SparkEnv
源码版本2.4.7
shufflemanager实例是SortShuffleManager spark数据shuffle读写是通过
SparkEnv.get.shuffleManager控制完成的
shuffleRdd的compute —>SparkEnv.get.shuffleManager.getReader
shuffleMaptask的write —>SparkEnv.get.shuffleManager.getWriter
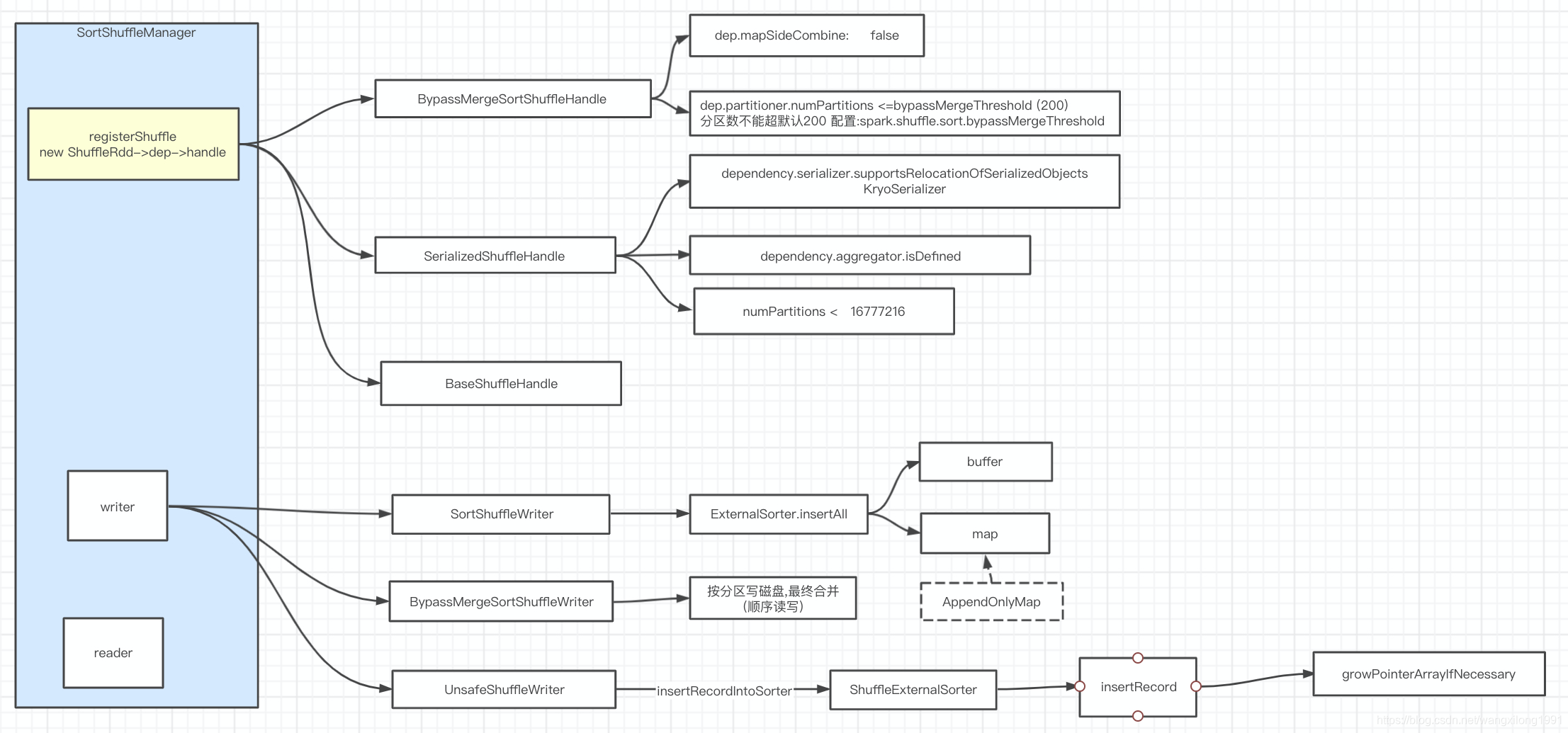
shufflerdd->getDependencies->new ShuffleDependency->registerShuffle
// Let the user specify short names for shuffle managers
val shortShuffleMgrNames = Map(
"sort" -> classOf[org.apache.spark.shuffle.sort.SortShuffleManager].getName,
"tungsten-sort" -> classOf[org.apache.spark.shuffle.sort.SortShuffleManager].getName)
val shuffleMgrName = conf.get("spark.shuffle.manager", "sort")
val shuffleMgrClass =
shortShuffleMgrNames.getOrElse(shuffleMgrName.toLowerCase(Locale.ROOT), shuffleMgrName)
val shuffleManager = instantiateClass[ShuffleManager](shuffleMgrClass)
override def getDependencies: Seq[Dependency[_]] = {
val serializer = userSpecifiedSerializer.getOrElse {
val serializerManager = SparkEnv.get.serializerManager
if (mapSideCombine) {
serializerManager.getSerializer(implicitly[ClassTag[K]], implicitly[ClassTag[C]])
} else {
serializerManager.getSerializer(implicitly[ClassTag[K]], implicitly[ClassTag[V]])
}
}
List(new ShuffleDependency(prev, part, serializer, keyOrdering, aggregator, mapSideCombine))
}
//ShuffleDependency
val shuffleHandle: ShuffleHandle = _rdd.context.env.shuffleManager.registerShuffle(
shuffleId, _rdd.partitions.length, this)
/**
* Obtains a [[ShuffleHandle]] to pass to tasks.
