Given n non-negative integers representing the histogram's bar height where the width of each bar is 1, find the area of largest rectangle in the histogram.

Above is a histogram where width of each bar is 1, given height = [2,1,5,6,2,3].

The largest rectangle is shown in the shaded area, which has area = 10 unit.
For example,
Given height = [2,1,5,6,2,3],
return 10.
---
这两天参加JOB Fair感觉,有些基本方法还是要先能想出来写出来,把问题解决了再去想更好的方法。
对于小数据,也许最基本的方法就可以解决问题。
这题肯定能用O(N^2)先解出来
public class Solution { public int largestRectangleArea(int[] height) { int maxArea = 0; for(int i=0; i<height.length; i++){ int minH = height[i]; for(int j=i; j<height.length; j++){ // update min height if(height[j] < minH) minH=height[j]; int area = (j-i+1) * minH; // update maxArea if(area > maxArea) maxArea = area; } } return maxArea; } }
---
之后是O(N)
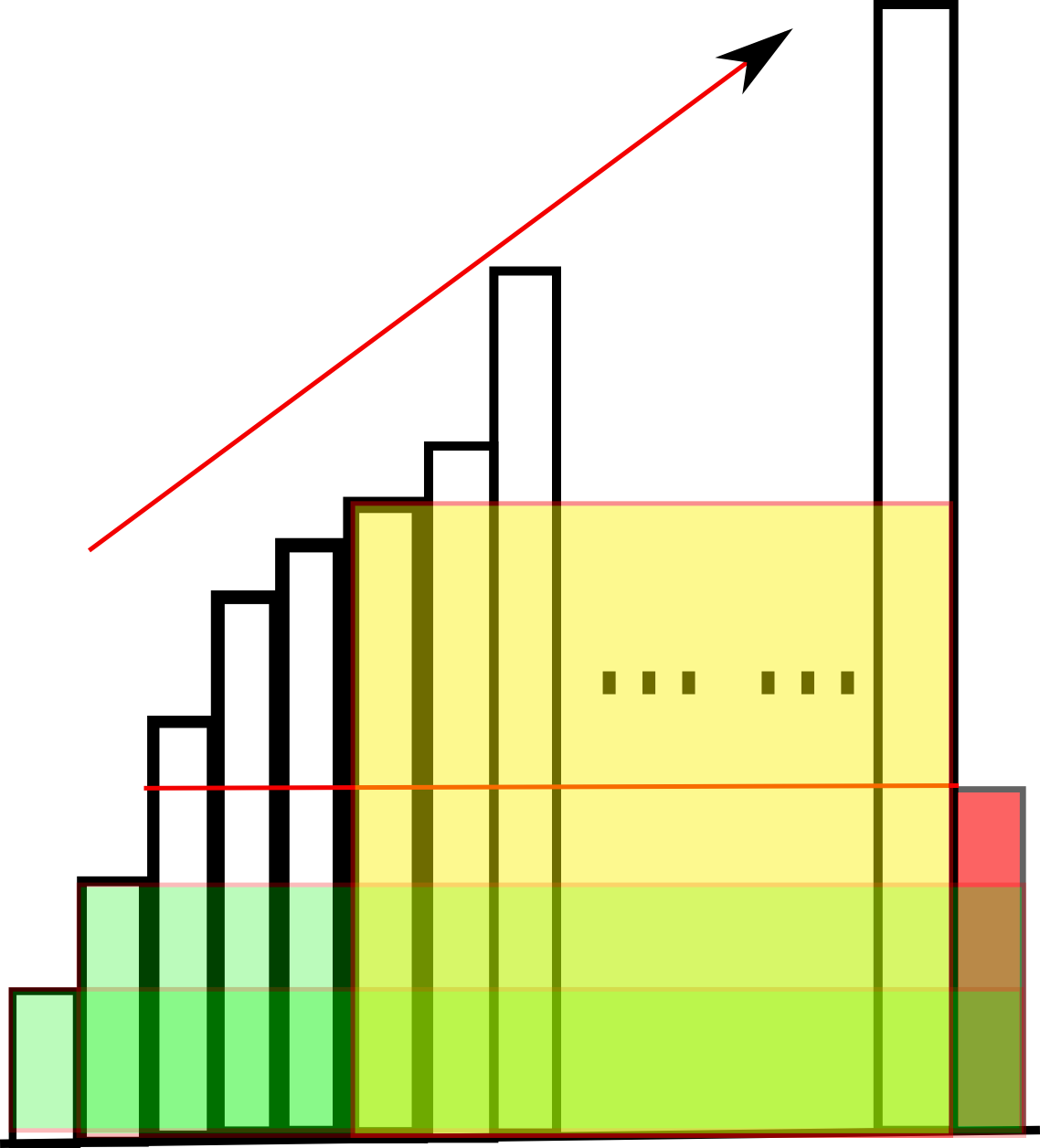
if stack空或者递增就入栈
如果出现个小的, 图中红色。
- 高度位于红线上方的, 也就是不红色高的Bar,不可能和红bar围成一个比大于在弹栈过程中的矩形面积了(黄色面积
- 但是红色可以与黄色bar之前的bar联合, 以长度的优势,获得maxarea, 所以弹栈到比红色bar小就停止了。
注意: 弹栈过程中面积的计算。
h[t] * (stack.isEmpty() ? i : i - stack.peek() - 1)
h[t]是刚刚弹出的栈顶端元素。
栈内索引指向的元素都是比h[t]小的,如果h[t]是目前最小的,那么栈内就是空哦。
而在目前栈顶元素和h[t]之间(不包括h[t]和栈顶元素),都是大于他们两者的。
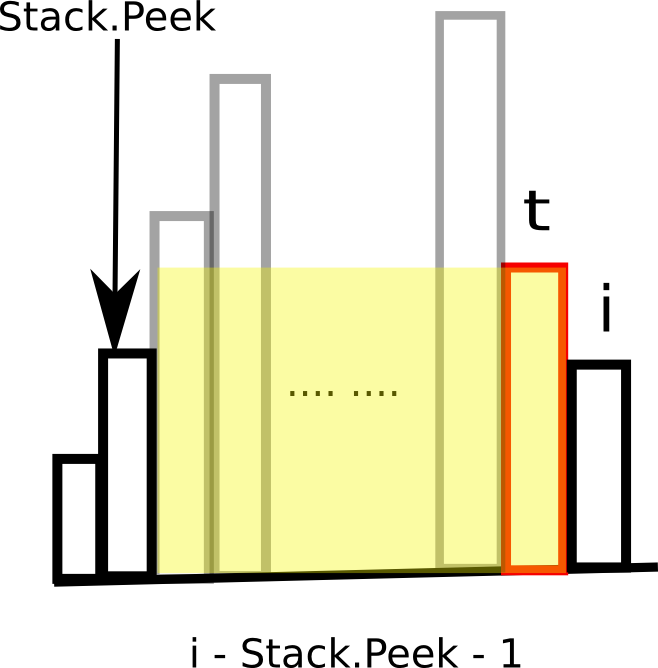
那h[t]无疑就是Stack.Peek和t之间那些上流社会的短板啦,而它们的跨越就是i - Stack.Peek - 1。
10/01 YC version
copy 一个新数组,多家一个0, 太consuming
最后pop到stack empty为止就好
