- 综述
- TensorFlow是一个编程系统,用图来表示计算任务,描述了计算过程
- 图中结点表示为op(operation),一个op获得0或多个tersor
- tensor是一个多维数组,在图中表示边
- 图必须在会话Session里启动
- 变量需初始化tf.global_variables_initializer()
- TensorFlow程序可以看做独立的两部分:构建计算图 与 运行计算图
1、Session
当要获取tensor值时,需要初始化一个tf.Session对象,调用Session.run()方法获取张量的值
from __future__ import print_function
import tensorflow as tf
matrix1 = tf.constant([[3, 3]])
matrix2 = tf.constant([[2],
[2]])
product = tf.matmul(matrix1, matrix2) # matrix multiply np.dot(m1, m2)
# method 1
sess = tf.Session()
result = sess.run(product)
print(result)
sess.close()
# method 2
with tf.Session() as sess:
result2 = sess.run(product)
print(result2)
可以通过Session.run()方法运行操作或变量的值。但如果参数只有一个的话,那么可以使用eval()方法会比较简便
assign_add是TensorFlow中的运算函数,会将第一个参数和第二个参数的值相加后赋值给第一个参数。类似于C语言中的+=
constant = tf.constant([1, 2, 3])
tensor = constant * constant
print(tensor.eval())
p = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
t = p + 1.0
t.eval() # 错误!p没有初始化
t.eval(feed_dict={p:2.0}) # 正确!因为p被初始化了
#值得注意的是,不只是张量的值,操作也可以使用eval()方法,如下:
v=tf.Varibale(1)
sess=tf.Session()
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
tf.assign_add(v,tf.constant(1)).eval()
print(v.eval())2、Constant
tf.constant(value,dtype=None,shape=None,name='Const',verify_shape=False)
value的值可以为3、1,2,3,4,5],[[22,32],[32,4]]等
3、Variable
from __future__ import print_function
import tensorflow as tf
state = tf.Variable(0, name='counter')
#print(state.name)
one = tf.constant(1)
new_value = tf.add(state, one)
update = tf.assign(state, new_value)
# tf.initialize_all_variables() no long valid from
# 2017-03-02 if using tensorflow >= 0.12
if int((tf.__version__).split('.')[1]) < 12 and int((tf.__version__).split('.')[0]) < 1:
init = tf.initialize_all_variables()
else:
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
for _ in range(3):
sess.run(update)
print(sess.run(state))
4、placeholder:run的时候才赋值
tf.placeholder(dtype,shape=None,name=None)
placeholder在运算时得通过Session.run()方法中的feed_dict参数获得初值
from __future__ import print_function
import tensorflow as tf
input1 = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
input2 = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
output = tf.multiply(input1, input2)
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(sess.run(output, feed_dict={input1: [7.], input2: [2.]}))
5、tensor间运算
注意:给张量赋值必须用tf.assign()系列函数,不能直接用=
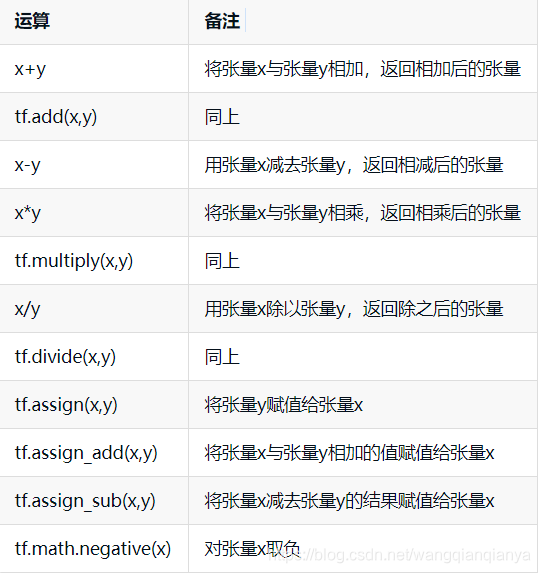
6、activation function
from __future__ import print_function
import tensorflow as tf
def add_layer(inputs, in_size, out_size, activation_function=None):
Weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_size, out_size]))
biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, out_size]) + 0.1)
Wx_plus_b = tf.matmul(inputs, Weights) + biases
if activation_function is None:#线性
outputs = Wx_plus_b
else:
outputs = activation_function(Wx_plus_b)
return outputs6、tensorflow搭建自己的神经网络(输入输出1个神经元,隐层10个神经元) 画出
from __future__ import print_function
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def add_layer(inputs, in_size, out_size, activation_function=None):
Weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_size, out_size]))
biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, out_size]) + 0.1)
Wx_plus_b = tf.matmul(inputs, Weights) + biases