*/
override def registerShuffle[K, V, C](
shuffleId: Int,
numMaps: Int,
dependency: ShuffleDependency[K, V, C]): ShuffleHandle = {
if (SortShuffleWriter.shouldBypassMergeSort(conf, dependency)) {
// If there are fewer than spark.shuffle.sort.bypassMergeThreshold partitions and we don't
// need map-side aggregation, then write numPartitions files directly and just concatenate
// them at the end. This avoids doing serialization and deserialization twice to merge
// together the spilled files, which would happen with the normal code path. The downside is
// having multiple files open at a time and thus more memory allocated to buffers.
new BypassMergeSortShuffleHandle[K, V](
shuffleId, numMaps, dependency.asInstanceOf[ShuffleDependency[K, V, V]])
} else if (SortShuffleManager.canUseSerializedShuffle(dependency)) {
// Otherwise, try to buffer map outputs in a serialized form, since this is more efficient:
new SerializedShuffleHandle[K, V](
shuffleId, numMaps, dependency.asInstanceOf[ShuffleDependency[K, V, V]])
} else {
// Otherwise, buffer map outputs in a deserialized form:
new BaseShuffleHandle(shuffleId, numMaps, dependency)
}
}
shuffle有三种处理器:
- BypassMergeSortShuffleHandle
map端无聚合,且分区数少于默认200
分区数不大且不需要map端聚合,直接溢写分区文件,避免合并溢写文件序列化、反序列化操作,缺点open many files 需要更多的内存缓冲
def shouldBypassMergeSort(conf: SparkConf, dep: ShuffleDependency[_, _, _]): Boolean = {
// We cannot bypass sorting if we need to do map-side aggregation.
if (dep.mapSideCombine) {
false
} else {
val bypassMergeThreshold: Int = conf.getInt("spark.shuffle.sort.bypassMergeThreshold", 200)
dep.partitioner.numPartitions <= bypassMergeThreshold
}
- SerializedShuffleHandle
serializer参数支持relocation–>KryoSerializer,
支持relocation是指,Serializer可以对已经序列化的对象进行排序,这种排序起到的效果和先对数据排序再序列化一致。
支持relocation的Serializer是KryoSerializer
且map端不聚合,分区数少于16777216
序列化的方式缓冲map输出,效率会高一些
/**
* Helper method for determining whether a shuffle should use an optimized serialized shuffle
* path or whether it should fall back to the original path that operates on deserialized objects.
*/
def canUseSerializedShuffle(dependency: ShuffleDependency[_, _, _]): Boolean = {
val shufId = dependency.shuffleId
val numPartitions = dependency.partitioner.numPartitions
if (!dependency.serializer.supportsRelocationOfSerializedObjects) {
log.debug(s"Can't use serialized shuffle for shuffle $shufId because the serializer, " +
s"${dependency.serializer.getClass.getName}, does not support object relocation")
false
} else if (dependency.mapSideCombine) {
log.debug(s"Can't use serialized shuffle for shuffle $shufId because we need to do " +
s"map-side aggregation")
false
} else if (numPartitions > MAX_SHUFFLE_OUTPUT_PARTITIONS_FOR_SERIALIZED_MODE) {
log.debug(s"Can't use serialized shuffle for shuffle $shufId because it has more than " +
s"$MAX_SHUFFLE_OUTPUT_PARTITIONS_FOR_SERIALIZED_MODE partitions")
false
} else {
log.debug(s"Can use serialized shuffle for shuffle $shufId")
true
}
}
- BaseShuffleHandle
以反序列化形式缓冲
即序列化的数据不支持排序
看ShuffleMapTask的runTask
override def runTask(context: TaskContext): MapStatus = {
// Deserialize the RDD using the broadcast variable.
