内置函数
| 内置函数 | ||||
| abs() | dict() | help() | min() | setattr() |
| all() | dir() | hex() | next() | slice() |
| any() | divmod() | id() | object() | sorted() |
| ascii() | enumerate() | input() | oct() | staticmethod() |
| bin() | eval() | int() | open() | str() |
| bool() | exec() | isinstance() | ord() | sum() |
| bytearray() | filter() | issubclass() | pow() | super() |
| bytes() | float() | iter() | print() | tuple() |
| callable() | format() | len() | property() | type() |
| chr() | frozenset() | list() | range() | vars() |
| classmethod() | getattr() | locals() | repr() | zip() |
| compile() | globals() | map() | reversed() | __import__() |
| complex() | hasattr() | max() | round() | |
| delattr() | hash() | memoryview() | set() |
1.作用域
locals :函数会以字典的类型返回当前位置的全部局部变量。
globals:函数以字典的类型返回全部全局变量。
a = 1
b = 2
print(locals())
print(globals())
# 这两个一样,因为是在全局执行的。
##########################
def func(argv):
c = 2
print(locals())
print(globals())
func(3)
#这两个不一样,locals() {'argv': 3, 'c': 2}
#globals() {'__doc__': None, '__builtins__': <module 'builtins' (built-in)>, '__cached__': None, '__loader__': <_frozen_importlib_external.SourceFileLoader object at 0x0000024409148978>, '__spec__': None, '__file__': 'D:/lnh.python/.../内置函数.py', 'func': <function func at 0x0000024408CF90D0>, '__name__': '__main__', '__package__': None}
1.1字符串类型代码的执行 eval,exec,complie
eval:执行字符串类型的代码,并返回最终结果。
eval('2 + 2') # 4
n=81
eval("n + 4") # 85
eval('print(666)') # 666
1.1.1 exec:执行字符串类型的代码
s = '''
for i in [1,2,3]:
print(i)
'''
exec(s)
1.1.2 compile:将字符串类型的代码编译。代码对象能够通过exec语句来执行或者eval()进行求值。
'''
参数说明:
1. 参数source:字符串或者AST(Abstract Syntax Trees)对象。即需要动态执行的代码段。
2. 参数 filename:代码文件名称,如果不是从文件读取代码则传递一些可辨认的值。当传入了source参数时,filename参数传入空字符即可。
3. 参数model:指定编译代码的种类,可以指定为 ‘exec’,’eval’,’single’。当source中包含流程语句时,model应指定为‘exec’;当source中只包含一个简单的求值表达式,model应指定为‘eval’;当source中包含了交互式命令语句,model应指定为'single'。
'''
>>> #流程语句使用exec
>>> code1 = 'for i in range(0,10): print (i)'
>>> compile1 = compile(code1,'','exec')
>>> exec (compile1)
>>> #简单求值表达式用eval
>>> code2 = '1 + 2 + 3 + 4'
>>> compile2 = compile(code2,'','eval')
>>> eval(compile2)
>>> #交互语句用single
>>> code3 = 'name = input("please input your name:")'
>>> compile3 = compile(code3,'','single')
>>> name #执行前name变量不存在
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<pyshell#29>", line 1, in <module>
name
NameError: name 'name' is not defined
>>> exec(compile3) #执行时显示交互命令,提示输入
please input your name:'pythoner'
>>> name #执行后name变量有值
"'pythoner'"
1.1.3 输入输出相关 input,print
input:函数接受一个标准输入数据,返回string类型。
print:打印输出。
''' 源码分析
def print(self, *args, sep=' ', end='\n', file=None): # known special case of print
"""
print(value, ..., sep=' ', end='\n', file=sys.stdout, flush=False)
file: 默认是输出到屏幕,如果设置为文件句柄,输出到文件
sep: 打印多个值之间的分隔符,默认为空格
end: 每一次打印的结尾,默认为换行符
flush: 立即把内容输出到流文件,不作缓存
"""
'''
print(111,222,333,sep='*') # 111*222*333
print(111,end='')
print(222) #两行的结果 111222
f = open('log','w',encoding='utf-8')
print('写入文件',file=f,flush=True)
1.1.4 内存相关 hash id
hash:获取一个对象(可哈希对象:int,str,Bool,tuple)的哈希值。
print(hash(12322))
print(hash('123'))
print(hash('arg'))
print(hash('alex'))
print(hash(True))
print(hash(False))
print(hash((1,2,3)))
'''
12322
-2996001552409009098
-4637515981888139739
2311495795356652852
1
0
2528502973977326415
'''
1.1.4 help
函数用于查看函数或模块用途的详细说明。
print(help(list))
Help on class list in module builtins:
class list(object)
| list() -> new empty list
| list(iterable) -> new list initialized from iterable's items
|
| Methods defined here:
|
| __add__(self, value, /)
| Return self+value.
