大部分内容来自http://www.w3schools.com。
本文主要是个人学习笔记,将替代手写的笔记。以此记录自己的学习过程,记录不懂的,可以逐渐增加新知识点。
What is XML?
- XML stands for EXtensible Markup Language
- XML is a markup language much like HTML
- XML was designed to carry data, not to display data
- XML tags are not predefined. You must define your own tags
- XML is designed to be self-descriptive
- XML is a W3C Recommendation
The Difference Between XML and HTML
XML is not a replacement for HTML.
XML and HTML were designed with different goals:
- XML was designed to transport and store data, with focus on what data is
- HTML was designed to display data, with focus on how data looks
HTML is about displaying information, while XML is about carrying information.
An Example XML Document
XML documents use a self-describing and simple syntax:<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?>
<note>
<to>Tove</to>
<from>Jani</from>
<heading>Reminder</heading>
<body>Don't forget me this weekend!</body>
</note>The first line is the XML declaration. It defines the XML version (1.0) and the encoding used (ISO-8859-1 = Latin-1/West European character set).
The next line describes the root element of the document (like saying: "this document is a note"):
The next 4 lines describe 4 child elements of the root (to, from, heading, and body):XML Documents Form a Tree Structure
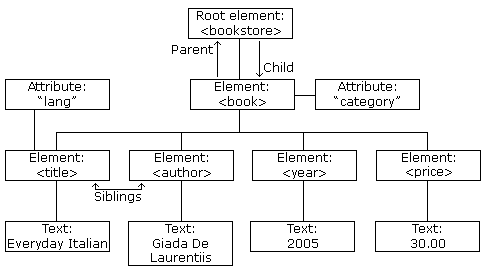
<bookstore>
<book category="COOKING">
<title lang="en">Everyday Italian</title>
<author>Giada De Laurentiis</author>
<year>2005</year>
<price>30.00</price>
</book>
<book category="CHILDREN">
<title lang="en">Harry Potter</title>
<author>J K. Rowling</author>
<year>2005</year>
<price>29.99</price>
</book>
<book category="WEB">
<title lang="en">Learning XML</title>
<author>Erik T. Ray</author>
<year>2003</year>
<price>39.95</price>
</book>
</bookstore>
XML Syntax Rules
All XML Elements Must Have a Closing Tag
XML Tags are Case Sensitive
XML tags are case sensitive. The tag <Letter> is different from the tag <letter>.XML Elements Must be Properly Nested
In XML, all elements must be properly nested within each other:<b><i>This text is bold and italic</i></b>In the example above, "Properly nested" simply means that since the <i> element is opened inside the <b> element, it must be closed inside the <b> element.
XML Documents Must Have a Root Element
<root>
<child>
<subchild>.....</subchild>
</child>
</root>
XML Attribute Values Must be Quoted
XML elements can have attributes in name/value pairs just like in HTML.
In XML, the attribute values must always be quoted.
Study the two XML documents below. The first one is incorrect, the second is correct:
<note date=12/11/2007>
<to>Tove</to>
<from>Jani</from>
</note><note date="12/11/2007">
<to>Tove</to>
<from>Jani</from>
</note>Entity References
Some characters have a special meaning in XML.
If you place a character like "<" inside an XML element, it will generate an error because the parser interprets it as the start of a new element.
This will generate an XML error:
<message>if salary < 1000 then</message>To avoid this error, replace the "<" character with an entity reference :
<message>if salary < 1000 then</message>There are 5 predefined entity references in XML:
| < | < | less than |
| > | > | greater than |
| & | & | ampersand |
| ' | ' | apostrophe |
| " | " | quotation mark |
Comments in XML
The syntax for writing comments in XML is similar to that of HTML.
<!-- This is a comment -->
White-space is Preserved in XML
| HTML: | Hello Tove |
| Output: | Hello Tove |
XML Stores New Line as LF
In Windows applications, a new line is normally stored as a pair of characters: carriage return (CR) and line feed (LF). In Unix applications, a new line is normally stored as an LF character. Macintosh applications also use an LF to store a new line.
XML stores a new line as LF.
XML Elements
What is an XML Element?
An XML element is everything from (including) the element's start tag to (including) the element's end tag.
An element can contain:
- other elements
- text
- attributes
- or a mix of all of the above...
XML Naming Rules
XML elements must follow these naming rules:
- Names can contain letters, numbers, and other characters
- Names cannot start with a number or punctuation character
- Names cannot start with the letters xml (or XML, or Xml, etc)
- Names cannot contain spaces
Any name can be used, no words are reserved.
Best Naming Practices
Make names descriptive. Names with an underscore separator are nice: <first_name>, <last_name>.
Names should be short and simple, like this: <book_title> not like this: <the_title_of_the_book>.
Avoid "-" characters. If you name something "first-name," some software may think you want to subtract name from first.
Avoid "." characters. If you name something "first.name," some software may think that "name" is a property of the object "first."
Avoid ":" characters. Colons are reserved to be used for something called namespaces (more later).
XML documents often have a corresponding database. A good practice is to use the naming rules of your database for the elements in the XML documents.
Non-English letters like éòá are perfectly legal in XML, but watch out for problems if your software vendor doesn't support them.





 本文介绍了XML的基础知识,包括XML的设计理念、与HTML的区别、基本语法、文档结构及常用规范等。
本文介绍了XML的基础知识,包括XML的设计理念、与HTML的区别、基本语法、文档结构及常用规范等。
















 2548
2548

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








