题目大意:给定一张无向图,问图中是否存在两个点,使得这两个点之间有三条路径,而且三条路径没有公共点。
解法:
我们可以先走出来一个环,再出环上任意一点走到另外一点。就像这样:
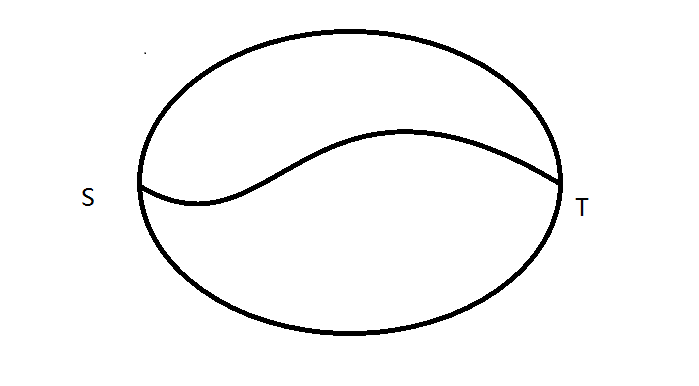
这种图有什么性质?有环。
这是什么图我们可能不知道,但是我们知道这不是什么图啊!这张图一定不是仙人掌!
然后就是如何判断仙人掌和如何输出答案的问题了
参考了这个大佬的博客,我们了解到,可以利用返祖边来判断仙人掌
显然仙人掌中的一条边不能同时出现两个环内
正如大佬所说的“如果一条树边被两条或者以上的返祖边覆盖,那么图就肯定不是一个仙人掌”
我们建出DFS树,可以发现,第一条返祖边能确定一个环,而第二条返祖边能确定三条路径的起点和终点
设起点深度小,终点深度大,我们可以发现终点是两个返祖边中深度最大的两个点的LCA
而起点则是第二条返祖边上深度最大的点与DFS树上一点相连接的一点
然后再xjbDFS一下输出路径即可代码:
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<cstring> 4 #define M 200010 5 using namespace std; 6 struct point{ 7 int to,next; 8 }e[M<<1]; 9 int n,m,num,top,l1,l2,r1,r2,S,T; 10 int ans[M],head[M],deep[M],f[M]; 11 int fa[M][20]; 12 bool vis[M]; 13 void add(int from,int to) 14 { 15 e[++num].next=head[from]; 16 e[num].to=to; 17 head[from]=num; 18 } 19 void dfs(int x) 20 { 21 vis[x]=true; 22 for(int i=head[x];i;i=e[i].next) 23 { 24 int to=e[i].to; 25 if(to==fa[x][0]) continue; 26 if(!vis[to]) 27 { 28 deep[to]=deep[x]+1; 29 fa[to][0]=x; 30 dfs(to); 31 } 32 else if(deep[to]<deep[x])//返祖 33 { 34 f[to]--; 35 f[x]++; 36 } 37 } 38 f[fa[x][0]]+=f[x]; 39 } 40 void DFS(int x) 41 { 42 for(int i=head[x];i;i=e[i].next) 43 { 44 int to=e[i].to; 45 if(to==fa[x][0]) continue; 46 if(deep[to]==deep[x]+1) 47 { 48 DFS(to); 49 if(l2) return; 50 } 51 else if(deep[to]<deep[S])//找到两条返祖边 52 { 53 if(l1) r2=x,l2=to; 54 else r1=x,l1=to; 55 if(l2) return; 56 } 57 } 58 } 59 int lca(int x,int y) 60 { 61 if(deep[x]<deep[y]) swap(x,y); 62 for(int i=18;i>=0;i--) 63 if(deep[fa[x][i]]>=deep[y]) 64 x=fa[x][i]; 65 if(x==y) return y; 66 for(int i=18;i>=0;i--) 67 if(fa[x][i]!=fa[y][i]) 68 { 69 x=fa[x][i]; 70 y=fa[y][i]; 71 } 72 return fa[x][0]; 73 } 74 int main() 75 { 76 scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); 77 for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) 78 { 79 int x,y; scanf("%d%d",&x,&y); 80 add(x,y); add(y,x); 81 } 82 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 83 if(!vis[i]) 84 dfs(i); 85 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 86 if(f[i]>1) 87 { 88 S=i; 89 break; 90 } 91 if(S==0) {printf("NO"); return 0;} 92 printf("YES\n"); 93 DFS(S); 94 for(int j=1;j<=18;j++) 95 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 96 fa[i][j]=fa[fa[i][j-1]][j-1]; 97 T=lca(r1,r2); 98 if(deep[l1]<deep[l2]) swap(l1,l2),swap(r1,r2); 99 S=l1; 100 int now=T; 101 top=0; 102 while(1) 103 { 104 ans[++top]=now; 105 if(now==S) break; 106 now=fa[now][0]; 107 } 108 printf("%d ",top); 109 for(int i=top;i>=1;i--) printf("%d ",ans[i]); 110 printf("\n"); 111 top=0; 112 ans[++top]=S; 113 now=r1; 114 while(1) 115 { 116 ans[++top]=now; 117 if(now==T) break; 118 now=fa[now][0]; 119 } 120 printf("%d ",top); 121 for(int i=1;i<=top;i++) printf("%d ",ans[i]); 122 printf("\n"); 123 top=0; 124 if(S==l2) 125 { 126 ans[++top]=S; 127 now=r2; 128 while(1) 129 { 130 ans[++top]=now; 131 if(now==T) break; 132 now=fa[now][0]; 133 } 134 } 135 else 136 { 137 now=S; 138 while(1) 139 { 140 ans[++top]=now; 141 if(now==l2) break; 142 now=fa[now][0]; 143 } 144 now=r2; 145 while(1) 146 { 147 ans[++top]=now; 148 if(now==T) break; 149 now=fa[now][0]; 150 } 151 } 152 printf("%d ",top); 153 for(int i=1;i<=top;i++) printf("%d ",ans[i]); 154 return 0; 155 }







 本文探讨了一种算法,用于检测无向图中是否存在两个节点间有三条无公共点的路径。通过构建DFS树和利用返祖边概念,判断图是否为仙人掌图,并找出符合条件的路径。
本文探讨了一种算法,用于检测无向图中是否存在两个节点间有三条无公共点的路径。通过构建DFS树和利用返祖边概念,判断图是否为仙人掌图,并找出符合条件的路径。
















 716
716

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








