文章目录
可以先参看博文 ffmpeg学习(19)文件流、网络流的格式解析(纯净版av_parser_parse2),避免本文方法中数据在回调中的处理问题。
在 ffmpeg学习(4)协议解析、封装解析 中介绍如何对本地文件(如tantic.mp4)、网络协议流(http/rtmp/rtsp等)进行封装格式的解析。在下面左侧流程图中,解析一个输入封装仅需要执行avformat_open_input 打开一个封装上下文AVFormatContext,之后使用avformat_find_stream_info探测封装中的格式,仅需两个步骤完成任务。
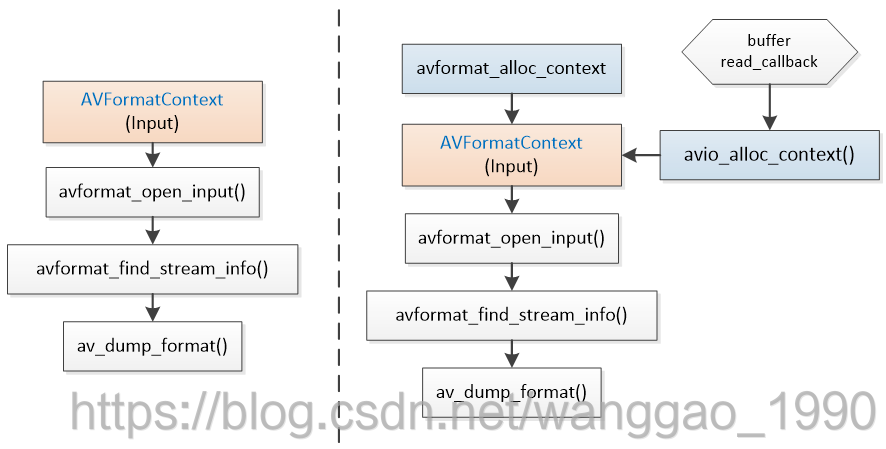
如果音视频来源于内存数据(文件流)、网络数据(如socket接收)等,无法直接使用avformat_open_input打开,如图所示,需要先分配一个AVFormatContext,再创建一个AVIoContext对赋值给AVFormatContext的pb指针,调用avformat_open_input时要求从自定义IO数据来源中进行格式解析。这里是输入解析,因此avio_alloc_context仅注册了读IO数据的回调;对于自定义的输出,仅注册写IO数据的回调,本文不做代码说明。
本文仅介绍内存数据(文件流)、网络数据(如socket接收)的流格式解析的两种使用方式,同时结合例子说明缓冲区大小设置的影响,最后说明一些问题和优化点。
1、函数avio_alloc_context说明
AVIOContext *avio_alloc_context(
unsigned char *buffer,
int buffer_size,
int write_flag,
void *opaque,
int (*read_packet)(void *opaque, uint8_t *buf, int buf_size),
int (*write_packet)(void *opaque, uint8_t *buf, int buf_size),
int64_t (*seek)(void *opaque, int64_t offset, int whence));
首要要开辟一块缓冲区,供ffmpeg读数据、用户写数据。
再至少指定输入数据来自于内存、网络时,需要提供一个int (*read_packet)(void *opaque, uint8_t *buf, int buf_size)回调函数。
当ffmpeg需要数据时,自动回调read_packet函数,要求用户至多读取buf_size字节到buf指针指向的内存中。
对于读IO数据,write_flag为0,回调write_packet和seek这里均为NULL。
2、读文件示例代码
注意,这里使用的ts流式文件(却别与MP4文件),没有将数据一次性读入内存。
#include <iostream>
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
#include "libavformat/avformat.h"
#include "libavutil/time.h"
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
int read_packet(void *opaque, uint8_t *buf, int buf_size)
{
int sz = fread(buf, 1, buf_size, (FILE *)opaque);
printf("[%lld]read callback: need %d, read %d\n", av_gettime(), buf_size, sz);
return sz;
}
int main()
{
int ret;
// 文件流
//const char* input_file = "../files/Titanic.mp4";
const char* input_file = "../files/Titanic.ts";
//// 打开输入
//AVFormatContext* input_fmt_ctx = NULL;
//if((ret = avformat_open_input(&input_fmt_ctx, input_file, NULL, NULL)) < 0) {
// av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Cannot open input file\n");
// return ret;
//}
//// 自定义pb
FILE *pFile = fopen(input_file, "rb");
