一、spring事件介绍
1、简介
ApplicationContext提供事件处理通过ApplicationEvent类和ApplicationListener接口。如果一个bean实现ApplicationListener接口在容器中,每次一个ApplicationEvent被发布到ApplicationContext中,这类bean就会收到这些通知。
2、相关类
实现Spring事件机制主要有4个类:
ApplicationEvent:事件,每个实现类表示一类事件,可携带数据。
ApplicationListener:事件监听器,用于接收事件处理时间。
ApplicationEventMulticaster:事件管理者,用于事件监听器的注册和事件的广播。
ApplicationEventPublisher:事件发布者,委托ApplicationEventMulticaster完成事件发布。
3、使用场景
同步逻辑就不建议使用事件处理了,代码过于分散,不利于维护。
大多数情况下分支功能与主业务需要解耦,spring event一般使用异步逻辑,功能上相当于开启子线程调用一段异步代码,但是使用event更加优雅。
(1)业务解耦
发布/订阅是常见的业务解耦方式,跨项目可以使用kafka等MQ,同一个springboot项目则可以使用Spring自带的event实现发布/监听,简单快捷。
(2)系统日志记录
相当于AOP的功能,
监控指标记录、数据埋点记录。
4、使用方法
实现spring event,至少需要以下几个角色:
(1)Event事件:分内置事件和自定义事件两种。
(2)监听器:内置事件和自定义事件都需要自定义监听器。
(3)发布事件:如果是自定义的Event,则需要手动发布;内置事件无需手动发布。
二、event事件
spring的事件都是ApplicationEvent,又可以分为内置事件和自定义事件。
内置事件实际上也是继承了ApplicationEvent,常见的有ContextRefreshedEvent。
内置事件不需要手动发布,自定义监听事件需要手动发布。
1、spring的内置事件
常见的内置事件有:
Spring 提供了以下5种标准的事件:
(1)上下文更新事件(ContextRefreshedEvent):在调用ConfigurableApplicationContext 接口中的refresh()方法时被触发。
(2)上下文开始事件(ContextStartedEvent):当容器调用ConfigurableApplicationContext的Start()方法开始/重新开始容器时触发该事件。
(3)上下文停止事件(ContextStoppedEvent):当容器调用ConfigurableApplicationContext的Stop()方法停止容器时触发该事件。
(4)上下文关闭事件(ContextClosedEvent):当ApplicationContext被关闭时触发该事件。容器被关闭时,其管理的所有单例Bean都被销毁。
(5)请求处理事件(RequestHandledEvent):在Web应用中,当一个http请求(request)结束触发该事件。
如果一个bean实现了ApplicationListener接口,当一个ApplicationEvent 被发布以后,bean会自动被通知。
以ContextRefreshedEvent看下结构:可以看到最终都是 ApplicationEvent
package org.springframework.context.event;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
public class ContextRefreshedEvent extends ApplicationContextEvent {
public ContextRefreshedEvent(ApplicationContext source) {
super(source);
}
}
package org.springframework.context.event;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent;
public abstract class ApplicationContextEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
public ApplicationContextEvent(ApplicationContext source) {
super(source);
}
public final ApplicationContext getApplicationContext() {
return (ApplicationContext)this.getSource();
}
}2、自定义事件
(1)低版本spring
通过extends ApplicationEvent 实现自定义事件
public class MyEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
private String time = new SimpleDateFormat("hh:mm:ss").format(new Date());
private String msg;
public MyEvent(Object source, String msg) {
super(source);
this.msg = msg;
}
public MyEvent(Object source) {
super(source);
}
public String getTime() {
return time;
}
public void setTime(String time) {
this.time = time;
}
public String getMsg() {
return msg;
}
public void setMsg(String msg) {
this.msg = msg;
}
}
(2)高版本spring
从 Spring 4.2 开始,发布事件不再强制要求继承 ApplicationEvent,可以使用任何普通的 Java 对象作为事件类。这是一项明确的设计更新,旨在简化事件发布机制。
