编程总结
每每刷完一道题后,其思想和精妙之处没有地方记录,本篇博客用以记录刷题过程中的遇到的算法和技巧
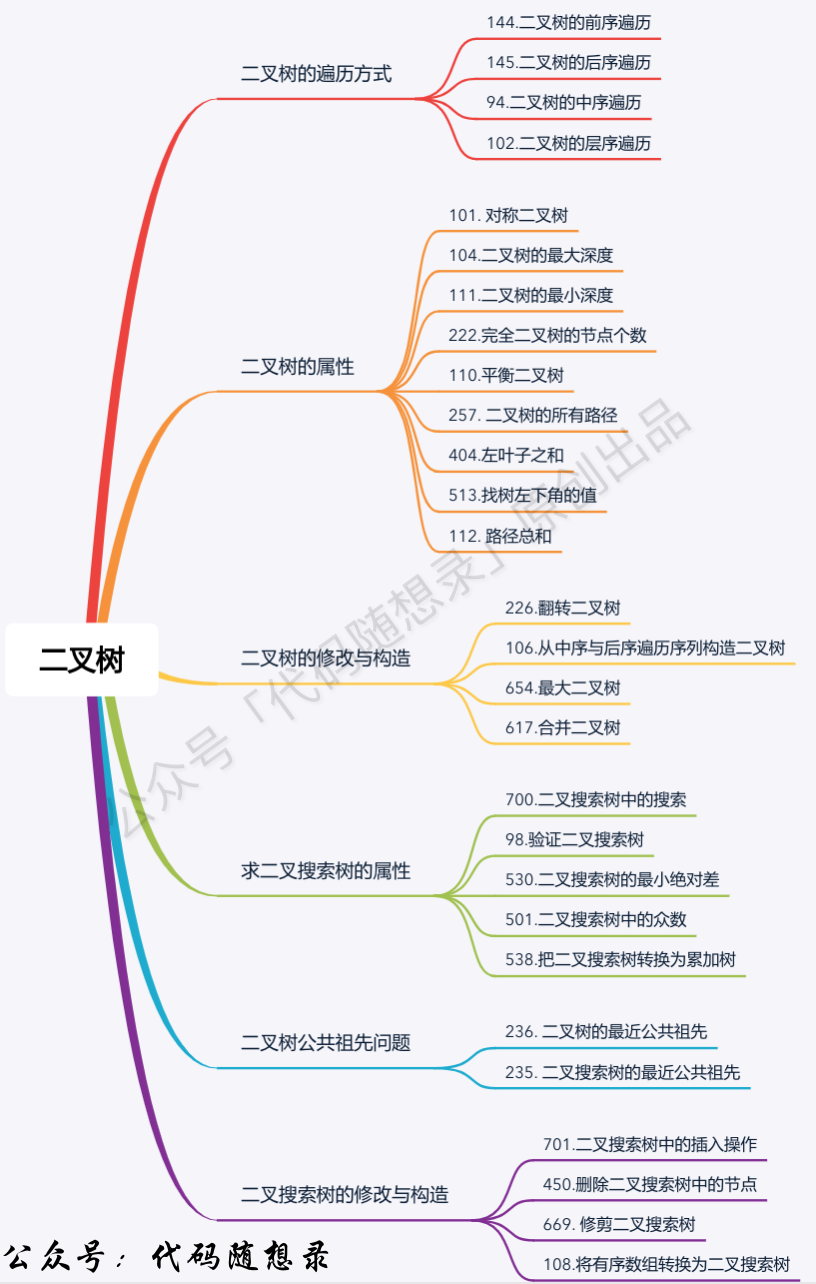
二叉树的遍历方式
前中后序遍历–递归法_一刷(80%)
- 确定递归函数的参数和返回值
- 确定终止条件
- 确定单层递归的逻辑
// 前序 根左右
void PreOrder(struct TreeNode *root, int *ret, int *retIndex)
{
if (root == NULL) {
return;
}
ret[(*retIndex)++] = root->val; // 根计算
PreOrder(root->left, ret, retIndex); // 左
PreOrder(root->right, ret, retIndex); // 右
}
// 中序 左根右
void inorder(struct TreeNode *root, int *res, int *resSize)
{
if (root == NULL) {
return;
}
inorder(root->left, res, resSize); // 左
res[(*resSize)++] = root->val; // 根
inorder(root->right, res, resSize); // 右
}
// 后序 左右根
void postorder(struct TreeNode *root, int *res, int *resSize)
{
if (root == NULL) {
return;
}
postorder(root->left, res, resSize);
postorder(root->right, res, resSize);
res[(*resSize)++] = root->val;
}
// 调用函数
int *preorderTraversal(struct TreeNode *root, int *returnSize)
{
int retIndex = 0;
int *ret = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * 100);
memset(ret, 0, sizeof(int) * 100);
PreOrder(root, ret, &retIndex);
*returnSize = retIndex;
return ret;
}
102. 二叉树的层序遍历 – BFS__一刷(80%)

注意结果res的手法处理,同样重要
思路:BFS
int **levelOrder(struct TreeNode *root, int *returnSize, int **returnColumnSizes)
{
if (root == NULL) {
*returnSize = 0; // 代码入口如果是空的话,应该给设定返回值为0,不能只简单的返回NULL就结束
return NULL;
}
struct TreeNode *queue[2001];
int tail = 0, head = 0, len = 0;
int idx = 0;
int **res = (int **)malloc(sizeof(int *) * 2001);
*returnColumnSizes = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * 2001);
queue[tail++] = root; // 1. 根节点入队列
*returnSize = 0;
while ((tail - head) > 0) {
// 队列不为空
len = tail - head;
idx = 0;
res[*returnSize] = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * len);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
struct TreeNode *tmp = queue[head++]; // 出队列
res[*returnSize][idx++] = tmp->val;
if (tmp->left != NULL) {
queue[tail++] = tmp->left;
}
if (tmp->right != NULL) {
queue[tail++] = tmp->right;
}
}
(*returnColumnSizes)[*returnSize] = len;
*returnSize = *returnSize + 1;