|
| __contains__(self, key, /)
| Return key in self.
|
| __delitem__(self, key, /)
| Delete self[key].
|
| __eq__(self, value, /)
| Return self==value.
|
| __ge__(self, value, /)
| Return self>=value.
|
| __getattribute__(self, name, /)
| Return getattr(self, name).
|
| __getitem__(...)
| x.__getitem__(y) <==> x[y]
|
| __gt__(self, value, /)
| Return self>value.
|
| __iadd__(self, value, /)
| Implement self+=value.
|
| __imul__(self, value, /)
| Implement self*=value.
|
| __init__(self, /, *args, **kwargs)
| Initialize self. See help(type(self)) for accurate signature.
|
| __iter__(self, /)
| Implement iter(self).
|
| __le__(self, value, /)
| Return self<=value.
|
| __len__(self, /)
| Return len(self).
|
| __lt__(self, value, /)
| Return self<value.
|
| __mul__(self, value, /)
| Return self*value.n
|
| __ne__(self, value, /)
| Return self!=value.
|
| __new__(*args, **kwargs) from builtins.type
| Create and return a new object. See help(type) for accurate signature.
|
| __repr__(self, /)
| Return repr(self).
|
| __reversed__(...)
| L.__reversed__() -- return a reverse iterator over the list
|
| __rmul__(self, value, /)
| Return self*value.
|
| __setitem__(self, key, value, /)
| Set self[key] to value.
|
| __sizeof__(...)
| L.__sizeof__() -- size of L in memory, in bytes
|
| append(...)
| L.append(object) -> None -- append object to end
|
| clear(...)
| L.clear() -> None -- remove all items from L
|
| copy(...)
| L.copy() -> list -- a shallow copy of L
|
| count(...)
| L.count(value) -> integer -- return number of occurrences of value
|
| extend(...)
| L.extend(iterable) -> None -- extend list by appending elements from the iterable
|
| index(...)
| L.index(value, [start, [stop]]) -> integer -- return first index of value.
| Raises ValueError if the value is not present.
|
| insert(...)
| L.insert(index, object) -- insert object before index
|
| pop(...)
| L.pop([index]) -> item -- remove and return item at index (default last).
| Raises IndexError if list is empty or index is out of range.
|
| remove(...)
| L.remove(value) -> None -- remove first occurrence of value.
| Raises ValueError if the value is not present.
|
| reverse(...)
| L.reverse() -- reverse *IN PLACE*
|
| sort(...)