val threadMXBean = ManagementFactory.getThreadMXBean
val deserializeStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis()
val deserializeStartCpuTime = if (threadMXBean.isCurrentThreadCpuTimeSupported) {
threadMXBean.getCurrentThreadCpuTime
} else 0L
val ser = SparkEnv.get.closureSerializer.newInstance()
val (rdd, dep) = ser.deserialize[(RDD[_], ShuffleDependency[_, _, _])](
ByteBuffer.wrap(taskBinary.value), Thread.currentThread.getContextClassLoader)
_executorDeserializeTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - deserializeStartTime
_executorDeserializeCpuTime = if (threadMXBean.isCurrentThreadCpuTimeSupported) {
threadMXBean.getCurrentThreadCpuTime - deserializeStartCpuTime
} else 0L
var writer: ShuffleWriter[Any, Any] = null
try {
val manager = SparkEnv.get.shuffleManager
writer = manager.getWriter[Any, Any](dep.shuffleHandle, partitionId, context)
writer.write(rdd.iterator(partition, context).asInstanceOf[Iterator[_ <: Product2[Any, Any]]])
writer.stop(success = true).get
} catch {
case e: Exception =>
try {
if (writer != null) {
writer.stop(success = false)
}
} catch {
case e: Exception =>
log.debug("Could not stop writer", e)
}
throw e
}
}
Handle决定了ShuffleWriter的类型
**SortShuffleManager**
/** Get a writer for a given partition. Called on executors by map tasks. */
override def getWriter[K, V](
handle: ShuffleHandle,
mapId: Int,
context: TaskContext): ShuffleWriter[K, V] = {
numMapsForShuffle.putIfAbsent(
handle.shuffleId, handle.asInstanceOf[BaseShuffleHandle[_, _, _]].numMaps)
val env = SparkEnv.get
handle match {
case unsafeShuffleHandle: SerializedShuffleHandle[K @unchecked, V @unchecked] =>
new UnsafeShuffleWriter(
env.blockManager,
shuffleBlockResolver.asInstanceOf[IndexShuffleBlockResolver],
context.taskMemoryManager(),
unsafeShuffleHandle,
mapId,
context,
env.conf)
case bypassMergeSortHandle: BypassMergeSortShuffleHandle[K @unchecked, V @unchecked] =>
new BypassMergeSortShuffleWriter(
env.blockManager,
shuffleBlockResolver.asInstanceOf[IndexShuffleBlockResolver],
bypassMergeSortHandle,
mapId,
context,
env.conf)
case other: BaseShuffleHandle[K @unchecked, V @unchecked, _] =>
new SortShuffleWriter(shuffleBlockResolver, other, mapId, context)
}
}
- SerializedShuffleHandle – UnsafeShuffleWriter
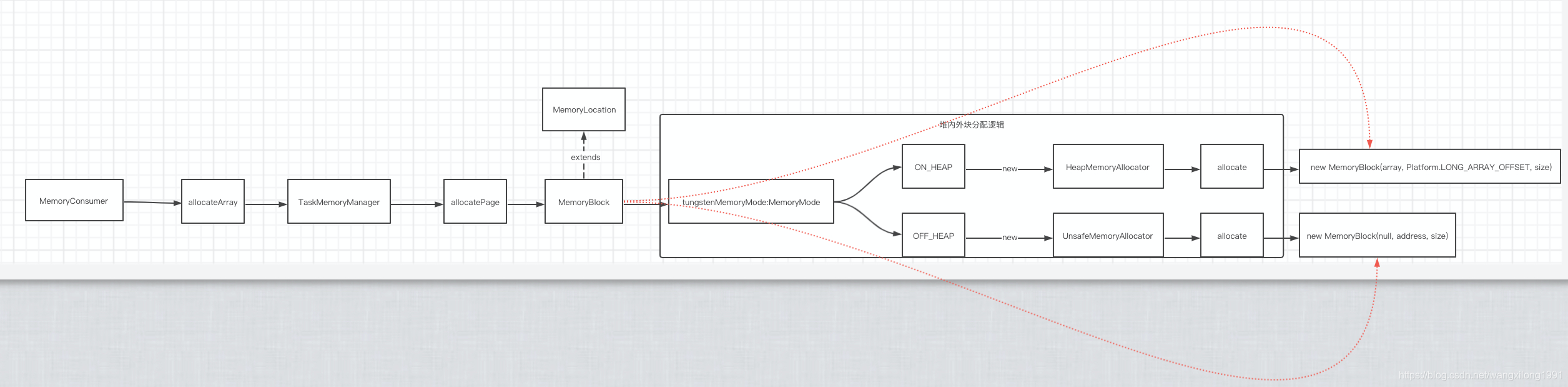
write->insertRecordIntoSorter->serOutputStream->ShuffleExternalSorter sorter->sorter.insertRecord->spill->writeSortedFile
ShuffleInMemorySorter用来排序,ShuffleExternalSorter管理释放内存
@Override
public void write(scala.collection.Iterator<Product2<K, V>> records) throws IOException {
// Keep track of success so we know if we encountered an exception
// We do this rather than a standard try/catch/re-throw to handle
// generic throwables.
