介绍
本文主要是通过引入信息最大化来解决HiAGM(应该是对于HiAGM-LA)存在的两个限制。
问题:
HiAGM存在两个问题:
1)对每个样本都使用相同的标签层次信息,这样就不能区分与特定文本样本有关和无关的标签。尽管HiAGM-LA能够通过注意力权重隐含地来让每个样本和与其对应的标签联系起来,但仍然存在不相关和噪音信息。
2)HiAGM-LA中产生的label embedding没有统计约束(这是个啥?),然而这种统计约束在之前的论文中被证明是非常有效的。
IDEA:
引入信息最大化来解决HiAGM-LA中的限制,该方法由两个模块组成:text-label交互信息最大化和HiAGM-LA上的标签预先匹配。在第一个模块中,通过最大化每个文本样本和它对应标签之间的互信息(互信息好像是信息论里面的一个概念,作者在本文中提到了一篇相关论文Deep InfoMax 具体论文解读可以看这个文章 对 Deep InfoMax(DIM)的理解 - 知乎 )来建立明确的连接,这样就能对特定的样本过滤掉不相干的标签信息。标签预先匹配模块,对每个标签学习到的表征增加一些约束,迫使结构编码器能够对所有标签学习到理想的表征,这样也提高了低频率标签表征的质量,有助于更好的处理标签不平衡的问题。
方法
模型整体结构如下图所示,作者在HiAGM-LA的基础上增加了text-label mutual information和label prior matching模块。
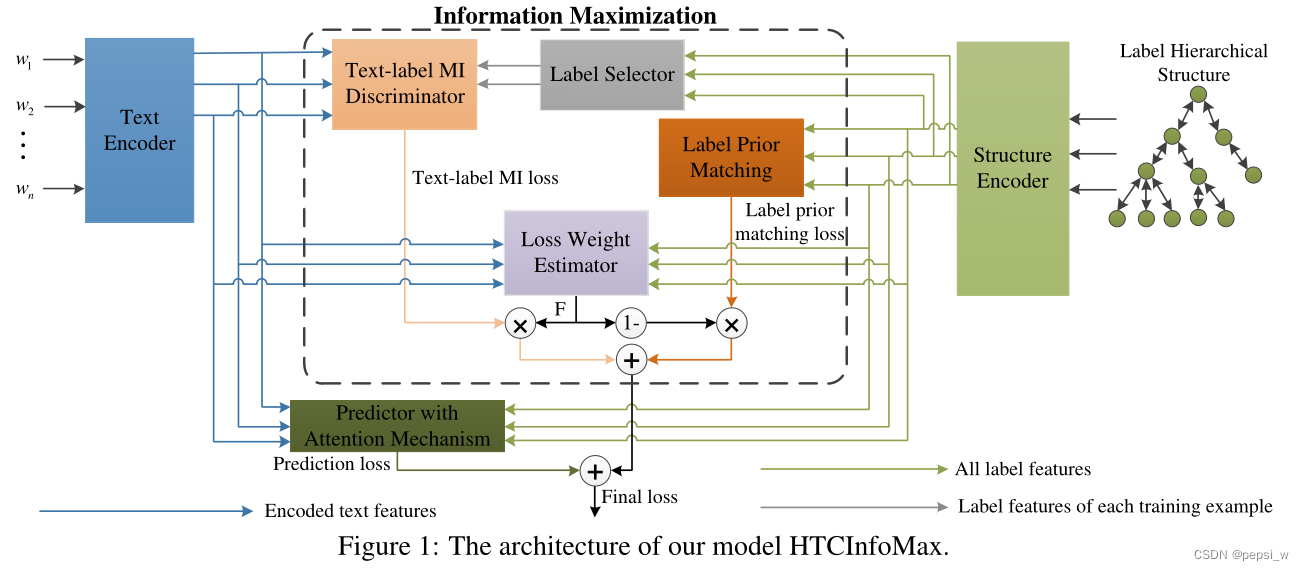
Text-label mutual information estimation and maximization
HiAGM-LA通过多标签注意力将标签信息和文本信息进行交互,虽然能让文本信息得到一些标签信息,但这样也引入了一些其他无关的标签信息。因此作者提出了text-label交互信息最大化模块,移除不相干的标签信息同时也能让文本信息与它对应的标签信息进行交互。(感觉就是通过对比label和text之间的表征,训练编码器,学到与label更加相关的表征)
首先在训练过程中,为每个文本样本选择正确的标签,然后使用一个鉴别器(discriminator)来对文本和它标签之间的互信息进行估计。Pt和Py分别表示文本特征和标签表征的分布,Pty表示文本和标签的联合分布,从中抽取出正样本对,在pt和py边缘分布的乘积中抽取负样本
,也就是将y与同一批次中的其他文本
进行配对。将正负样本送服到鉴别器
中进行分类以及估计交互信息
,其中
、
分别表示判别器认为是正负样本的概率分数。
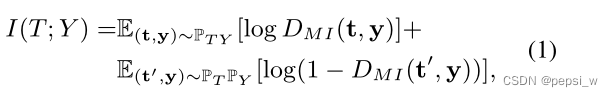
该模块的目标是最大化,因此其损失函数:
![]()
Label prior matching
HTC任务中存在标签不平衡的问题,由于训练样本较少导致对低频率的label embedding欠拟合。label prior matching模块对每个标签学到的表征加入了一些统计约束。作者使用了一种类似于对抗自动编码器中对抗训练的方法,但没有用一个生成器来强制学习的标签表征和先验分布进行匹配。