| L.sort(key=None, reverse=False) -> None -- stable sort *IN PLACE*
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Data and other attributes defined here:
|
| __hash__ = None
None
Process finished with exit code 0
1.1.5 调用
callable:函数用于检查一个对象是否是可调用的。如果返回True,object仍然可能调用失败;但如果返回False,调用对象ojbect绝对不会成功。
name = 'alex'
def func1():
print(111)
print(callable(name))
print(callable(func1))
=====》输出
False
True
1.1.6 查看内置属性
dir:函数不带参数时,返回当前范围内的变量、方法和定义的类型列表;带参数时,返回参数的
属性、方法列表。如果参数包含方法__dir__(),该方法将被调用。如果参数不包含__dir__(),该方法
将最大限度地收集参数信息。
>>>dir() # 获得当前模块的属性列表
['__builtins__', '__doc__', '__name__', '__package__', 'arr', 'myslice']
>>> dir([ ]) # 查看列表的方法
['__add__', '__class__', '__contains__', '__delattr__', '__delitem__', '__delslice__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__getitem__', '__getslice__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__iadd__', '__imul__', '__init__', '__iter__', '__le__', '__len__', '__lt__', '__mul__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__reversed__', '__rmul__', '__setattr__', '__setitem__', '__setslice__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', 'append', 'count', 'extend', 'index', 'insert', 'pop', 'remove', 'reverse', 'sort']
1.1.7 迭代器生成器
range:函数可创建一个整数对象,一般用在 for 循环中。
next:内部实际使用了__next__方法,返回迭代器的下一个项目。
# 首先获得Iterator对象:
it = iter([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
# 循环:
while True:
try:
# 获得下一个值:
x = next(it)
print(x)
except StopIteration:
# 遇到StopIteration就退出循环
break
iter:函数用来生成迭代器(讲一个可迭代对象,生成迭代器)。
from collections import Iterable
from collections import Iterator
l = [1,2,3]
print(isinstance(l,Iterable)) # True
print(isinstance(l,Iterator)) # False
l1 = iter(l)
print(isinstance(l1,Iterable)) # True
print(isinstance(l1,Iterator)) # True
1.1.8 基础数据类型
1.4.1数字相关(14)
数据类型(4):
bool :用于将给定参数转换为布尔类型,如果没有参数,返回 False。
int:函数用于将一个字符串或数字转换为整型。
==============
**int:函数用于将一个字符串或数字转换为整型。
print(int()) # 0
print(int('12')) # 12
print(int(3.6)) # 3
==============
*float:函数用于将整数和字符串转换成浮点数。
i = 2.456
print(i,type(i))
print(float(1.1))
==============
complex:函数用于创建一个值为 real + imag * j 的复数或者转化一个字符串或数为复数。
如果第一个参数为字符串,则不需要指定第二个参数。。
i = 1 + 2j
print(type(i))
import math
print(math.pi)
===============
进制转换(3):*
bin:将十进制转换成二进制并返回。
oct:将十进制转化成八进制字符串并返回。
hex:将十进制转化成十六进制字符串并返回。
print(bin(19))
print(oct(9))
print(hex(15))
===============
数学运算(7):
abs:函数返回数字的绝对值。
print(abs(-1.2))
*** divmod:计算除数与被除数的结果,
返回一个包含商和余数的元组(a // b, a % b)。
print(divmod(100,7)) # (商,余数)
*round:保留浮点数的小数位数,默认保留整数。
print(round(3.43543656,4))
*pow:求x**y次幂。(三个参数为x**y的结果对z取余)
print(pow(2,3))
print(pow(2, 3, 3))
*** sum:对可迭代对象进行求和计算(可设置初始值)。
l1 = [i for i in range(100)]
print(sum(l1))
print(sum(l1,100))
l2 = [2, 5, 6, -7]
***min:返回可迭代对象的最小值(可加key,key为函数名,
通过函数的规则,返回最小值)。
print(min(l2))
print(min(l2,key=abs))
*** max:返回可迭代对象的最大值(可加key,key为函数名,通过函数的规则,返回最大值)。
print(max(l2,key=abs))
reversed:将一个序列翻转,并返回此翻转序列的迭代器。
l3 = [2, 3, 9, 8, 7, 4]
l3.reverse()
print(l3)
l_obj = reversed(l3)
print(l_obj)
for i in l_obj:
print(i)
=================
* slice:构造一个切片对象,用于列表的切片。
l3 = [2, 3, 9, 8, 7, 4]
rule = slice(0,3)
print(l3[rule])
* format 科学计算
print(format('test', '<30'))
print(format('test', '>20'))
print(format('test', '^20'))
bytes 将unicode 转化成bytes
s = 'alex'
b1 = s.encode('utf-8')
print(b1)
print(bytes(s, encoding='utf-8'))
ret = bytearray('alex',encoding='utf-8')
print(id(ret))
print(ret)
print(ret[0])
ret[0] = 65
print(ret)
print(id(ret))
ret = memoryview(bytes('你好',encoding='utf-8')) # [xe31,x312,x3 ]
print(len(ret))
print(ret)
print(bytes(ret[:3]).decode('utf-8'))
print(bytes(ret[3:]).decode('utf-8'))
ord 输入字符找该字符编码的位置 unicode
print(ord('a'))
print(ord('中'))
chr 输入位置数字找出其对应的字符
print(chr(97))
print(chr(20013))
是ascii码中的返回该值,不是就返回/u...
