String类:



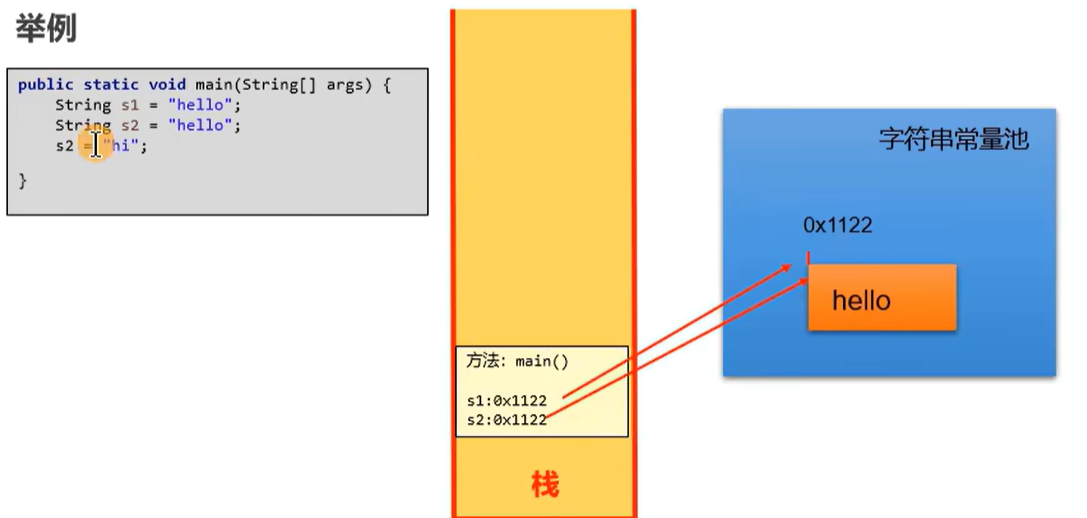
因为不允许存放两个相同的字符串常量,所以下面两个hello在字符串常量池中地址相同
public class StringDemo {
@Test
public void test1(){
String s1 = "hello";
String s2 = "hello";
System.out.println(s1 == s2);//true
}
}
String的不可变性:

public class StringDemo {
@Test
public void test1(){
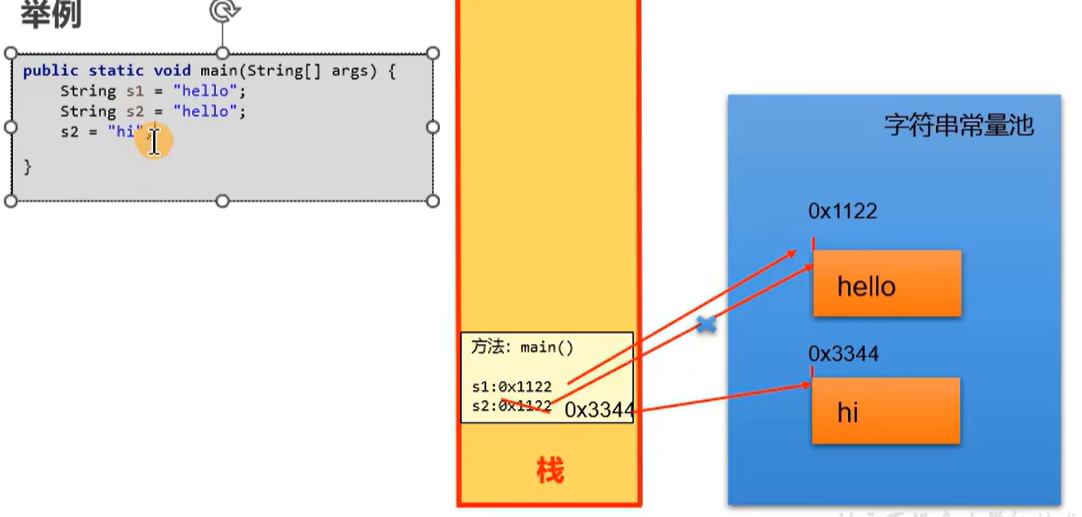
String s1 = "hello";
String s2 = "hello";
s2 += "stguigu";
System.out.println(s1);//hello
System.out.println(s2);//hellostguigu
String s3 =s1.replace("l","w");
System.out.println(s3);//hewwo
}
}
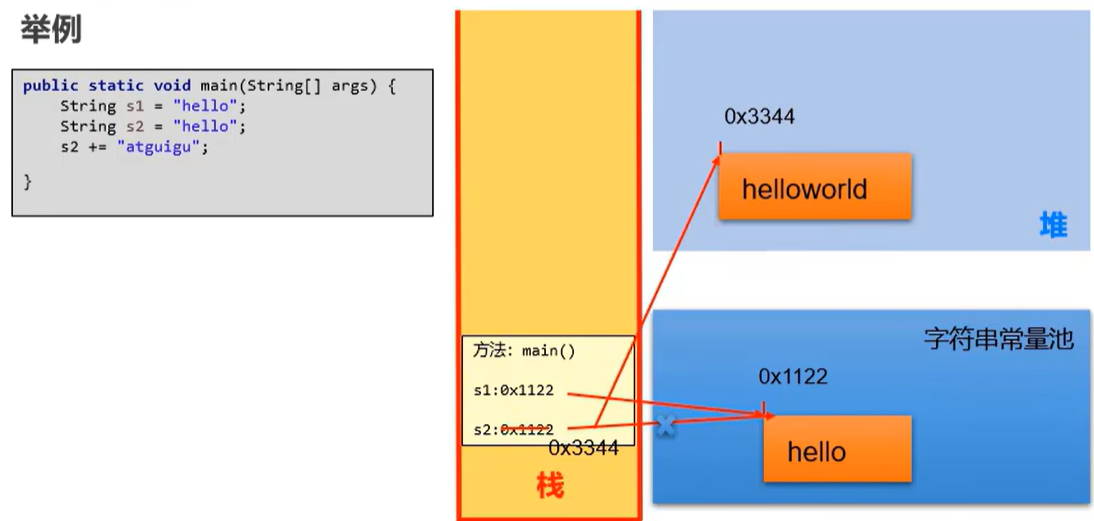
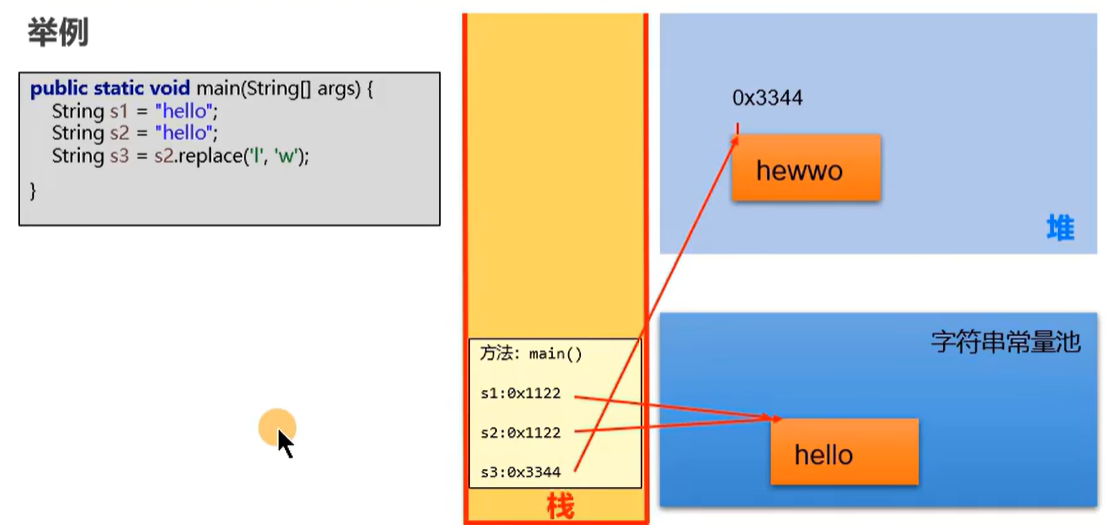
意思就是说:假设如果想改变某个字符串变量,就要重新在内存中开辟一个位置去保存修改后的字符串,不能在原来的位置修改