对于每个标签,我们利用Dpr来计算其相应的先验匹配损失lpr,损失函数是为了将标签的学习表征分布P推向其先验分布Q,最终的匹配损失是所有标签损失的平均值。这个想法是受到DIM的启发,但与其不太一样的是,它通过对每个标签的表征增加约束,来训练结构编码器学习所有标签的理想表征。
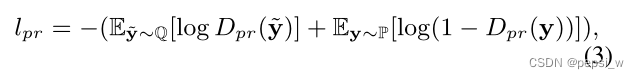
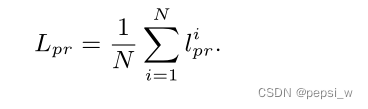
该模块采用区间上[1,0)的均匀分布作为先验分布Q,这是根据DIM来的。
Final loss of HTCInfoMax
使用损失权重估计器来学习text-label互信息损失和标签先验匹配损失,w1和w2都是可训练的参数:
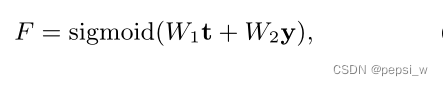
来自predictor采用交叉熵损失,总损失如下:
![]()
实验
与HiAGM进行对比实验,结果如下:
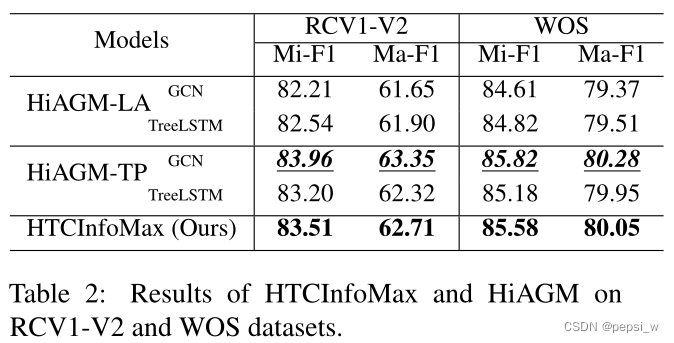
由于我们的模型主要是去解决HiAGM-LA的限制,可以看出作者提出的HTCInfoMax在两个数据集上都比HiAGM-LA表现得好,特别是在RCV1-V2数据集上得提升更大一点,表示作者提出的模型在更复杂的数据集上效果会更好。
虽然效果不如HiAGM-TP,但作者提出的模型也达到了与其相似的水平。表明信息最大化也可以将文本特征和标签信息融合在一起来提高模型性能的一种方法。除了产生文本标注,通过信息最大化,模型还能产生用于推理的细粒度标签表征。但HiAGM-TP由于是直接将文本特征送到结构编码器中来获得用于预测的文本表征,所有他在预测阶段不能生成这种标签embedding。
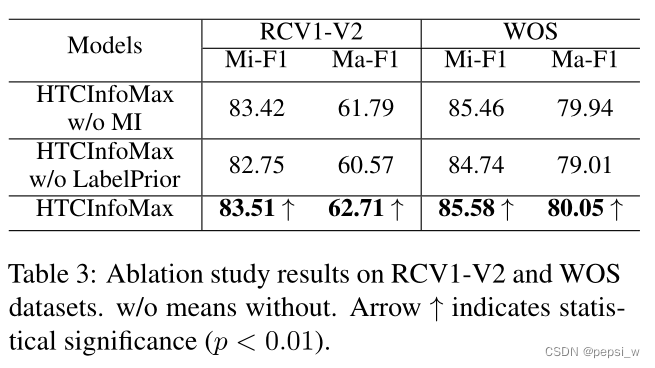
作者对模型中的两个模块进行了消融实验,结果如下:
总结
我们提出HTCInfoMax来解决HiAGM的局限性,它包括两个模块:文本-标签相互信息最大化和标签先验匹配。标签先验匹配可以驱动模型为所有的标签学习更好的表征,而另一个模块则进一步将这些学习到的标签表征融合到文本中,以学习包含有效标签信息的更好的文本表征,用于预测。





 针对HiAGM-LA存在的标签信息无法个性化及标签表征缺乏统计约束的问题,提出HTCInfoMax模型,通过文本-标签互信息最大化及标签先验匹配两个模块,解决了标签不平衡及噪声信息干扰等问题。
针对HiAGM-LA存在的标签信息无法个性化及标签表征缺乏统计约束的问题,提出HTCInfoMax模型,通过文本-标签互信息最大化及标签先验匹配两个模块,解决了标签不平衡及噪声信息干扰等问题。
















 8843
8843

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