if activation_function is None:
outputs = Wx_plus_b
else:
outputs = activation_function(Wx_plus_b)
return outputs
# Make up some real data
x_data = np.linspace(-1, 1, 300)[:, np.newaxis]
noise = np.random.normal(0, 0.05, x_data.shape)
y_data = np.square(x_data) - 0.5 + noise
##plt.scatter(x_data, y_data)
##plt.show()
# define placeholder for inputs to network
xs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1])
ys = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1])
# add hidden layer
l1 = add_layer(xs, 1, 10, activation_function=tf.nn.relu)
# add output layer
prediction = add_layer(l1, 10, 1, activation_function=None)
# the error between prediction and real data
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(ys-prediction), reduction_indices=[1]))
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1).minimize(loss)
# important step
sess = tf.Session()
# tf.initialize_all_variables() no long valid from
# 2017-03-02 if using tensorflow >= 0.12
if int((tf.__version__).split('.')[1]) < 12 and int((tf.__version__).split('.')[0]) < 1:
init = tf.initialize_all_variables()
else:
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init)
# plot the real data
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
ax.scatter(x_data, y_data)
plt.ion()
plt.show()
for i in range(1000):
# training
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={xs: x_data, ys: y_data})
if i % 50 == 0:
# to visualize the result and improvement
try:
ax.lines.remove(lines[0])
except Exception:
pass
prediction_value = sess.run(prediction, feed_dict={xs: x_data})
# plot the prediction
lines = ax.plot(x_data, prediction_value, 'r-', lw=5)
plt.pause(1)
拟合多项式:3x^2+4x+5
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plotdata = {"batchsize": [], "loss": []}
def moving_average(a, w=10):
if len(a) < w:
return a[:]
return [val if idx < w else sum(a[(idx - w):idx]) / w for idx, val in enumerate(a)]
# 生成模拟数据
train_X = np.linspace(-1, 1, 200)
train_Y = 3 * train_X * train_X + 4 * train_X + 5 + np.random.randn(*train_X.shape) * 0.3 # y=2x,但是加入了噪声
# 显示模拟数据点
plt.plot(train_X, train_Y, 'ro', label='Original data')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
# 创建模型
# 占位符
X = tf.placeholder("float")
Y = tf.placeholder("float")
# 模型参数
W = tf.Variable([0.]*3, name="weight")
# 前向结构
terms=[]
for i in range(3):#修改3为多项式项数
term=tf.multiply(W[i],tf.pow(X,i))
terms.append(term)
z = tf.add_n(terms)#实现列表元素累加
# 反向优化
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(Y - z))
learning_rate = 0.01
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(cost) # Gradient descent
# 初始化变量
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
# 训练参数
training_epochs = 20
display_step = 2
# 启动session
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
# Fit all training data
for epoch in range(training_epochs):
for (x, y) in zip(train_X, train_Y):
sess.run(optimizer, feed_dict={X: x, Y: y})
print(z.dtype)
# 显示训练中的详细信息
if epoch % display_step == 0:
loss = sess.run(cost, feed_dict={X: train_X, Y: train_Y})
print("Epoch:", epoch + 1, "cost=", loss, "W=", sess.run(W))
if not (loss == "NA"):
plotdata["batchsize"].append(epoch)
plotdata["loss"].append(loss)
print(" Finished!")
