线程中断参考视频
1.判断线程是否中断,只有在线程上打上中断标记位,才会认为线程中断
Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); 打中断标记,
如果线程是运行状态,虽然打了中断标记,但是线程会继续运行,只是标记了线程中断,这会影响哪里呢?影响的地方是:
Thread.sleep(5000);
lock.wait();
这2个方法都会抛出throws InterruptedException这个中断异常。意思就是如果线程打了中断标记,再调用这2个方法的时候就会抛出异常,并且不会阻塞,如果自己捕获了异常,线程就会继续运行。
示例代码:
@Test
public void test1(){
Thread thread1 = new Thread(() -> {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
System.out.println("时间"+System.currentTimeMillis()+"---线程状态是否中断0--"+Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
},"thread1");
thread1.start();
LockSupport.parkNanos(1000000000L);
System.out.println("线程状态1"+thread1.getState());
System.out.println("时间"+System.currentTimeMillis()+"---线程状态是否中断1--"+Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());
}运行结果
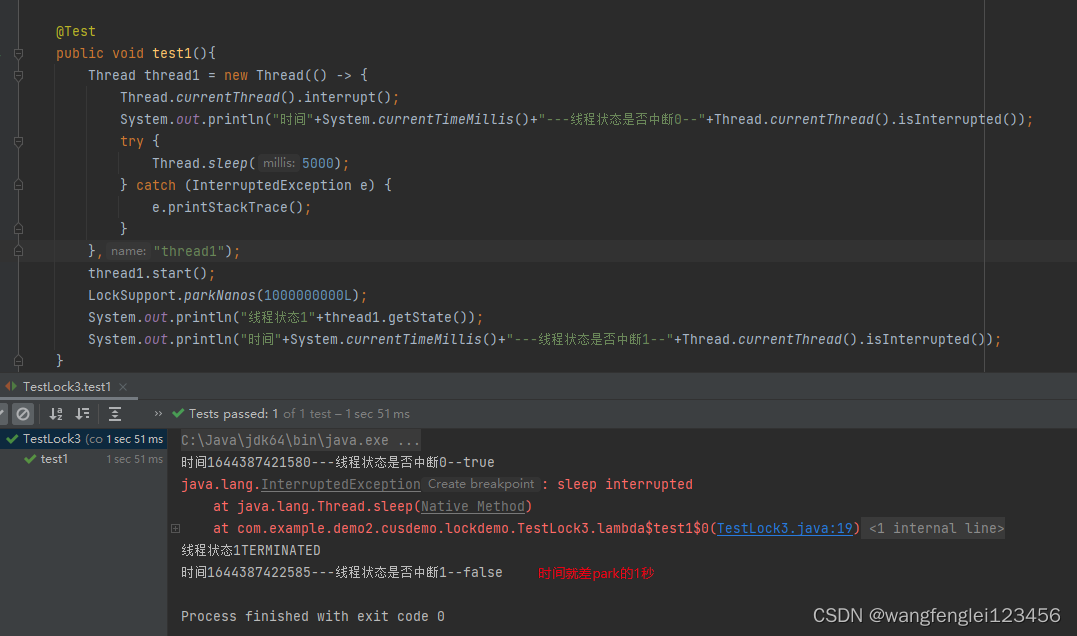
从结果可以看出,sleep方法没有阻塞,而是抛出异常了,造成了线程终止
线程所有状态打印代码
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread1 = new Thread(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("线程状态0"+Thread.currentThread().getState());
System.out.println("线程状态是否中断"+Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());
System.out.println("线程开始进入代码块0"+Thread.currentThread().getState());
synchronized (lock) {
try {
System.out.println("线程开始进入wait----"+Thread.currentThread().getState());
lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("线程进入代码块1"+Thread.currentThread().getState());
}
System.out.println("线程1运行结束了");
},"thread1");
Thread thread2 = new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println("线程2开启了");
synchronized (lock) {
System.out.println("线程2先拿到锁");
LockSupport.parkNanos(7000000000L);
}
LockSupport.parkNanos(1000000000L);
synchronized (lock) {
LockSupport.parkNanos(2000000000L);
System.out.println("线程2开始唤醒线程1");
lock.notify();
}
},"thread2");
System.out.println("线程状态1"+thread1.getState());
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
LockSupport.parkNanos(4000000000L);
System.out.println("线程状态2"+thread1.getState());
LockSupport.parkNanos(2000000000L);
System.out.println("线程状态3"+thread1.getState());
LockSupport.parkNanos(2000000000L);
System.out.println("线程状态4"+thread1.getState());
LockSupport.parkNanos(2000000000L);
System.out.println("线程状态5"+thread1.getState());
LockSupport.parkNanos(2000000000L);
System.out.println("线程状态6"+thread1.getState());
}运行结果
线程状态1NEW
线程2开启了
线程2先拿到锁
线程状态2TIMED_WAITING
线程状态0RUNNABLE
线程状态是否中断false
线程开始进入代码块0RUNNABLE
线程状态3BLOCKED
线程开始进入wait----RUNNABLE
线程状态4WAITING
线程2开始唤醒线程1
线程状态5WAITING
线程进入代码块1RUNNABLE
线程1运行结束了
线程状态6TERMINATED分析:在进入synchronized代码时,但是没有拿到锁,就会处于BLOCKED阻塞状态。
线程状态查看Thread类中的这个枚举
