驱动代码:
#include <linux/module.h> #include <linux/kernel.h> #include <linux/fs.h> #include <asm/irq.h> #include <linux/init.h> #include <linux/delay.h> #include <linux/device.h> //包含了device、class 等结构的定义 #include <asm/io.h> //包含了ioremap、iowrite等内核访问IO内存等函数 #include <linux/uaccess.h> //包含了copy_to_user、copy_from_user等 #define DEVICE_NAME "axiled" #define CLASS_NAME "zynqebb" /* XGPIO Physical address */ #define XGPIO_PHY_ADDR 0x41200000 //This Address is based SDK /* Register Offset Definitions */ #define XGPIO_DATA_OFFSET (0x0) /* Data register */ #define XGPIO_TRI_OFFSET (0x4) /* I/O direction register */ volatile unsigned long *Gpio_DIR = NULL; volatile unsigned long *Gpio_DATA = NULL; MODULE_AUTHOR("Xilinx "); MODULE_DESCRIPTION("AXI GPIO moudle dirver"); MODULE_VERSION("v1.0"); MODULE_LICENSE("GPL"); static int axi_gpio_driver_major; static struct class* axi_gpio_driver_class = NULL; static struct device* axi_gpio_driver_device = NULL; unsigned long axi_gpio_virt_addr = 0; //AXI_GPIO moulde's visual address static ssize_t axi_gpio_write(struct file * file, const char * buf, size_t count,loff_t *off) { //printk("axi_gpio_write\n"); int val; copy_from_user(&val,buf,count); printk("before Gpio_DATA:%lx,%lx.\n",Gpio_DATA,ioread32(Gpio_DATA)); if(val == 1) { //点灯 //*Gpio_DATA = (unsigned long )0x00000005; //设置AXI GPIO的方向输出全为高 iowrite32(0x0000000F,Gpio_DATA); //设置AXI GPIO的方向输出全为高 } else { //灭灯 iowrite32(0x00000000,Gpio_DATA); //设置AXI GPIO的方向输出全为低 } printk("after Gpio_DATA:%lx,%lx.\n",Gpio_DATA,ioread32(Gpio_DATA)); return 0; } static int axi_gpio_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp) { //printk("axi_gpio_open\n"); //配置led管脚为输出 printk("before Gpio_DIR:%lx,%lx.\n",Gpio_DIR,ioread32(Gpio_DIR)); //*Gpio_DIR = (unsigned long )0x00000000; //设置AXI GPIO的方向输出 iowrite32(0x00000000,Gpio_DIR); //设置AXI GPIO的方向输出 printk("after Gpio_DIR:%lx,%lx.\n",Gpio_DIR,ioread32(Gpio_DIR)); return 0; } static struct file_operations axi_gpio_fops = { .owner = THIS_MODULE, .write = axi_gpio_write, .open = axi_gpio_open, }; static int __init axi_gpio_driver_module_init(void) { int ret; axi_gpio_driver_major=register_chrdev(0, DEVICE_NAME, &axi_gpio_fops );//内核注册设备驱动 if (axi_gpio_driver_major < 0){ printk("failed to register device.\n"); return -1; } axi_gpio_driver_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, CLASS_NAME);//创建设备类 if (IS_ERR(axi_gpio_driver_class)){ printk("failed to create zxi_gpio moudle class.\n"); unregister_chrdev(axi_gpio_driver_major, DEVICE_NAME); return -1; } axi_gpio_driver_device = device_create(axi_gpio_driver_class, NULL, MKDEV(axi_gpio_driver_major, 0), NULL, DEVICE_NAME); if (IS_ERR(axi_gpio_driver_device)){ printk("failed to create device .\n"); unregister_chrdev(axi_gpio_driver_major, DEVICE_NAME); return -1; } //To get Custom IP--gpio moudle's virtual address #if 1 if(request_mem_region(XGPIO_PHY_ADDR, 0x1000,DEVICE_NAME) == NULL ){ printk( "request_mem_region failed\n"); return -1; } #endif axi_gpio_virt_addr = (unsigned long)ioremap(XGPIO_PHY_ADDR, sizeof(u32)); //将模块的物理地址映射到虚拟地址上 printk( "ioremap called: phys %#08x -> virt %#08x\n",XGPIO_PHY_ADDR, axi_gpio_virt_addr ); //指定需要操作的寄存器的地址 Gpio_DIR = (unsigned long *)(axi_gpio_virt_addr + XGPIO_TRI_OFFSET); Gpio_DATA = (unsigned long *)(axi_gpio_virt_addr + XGPIO_DATA_OFFSET); return 0; } static void __exit axi_gpio_driver_module_exit(void) { //撤销映射关系 iounmap((void *)axi_gpio_virt_addr); #if 1 release_mem_region(XGPIO_PHY_ADDR, 0x1000); #endif device_destroy(axi_gpio_driver_class, MKDEV(axi_gpio_driver_major, 0)); class_unregister(axi_gpio_driver_class); class_destroy(axi_gpio_driver_class); unregister_chrdev(axi_gpio_driver_major, DEVICE_NAME); printk("axi_gpio module exit.\n"); } module_init(axi_gpio_driver_module_init); module_exit(axi_gpio_driver_module_exit);
应用层代码:
#include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <stdio.h> /* firstdrvtest on * firstdrvtest off */ int main(int argc, char **argv) { int fd; int val = 1; fd = open("/dev/axiled", O_RDWR); if (fd < 0) { printf("can't open!\n"); } if (argc != 2) { printf("Usage :\n"); printf("%s <on|off>\n", argv[0]); return 0; } if (strcmp(argv[1], "on") == 0) { val = 1; } else { val = 0; } write(fd, &val, 4); return 0; }
插入模块:
root@plnx_arm:/mnt# insmod mytest.ko
ioremap called: phys 0x41200000 -> virt 0xf09f0000
测试设备号:

运行应用程序:
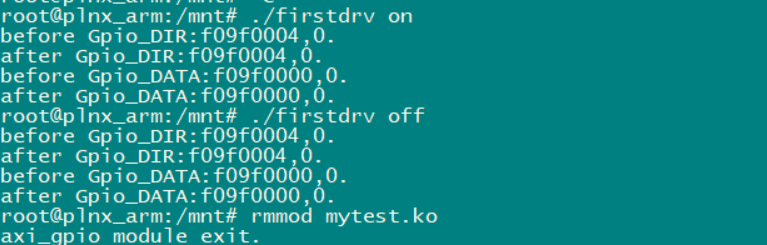




 本文介绍了一个AXI GPIO设备驱动的实现过程,包括内核模块的初始化、设备注册、文件操作函数的实现等内容,并提供了一段完整的驱动代码及应用层示例。该驱动实现了LED灯的开关控制功能。
本文介绍了一个AXI GPIO设备驱动的实现过程,包括内核模块的初始化、设备注册、文件操作函数的实现等内容,并提供了一段完整的驱动代码及应用层示例。该驱动实现了LED灯的开关控制功能。
















 1495
1495

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