if(!pFile) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Cannot open input file\n");
}
size_t buff_size = 10 * 1024;
unsigned char * buff;
buff = (unsigned char *)av_malloc(buff_size);
AVIOContext *avio_ctx = avio_alloc_context(buff, buff_size, 0, pFile, read_packet, NULL, NULL);
if(!avio_ctx) {
ret = AVERROR(ENOMEM);
exit(1);
}
AVFormatContext* input_fmt_ctx = avformat_alloc_context();
if(!input_fmt_ctx) {
ret = AVERROR(ENOMEM);
goto end;
}
input_fmt_ctx->pb = avio_ctx;
ret = avformat_open_input(&input_fmt_ctx, NULL, NULL, NULL);
if(ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Could not open input\n");
goto end;
}
// 分析流信息
if((ret = avformat_find_stream_info(input_fmt_ctx, NULL)) < 0) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Cannot find stream information\n");
return ret;
}
// 打印信息
av_dump_format(input_fmt_ctx, 0, input_file, 0);
end:
// 关闭输入
avformat_close_input(&input_fmt_ctx);
}
文件Titanic.ts文件大小2778076字节,设置缓冲区大小10k,程序运行结果如下
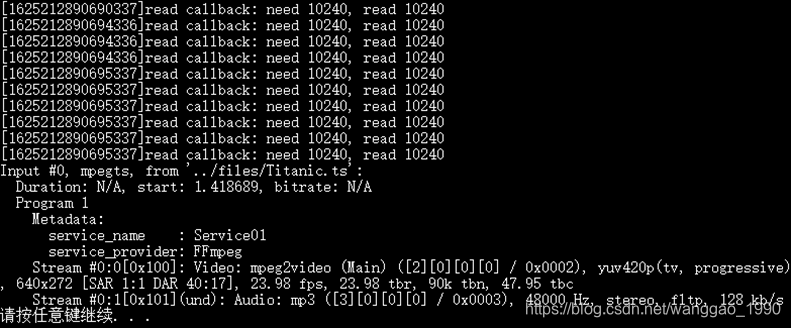
读IO的回调函数执行了10次。缓冲数据大小决定了解析成功前的读IO回调函数的次数,将缓冲区从10k调整为20k,仅需要回调执行5次。
2.1 解析包
接着在 av_dump_format(input_fmt_ctx, 0, input_file, 0); 之后加入解析包的代码
// 解析流
AVPacket *pkt = av_packet_alloc();
while(av_read_frame(input_fmt_ctx, pkt) >= 0) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_INFO, "[%lld] packet: stream index %d, length %d\n", av_gettime(), pkt->stream_index, pkt->size);
//_usleep(33*1000);
av_packet_unref(pkt);
}
当流格式解析出后,不断使用av_read_frame()函数从封装中读取包数据,如果缓冲区的大小不同,解析一定数量的包,回调执行次数有不同。对比缓冲区大小20k和10k的区别。
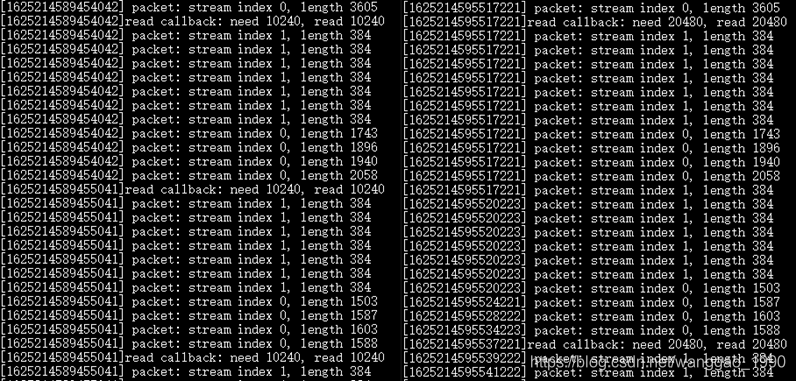
2.2 输入文件为MP4的问题
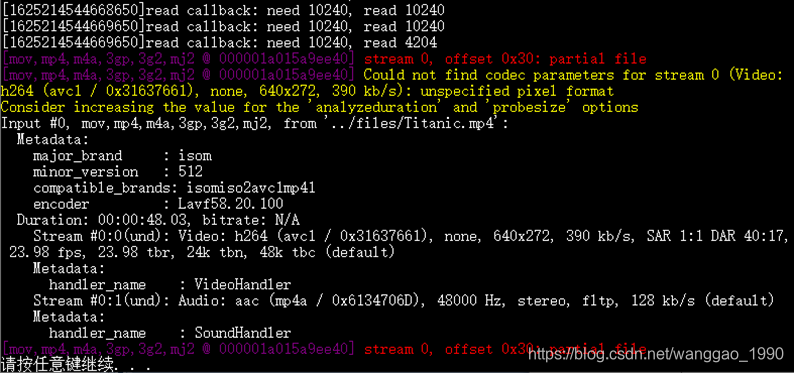
ts文件来源于实时流的保存,可以从任何地方保存与播放,不能计算视频时长;MP4文件容器封装数据,能得到视频的时长、帧数等数据,且能从开头播放。
代码保持不变,替换文件流来源于Titanic.mp4文件后,程序运行结果如下图。回调执行多次,直到整个文件被读取结束,才打印输出探测得到的流格式,并且没有进入解析包的循环中。
3、读网络数据示例代码
网络数据设计数据收、发,缓冲区还要避免data race,因此这里用一大堆有序的的h264 packet文件(数据包编号为0043~2207)来模拟网络流数据。这里给出回调函数和部分main代码。
char bin_file_name[128] = {};
int bin_no = 43;
int read_packet(void *opaque, uint8_t *buf, int buf_size)
{
int sz = 0;
sprintf(bin_file_name, "E:/0、其他项目/2、mask_detect/rtmp2rtmp/x64/bin/%04d.bin", bin_no);
FILE* pFile = fopen(bin_file_name, "rb");