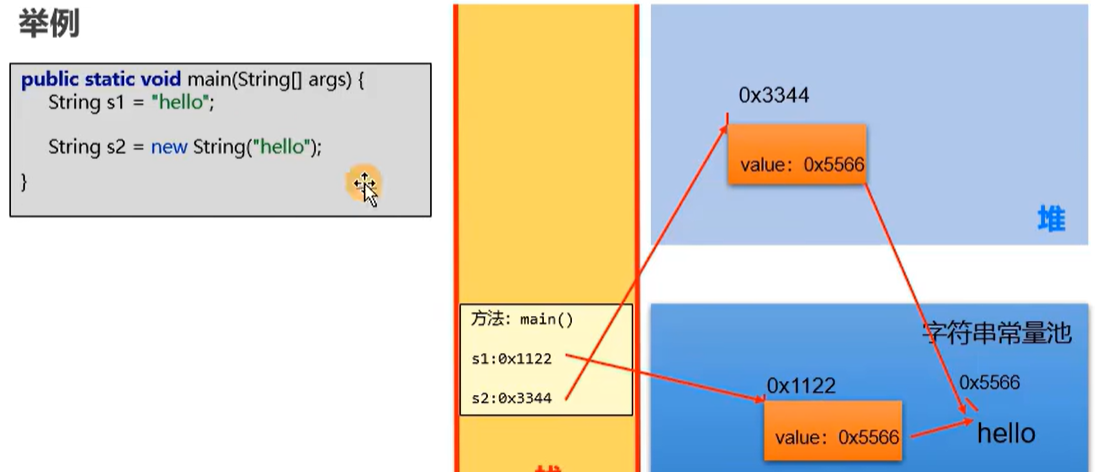
举例:
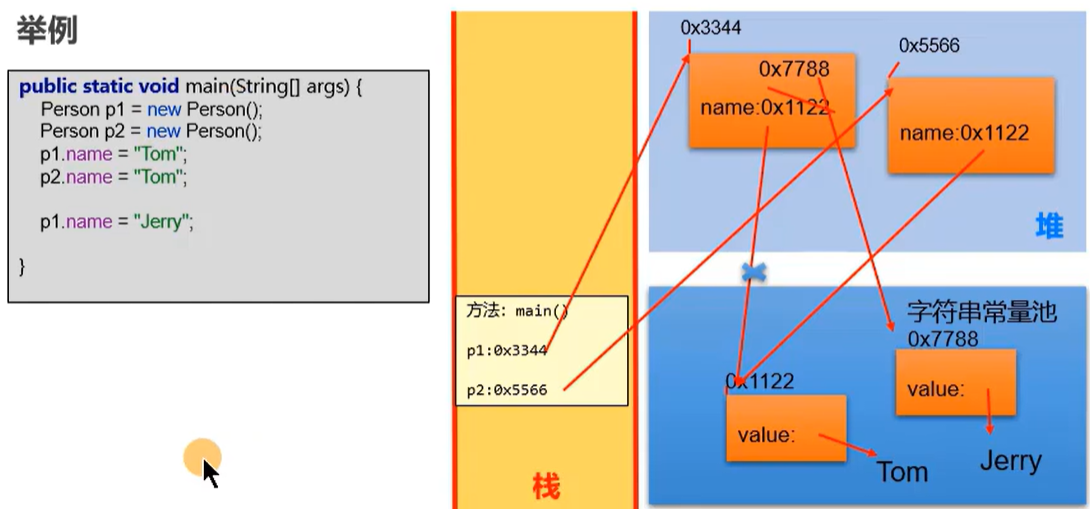
String的连接操作以及concat方法:

情况1中的常量:可能是字面量,也可能是final修饰的常量
举例:

如果变量加了final就会变成常量:
比如:
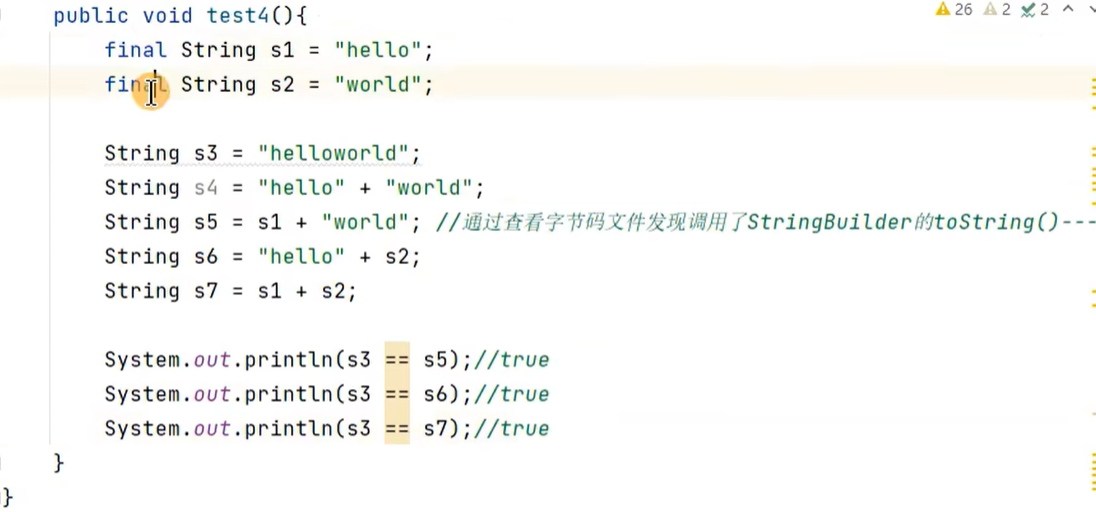

比如:
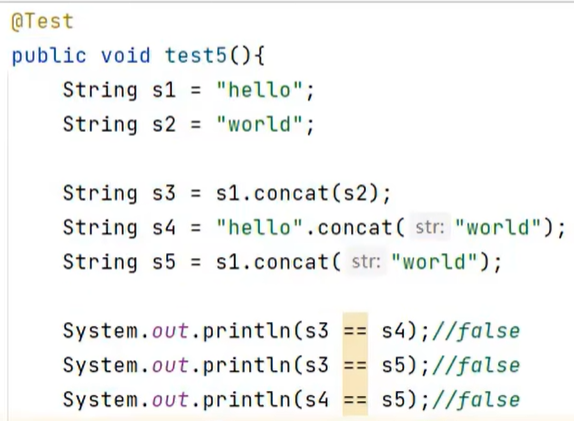
String和byte[]数组之间的转换:
ublic class StringMethod {
@Test
public void test1() {
String s1 = new String();
String s2 = new String("");
String s3 = new String(new char[]{'a','b','c'});
System.out.println(s3);//abc
}
@Test
public void test2(){//复习
int num = 10;
//基本数据类型转换为String类型
//方法一:
String s1 = num + "";
//方法二
String s2 = String.valueOf(num);
String s3 = "123";
//String类型转换为基本数据类型
int i1 = Integer.parseInt(s1);
}
@Test
public void test3(){
//String类型转换为char[]型数组
String str = "Hello";
//调用String的toCharArray()方法
char[] arr = str.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
//char[]型数组转化为String类型
//调用String的构造器
String str2 = new String(arr);
System.out.println(str2);
}
@Test
public void test4() throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
//String类型和byte[]之间的转换
/*
在utf8字符集中,一个汉字占用三个字节,一个字母占用一个字节
在gbk字符集中,一个汉字占用两个字节,一个字母占用一个字节
utf8和gbk都向下兼容了ASCII码
编码与解码:
编码:看得懂的(编写的代码)转换成看不懂的(二进制),就是编码
解码:看不懂的(二进制)转换成看得懂的(编写的代码),就是解码
编码和解码使用的要是相同的字符集,如果不是相同的字符集就会乱码
*/
//String转换为byte[]数组:调用String的getBytes()方法
String s1 = "hello中国";
byte[] arr = s1.getBytes();//使用的是默认字符集,utf8
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
System.out.println();
//getBytes(String charsetName)使用指定的字符集
byte[] arr2 = s1.getBytes("gbk");
for(int i = 0;i < arr2.length; i++) {
System.out.println(arr2[i]);
}
System.out.println();
//byte[]转换为String类型:使用String的构造器
String str1 = new String(arr);
System.out.println(str1);
String str2 = new String(arr,"gbk");//乱码,hello涓浗
System.out.println(str2);
String str3 = new String(arr2,"gbk");
System.out.println(str3);
}
}
String类型的常用方法:

//方法一:isEmpty;
String s1 = "";
String s2 = new String("");
String s3 = new String();
System.out.println(s1.isEmpty());//true
System.out.println(s2.isEmpty());//true
System.out.println(s3.isEmpty());//true
// String s4 = null;
// System.out.println(s4.isEmpty());//报错,空指针异常
//方法二:lenth
String s5 = "abc";
System.out.println(s5.length());//3
//equalsIgnoreCase:
String s6 = "abc";
String s7 = "AbC";
System.out.println(s6.equalsIgnoreCase(s7));//true
//compareTo
String s8 = "abcd";
String s9 = "abef";
System.out.println(s8.compareTo(s9));//-2
//compareToIgnoreCase
String s10 = "abcd";
String s11 = "AbeF";
System.out.println(s10.compareToIgnoreCase(s11));//-2
}
}

@Test
public void test2() {
String s1 = "妄汐霜编程";
System.out.println(s1.contains("编程"));//true
System.out.println(s1.indexOf("编程"));//3
}

@Test
public void test3(){
String s1 = "编程妄汐霜编程";
System.out.println(s1.substring(2));//妄汐霜编程
System.out.println(s1.substring(2,5));//妄汐霜
}

@Test
public void test4(){
String s1 = "编程妄汐霜编程";
System.out.println(s1.charAt(2));//妄
String s2 = String.valueOf(new char[]{'a','b','c'});
String s3 = String.copyValueOf(new char[]{'a','b','c'});
System.out.println(s2);//abc
System.out.println(s3);//abc
System.out.println(s2 == s3);//false,都是新new的
System.out.println(s1.startsWith("编程"));//true
System.out.println(s1.startsWith("妄汐霜"));//false
System.out.println(s1.startsWith("编程",2));//false
System.out.println(s1.startsWith("妄汐霜",2));//true
}

@Test
public void test5(){
String s1 = "hello";
String s2 = s1.replace("e", "www");
System.out.println(s2);//hwwwllo
}
练习1:
public class StringTest {
String str = "good";
char[] ch = {'t', 'e', 's', 't'};
public void change(String str,char ch[]){
str = "test ok";
ch[0] = 'b';
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringTest ex = new StringTest();
ex.change(ex.str,ex.ch);
System.out.println(ex.str);//good
System.out.println(ex.ch);//best
}
}
练习2:

public class StringTest {
@Test
public void test(){
String s = "abcdefg";
String s2 = reverse(s,2,6);
System.out.println(s2);
}
public String reverse(String str,int formIndex,int toIndex){
char[] arr = str.toCharArray();
for(int i = formIndex,j = toIndex - 1;i < j;i++,j--){
char temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
return new String(arr);
}
}
练习3:

public class StringTest1 {
private String name;
private String password;
public StringTest1() {
}
public StringTest1(String name, String password) {
this.name = name;
this.password = password;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "StringTest1{" +
"name='" + name + '-' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
'}';
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建数组,并初始化对象
StringTest1[] arr = new StringTest1[3];
arr[0] = new StringTest1("Tom","8888");
arr[1] = new StringTest1("Jack","123");
arr[2] = new StringTest1("Mary","6666");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean isFlag = false;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.println("库中已有数据" + arr[i].name + "\t" + arr[i].password);
}
System.out.println("请输入用户名");
String name = sc.next();
System.out.println("请输入密码");
String password = sc.next();
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
// 用用户输入的 name 匹配数组中的用户
if (name.equals(arr[i].name)) {
isFlag = true; // 标记找到用户
// 用用户输入的 password 验证密码
if (password.equals(arr[i].password)) {
System.out.println(arr[i].name + "登陆成功");
} else {
System.out.println("密码有误");
}
break; // 找到用户后直接退出循环,无需再遍历
}
}
if(!isFlag){
System.out.println("该用户不存在");
}
sc.close();
}
}
String,StringBuffer()和StringBuilder():

从底层代码上看StringBuffer和StringBuilderB并没有什么太大的区别,就是因为StringBuffer()是线程安全的,
StringBuilder()是线程不安全的,所以要区分成两个方法

不断添加,一旦count要超过value.length时,就需要扩容,默认扩容为原有容量的2倍 + 2

如果提前大体上知道了要操作的字符个数,就使用带int capacity这个参数的构造器。
StringBuffer和StringBuilder中常用方法:
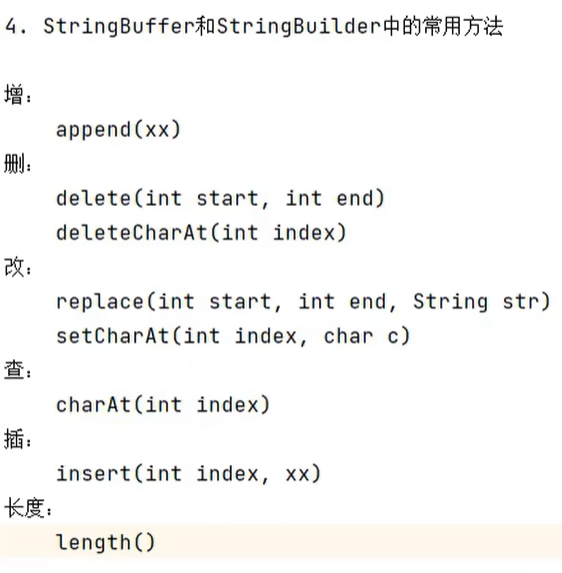
还有一个反转:StringBuffer reverse()
括号里的范围都是左闭右开。
那个length()返回的是实际存储的字符的个数
方法测试:
public void test1(){
StringBuilder sBuilder = new StringBuilder("hello");
sBuilder.insert(2,"妄汐霜");//插入字符串
System.out.println(sBuilder);//he妄汐霜llo
sBuilder.insert(2,4);//插入数字
System.out.println(sBuilder);//he4妄汐霜llo
StringBuffer sBuffer1 = new StringBuffer("hello妄汐霜");
StringBuffer stringBuffer = sBuffer1.reverse();
System.out.println(sBuffer1);//霜汐妄olleh
System.out.println(stringBuffer);//霜汐妄olleh
System.out.println(sBuffer1 == stringBuffer);//true
可以看到,对StringBuffer和StringBuilder类已创建的对象使用方法时,会对已创建的对象进行修改,这就是StringBuffer和StringBuilder的可变性。和String的不可变性不同。
其他API:

5.对比三者的效率:
效率从高到低排列:
StringBuilder > StringBuffer > String
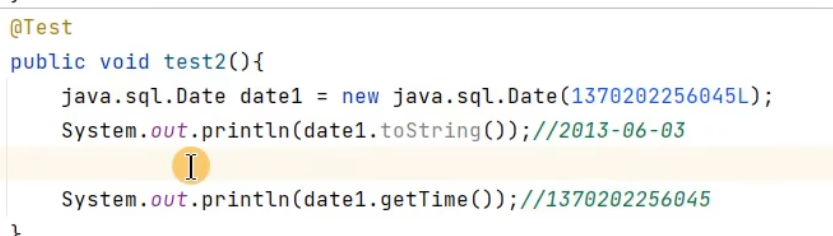
JDK8之前日期时间API的使用:



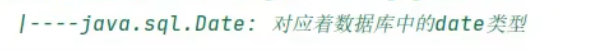
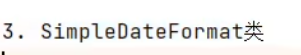

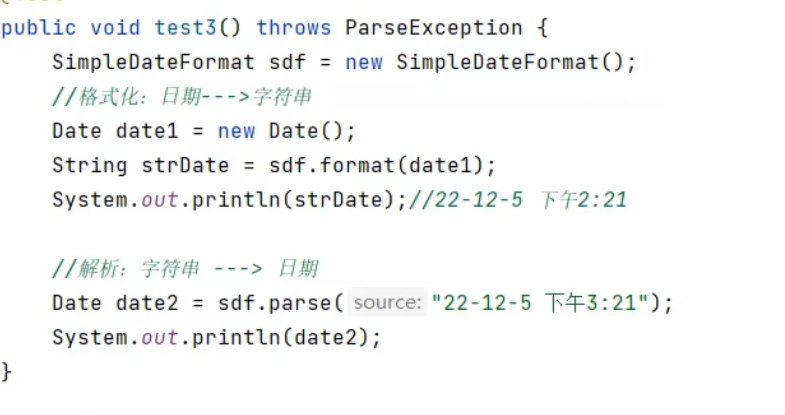
指定格式:

