1、introduction
这篇文章提出了一种将语义与视觉知识相结合的自适应的cross-modal。视觉和语义特征空间根据定义具有不同的结构。对于某些概念,视觉特征可能比文本特征更丰富,更具辨别力。但当视觉信息在图像分类中受到限制时,语义表示(从无监督的文本语料库中学习)可以提供强大的先验知识和上下文以帮助学习。此文就是基于此开展研究的,提出了Adaptive Modality Mixture Mechanism(AM3),an approach that adaptively and selectively combines information from two modalities, visual and semantic, for few-shot learning。AM3在基于度量的元学习方法上形成的,通过比较在已学习的度量空间中的距离来实现分类。文章在原型网络Prototypical Networks for Few-shot Learning的思想基础上,加入了文本信息(即语义表达)。
2、algorithm
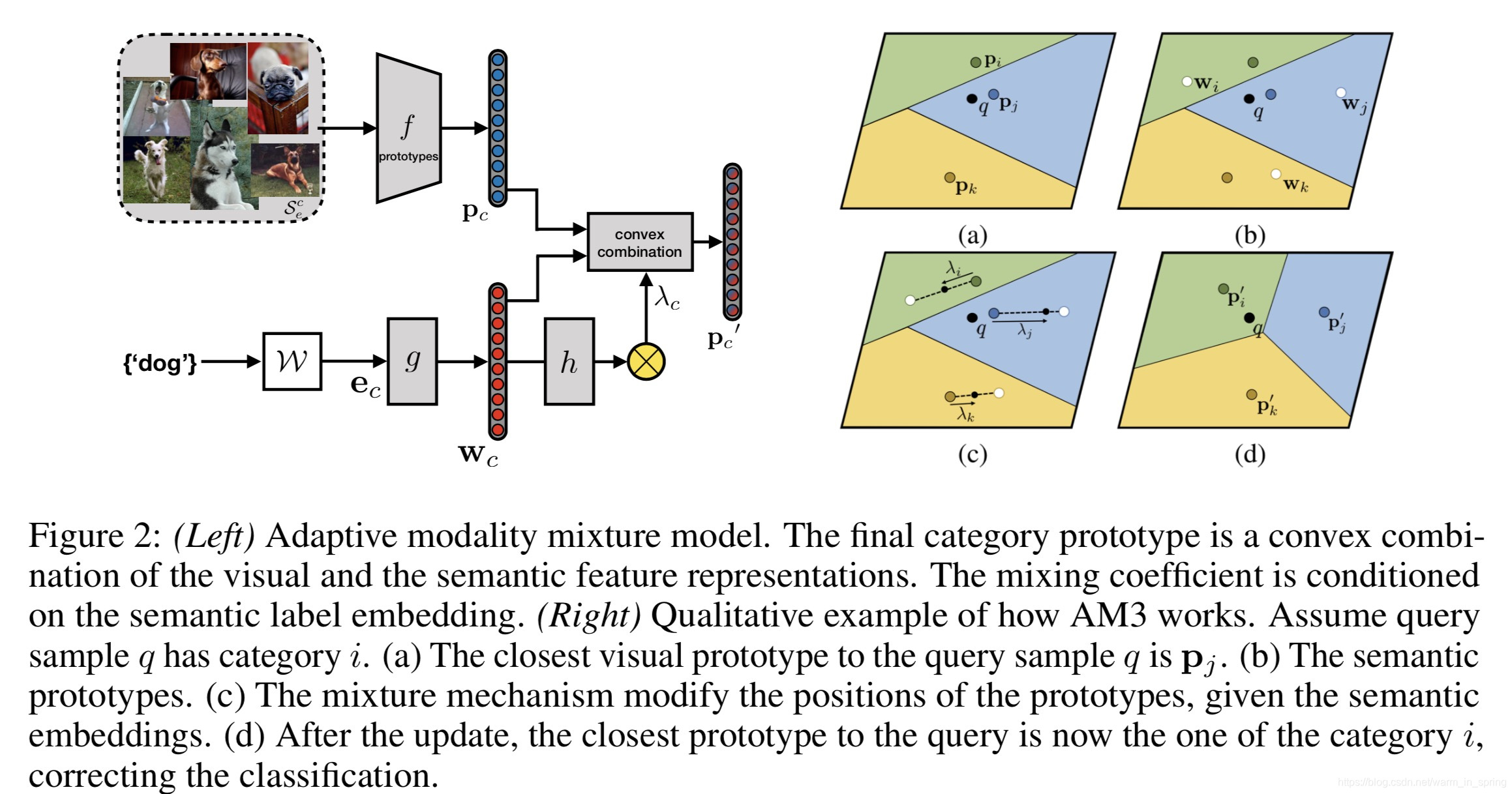
在AM3中,文章增加了基于度量的FSL方法,以结合由词嵌入模型W学习的语言结构(pre-trained on unsupervised large text corpora),在所有类别中包含了label embeddings。由于考虑到了label embeddings,AM3对每个类修改了原型表达(prototype representation)。有上图(左)就可以看出AM3将视觉和语义特征表达的凸组合形成最终的类原型(category prototype),参数化表示为:





 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 967
967

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