public enum State {
/**
* Thread state for a thread which has not yet started.
*/
NEW,
/**
* Thread state for a runnable thread. A thread in the runnable
* state is executing in the Java virtual machine but it may
* be waiting for other resources from the operating system
* such as processor.
*/
RUNNABLE,
/**
* Thread state for a thread blocked waiting for a monitor lock.
* A thread in the blocked state is waiting for a monitor lock
* to enter a synchronized block/method or
* reenter a synchronized block/method after calling
* {@link Object#wait() Object.wait}.
*/
BLOCKED,
/**
* Thread state for a waiting thread.
* A thread is in the waiting state due to calling one of the
* following methods:
* <ul>
* <li>{@link Object#wait() Object.wait} with no timeout</li>
* <li>{@link #join() Thread.join} with no timeout</li>
* <li>{@link LockSupport#park() LockSupport.park}</li>
* </ul>
*
* <p>A thread in the waiting state is waiting for another thread to
* perform a particular action.
*
* For example, a thread that has called <tt>Object.wait()</tt>
* on an object is waiting for another thread to call
* <tt>Object.notify()</tt> or <tt>Object.notifyAll()</tt> on
* that object. A thread that has called <tt>Thread.join()</tt>
* is waiting for a specified thread to terminate.
*/
WAITING,
/**
* Thread state for a waiting thread with a specified waiting time.
* A thread is in the timed waiting state due to calling one of
* the following methods with a specified positive waiting time:
* <ul>
* <li>{@link #sleep Thread.sleep}</li>
* <li>{@link Object#wait(long) Object.wait} with timeout</li>
* <li>{@link #join(long) Thread.join} with timeout</li>
* <li>{@link LockSupport#parkNanos LockSupport.parkNanos}</li>
* <li>{@link LockSupport#parkUntil LockSupport.parkUntil}</li>
* </ul>
*/
TIMED_WAITING,
/**
* Thread state for a terminated thread.
* The thread has completed execution.
*/
TERMINATED;
}




 本文详细探讨了Java中线程中断的机制,包括如何使用`Thread.interrupt()`设置中断标记,以及该操作如何影响`Thread.sleep()`和`Object.wait()`等方法。通过示例代码展示了中断标记如何导致线程提前退出阻塞状态,并分析了线程在不同状态下如何转换。同时,讲解了线程的几种状态,如NEW、RUNNABLE、BLOCKED、WAITING和TERMINATED,帮助理解线程执行流程。
本文详细探讨了Java中线程中断的机制,包括如何使用`Thread.interrupt()`设置中断标记,以及该操作如何影响`Thread.sleep()`和`Object.wait()`等方法。通过示例代码展示了中断标记如何导致线程提前退出阻塞状态,并分析了线程在不同状态下如何转换。同时,讲解了线程的几种状态,如NEW、RUNNABLE、BLOCKED、WAITING和TERMINATED,帮助理解线程执行流程。
 https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1CM4y157vc/?spm_id_from=pageDriver
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1CM4y157vc/?spm_id_from=pageDriver















 663
663

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








