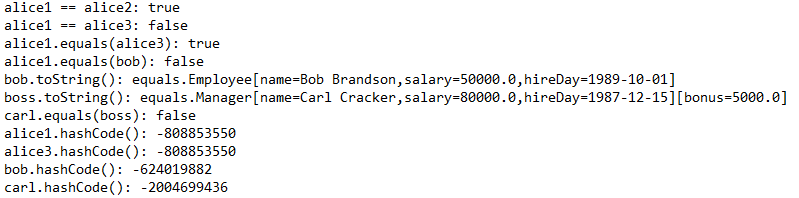
package equals; /** * This program demonstrates the equals method. * @version 1.12 2012-01-26 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class EqualsTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Employee alice1 = new Employee("Alice Adams", 75000, 1987, 12, 15); Employee alice2 = alice1; Employee alice3 = new Employee("Alice Adams", 75000, 1987, 12, 15); Employee bob = new Employee("Bob Brandson", 50000, 1989, 10, 1); System.out.println("alice1 == alice2: " + (alice1 == alice2)); System.out.println("alice1 == alice3: " + (alice1 == alice3));//是否引用同一个对象 System.out.println("alice1.equals(alice3): " + alice1.equals(alice3)); //两个参数不为NULL,用a.equals(b) System.out.println("alice1.equals(bob): " + alice1.equals(bob)); System.out.println("bob.toString(): " + bob); Manager carl = new Manager("Carl Cracker", 80000, 1987, 12, 15); Manager boss = new Manager("Carl Cracker", 80000, 1987, 12, 15); boss.setBonus(5000); System.out.println("boss.toString(): " + boss); System.out.println("carl.equals(boss): " + carl.equals(boss)); System.out.println("alice1.hashCode(): " + alice1.hashCode());//地址值 System.out.println("alice3.hashCode(): " + alice3.hashCode()); System.out.println("bob.hashCode(): " + bob.hashCode()); System.out.println("carl.hashCode(): " + carl.hashCode()); } }


package equals; public class Manager extends Employee { private double bonus; public Manager(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day) { super(name, salary, year, month, day); bonus = 0; } public double getSalary() { double baseSalary = super.getSalary(); return baseSalary + bonus; } public void setBonus(double bonus) { this.bonus = bonus; } public boolean equals(Object otherObject) { if (!super.equals(otherObject)) return false; Manager other = (Manager) otherObject; // super.equals checked that this and other belong to the same class return bonus == other.bonus; } public int hashCode() { return java.util.Objects.hash(super.hashCode(), bonus); } public String toString() { return super.toString() + "[bonus=" + bonus + "]"; } }
test 2


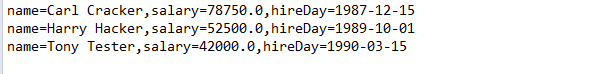
package arrayList; import java.util.*; /** * This program demonstrates the ArrayList class. * @version 1.11 2012-01-26 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class ArrayListTest { public static void main(String[] args) { // fill the staff array list with three Employee objects ArrayList<Employee> staff = new ArrayList<>(); staff.add(new Employee("Carl Cracker", 75000, 1987, 12, 15)); staff.add(new Employee("Harry Hacker", 50000, 1989, 10, 1)); staff.add(new Employee("Tony Tester", 40000, 1990, 3, 15)); // raise everyone's salary by 5% for (Employee e : staff) e.raiseSalary(5); // print out information about all Employee objects for (Employee e : staff) System.out.println("name=" + e.getName() + ",salary=" + e.getSalary() + ",hireDay=" + e.getHireDay()); } }


package arrayList; import java.time.*; public class Employee { private String name; private double salary; private LocalDate hireDay; public Employee(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day) { this.name = name; this.salary = salary; hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day); } public String getName() { return name; } public double getSalary() { return salary; } public LocalDate getHireDay() { return hireDay; } public void raiseSalary(double byPercent) { double raise = salary * byPercent / 100; salary += raise; } }
test 3


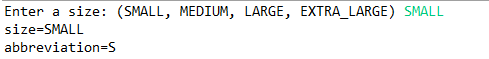
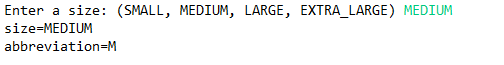
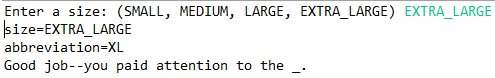
import java.util.*; public class EnumTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("Enter a size: (SMALL, MEDIUM, LARGE, EXTRA_LARGE) "); String input = in.next().toUpperCase(); Size size = Enum.valueOf(Size.class, input);//将size设置成输入的() System.out.println("size=" + size);//printf size System.out.println("abbreviation=" + size.getAbbreviation()); //输出缩写后的大小 if (size == Size.EXTRA_LARGE) System.out.println("Good job--you paid attention to the _."); //如果是xl号 输出Good job--you paid attention to the _. } } enum Size //枚举类 { SMALL("S"), MEDIUM("M"), LARGE("L"), EXTRA_LARGE("XL"); private Size(String abbreviation) { this.abbreviation = abbreviation; } public String getAbbreviation() { return abbreviation; } //缩写函数 private String abbreviation; }
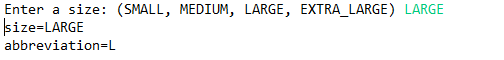


public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { TEST2 test2 = new TEST2(); /*在下面分别调用 demo1 demo2 demo3 demo4 test1 test2 test3 test4方法 和t1 t2 t3 t3 e1 e2 e3 e4属性,好好理解继承和权限修饰符的用法与区别*/ System.out.println(test2.e2); System.out.println(test2.e3); System.out.println(test2.e4); System.out.println(test2.t2); System.out.println(test2.t3); System.out.println(test2.t4); test2.demo1(); test2.demo3(); test2.demo4(); test2.tese2(); test2.tese3(); test2.tese4(); } }


public class TEST1 { private String t1 = "这是TEST1的私有属性"; public String t2 = "这是TEST1的公有属性"; protected String t3 = "这是TEST1受保护的属性"; String t4 = "这是TEST1的默认属性"; private void tese1() { System.out.println("我是TEST1用private修饰符修饰的方法"); } public void tese2() { System.out.println("我是TEST1用public修饰符修饰的方法"); } protected void tese3() { System.out.println("我是TEST1用protected修饰符修饰的方法"); } void tese4() { System.out.println("我是TEST1无修饰符修饰的方法"); } }


public class TEST2 extends TEST1{ private String e1 = "这是TEST1的私有属性"; public String e2 = "这是TEST1的公有属性"; protected String e3 = "这是TEST1受保护的属性"; String e4 = "这是TEST1的默认属性"; public void demo1() { System.out.println("我是TEST2用public修饰符修饰的方法"); } private void demo2() { System.out.println("我是TEST2用private修饰符修饰的方法"); } protected void demo3() { System.out.println("我是TEST2用protected修饰符修饰的方法"); } void demo4() { System.out.println("我是TEST2无修饰符修饰的方法"); } }





















 8191
8191

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








