51 java集合和泛型_1 _集合概述与Collection体系集合
集合概念
- 概念:对象的容器,实现了对对象常用的操作,类似数组功能。(里面定义了对多个对象进行操作的常用方法,可实现数组的功能)
- 和数组的相同点:都是容器
- 和数组的区别:
- 数组长度固定,集合长度不固定
- 数组可以存储基本类型和引用类型,集合只能存储引用类型(基本类型可以进行装箱操作之后,在放入集合中)
- 位置:java.util.*;
Collection体系集合
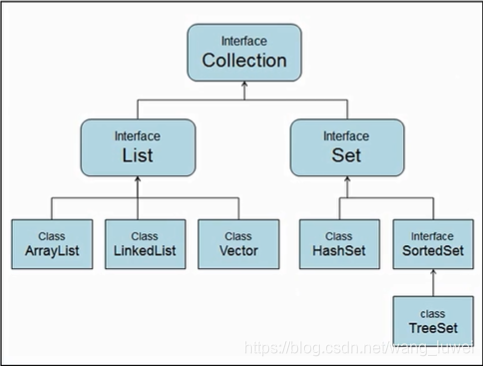
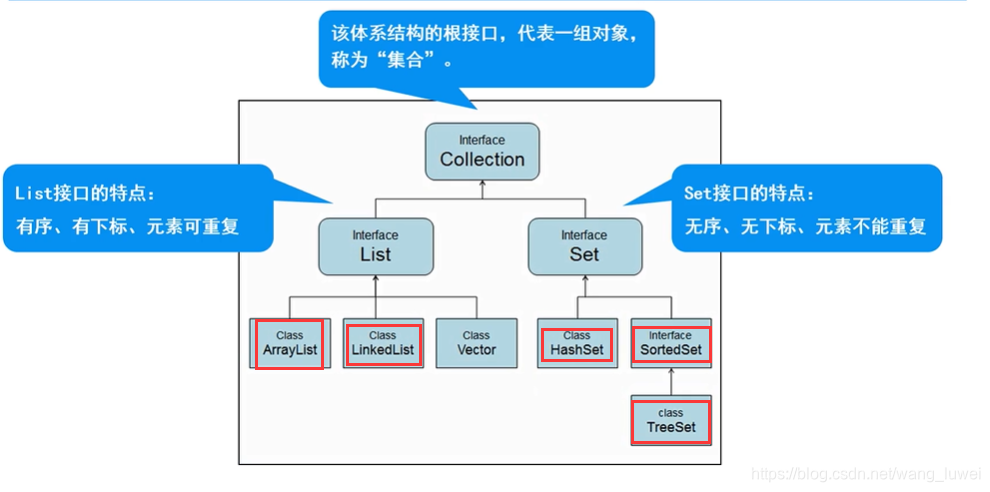
Collection父接口
- 特点:代表一组任意类型的对象,一些集合允许重复,而其他的则不允许;一些 collection 是有序的,而另一些则是无序的;JDK 不提供此接口的任何直接 实现:它提供更具体的子接口(如 Set 和 List)实现
- 方法:
- boolean add(Object obj) //添加一个对象。
- boolean addAll (Collection c) //将一个集合中的所有对象添加到此集合中。
- void clear() //清空此集合中的所有对象。
- boolean contains (Object o) //检查此集合中是否包含o对象
- boolean equals (Object o) //比较此集合是否与指定对象相等。
- boolean isEmpty() //判断此集合是否为空
- boolean remove (Object o) //在此集合中移除o对象
- int size() //返回此集合中的元素个数。
- Object[] toArray() //将此集合转换成数组。
- 等…(可查看api学习)
代码如下:(collection使用1:)
package com.wlw.collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
/**
* collection 接口的使用
* 1.添加
* 2.删除
* 3.遍历(*****重点)
* 4.判断
*/
public class Collection_Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Collection 本身是不能实例化的(它是一个接口)
//创建集合
Collection collection = new ArrayList();
//1.添加
collection.add("苹果");
collection.add("西瓜");
collection.add("榴莲");
System.out.println("元素个数:"+collection.size());
System.out.println(collection); //相当于调用collection.toString() Arraylist中把toString()方法重写了
//2.删除
/*
collection.remove("榴莲");
//collection.clear();//清空
System.out.println("删除之后,元素个数:"+collection.size());
System.out.println(collection);
*/
//3.遍历【*****重点】
//两种方式
//3.1 增强for循环(不能使用普通的for循环来遍历,因为collection无下标)
System.out.println("-------------3.1 增强for循环------------------");
for (Object o : collection) {
System.out.println(o);
}
//3.2使用Iterator迭代器(Iterator迭代器是专门用来遍历集合的一种方式)
/*
Iterator是一个接口,里面定义了三个方法
hasNext();判断有没有下一个元素
next(); 读取下一个元素
remove(); 删除当前元素
在迭代过程中:是不允许使用collection的remove()方法的,
要想删除元素可以使用Iterator的remove()方法
*/
System.out.println("-------------3.2使用Iterator迭代器------------------");
Iterator iterator = collection.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){ //迭代过程
Object o = iterator.next();
System.out.println(o);
//collection.remove(o); //异常ConcurrentModificationException(并发修改异常)
//iterator.remove();
}
System.out.println("元素个数:"+collection.size());
//4.判断
System.out.println(collection.contains("西瓜")); //true
System.out.println(collection.isEmpty()); //false
}
}
/*
执行结果:
元素个数:3
[苹果, 西瓜, 榴莲]
-------------3.1 增强for循环------------------
苹果
西瓜
榴莲
-------------3.2使用Iterator迭代器------------------
苹果
西瓜
榴莲
元素个数:3
true
false
*/
代码如下:(collection使用2:保存学生信息)
package com.wlw.collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
/**
* collection 接口的使用 2 :保存学生信息
* 1.添加