public class MyEvent {
private String message;
public MyEvent(String message) {
this.message = message;
}
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
}
三、ApplicationListener
1、简介
ApplicationListener 是spring提供的一个监听器,它可以实现一个简单的发布-订阅功能,用有点外行但最简单通俗的话来解释:监听到主业务在执行到了某个节点之后,在监听器里面做出相应的其它业务变更。
好处:事件监听也是设计模式中 发布-订阅模式、观察者模式的一种实现。
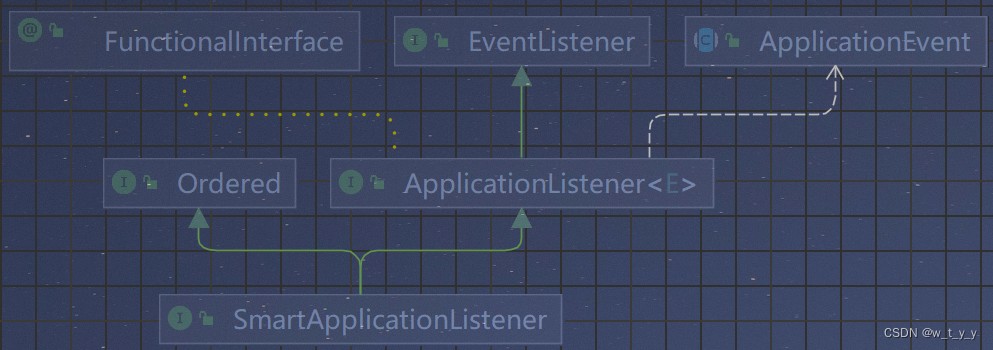
2、ApplicationListener 源码:
package org.springframework.context;
import java.util.EventListener;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ApplicationListener<E extends ApplicationEvent> extends EventListener {
void onApplicationEvent(E event);
default boolean supportsAsyncExecution() {
return true;
}
static <T> ApplicationListener<PayloadApplicationEvent<T>> forPayload(Consumer<T> consumer) {
return (event) -> {
consumer.accept(event.getPayload());
};
}
}
3、ApplicationListener与其他Listener的区别
看下ApplicationListener与SpringApplicationRunListener、EventPublishingRunListener的区别和联系。前提:springboot是基于spring的,一个springboot应用其核心是调用了spring的SpringApplication.run()方法,也就是说,springboot是为简化spring开发进行的封装。现在我们来分析三者关系。
(1)SpringApplicationRunListener 和 EventPublishingRunListener是由springboot提供的,且EventPublishingRunListener是SpringApplicationRunListener 的唯一实现。
(2)ApplicationListener:是由spring提供的,监听目标是ApplicationEvent类或者其子类,所有定制化的事件都直接或间接的继承ApplicationEvent,也就是说,定制化的事件都是ApplicationEvent的子类,都是ApplicationListener监听器的监听目标,EventPublishingRunListener发布的定制化事件间接受ApplicationListener监听。
4、ApplicationListener原理
ApplicationListener监听器本身是一个函数式接口,监听对象为ApplicationEvent事件的子类,ApplicationEvent事件本身是一个抽象类,它拥有各式各样的子类,这些子类就是定制化的事件,专门用于特定的场景。ApplicationEvent事件继承EventObject这个事件本体,EventObject事件本体是所有事件的基础,EventObject事件本体拥有一个protected transient Object source;这样一个Object类型的source属性,用于存放事件。
那这个事件数据是如何传递的呢?通过观察源码,我们发现,在事件类继承的层层嵌套链中,子类都需要通过super()方法调用父类的构造方法,通过在super()中传递事件参数可以实现事件数据的层层传递,最终传递到EventObject,然后,在EventObject的构造方法中就可以完成source属性的初始化,也就完成了事件的传递以及最终存储。
5、使用
内置事件和自定义事件都需要自定义监听器。两个步骤:实现+注册。
5.1、实现
通过implements ApplicationListener<E extends ApplicationEvent> 接口并重写
onApplicationEvent方法即可。
(1)单事件
如果只有一个事件,可以直接在方法中写事件的名称,如
@Slf4j
@Component
public class MyListener implements ApplicationListener<MyLogEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(MyLogEvent event) {
UserLogDTO source = event.getSource();
log.info("监听到:url={},detail={}",source.getUrl(),source.getDetail());
//其他处理,比如存储日志
}
}(2)多个事件
如果有多个事件,又不想写多个监听器,则可以不指定名称
package com.listener.demo.listener;
import com.listener.demo.dto.UserLogDTO;
import com.listener.demo.event.MyLogEvent;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;
import org.springframework.context.event.ContextRefreshedEvent;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Slf4j