if(!pFile) {
break;
}
sz = fread(buf, 1, buf_size, pFile);
fclose(pFile);
bin_no++;
printf("[%lld]read callback: need %d, read %d\n", av_gettime(), buf_size, sz);
if(bin_no == 2208) {
printf("-------------------------------------- again \n");
bin_no = 43;
}
return sz;
}
int main()
{
int ret;
//// 自定义pb
size_t buff_size = 10*1024;
unsigned char * buff;
buff = (unsigned char *)av_malloc(buff_size);
AVIOContext *avio_ctx = avio_alloc_context(buff, buff_size, 0, NULL, read_packet, NULL, NULL);
if(!avio_ctx) {
ret = AVERROR(ENOMEM);
exit(1);
}
// ...
}
3.1 解析包
当流格式解析出后,不断使用av_read_frame从封装中读取包数据。在探测得到流格式前,已经取得一定数量的数据,经过一定次数的av_read_frame之后才有回调。
由于回调的代码中没有按照要求的数据量大小读取,而是一次读取一个h264报数据,显而易见,会出现ffmpeg解析一次、回调一次,且数据量大小相等。
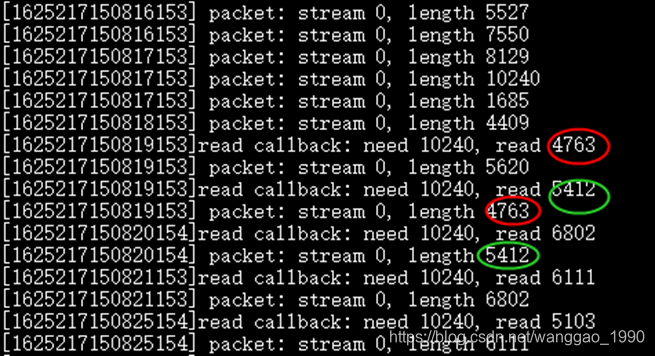
3.2 使用文件包解析后推流,缓冲区设置的影响
上述示例中使用的h264数据包来源于一个帧率30、码率2M的视频,I帧数据包基本在50KB大小,最大为160K。如果缓冲区设置小于50k,回调函数读取文件将不完整,如果将解析包发送到流媒体服务器,客户端可能由于I帧数据不完整导致解码播放画面花屏、部分马赛克等现象。
加入推流代码,注意由于是裸流,解析的AVPacket没有pts,并且需要做适当的延时。增加的推流部分代码为
const char* out_url = "rtmp://192.168.3.100:1935/live/xcp1_re";
AVFormatContext *ofmt_ctx = NULL;
ret = avformat_alloc_output_context2(&ofmt_ctx, NULL, "flv", out_url);
if(ret != 0) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "avformat alloc output context failed\n");
return false;
}
int stream_index_video = -1;
for(int i = 0; i < input_fmt_ctx->nb_streams; i++) {
AVStream *in_stream = input_fmt_ctx->streams[i];
AVStream *out_stream = avformat_new_stream(ofmt_ctx, NULL);
if(!out_stream) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Cannot add stream\n");
return AVERROR_UNKNOWN;
}
ret = avcodec_parameters_copy(out_stream->codecpar, in_stream->codecpar);
out_stream->codecpar->codec_tag = 0;
if(in_stream->codecpar->codec_type == AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO) {
stream_index_video = i;
break;
}
}
ret = avio_open(&ofmt_ctx->pb, out_url, AVIO_FLAG_WRITE);
if(ret < 0) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Cannot open output io\n");
return false;
}
//write mux header
ret = avformat_write_header(ofmt_ctx, NULL);
if(ret != 0) {