boolean success = false;
try {
while (records.hasNext()) {
insertRecordIntoSorter(records.next());
}
closeAndWriteOutput();
success = true;
} finally {
if (sorter != null) {
try {
sorter.cleanupResources();
} catch (Exception e) {
// Only throw this error if we won't be masking another
// error.
if (success) {
throw e;
} else {
logger.error("In addition to a failure during writing, we failed during " +
"cleanup.", e);
}
}
}
}
}
void insertRecordIntoSorter(Product2<K, V> record) throws IOException {
assert(sorter != null);
final K key = record._1();
final int partitionId = partitioner.getPartition(key);
serBuffer.reset();
serOutputStream.writeKey(key, OBJECT_CLASS_TAG);
serOutputStream.writeValue(record._2(), OBJECT_CLASS_TAG);
serOutputStream.flush();
final int serializedRecordSize = serBuffer.size();
assert (serializedRecordSize > 0);
sorter.insertRecord(
serBuffer.getBuf(), Platform.BYTE_ARRAY_OFFSET, serializedRecordSize, partitionId);
}
/**
* Write a record to the shuffle sorter.
*/
public void insertRecord(Object recordBase, long recordOffset, int length, int partitionId)
throws IOException {
// for tests
assert(inMemSorter != null);
if (inMemSorter.numRecords() >= numElementsForSpillThreshold) {
logger.info("Spilling data because number of spilledRecords crossed the threshold " +
numElementsForSpillThreshold);
spill();
}
growPointerArrayIfNecessary();
final int uaoSize = UnsafeAlignedOffset.getUaoSize();
// Need 4 or 8 bytes to store the record length.
final int required = length + uaoSize;
acquireNewPageIfNecessary(required);
assert(currentPage != null);
final Object base = currentPage.getBaseObject();
final long recordAddress = taskMemoryManager.encodePageNumberAndOffset(currentPage, pageCursor);
UnsafeAlignedOffset.putSize(base, pageCursor, length);
pageCursor += uaoSize;
Platform.copyMemory(recordBase, recordOffset, base, pageCursor, length);
pageCursor += length;
inMemSorter.insertRecord(recordAddress, partitionId);
}
/**
* Sort and spill the current records in response to memory pressure.
*/
@Override
public long spill(long size, MemoryConsumer trigger) throws IOException {
if (trigger != this || inMemSorter == null || inMemSorter.numRecords() == 0) {
return 0L;
}
logger.info("Thread {} spilling sort data of {} to disk ({} {} so far)",
Thread.currentThread().getId(),
Utils.bytesToString(getMemoryUsage()),
spills.size(),
spills.size() > 1 ? " times" : " time");
writeSortedFile(false);
final long spillSize = freeMemory();
inMemSorter.reset();
// Reset the in-memory sorter's pointer array only after freeing up the memory pages holding the
// records. Otherwise, if the task is over allocated memory, then without freeing the memory
// pages, we might not be able to get memory for the pointer array.
taskContext.taskMetrics().incMemoryBytesSpilled(spillSize);
return spillSize;
}
/**
* Sorts the in-memory records and writes the sorted records to an on-disk file.
