本文同步发表于我的微信公众号,微信搜索 程语新视界 即可关注,每个工作日都有文章更新
一、核心原则总结
状态刷新控制的核心目标:在保证UI与状态一致性的同时,最小化不必要的刷新,优化应用性能。
二、状态管理装饰器选择策略
1. 按共享范围选择(优先级排序)
| 装饰器组合 | 共享范围 | 生命周期 | 适用场景 | 性能特点 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| @State + @Prop | 从@State组件到@Prop组件的路径 | 组件级 | 父子组件单向通信 | 深拷贝,内存占用高 |
| @State + @Link | 同上 | 组件级 | 父子组件双向实时同步 | 引用传递,性能更优 |
| @State + @Observed + @ObjectLink | 同上 | 组件级 | 嵌套对象属性监听 | 精细控制,复杂对象 |
| @Provide + @Consume | @Provide所在组件的整棵子树 | 组件级 | 跨层级共享状态 | 全局访问,维护简单 |
| LocalStorage | UIAbility内所有组件树 | 应用级 | 页面间数据共享 | 持久化存储 |
| AppStorage | 应用全局 | 进程级 | 全局配置管理 | 全局状态管理 |
2. 选择决策流程
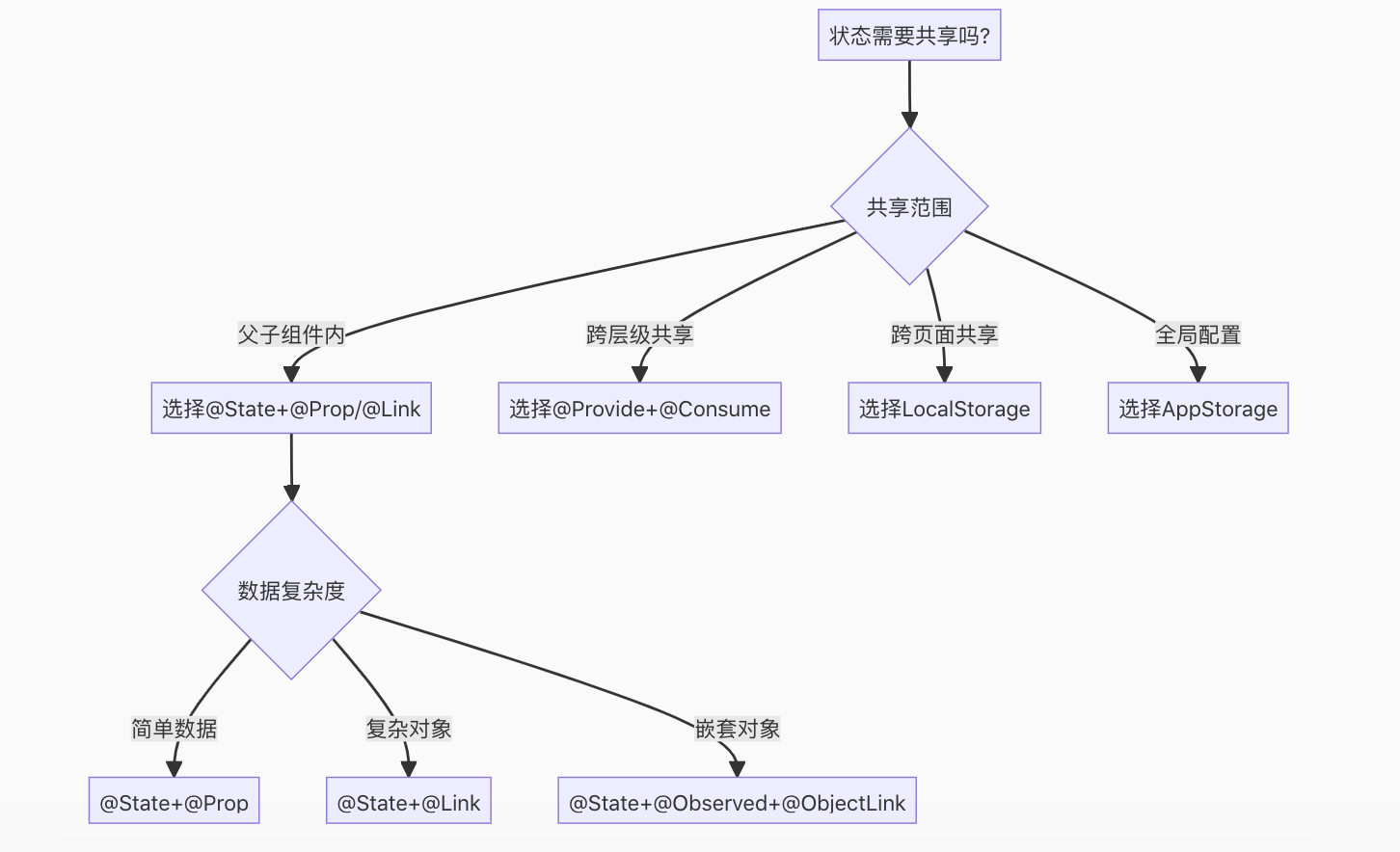
三、优化实践
1. 避免冗余状态变量
反例:
@Component
struct MyComponent {
// ❌ 没有UI关联的状态变量
@State translateObj: {x: number, y: number} = {x: 0, y: 0}
@State buttonMsg: string = "点击"
build() {
Column() {
// 没有使用translateObj的UI
Text(this.buttonMsg)
Button("增加")
.onClick(() => {
// ❌ 修改无UI关联的状态变量
this.translateObj.x++
this.buttonMsg = "已点击"
})
}
}
}正例:
@Component
struct MyComponent {
// ✅ 只声明有UI关联的状态变量
@State buttonMsg: string = "点击"
// 普通变量用于逻辑处理
translateObj: {x: number, y: number} = {x: 0, y: 0}
build() {
Column() {
Text(this.buttonMsg)
Button("增加")
.onClick(() => {
// ✅ 临时变量计算后再更新状态
const newTranslate = {
x: this.translateObj.x + 1,
y: this.translateObj.y
}
// 只在最后更新状态变量
this.buttonMsg = "已点击"
})
}
}
}2. 批量更新优化
反例(多次刷新):
@Component
struct UserCard {
@State userInfo: UserInfo = new UserInfo()
build() {
Column() {
Text(userInfo.name)
Text(userInfo.age.toString())
Text(userInfo.email)
}
}
// ❌ 多次修改状态导致多次刷新
updateUserInfo(newData: Partial<UserInfo>) {
this.userInfo.name = newData.name || this.userInfo.name
this.userInfo.age = newData.age || this.userInfo.age
this.userInfo.email = newData.email || this.userInfo.email
}
}正例(单次刷新):
@Component
struct UserCard {
@State userInfo: UserInfo = new UserInfo()
build() {
Column() {
Text(userInfo.name)
Text(userInfo.age.toString())
Text(userInfo.email)
}
}
// ✅ 批量合并更新,单次刷新
updateUserInfo(newData: Partial<UserInfo>) {
const updatedInfo = {...this.userInfo, ...newData}
this.userInfo = updatedInfo // 单次赋值,单次刷新
}
}四、@Watch装饰器应用
1. 基础使用
@Component
struct CounterDisplay {
