You are given a 0-indexed string s that you must perform k replacement operations on. The replacement operations are given as three 0-indexed parallel arrays, indices, sources, and targets, all of length k.
To complete the ith replacement operation:
Check if the substring sources[i] occurs at index indices[i] in the original string s.
If it does not occur, do nothing.
Otherwise if it does occur, replace that substring with targets[i].
For example, if s = “abcd”, indices[i] = 0, sources[i] = “ab”, and targets[i] = “eee”, then the result of this replacement will be “eeecd”.
All replacement operations must occur simultaneously, meaning the replacement operations should not affect the indexing of each other. The testcases will be generated such that the replacements will not overlap.
For example, a testcase with s = “abc”, indices = [0, 1], and sources = [“ab”,“bc”] will not be generated because the “ab” and “bc” replacements overlap.
Return the resulting string after performing all replacement operations on s.
A substring is a contiguous sequence of characters in a string.
Example 1:

Input: s = “abcd”, indices = [0, 2], sources = [“a”, “cd”], targets = [“eee”, “ffff”]
Output: “eeebffff”
Explanation:
“a” occurs at index 0 in s, so we replace it with “eee”.
“cd” occurs at index 2 in s, so we replace it with “ffff”.
Example 2:
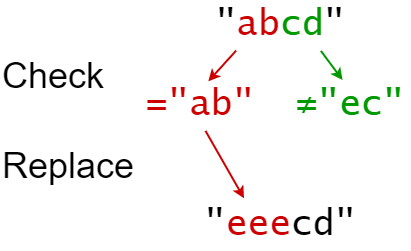
Input: s = “abcd”, indices = [0, 2], sources = [“ab”,“ec”], targets = [“eee”,“ffff”]
Output: “eeecd”
Explanation:
“ab” occurs at index 0 in s, so we replace it with “eee”.
“ec” does not occur at index 2 in s, so we do nothing.
Constraints:
- 1 <= s.length <= 1000
- k == indices.length == sources.length == targets.length
- 1 <= k <= 100
- 0 <= indexes[i] < s.length
- 1 <= sources[i].length, targets[i].length <= 50
- s consists of only lowercase English letters.
- sources[i] and targets[i] consist of only lowercase English letters.
单纯动手的题, 好想,不好实现。首先将 indices、sources、targets 组合起来进行排序, 然后遍历 s, 遇到 indices 里的 index 就检查是否符合 source, 如果符合则往答案中 push target, 并且 i += source.len(), 如果不符合则 push current_char, i += 1。注意各种数组越界检查
impl Solution {
pub fn find_replace_string(
s: String,
indices: Vec<i32>,
sources: Vec<String>,
targets: Vec<String>,
) -> String {
let mut l: Vec<(i32, String, String)> = indices
.into_iter()
.zip(sources)
.zip(targets)
.map(|((i, s), t)| (i, s, t))
.collect();
l.sort();
let mut ans = String::new();
let chars: Vec<char> = s.chars().collect();
let mut i = 0;
while i < chars.len() {
if !l.is_empty() && i == l[0].0 as usize {
let (_, src, tgt) = l.remove(0);
if i + src.len() <= chars.len() {
let ss: String = chars[i..i + src.len()].into_iter().collect();
if ss == src {
ans.push_str(&tgt);
i += src.len();
continue;
}
}
}
ans.push(chars[i]);
i += 1;
}
ans
}
}







 本文介绍了一种字符串处理算法,该算法可以在指定位置用特定目标字符串替换源字符串,若源字符串不存在则不做更改。所有替换操作同时进行,确保相互间不产生影响。文章通过实例展示了如何实现这一算法,并提供了一个具体的 Rust 代码实现。
本文介绍了一种字符串处理算法,该算法可以在指定位置用特定目标字符串替换源字符串,若源字符串不存在则不做更改。所有替换操作同时进行,确保相互间不产生影响。文章通过实例展示了如何实现这一算法,并提供了一个具体的 Rust 代码实现。
















 707
707

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