public class Solution { public int largestRectangleArea(int[] height) { int maxArea = 0; Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>(); int i=0; while(i<height.length){ if(stack.isEmpty() || height[stack.peek()] <= height[i]){ stack.push(i); i++; }else{ // current min height index t int t = stack.pop(); int area = (stack.isEmpty() ? i : i-stack.peek()-1) * height[t]; // update if(area > maxArea) maxArea = area; } } while(!stack.isEmpty()){ int t = stack.pop(); int area = (stack.isEmpty() ? i : i-stack.peek()-1) * height[t]; // update if(area > maxArea) maxArea = area; } return maxArea; } }
---
reference
public int largestRectangleArea2(int[] height) { Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>(); int i = 0; int maxArea = 0; int[] h = new int[height.length + 1]; h = Arrays.copyOf(height, height.length + 1); while(i < h.length){ if(stack.isEmpty() || h[stack.peek()] <= h[i]){ stack.push(i++); }else { int t = stack.pop(); maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, h[t] * (stack.isEmpty() ? i : i - stack.peek() - 1)); } } return maxArea; }
http://www.cnblogs.com/lichen782/p/leetcode_Largest_Rectangle_in_Histogram.html







 本文深入探讨了求解直方图中最大矩形面积的问题,从基本的O(N^2)算法出发,逐步引入更高效的O(N)算法,并详细解释了优化思路和关键步骤,旨在帮助读者理解和实现复杂度更低的解决方案。
本文深入探讨了求解直方图中最大矩形面积的问题,从基本的O(N^2)算法出发,逐步引入更高效的O(N)算法,并详细解释了优化思路和关键步骤,旨在帮助读者理解和实现复杂度更低的解决方案。
















 261
261

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