* This method does not free the sort data structures.
*
* @param isLastFile if true, this indicates that we're writing the final output file and that the
* bytes written should be counted towards shuffle spill metrics rather than
* shuffle write metrics.
*/
private void writeSortedFile(boolean isLastFile) {
final ShuffleWriteMetrics writeMetricsToUse;
if (isLastFile) {
// We're writing the final non-spill file, so we _do_ want to count this as shuffle bytes.
writeMetricsToUse = writeMetrics;
} else {
// We're spilling, so bytes written should be counted towards spill rather than write.
// Create a dummy WriteMetrics object to absorb these metrics, since we don't want to count
// them towards shuffle bytes written.
writeMetricsToUse = new ShuffleWriteMetrics();
}
// This call performs the actual sort.
final ShuffleInMemorySorter.ShuffleSorterIterator sortedRecords =
inMemSorter.getSortedIterator();
// Small writes to DiskBlockObjectWriter will be fairly inefficient. Since there doesn't seem to
// be an API to directly transfer bytes from managed memory to the disk writer, we buffer
// data through a byte array. This array does not need to be large enough to hold a single
// record;
final byte[] writeBuffer = new byte[diskWriteBufferSize];
// Because this output will be read during shuffle, its compression codec must be controlled by
// spark.shuffle.compress instead of spark.shuffle.spill.compress, so we need to use
// createTempShuffleBlock here; see SPARK-3426 for more details.
final Tuple2<TempShuffleBlockId, File> spilledFileInfo =
blockManager.diskBlockManager().createTempShuffleBlock();
final File file = spilledFileInfo._2();
final TempShuffleBlockId blockId = spilledFileInfo._1();
final SpillInfo spillInfo = new SpillInfo(numPartitions, file, blockId);
// Unfortunately, we need a serializer instance in order to construct a DiskBlockObjectWriter.
// Our write path doesn't actually use this serializer (since we end up calling the `write()`
// OutputStream methods), but DiskBlockObjectWriter still calls some methods on it. To work
// around this, we pass a dummy no-op serializer.
final SerializerInstance ser = DummySerializerInstance.INSTANCE;
final DiskBlockObjectWriter writer =
blockManager.getDiskWriter(blockId, file, ser, fileBufferSizeBytes, writeMetricsToUse);
int currentPartition = -1;
final int uaoSize = UnsafeAlignedOffset.getUaoSize();
while (sortedRecords.hasNext()) {
sortedRecords.loadNext();
final int partition = sortedRecords.packedRecordPointer.getPartitionId();
assert (partition >= currentPartition);
if (partition != currentPartition) {
// Switch to the new partition
if (currentPartition != -1) {
final FileSegment fileSegment = writer.commitAndGet();
spillInfo.partitionLengths[currentPartition] = fileSegment.length();
}
currentPartition = partition;
}
final long recordPointer = sortedRecords.packedRecordPointer.getRecordPointer();
final Object recordPage = taskMemoryManager.getPage(recordPointer);
final long recordOffsetInPage = taskMemoryManager.getOffsetInPage(recordPointer);
int dataRemaining = UnsafeAlignedOffset.getSize(recordPage, recordOffsetInPage);
long recordReadPosition = recordOffsetInPage + uaoSize; // skip over record length
while (dataRemaining > 0) {
final int toTransfer = Math.min(diskWriteBufferSize, dataRemaining);
Platform.copyMemory(
recordPage, recordReadPosition, writeBuffer, Platform.BYTE_ARRAY_OFFSET, toTransfer);
writer.write(writeBuffer, 0, toTransfer);
recordReadPosition += toTransfer;
dataRemaining -= toTransfer;
}
writer.recordWritten();
}
final FileSegment committedSegment = writer.commitAndGet();
writer.close();
// If `writeSortedFile()` was called from `closeAndGetSpills()` and no records were inserted,
// then the file might be empty. Note that it might be better to avoid calling
// writeSortedFile() in that case.
if (currentPartition != -1) {
spillInfo.partitionLengths[currentPartition] = committedSegment.length();
spills.add(spillInfo);
}
if (!isLastFile) { // i.e. this is a spill file
// The current semantics of `shuffleRecordsWritten` seem to be that it's updated when records
// are written to disk, not when they enter the shuffle sorting code. DiskBlockObjectWriter
// relies on its `recordWritten()` method being called in order to trigger periodic updates to
// `shuffleBytesWritten`. If we were to remove the `recordWritten()` call and increment that
// counter at a higher-level, then the in-progress metrics for records written and bytes
// written would get out of sync.