@Component
public class MyListener implements ApplicationListener {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
if (event instanceof MyLogEvent) {
MyLogEvent myLogEvent = (MyLogEvent) event;
UserLogDTO source = myLogEvent.getSource();
log.info("监听到:url={},detail={}",source.getUrl(),source.getDetail());
} else if (event instanceof ContextRefreshedEvent) {
log.info("这是内置事件");
}
}
}
启动打印:
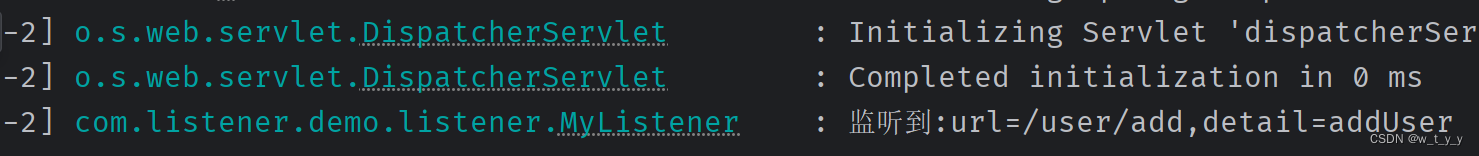
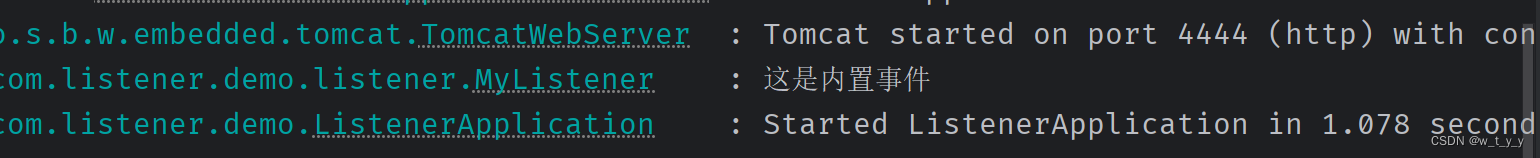 访问业务打印:
访问业务打印:
5.2、注册
注册监听器有以下几个方法:
(1)通过启动类注册
@SpringBootApplication
public class MyApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//SpringApplication.run(MyApplication.class, args);
//等价于上面的启动只不过把过程进行拆分,扩展了中间操作
SpringApplication application = new SpringApplication(MyApplication.class);
application.addListeners(new MyApplicationListener());
application.run(args);
}
}(2)通过自动配置文件spring.factories文件注册
org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=\
com.classloader.listener.CustomeApplicationListener(3)通过注解注册
直接在自定义监听器上加上@Component、@Configuration等注解注册,这是自定义监听器常用的方法。
注意:通过注解注册监听不到容器加载之前的事件。
@Slf4j
@Component
public class MyTask implements ApplicationListener {
private static boolean aFlag = false;
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
if (event instanceof ContextRefreshedEvent) {
log.info("监听到 ContextRefreshedEvent...");
}
if (event instanceof MyEvent) {
log.info("监听到 MyEvent...");
MyEvent myEvent = (MyEvent) event;
System.out.println("时间:" + myEvent.getTime() + " 信息:" + myEvent.getMsg());
}
}
}
@Component
public class CustomeApplicationListener implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationStartedEvent> , Ordered {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationStartedEvent applicationStartingEvent) {
System.out.println("自定义监听器CustomeApplicationListener,监听springboot启动,监听EventPublishingRunListener发布的启动开始事件");
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return 0;
}
}四、(自定义)事件发布
1、发布方法
自定义事件需要手动发布监听器才能监听到,内置事件的发布者则是spring本身(见原理部分)。
(1)可以使用ApplicationContext 发布;
(2)还可以使用ApplicationEventPublisher发布。ApplicationEventPublisher是ApplicationContext的父接口之一。可以发布单个事件,还可以发布List等Object类型的事件。
package org.springframework.context;
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ApplicationEventPublisher {
default void publishEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
this.publishEvent((Object)event);
}
void publishEvent(Object event);
}public interface ApplicationContext extends EnvironmentCapable, ListableBeanFactory, HierarchicalBeanFactory, MessageSource, ApplicationEventPublisher, ResourcePatternResolver {
}如:
@Autowired
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Autowired
private ApplicationEventPublisher applicationEventPublisher;
