D. Slalom
Little girl Masha likes winter sports, today she's planning to take part in slalom skiing.
The track is represented as a grid composed of n × m squares. There are rectangular obstacles at the track, composed of grid squares. Masha must get from the square (1, 1) to the square (n, m). She can move from a square to adjacent square: either to the right, or upwards. If the square is occupied by an obstacle, it is not allowed to move to that square.
One can see that each obstacle can actually be passed in two ways: either it is to the right of Masha's path, or to the left. Masha likes to try all ways to do things, so she would like to know how many ways are there to pass the track. Two ways are considered different if there is an obstacle such that it is to the right of the path in one way, and to the left of the path in the other way.
Help Masha to find the number of ways to pass the track. The number of ways can be quite big, so Masha would like to know it modulo109 + 7.
The pictures below show different ways to pass the track in sample tests.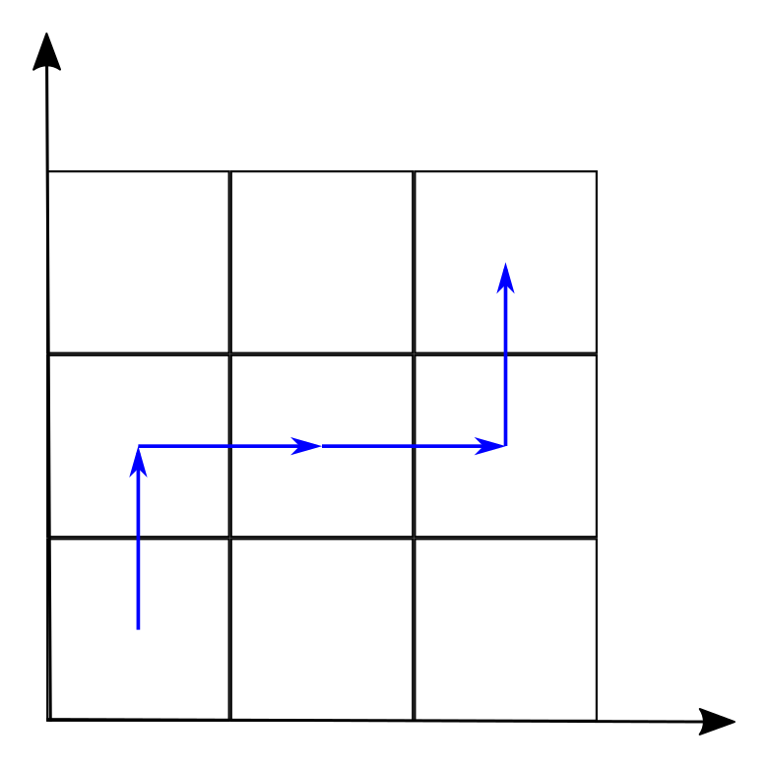
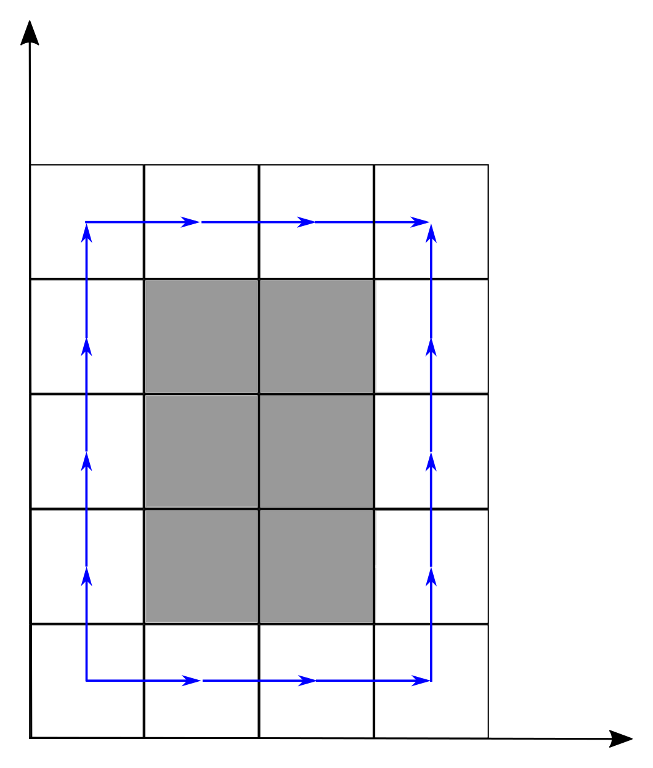
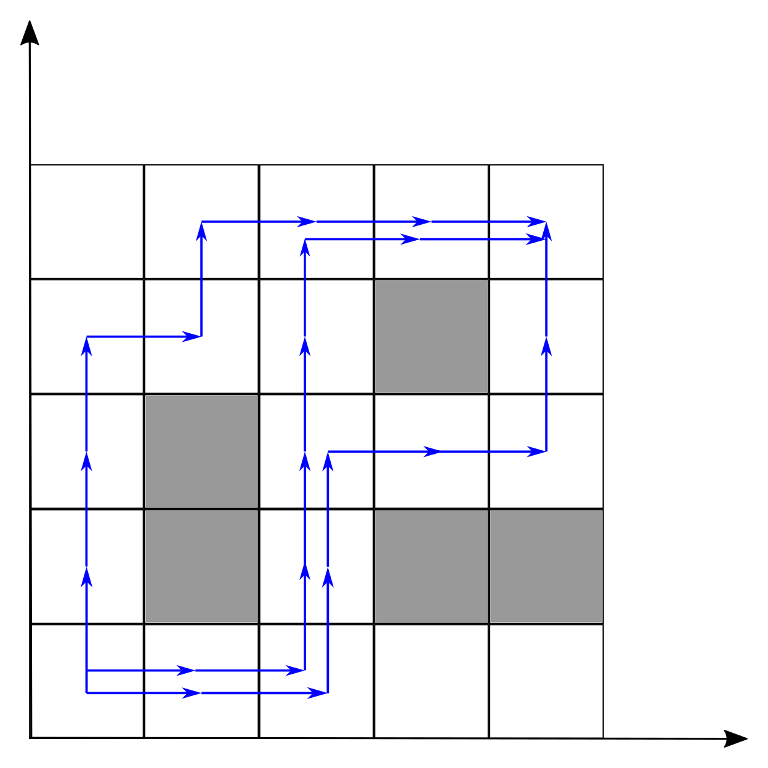
Input
The first line of input data contains three positive integers: n, m and k (3 ≤ n, m ≤ 106, 0 ≤ k ≤ 105) — the size of the track and the number of obstacles.
The following k lines contain four positive integers each: x1, y1, x2, y2 (1 ≤ x1 ≤ x2 ≤ n, 1 ≤ y1 ≤ y2 ≤ m) — coordinates of bottom left, and top right squares of the obstacle.
It is guaranteed that there are no obstacles at squares (1, 1) and (n, m), and no obstacles overlap (but some of them may touch).
Output
Output one integer — the number of ways to pass the track modulo 109 + 7.
Examples
3 3 0
1
4 5 1
2 2 3 4
2
5 5 3
2 2 2 3
4 2 5 2
4 4 4 4
3
Solution
和BZOJ4422是一个类型的题。线段树扫描线+差分 优化DP (传送门)
这个题也是一样的,转移比较好想就不说了.