@State @Watch('onCounterChanged') counter: number = 0
@State total: number = 0
// @Watch回调方法
onCounterChanged(propertyName: string): void {
console.log(`属性 ${propertyName} 发生变化`)
// 根据counter变化更新total
this.total += this.counter
}
build() {
Column() {
Text(`计数器: ${this.counter}`)
Text(`总计: ${this.total}`)
Button('增加')
.onClick(() => {
this.counter++ // 触发@Watch回调
})
}
}
}2. 多状态监听处理
@Component
struct UserForm {
@State @Watch('onFormChanged') userName: string = ''
@State @Watch('onFormChanged') userEmail: string = ''
@State @Watch('onFormChanged') userAge: number = 18
onFormChanged(propertyName: string): void {
switch(propertyName) {
case 'userName':
console.log('用户名变化:', this.userName)
break
case 'userEmail':
console.log('邮箱变化:', this.userEmail)
break
case 'userAge':
console.log('年龄变化:', this.userAge)
break
}
// 统一验证逻辑
this.validateForm()
}
validateForm(): void {
// 表单验证逻辑
}
build() {
Column() {
TextInput({ placeholder: '用户名' })
.onChange((value: string) => {
this.userName = value
})
TextInput({ placeholder: '邮箱' })
.onChange((value: string) => {
this.userEmail = value
})
NumberInput({ value: this.userAge, min: 1, max: 120 })
.onChange((value: number) => {
this.userAge = value
})
}
}
}五、复杂对象优化
1. @Track装饰器精细控制
class UserSettings {
@Track theme: string = 'light' // 变化时触发刷新
@Track fontSize: number = 16 // 变化时触发刷新
language: string = 'zh-CN' // 不触发刷新
}
@Component
struct SettingsPanel {
@State settings: UserSettings = new UserSettings()
build() {
Column() {
// 只有theme变化时才会刷新
Text(`主题: ${this.settings.theme}`)
.fontColor(this.settings.theme === 'dark' ? Color.White : Color.Black)
// 只有fontSize变化时才会刷新
Text(`字体大小: ${this.settings.fontSize}`)
.fontSize(this.settings.fontSize)
Button('切换主题')
.onClick(() => {
this.settings.theme = this.settings.theme === 'light' ? 'dark' : 'light'
})
Button('增大字体')
.onClick(() => {
this.settings.fontSize += 2
})
}
}
}2. @Observed + @ObjectLink组合
// 需要被观察的类
@Observed
class Product {
name: string = ''
price: number = 0
stock: number = 0
}
@Component
struct ProductCard {
@ObjectLink product: Product // 只读引用
build() {
Column() {
Text(`商品: ${this.product.name}`)
Text(`价格: ¥${this.product.price}`)
Text(`库存: ${this.product.stock}`)
Button('购买')