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
struct TreeNode root, left, right;
struct TreeNode r_left, r_right;
left = (struct TreeNode) {
9, NULL, NULL };
r_right = (struct TreeNode) {
7, NULL, NULL};
r_left = (struct TreeNode) {
15, NULL, NULL };
right = (struct TreeNode) {
20, &r_left, &r_right };
root = (struct TreeNode) {
3, &left, &right };
int returnSize;
int *returnColumnSizes;
int **ret = levelOrder(&root, &returnSize, &returnColumnSizes);
for (int i = 0; i < returnSize; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < returnColumnSizes[i]; j++) {
printf("%d ", ret[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
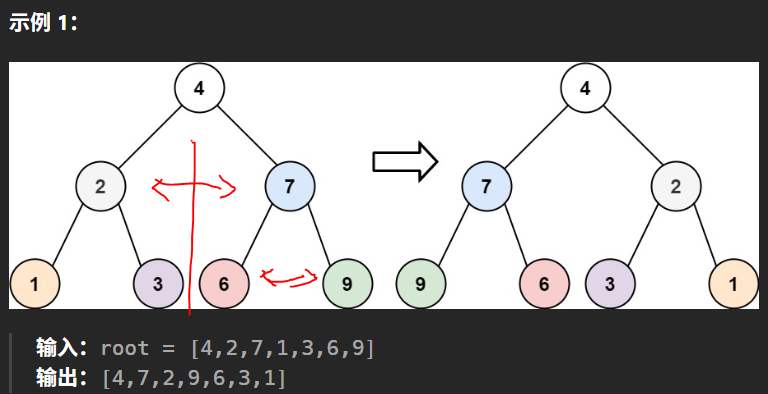
226. 翻转二叉树_一刷(80%)
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,翻转这棵二叉树,并返回其根节点。
90% of our engineers use the softwar you wrote(Homebrew), but you can’t invert a binary tree on a whiteboard so fuck off.
思路:前序遍历,两两交换节点
1)确认返回是 TreeNode
2)确定终止条件
3)交换两两节点
前序遍历:
struct TreeNode *invertTree(struct TreeNode *root)
{
if (root == NULL) {
// 1.递归终止条件
return NULL;
}
// 前序遍历,根左右
// 交换 root 的左右孩子
struct TreeNode *left = root->left;
struct TreeNode *right = root->right;
root->left = right; // 先递下去,归的时候遇到节点时,交换其左右节点
root->right = left; // 本质时交换每个除根节点外节点的左右子节点
invertTree(root->left);
invertTree(root->right);
return root;
}
int main()
{
struct TreeNode root, left, right;
struct TreeNode r_left, r_right;
struct TreeNode l_left, l_right;
r_right = (struct TreeNode) {
6, NULL, NULL};
r_left = (struct TreeNode) {
9, NULL, NULL };
l_right = (struct TreeNode) {
3, NULL, NULL };
l_left = (struct TreeNode) {
1, NULL, NULL };
left = (struct TreeNode) {
2, &l_left, &l_right };
right = (struct TreeNode) {
7, &r_left




 本文深入探讨二叉树的多种遍历方法,包括前序、中序、后序及层序遍历,并解析二叉树的翻转、对称性判断、深度计算等核心算法。同时,讲解了如何解决诸如平衡二叉树、二叉树坡度、合并二叉树等进阶问题,以及二叉树展开为链表和二叉搜索树的第k大节点等挑战性任务。
本文深入探讨二叉树的多种遍历方法,包括前序、中序、后序及层序遍历,并解析二叉树的翻转、对称性判断、深度计算等核心算法。同时,讲解了如何解决诸如平衡二叉树、二叉树坡度、合并二叉树等进阶问题,以及二叉树展开为链表和二叉搜索树的第k大节点等挑战性任务。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 176万+
176万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