//
// When writing the last file, we pass `writeMetrics` directly to the DiskBlockObjectWriter;
// in all other cases, we pass in a dummy write metrics to capture metrics, then copy those
// metrics to the true write metrics here. The reason for performing this copying is so that
// we can avoid reporting spilled bytes as shuffle write bytes.
//
// Note that we intentionally ignore the value of `writeMetricsToUse.shuffleWriteTime()`.
// Consistent with ExternalSorter, we do not count this IO towards shuffle write time.
// This means that this IO time is not accounted for anywhere; SPARK-3577 will fix this.
writeMetrics.incRecordsWritten(writeMetricsToUse.recordsWritten());
taskContext.taskMetrics().incDiskBytesSpilled(writeMetricsToUse.bytesWritten());
}
}
- BypassMergeSortShuffleHandle – BypassMergeSortShuffleWriter
先按分区独立输出到文件,最后线性拼接(随机读写->顺序读写)
index -> [record(K,V,P)]
@Override
public void write(Iterator<Product2<K, V>> records) throws IOException {
assert (partitionWriters == null);
if (!records.hasNext()) {
partitionLengths = new long[numPartitions];
shuffleBlockResolver.writeIndexFileAndCommit(shuffleId, mapId, partitionLengths, null);
mapStatus = MapStatus$.MODULE$.apply(blockManager.shuffleServerId(), partitionLengths);
return;
}
final SerializerInstance serInstance = serializer.newInstance();
final long openStartTime = System.nanoTime();
partitionWriters = new DiskBlockObjectWriter[numPartitions];
partitionWriterSegments = new FileSegment[numPartitions];
for (int i = 0; i < numPartitions; i++) {
final Tuple2<TempShuffleBlockId, File> tempShuffleBlockIdPlusFile =
blockManager.diskBlockManager().createTempShuffleBlock();
final File file = tempShuffleBlockIdPlusFile._2();
final BlockId blockId = tempShuffleBlockIdPlusFile._1();
partitionWriters[i] =
blockManager.getDiskWriter(blockId, file, serInstance, fileBufferSize, writeMetrics);
}
// Creating the file to write to and creating a disk writer both involve interacting with
// the disk, and can take a long time in aggregate when we open many files, so should be
// included in the shuffle write time.
writeMetrics.incWriteTime(System.nanoTime() - openStartTime);
while (records.hasNext()) {
final Product2<K, V> record = records.next();
final K key = record._1();
partitionWriters[partitioner.getPartition(key)].write(key, record._2());
}
for (int i = 0; i < numPartitions; i++) {
final DiskBlockObjectWriter writer = partitionWriters[i];
partitionWriterSegments[i] = writer.commitAndGet();
writer.close();
}
File output = shuffleBlockResolver.getDataFile(shuffleId, mapId);
File tmp = Utils.tempFileWith(output);
try {
partitionLengths = writePartitionedFile(tmp);
shuffleBlockResolver.writeIndexFileAndCommit(shuffleId, mapId, partitionLengths, tmp);
} finally {
if (tmp.exists() && !tmp.delete()) {
logger.error("Error while deleting temp file {}", tmp.getAbsolutePath());
}
}
mapStatus = MapStatus$.MODULE$.apply(blockManager.shuffleServerId(), partitionLengths);
}
- BaseShuffleHandle – SortShuffleWriter
map端是否合并,创建不同参数的ExternalSorter
ExternalSorter --> sorter.insertAll(records)
根据是否map是否聚合采用不同缓冲 map 和 buffer
data = new Array[AnyRef](2 * initialCapacity)
即map采用一个数组方式做内存缓冲,数组+链表浪费内存(java object有浪费内存嫌疑)
map看AppendOnlyMap 只用数组实现hashmap
maybeSpillCollection是溢写磁盘逻辑
ExternalSorter.spill实现写磁盘操作
/** Write a bunch of records to this task's output */
override def write(records: Iterator[Product2[K, V]]): Unit = {
sorter = if (dep.mapSideCombine) {
new ExternalSorter[K, V, C](
context, dep.aggregator, Some(dep.partitioner), dep.keyOrdering, dep.serializer)
} else {
// In this case we pass neither an aggregator nor an ordering to the sorter, because we don't
// care whether the keys get sorted in each partition; that will be done on the reduce side
// if the operation being run is sortByKey.