把每个障碍分左边右边记录下来,然后一维线段树一维扫描线。
线段树支持区间覆盖,单点修改,区间查询和即可。
写扫描线都用结构体,记录一下x,y1,y2,0/1。这样排序会比较麻烦...有个不错的姿势,就是对每个x建一个vector,vector里面存一个pair,这样会非常方便。
Code
#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> #include<cmath> #include<set> using namespace std; #define LL long long inline int read() { int x=0; char ch=getchar(); while (ch<'0' || ch>'9') {ch=getchar();} while (ch>='0' && ch<='9') {x=x*10+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();} return x; } #define MOD 1000000007 #define MAXN 1000010 int N,M,K,tp; namespace SegmentTree { struct SegmentTreeNode{int l,r,size,cov,sum;}tree[MAXN<<2]; #define ls now<<1 #define rs now<<1|1 inline void Update(int now) {tree[now].sum=tree[ls].sum+tree[rs].sum; tree[now].sum%=MOD;} inline void BuildTree(int now,int l,int r) { tree[now].l=l; tree[now].r=r; tree[now].size=r-l+1; tree[now].cov=-1; if (l==r) return; int mid=(l+r)>>1; BuildTree(ls,l,mid); BuildTree(rs,mid+1,r); Update(now); } inline void cover(int now,int D) {tree[now].cov=D; tree[now].sum=(LL)tree[now].size*D%MOD;} inline void PushDown(int now) { if (tree[now].l==tree[now].r) return; if (tree[now].cov!=-1) cover(ls,tree[now].cov),cover(rs,tree[now].cov),tree[now].cov=-1; } inline void Cover(int now,int L,int R,int D) { if (R<L) return; int l=tree[now].l,r=tree[now].r; PushDown(now); if (L<=l && R>=r) {cover(now,D); return;} int mid=(l+r)>>1; if (L<=mid) Cover(ls,L,R,D); if (R>mid) Cover(rs,L,R,D); Update(now); } inline void Modify(int now,int pos,int D) { int l=tree[now].l,r=tree[now].r; PushDown(now); if (l==r) {cover(now,D); return;} int mid=(l+r)>>1; if (pos<=mid) Modify(ls,pos,D); else Modify(rs,pos,D); Update(now); } inline int Query(int now,int L,int R) { if (R<L) return 0; int l=tree[now].l,r=tree[now].r; PushDown(now); if (L<=l && R>=r) return tree[now].sum; int mid=(l+r)>>1,re=0; if (L<=mid) (re+=Query(ls,L,R))%=MOD; if (R>mid) (re+=Query(rs,L,R))%=MOD; return re; } } struct LineNode{int x,y1,y2,f;}Line[MAXN<<1]; bool cmp(LineNode A,LineNode B) {return A.x==B.x? A.y1==B.y1? A.y2>B.y2 : A.y1>B.y1 : A.x<B.x;} #define Pa pair<int,int> set<Pa>mp; set<Pa>::iterator is; Pa loc; int main() { N=read(),M=read(),K=read(); for (int x1,x2,y1,y2,i=1; i<=K; i++) x1=read(),y1=read(),x2=read(),y2=read(), Line[++tp].x=x1,Line[tp].y1=y1,Line[tp].y2=y2,Line[tp].f=1, Line[++tp].x=x2+1,Line[tp].y1=y1,Line[tp].y2=y2,Line[tp].f=0; SegmentTree::BuildTree(1,1,M); SegmentTree::Modify(1,1,1); sort(Line+1,Line+tp+1,cmp); int X=1; for (int i=1; Line[i].x==1; X++,i++) if (Line[i].f) mp.insert(make_pair(Line[i].y1,Line[i].y2)); mp.insert(make_pair(0,0)); for (int i=2; i<=N; i++) { for (int j=X,tmp; Line[j].x==i; j++) if (Line[j].f) if (Line[j].y2<M) loc=(*--mp.lower_bound(make_pair(Line[j].y2+2,0))), tmp=SegmentTree::Query(1,loc.second+1,Line[j].y2+1), SegmentTree::Modify(1,Line[j].y2+1,tmp); for (int j=X; Line[j].x==i; j++) if (!Line[j].f) mp.erase(make_pair(Line[j].y1,Line[j].y2)); for (int j=X; Line[j].x==i; X++,j++) if (Line[j].f) mp.insert(make_pair(Line[j].y1,Line[j].y2)),SegmentTree::Cover(1,Line[j].y1,Line[j].y2,0); } loc=*(--mp.end()); printf("%d\n",SegmentTree::Query(1,loc.first+1,M)%MOD); return 0; }







 本文介绍了一个滑雪赛道通过路径计数的问题,并提供了一种解决方案。利用线段树扫描线结合差分优化DP的方法来解决该问题,详细阐述了如何处理障碍物,实现区间覆盖等关键步骤。
本文介绍了一个滑雪赛道通过路径计数的问题,并提供了一种解决方案。利用线段树扫描线结合差分优化DP的方法来解决该问题,详细阐述了如何处理障碍物,实现区间覆盖等关键步骤。
















 1454
1454

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