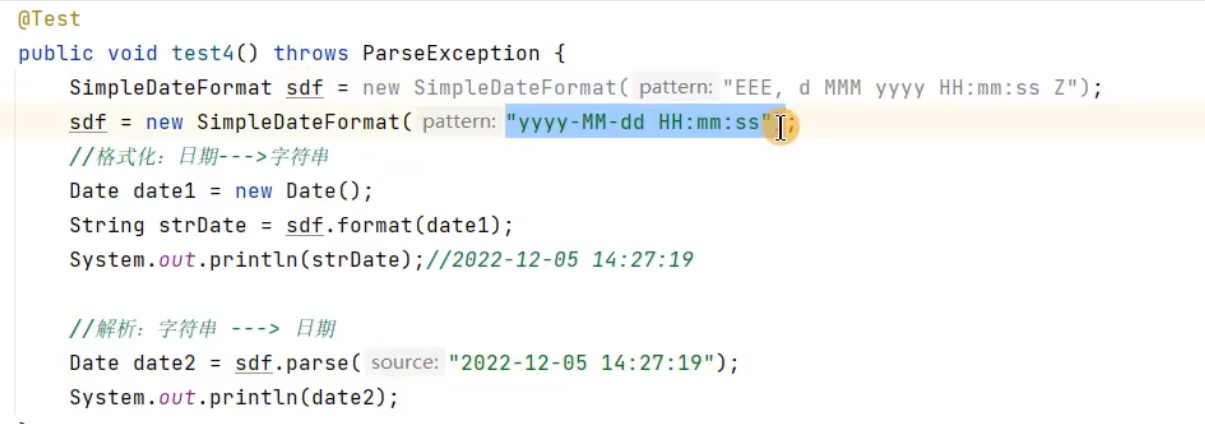


练习:

JDK8中新增的日期时间API的使用:

LocalDate/LocalTime/LocalDateTime
//JDK8中的API:LocalDate/LocalTime/LocalDateTime
//now()获取当前的时间
LocalDate localDate = LocalDate.now();
LocalDate localDate1 = LocalDate.of(2025,11,24);
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println(localDate);
System.out.println(localDateTime);
System.out.println(localDate1);
//of()获取指定的日期
LocalDate localDate2 = localDate.of(2025, 11, 24);
LocalDateTime localDateTime1 = localDateTime.of(2025,5,23,3,42);
System.out.println(localDate2);
System.out.println(localDateTime1);
now()和of()方法就相当于造对象
常用方法:
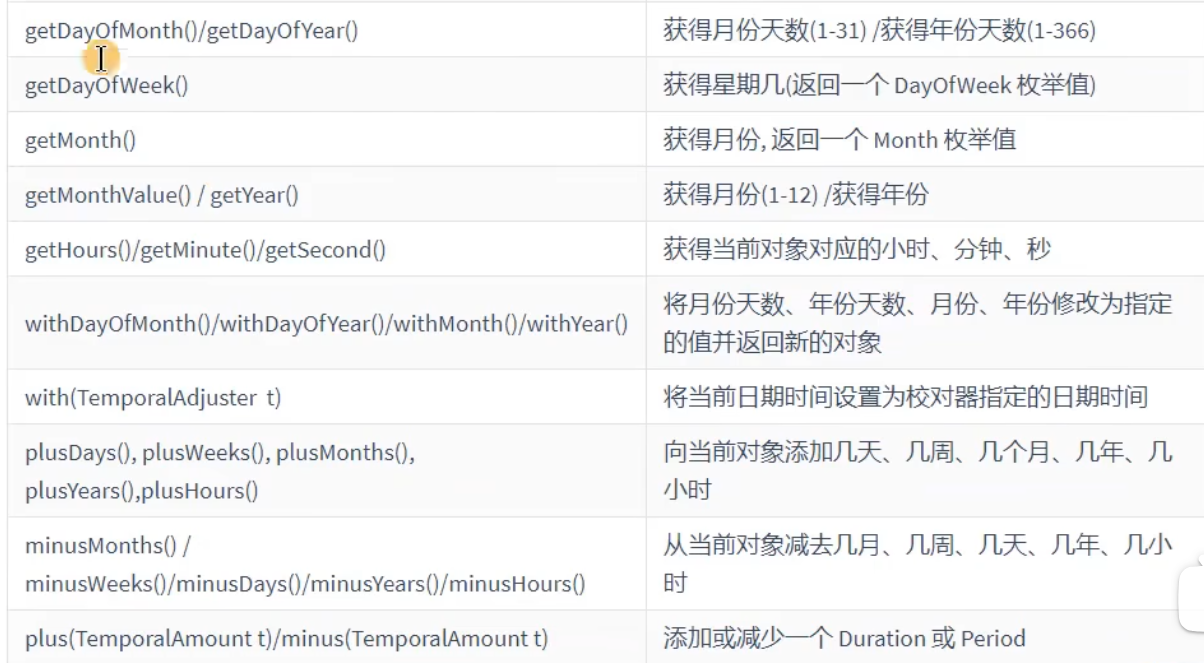
方法测试:
//of()获取指定的日期
LocalDate localDate2 = localDate.of(2025, 11, 24);
LocalDateTime localDateTime1 = localDateTime.of(2025,5,23,3,42);
System.out.println(localDate2);
System.out.println(localDateTime1);
//get
LocalDateTime localDateTime2 = LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println(localDateTime2.getDayOfMonth());
//体现不可变性
//with方法
LocalDateTime localDateTime3 = localDateTime2.withDayOfMonth(15);
System.out.println(localDateTime3);
System.out.println(localDateTime2);
//plus方法
//就是加天数,不测了