* 2.删除
* 3.遍历(*****重点)
* 4.判断
*/
public class Collection_Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Collection 本身是不能实例化的(它是一个接口)
//创建集合
Collection collection = new ArrayList();
Student s1 = new Student("张三",20);
Student s2 = new Student("张无忌",21);
Student s3 = new Student("张大头",22);
//1.添加(上面都是new出来的,都存放在堆里,而集合collection中存放的是Student对象(s1,s2,s3)的地址)
collection.add(s1);
collection.add(s2);
collection.add(s3);
System.out.println("元素个数:"+collection.size());
System.out.println(collection.toString());
//2.删除
/*
collection.remove(s3);
//collection.clear(); //清空
System.out.println("删除之后,元素个数:"+collection.size());
System.out.println("删除之后:"+collection.toString());
*/
//3.遍历【*****重点】
//两种方式
//3.1 增强for循环(不能使用普通的for循环来遍历,因为collection无下标)
//在对应的class文件中,此方法也是通过迭代器来实现的
System.out.println("-------------3.1 增强for循环------------------");
for (Object o : collection) {
Student s = (Student) o;
System.out.println(s.toString());
}
//3.2使用Iterator迭代器(Iterator迭代器是专门用来遍历集合的一种方式)
//hasNext(); next();remove(); 在迭代过程中:是不允许使用collection的remove()方法的,
// 要想删除元素可以使用Iterator的remove()方法
System.out.println("-------------3.2使用Iterator迭代器------------------");
Iterator iterator = collection.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
Object o = iterator.next();
Student s = (Student) o;
//Student s_it = (Student) iterator.next();
System.out.println(s.toString());
}
//4.判断
System.out.println(collection.contains(s1)); //true
System.out.println(collection.contains(new Student("张三",20)));//false,因为这个是在堆里新创建了一个Student对象
System.out.println(collection.isEmpty()); //false
}
}
/*
执行结果:
元素个数:3
[Student{name='张三', age=20}, Student{name='张无忌', age=21}, Student{name='张大头', age=22}]
-------------3.1 增强for循环------------------
Student{name='张三', age=20}
Student{name='张无忌', age=21}
Student{name='张大头', age=22}
-------------3.2使用Iterator迭代器------------------
Student{name='张三', age=20}
Student{name='张无忌', age=21}
Student{name='张大头', age=22}
true
false
false
*/
Iteraor 迭代器
-
他是一个接口:java.util 接口 Iterator
-
public interface Iterator
对 collection 进行迭代的迭代器。迭代器取代了 Java Collections Framework 中的 Enumeration(枚举)。迭代器与枚举有两点不同:
- 迭代器允许调用者利用定义良好的语义在迭代期间从迭代器所指向的 collection 移除元素。
- 方法名称得到了改进。
-
方法:
- boolean hasNext();判断有没有下一个元素 ( 如果仍有元素可以迭代,则返回 true。)
- E next(); 读取下一个元素 (返回迭代的下一个元素。)
- void remove(); 删除当前元素(从迭代器指向的 collection 中移除迭代器返回的最后一个元素(可选操作))





 本文深入讲解Java集合框架的核心概念,包括集合与数组的区别、Collection接口的功能特性及其子接口Set和List的使用。通过实例演示了如何添加、删除、遍历集合元素,并探讨了Iterator迭代器的正确使用方法。
本文深入讲解Java集合框架的核心概念,包括集合与数组的区别、Collection接口的功能特性及其子接口Set和List的使用。通过实例演示了如何添加、删除、遍历集合元素,并探讨了Iterator迭代器的正确使用方法。


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










