There is an m x n grid, where (0, 0) is the top-left cell and (m - 1, n - 1) is the bottom-right cell. You are given an integer array startPos where startPos = [startrow, startcol] indicates that initially, a robot is at the cell (startrow, startcol). You are also given an integer array homePos where homePos = [homerow, homecol] indicates that its home is at the cell (homerow, homecol).
The robot needs to go to its home. It can move one cell in four directions: left, right, up, or down, and it can not move outside the boundary. Every move incurs some cost. You are further given two 0-indexed integer arrays: rowCosts of length m and colCosts of length n.
If the robot moves up or down into a cell whose row is r, then this move costs rowCosts[r].
If the robot moves left or right into a cell whose column is c, then this move costs colCosts[c].
Return the minimum total cost for this robot to return home.
Example 1:
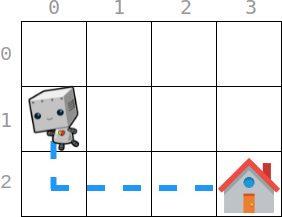
Input: startPos = [1, 0], homePos = [2, 3], rowCosts = [5, 4, 3], colCosts = [8, 2, 6, 7]
Output: 18
Explanation: One optimal path is that:
Starting from (1, 0)
-> It goes down to (2, 0). This move costs rowCosts[2] = 3.
-> It goes right to (2, 1). This move costs colCosts[1] = 2.
-> It goes right to (2, 2). This move costs colCosts[2] = 6.
-> It goes right to (2, 3). This move costs colCosts[3] = 7.
The total cost is 3 + 2 + 6





 给定一个机器人初始位置和目标位置,以及行和列的成本数组,计算机器人返回原点的最小总成本。问题的关键在于理解每条最短路径的消耗是相同的,因为消耗仅与进入特定行或列有关,而与当前列或行无关。
给定一个机器人初始位置和目标位置,以及行和列的成本数组,计算机器人返回原点的最小总成本。问题的关键在于理解每条最短路径的消耗是相同的,因为消耗仅与进入特定行或列有关,而与当前列或行无关。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 705
705

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