throw std::runtime_error("avformat_write_header");
}
uint64_t frame_index = 0;
int64_t start_time = av_gettime();
AVRational time_base_q = {1,AV_TIME_BASE}; // us
AVPacket *pkt = av_packet_alloc();
// 解析流
while(av_read_frame(input_fmt_ctx, pkt) >= 0) {
//av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_INFO, "[%lld] packet: stream %d, length %d\n", av_gettime(), pkt->stream_index, pkt->size);
AVStream *in_stream = input_fmt_ctx->streams[pkt->stream_index];
AVStream *out_stream = ofmt_ctx->streams[pkt->stream_index];
AVMediaType media_type = in_stream->codecpar->codec_type;
// // Fix: No PTS
if(pkt->pts == AV_NOPTS_VALUE) {
// calc pts and duration
int64_t duration = AV_TIME_BASE / av_q2d(in_stream->avg_frame_rate); // 一帧的时间 us
// parameters
pkt->pts = av_rescale_q(frame_index*duration, time_base_q, in_stream->time_base);
pkt->dts = pkt->pts;
pkt->duration = av_rescale_q(duration, time_base_q, in_stream->time_base);
}
// Important: Delay if input a disk file
if(media_type == AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO) {
int64_t pts_time = av_rescale_q(pkt->dts, in_stream->time_base, time_base_q); // us
int64_t now_time = av_gettime() - start_time;
if(pts_time > now_time)
av_usleep(pts_time - now_time);
}
// // prepare packet(输入、输出都是rtmp时,时基一样,可省略时间戳转换)
av_packet_rescale_ts(pkt, in_stream->time_base, out_stream->time_base);
//Print to Screen
if(media_type == AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO) {
printf("send frame: %llu, time: %lld, pkt size %d\n", frame_index, av_gettime() / 1000, pkt->size); // ms
frame_index++;
}
// write packet
ret = av_interleaved_write_frame(ofmt_ctx, pkt);
if(ret < 0) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "write packet failed.\n");
return ret;
}
av_packet_unref(pkt);
}
运行GIF示意图如下(缓冲区60K),下半部分经常马赛克;当设缓冲区10k,仅能显示画面上面一小部分。当提高缓冲区到200K(所有数据包大小都能读取正常),视频流播放无任何问题。
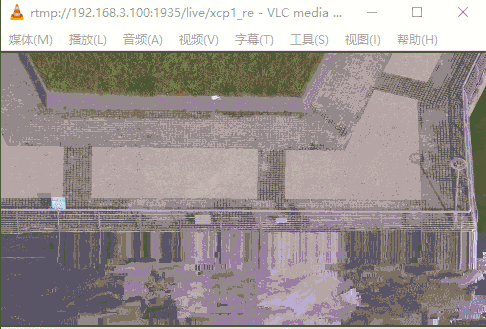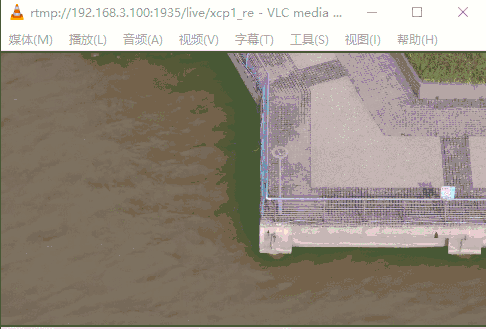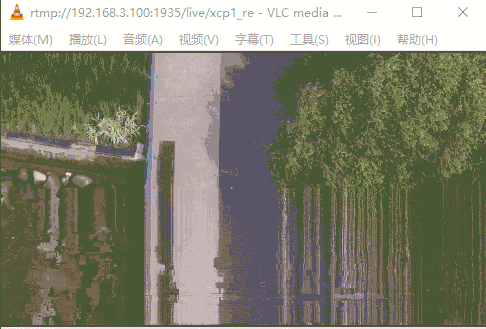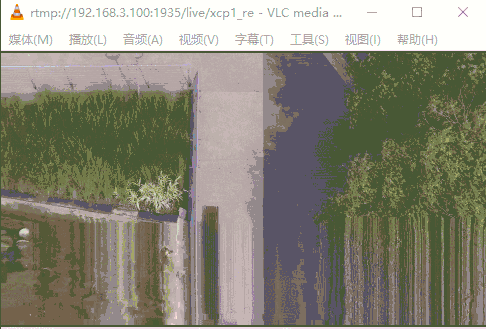
3.3 优化当前读IO数据回调函数
针对上面读取数据包、推流的场景出现回调次数较多情况,又因为文件IO效率慢,因此做适当的优化,让回调尽可能一次性读取足够量的数据。例如,这里缓冲区设置200k,需要读取多个数据包文件。