new ExternalSorter[K, V, V](
context, aggregator = None, Some(dep.partitioner), ordering = None, dep.serializer)
}
sorter.insertAll(records)
// Don't bother including the time to open the merged output file in the shuffle write time,
// because it just opens a single file, so is typically too fast to measure accurately
// (see SPARK-3570).
val output = shuffleBlockResolver.getDataFile(dep.shuffleId, mapId)
val tmp = Utils.tempFileWith(output)
try {
val blockId = ShuffleBlockId(dep.shuffleId, mapId, IndexShuffleBlockResolver.NOOP_REDUCE_ID)
val partitionLengths = sorter.writePartitionedFile(blockId, tmp)
shuffleBlockResolver.writeIndexFileAndCommit(dep.shuffleId, mapId, partitionLengths, tmp)
mapStatus = MapStatus(blockManager.shuffleServerId, partitionLengths)
} finally {
if (tmp.exists() && !tmp.delete()) {
logError(s"Error while deleting temp file ${tmp.getAbsolutePath}")
}
}
}
def insertAll(records: Iterator[Product2[K, V]]): Unit = {
// TODO: stop combining if we find that the reduction factor isn't high
val shouldCombine = aggregator.isDefined
if (shouldCombine) {
// Combine values in-memory first using our AppendOnlyMap
val mergeValue = aggregator.get.mergeValue
val createCombiner = aggregator.get.createCombiner
var kv: Product2[K, V] = null
val update = (hadValue: Boolean, oldValue: C) => {
if (hadValue) mergeValue(oldValue, kv._2) else createCombiner(kv._2)
}
while (records.hasNext) {
addElementsRead()
kv = records.next()
map.changeValue((getPartition(kv._1), kv._1), update)
maybeSpillCollection(usingMap = true)
}
} else {
// Stick values into our buffer
while (records.hasNext) {
addElementsRead()
val kv = records.next()
buffer.insert(getPartition(kv._1), kv._1, kv._2.asInstanceOf[C])
maybeSpillCollection(usingMap = false)
}
}
}
/**
* Spill the current in-memory collection to disk if needed.
*
* @param usingMap whether we're using a map or buffer as our current in-memory collection
*/
private def maybeSpillCollection(usingMap: Boolean): Unit = {
var estimatedSize = 0L
if (usingMap) {
estimatedSize = map.estimateSize()
if (maybeSpill(map, estimatedSize)) {
map = new PartitionedAppendOnlyMap[K, C]
}
} else {
estimatedSize = buffer.estimateSize()
if (maybeSpill(buffer, estimatedSize)) {
buffer = new PartitionedPairBuffer[K, C]
}
}
if (estimatedSize > _peakMemoryUsedBytes) {
_peakMemoryUsedBytes = estimatedSize
}
}
/**
* Spill our in-memory collection to a sorted file that we can merge later.
* We add this file into `spilledFiles` to find it later.
*
* @param collection whichever collection we're using (map or buffer)
*/
override protected[this] def spill(collection: WritablePartitionedPairCollection[K, C]): Unit = {
val inMemoryIterator = collection.destructiveSortedWritablePartitionedIterator(comparator)
val spillFile = spillMemoryIteratorToDisk(inMemoryIterator)
spills += spillFile
}








 本文主要分析Spark源码中SparkEnv的ShuffleManager如何控制数据shuffle的读写过程。详细探讨了不同类型的ShuffleHandle,包括BypassMergeSortShuffleHandle、SerializedShuffleHandle和BaseShuffleHandle,以及它们对应的ShuffleWriter。着重讲解了ShuffleMapTask的runTask过程中,Handle选择如何影响ShuffleWriter类型,并分析了各种ShuffleWriter的内部实现,如排序、溢写磁盘等操作。
本文主要分析Spark源码中SparkEnv的ShuffleManager如何控制数据shuffle的读写过程。详细探讨了不同类型的ShuffleHandle,包括BypassMergeSortShuffleHandle、SerializedShuffleHandle和BaseShuffleHandle,以及它们对应的ShuffleWriter。着重讲解了ShuffleMapTask的runTask过程中,Handle选择如何影响ShuffleWriter类型,并分析了各种ShuffleWriter的内部实现,如排序、溢写磁盘等操作。
















 2736
2736

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