print("cost=", sess.run(cost, feed_dict={X: train_X, Y: train_Y}), "W=", sess.run(W))
# print ("cost:",cost.eval({X: train_X, Y: train_Y}))
# 图形显示
plt.plot(train_X, train_Y, 'ro', label='Original data')
plt.plot(train_X, sess.run(W[2]) * train_X* train_X+sess.run(W[1]) * train_X +sess.run(W[0]), label='Fitted line')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
plotdata["avgloss"] = moving_average(plotdata["loss"])
plt.figure(1)
plt.subplot(211)
plt.plot(plotdata["batchsize"], plotdata["avgloss"], 'b--')
plt.xlabel('Minibatch number')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.title('Minibatch run vs. Training loss')
plt.show()
print("x=0.2,z=", sess.run(z, feed_dict={X: 0.2}))
6、Classification
from __future__ import print_function
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
# number 1 to 10 data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST_data', one_hot=True)
def add_layer(inputs, in_size, out_size, activation_function=None,):
# add one more layer and return the output of this layer
Weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_size, out_size]))
biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, out_size]) + 0.1,)
Wx_plus_b = tf.matmul(inputs, Weights) + biases
if activation_function is None:
outputs = Wx_plus_b
else:
outputs = activation_function(Wx_plus_b,)
return outputs
def compute_accuracy(v_xs, v_ys):
global prediction
y_pre = sess.run(prediction, feed_dict={xs: v_xs})
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_pre,1), tf.argmax(v_ys,1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
result = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={xs: v_xs, ys: v_ys})
return result
# define placeholder for inputs to network
xs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784]) # 28x28
ys = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10])
# add output layer
prediction = add_layer(xs, 784, 10, activation_function=tf.nn.softmax)
# the error between prediction and real data
cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(ys * tf.log(prediction),
reduction_indices=[1])) # loss
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.5).minimize(cross_entropy)
sess = tf.Session()
# important step
# tf.initialize_all_variables() no long valid from
# 2017-03-02 if using tensorflow >= 0.12
if int((tf.__version__).split('.')[1]) < 12 and int((tf.__version__).split('.')[0]) < 1:
init = tf.initialize_all_variables()
else:
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init)
for i in range(1000):
batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(100)
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={xs: batch_xs, ys: batch_ys})
if i % 50 == 0:
print(compute_accuracy(
mnist.test.images, mnist.test.labels))
过拟合解决方法:(训练误差不是越小越好)
1、增大训练数据(随着数据量的增大曲线会逐渐拉直)
2、正则化(cost在最小二乘基础上加上L1:|W| 或L2:W^2)
3、对于神经网络还可以采用dropout方法
tensorflow实现线性回归
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Tue Jun 6 18:52:37 2017
@author: 代码医生 qq群:40016981,公众号:xiangyuejiqiren
@blog:http://blog.youkuaiyun.com/lijin6249
"""
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plotdata = { "batchsize":[], "loss":[] }
def moving_average(a, w=10):
if len(a) < w:
return a[:]
return [val if idx < w else sum(a[(idx-w):idx])/w for idx, val in enumerate(a)]
#生成模拟数据
train_X = np.linspace(-1, 1, 100)
train_Y = 2 * train_X + np.random.randn(*train_X.shape) * 0.3 # y=2x,但是加入了噪声
#显示模拟数据点
plt.plot(train_X, train_Y, 'ro', label='Original data')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
# 创建模型
# 占位符
X = tf.placeholder("float")
Y = tf.placeholder("float")
# 模型参数
W = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1]), name="weight")
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1]), name="bias")
# 前向结构
z = tf.multiply(X, W)+ b
#反向优化
cost =tf.reduce_mean( tf.square(Y - z))
learning_rate = 0.01
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(cost) #Gradient descent
# 初始化变量
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
# 训练参数
training_epochs = 20
display_step = 2
# 启动session
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
# Fit all training data
for epoch in range(training_epochs):
for (x, y) in zip(train_X, train_Y):
sess.run(optimizer, feed_dict={X: x, Y: y})
#显示训练中的详细信息
if epoch % display_step == 0:
loss = sess.run(cost, feed_dict={X: train_X, Y:train_Y})
print ("Epoch:", epoch+1, "cost=", loss,"W=", sess.run(W), "b=", sess.run(b))
if not (loss == "NA" ):
plotdata["batchsize"].append(epoch)
plotdata["loss"].append(loss)
print (" Finished!")
print ("cost=", sess.run(cost, feed_dict={X: train_X, Y: train_Y}), "W=", sess.run(W), "b=", sess.run(b))
#print ("cost:",cost.eval({X: train_X, Y: train_Y}))
#图形显示
plt.plot(train_X, train_Y, 'ro', label='Original data')
plt.plot(train_X, sess.run(W) * train_X + sess.run(b), label='Fitted line')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
plotdata["avgloss"] = moving_average(plotdata["loss"])
plt.figure(1)
plt.subplot(211)
plt.plot(plotdata["batchsize"], plotdata["avgloss"], 'b--')
plt.xlabel('Minibatch number')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.title('Minibatch run vs. Training loss')
plt.show()
print ("x=0.2,z=", sess.run(z, feed_dict={X: 0.2}))
代码来源:https://github.com/MorvanZhou/tutorials/tree/master/tensorflowTUT
























 1087
1087

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