print(ascii('a'))
print(ascii('中'))
**repr:返回一个对象的string形式(原形毕露)。
print(repr('{"name":"alex"}'),type(repr('{"name":"alex"}')))
print('{"name":"alex"}')
print('python%s期' % '22')
print('python%r期' % '22')
l3 = [2, 3, 9, 8, 7, 4]
l3.sort()
print(l3)
*** sorted:对所有可迭代的对象进行排序操作。
ll = sorted(l3)
print(ll)
sorted()
def func(x): return x[1]
L = [('a', 3), ('d', 4), ('b', 2), ('c', 1), ]
print(sorted(L, key=func))
*** enumerate:枚举,返回一个枚举对象。
l1 = ['alex', 'laonanhai', 'taibai']
for index,content in enumerate(l1):
print(index,content)
for index,content in enumerate(l1,10):
print(index,content)
**all:可迭代对象中,全都是True才是True
**any:可迭代对象中,有一个True 就是True
l1 = [1, 'alex', 3]
l2 = [0, '', False,(), 1]
print(all(l1))
print(any(l2))
***zip 拉链方法
l1 = [1,2,3,]
l2 = ['a','b','c',5]
l3 = ('*','**',(1,2,3),666,777)
for i in zip(l1, l2, l3):
print(i)
***map:会根据提供的函数对指定序列做映射。返回的是迭代器
def square(x):
return x ** 2
print(map(square, [1,2,3,4,5]) )
for i in map(square, [1,2,3,4,5]):
print(i)
print((i**2 for i in [1,2,3,4,5]))
类似于[i for i in range(1,8) if i % 2 == 0 ]
def func(x):return x%2 == 0
ret = filter(func,[1,2,3,4,5,6,7])
print(ret)
for i in ret:
print(i)
min max sorted map filter
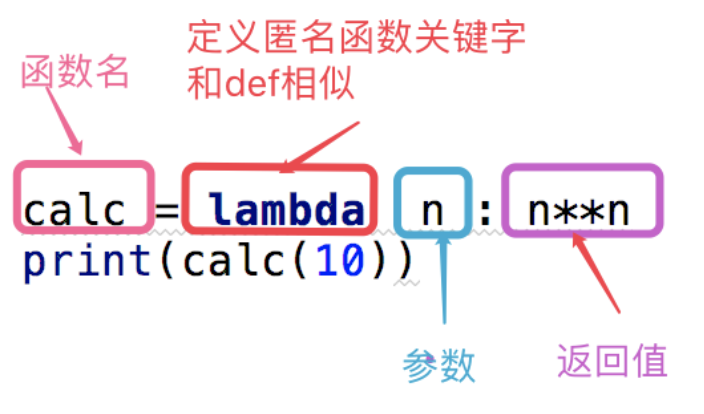
1.1.9 匿名函数
#这段代码
def calc(n):
return n**n
print(calc(10))
#换成匿名函数
calc = lambda n:n**n
print(calc(10))
==============
def func1(x): return x**2
res = map(lambda x: x**2,[1,5,7,4,8])
for i in res:
print(i)
=====》输出
1
25
49
16
64举例:
l1 = [ {'sales_volumn': 0},
{'sales_volumn': 108},
{'sales_volumn': 337},
{'sales_volumn': 475},
{'sales_volumn': 396},
{'sales_volumn': 172},
{'sales_volumn': 9},
{'sales_volumn': 58},
{'sales_volumn': 272},
{'sales_volumn': 456},
{'sales_volumn': 440},
{'sales_volumn': 239}]
print(sorted(l1,key= lambda x:x['sales_volumn']))
======》输出
[{'sales_volumn': 0}, {'sales_volumn': 9}, {'sales_volumn': 58}, {'sales_volumn': 108}, {'sales_volumn': 172}, {'sales_volumn': 239}, {'sales_volumn': 272}, {'sales_volumn': 337}, {'sales_volumn': 396}, {'sales_volumn': 440}, {'sales_volumn': 456}, {'sales_volumn': 475}]























 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