.onClick(() => {
// 通过父组件方法修改,触发刷新
this.product.stock--
})
}
}
}
@Component
struct ShoppingCart {
@State products: Array<Product> = [
new Product({ name: '商品A', price: 100, stock: 10 }),
new Product({ name: '商品B', price: 200, stock: 5 })
]
build() {
Column() {
ForEach(this.products, (product: Product) => {
ProductCard({ product: product })
})
}
}
}六、性能优化
1. 避免无限循环
// ❌ 错误示例:无限循环
@Component
struct Counter {
@State @Watch('onCountChange') count: number = 0
onCountChange(): void {
// 直接修改当前状态变量,导致无限循环
this.count++
}
build() {
Button('增加')
.onClick(() => {
this.count++
})
}
}
// ✅ 正确示例:避免直接修改
@Component
struct Counter {
@State @Watch('onCountChange') count: number = 0
@State tempCount: number = 0
onCountChange(): void {
// 通过中间变量避免直接修改
this.tempCount = this.count
}
build() {
Button('增加')
.onClick(() => {
this.count++
})
}
}2. @Watch性能优化
// ❌ 性能差的@Watch实现
@Component
struct HeavyComponent {
@State @Watch('processData') data: string = ''
processData(): void {
// 避免在@Watch中执行耗时操作
for(let i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) {
// 耗时计算
}
this.data = `处理后: ${this.data}`
}
build() {
Text(this.data)
}
}
// ✅ 优化后的实现
@Component
struct OptimizedComponent {
@State data: string = ''
@State processing: boolean = false
@Watch('onDataChange')
@State originalData: string = ''
onDataChange(): void {
// 快速计算,标记为需要处理
this.processing = true
}
aboutToAppear(): void {
// 在合适的时机执行耗时操作
this.scheduleHeavyProcessing()
}
scheduleHeavyProcessing(): void {
if(this.processing) {
// 使用定时器延迟处理
setTimeout(() => {
this.data = this.processHeavyData(this.originalData)
this.processing = false
}, 0)
}
}
processHeavyData(input: string): string {
// 耗时计算逻辑
return `处理后: ${input}`
}
build() {
Text(this.data)
}
}七、总结
1. 状态刷新控制的核心原则
- 最小化状态共享:优先选择共享范围最小的装饰器方案
- 精细化更新控制:使用@Track、@Observed等实现属性级更新
- 批量更新优化:避免频繁的单点状态更新
- 合理使用@Watch:用于重要状态变化的副作用处理,避免复杂逻辑
2. 性能优化关键点
- 避免在@Watch中执行耗时操作
- 使用临时变量减少不必要的状态更新
- 对复杂对象使用引用传递(@Link)而非深拷贝(@Prop)
- 优先使用组件内状态(@State)而非跨组件共享
3. 实际开发建议
- 新项目优先使用V2的@Provider/@Consumer
- 对性能敏感的场景使用@Track精细控制
- 跨层级通信使用@Provide+@Consume
- 全局状态使用AppStorage或LocalStorage
- 避免在@Watch中直接修改当前状态变量






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