int read_packet(void *opaque, uint8_t *buf, int buf_size)
{
int sz = 0;
while(1) {
sprintf(bin_file_name, "E:/0、其他项目/2、mask_detect/rtmp2rtmp/x64/bin/%04d.bin", bin_no);
FILE* pFile = fopen(bin_file_name, "rb");
if(!pFile) {
break;
}
fseek(pFile, 0, SEEK_END);
int fileLen = ftell(pFile);
fseek(pFile, 0, SEEK_SET);
// 缓冲区不足以放下当前数据包
if(fileLen > buf_size - sz) {
break;
}
int tmpSz = fread(buf + sz, 1, fileLen, pFile);
fclose(pFile);
sz += tmpSz;
bin_no ++;
if(bin_no == 2208) {
printf("-------------------------------------- again\n");
bin_no = 43;
}
}
printf("[%lld]read callback: need %d, read %d, packet num %d\n", av_gettime(), buf_size, sz, bin_no);
return sz;
}
使用while循环不断读取数据包文件,直到剩下的缓冲区大小不足以放下当前数据包,就结束本次回调。
4、其他说明
(1)使用输出较少,例如将解析或者解码后的数据以显示的方式写入到文件的函数部分,替换成写IO数据回调函数,通过av_write_frame/av_interleaved_write_frame实现相同的功能。
(2)前面的示例,均没有解决缓冲区设置过小导致数据读写不完整的情况。在解析网络流格式时,如果输入数据的码率过大,而缓冲区小时会导致解析格式失败。解决方式其一,设置较大的缓冲区;其二,使用额外的手段,对于较大的数据包进行拆分以完整的将所有数据逐次放入缓冲区。
(3)真实的网络数据解析,需要额外的数据结构(例如链表来代替示例中的数据包文件)来管理用户数据,依次、足量、完整的将数据包传递到缓冲区。
(4)探测到流之后,已经读取的数据会缓存起来,解析时将从头进行,这样会导致后面进来的包将堆积造成延迟。因此需要优化一些加速的选项,如
AVFormatContext* input_fmt_ctx = avformat_alloc_context();
if(!input_fmt_ctx) {
ret = AVERROR(ENOMEM);
goto end;
}
input_fmt_ctx->pb = avio_ctx;
printf("size %ld\tduration %ld\n", input_fmt_ctx->probesize,
input_fmt_ctx->max_analyze_duration);
//input_fmt_ctx->probesize = 500*1000;
//input_fmt_ctx->max_analyze_duration = 2000;
AVDictionary* options = NULL;
av_dict_set(&options, "fflags", "nobuffer", 0);
ret = avformat_open_input(&input_fmt_ctx, NULL, NULL, &options);
if(ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Could not open input\n");
goto end;
}








 本文探讨了使用FFmpeg处理内存文件流(TS/MP4)和网络数据流的格式解析,重点讲解了avio_alloc_context的作用,读写IO回调函数的优化,以及缓冲区大小对解析性能的影响。实例演示了如何处理网络数据包并适配流媒体推流,以及在实际操作中遇到的问题和解决方案。
本文探讨了使用FFmpeg处理内存文件流(TS/MP4)和网络数据流的格式解析,重点讲解了avio_alloc_context的作用,读写IO回调函数的优化,以及缓冲区大小对解析性能的影响。实例演示了如何处理网络数据包并适配流媒体推流,以及在实际操作中遇到的问题和解决方案。


















 1086
1086

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