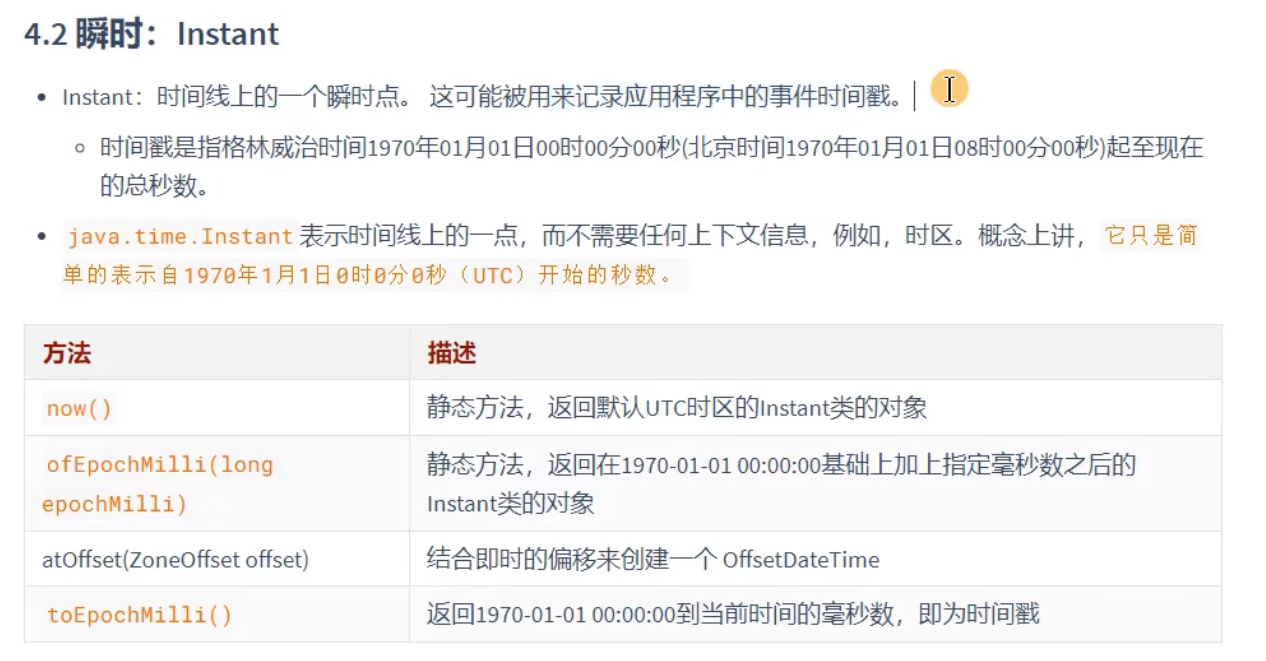
方法测试:
public class InstantTest {
@Test
public void test1(){
Instant instant = Instant.now();
System.out.println(instant);//获取到的是中时区的时间
//获取中国时间的话要加8
OffsetDateTime instant1 = instant.atOffset(ZoneOffset.ofHours(8));
System.out.println(instant1);//获取的就是北京时间
Instant instant2 = Instant.ofEpochMilli(12323252345253L);
System.out.println(instant2);//造对象
long millTime = instant.toEpochMilli();//获取毫秒数
System.out.println(millTime);
}
}

public void test2(){
//自定义的格式
DateTimeFormatter dateTimeFormatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
//格式化:日期,时间-->字符串
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.now();
String format = dateTimeFormatter.format(localDateTime);
System.out.println(format);
//解析:字符串-->日期,时间
TemporalAccessor t1 = dateTimeFormatter.parse("2020-01-01 01:01:01");
LocalDateTime localDateTime1 = LocalDateTime.from(t1);
System.out.println(localDateTime1);
}
练习:

public class Test1 {
@Test
public void test1(){
Calendar instance1 = Calendar.getInstance();
instance1.add(Calendar.DAY_OF_YEAR,100);
System.out.println(instance1.getTime());
}
@Test
public void test2() {
LocalDateTime l1 = LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println(l1);
LocalDateTime l2 = l1.plusDays(100);
System.out.println(l2);
}
}
使用Comparable接口实现自然排序:

这个是自然排序
具体的类实现接口:
public class Product implements Comparable{
private String name;
private double price;
public Product() {
}
public Product(String name, double price) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Product{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Object o) {
if(o == this){
return 0;
}
if(o instanceof Product){
Product p = (Product) o;
return Double.compare(this.price,p.price);
}
throw new RuntimeException("类型不匹配");
}
}
测试:
public void test2(){
Product[] arr = new Product[5];
arr[0] = new Product("apple", 3344);
arr[1] = new Product("computer", 4377);
arr[2] = new Product("tv", 6666);
arr[3] = new Product("phone", 9999);
arr[4] = new Product("vivo", 8888);
Arrays.sort(arr);
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
}
使用Comparator定制排序:

举例;
public class ComparableTest {
@Test
public void test1() {
Product[] arr = new Product[5];
arr[0] = new Product("Iphone", 9000);
arr[1] = new Product("Iqoo", 8000);
arr[2] = new Product("Ipad", 6000);
arr[3] = new Product("Iwatch", 5000);
arr[4] = new Product("vivo", 5000);
//创建一个实例实现comparator接口的实现类
Comparator c1 = new Comparator() {
//重写compare方法
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
if(o1 instanceof Product && o2 instanceof Product) {
Product p1 = (Product) o1;
Product p2 = (Product) o2;
return Double.compare(p1.getPrice(), p2.getPrice());
}
throw new RuntimeException("类型不匹配");
}
};
Arrays.sort(arr, c1);
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
}
}

其他常用类的使用:

System:


Runtime:

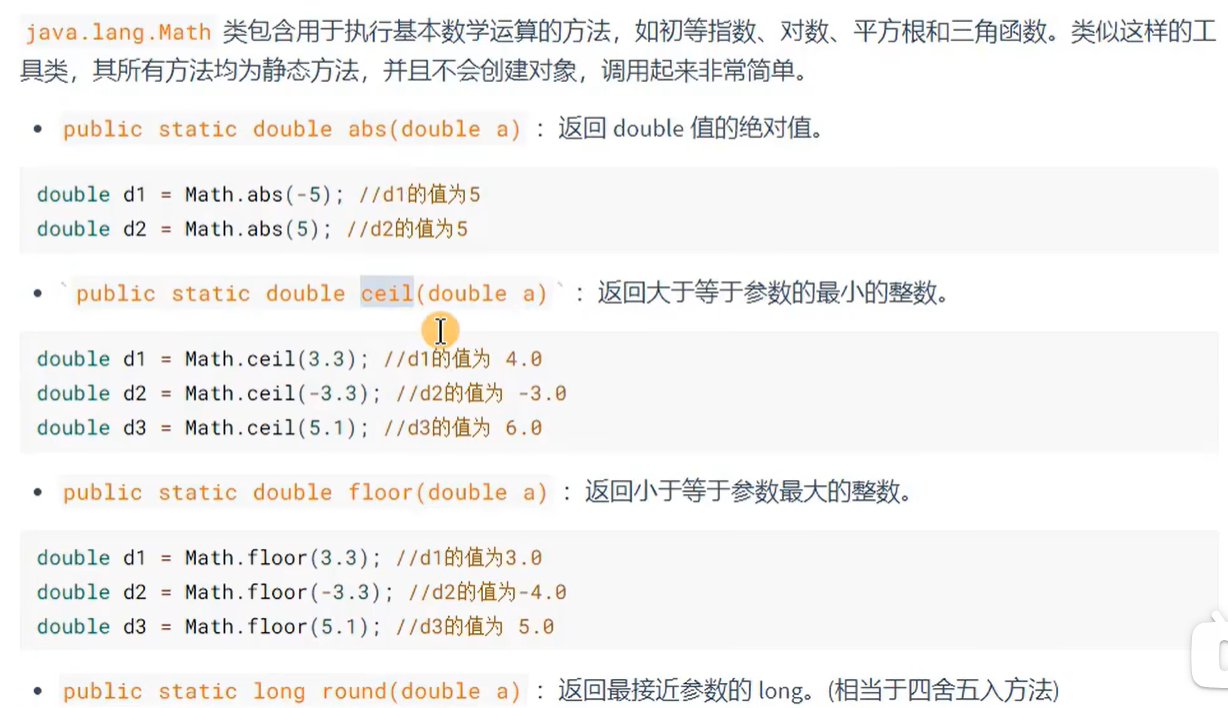
Math:
BigInteger/BigDecimal/:


Random:

企业真题:























 930
930

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