//以下两种方法都可以
applicationContext.publishEvent(myEvent);
applicationEventPublisher.publishEvent(myEvent);2、在哪里发布
至于在哪里发布,则看业务逻辑,如直接在启动类发布也是可以的:
@SpringBootApplication
public class TaskApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext run = SpringApplication.run(TaskApplication.class, args);
MyEvent event = new MyEvent("event", "忙中岁月忙中遣,我本愚来性不移");
// 发布事件
run.publishEvent(event);
}
}
@SpringBootApplication
public class TaskApplication implements CommandLineRunner {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(TaskApplication.class, args);
}
@Resource
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
MyEvent event = new MyEvent("event", "忙中岁月忙中遣,我本愚来性不移");
// 发布事件
applicationContext.publishEvent(event);
}
}
当然一般是在业务逻辑中发布的。如我删除用户需要删除相关联的其他业务,则可以在删除用户接口中发布删除事件,在监听器中处理来删除相关联的其他业务。
五、ApplicationEventMulticaster事件管理者
1、介绍
ApplicationEventMulticaster,一般使用的是SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster ,
SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster 是 Spring 框架中负责事件广播的一个类。它实现了 ApplicationEventMulticaster 接口,该接口定义了发布(广播)应用事件的方法。在 Spring 应用中,当某个事件发生时(比如,某个 bean 的状态发生了改变),可以使用 ApplicationEventMulticaster 来通知所有对该事件感兴趣的监听器。
2、功能
主要有以下功能:
(1)注册监听器:
通过 addApplicationListener 方法,可以向广播器注册事件监听器。监听器必须实现 ApplicationListener 接口,并指定它们感兴趣的事件类型。
(2)广播事件:使用 multicastEvent 方法来广播事件。当这个方法被调用时,它会遍历所有注册的监听器,并调用那些能够处理该事件的监听器的 onApplicationEvent 方法。
(3)默认事件类型:SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster 默认处理所有实现了 ApplicationEvent 接口的事件。
(4)任务执行器:SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster 还可以配置一个 TaskExecutor,用于异步地广播事件。如果未设置 TaskExecutor,事件将同步广播。
(5)错误处理:如果事件处理过程中发生异常,SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster 会记录一个错误消息,但不会抛出异常或中断事件广播。
3、源码
在 Spring 容器中,SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster 通常被自动配置为单例 bean,并且可以通过 @Autowired 注解注入到其他组件中,以便发布事件。同时,Spring 容器也会自动注册一些内置的事件监听器,用于处理如上下文刷新、上下文关闭等内置事件。
六、demo
内置事件+自定义事件 demo:
pom:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>listener-demo</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.2.4</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>启动类:
package com.listener.demo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class ListenerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ListenerApplication.class, args);
}
}
1、内置事件
package com.listener.demo.listener;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;
import org.springframework.context.event.ContextRefreshedEvent;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Slf4j
@Component
public class MyListener implements ApplicationListener<ContextRefreshedEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {
log.info("启动start...");
}
}
启动项目控制台打印:
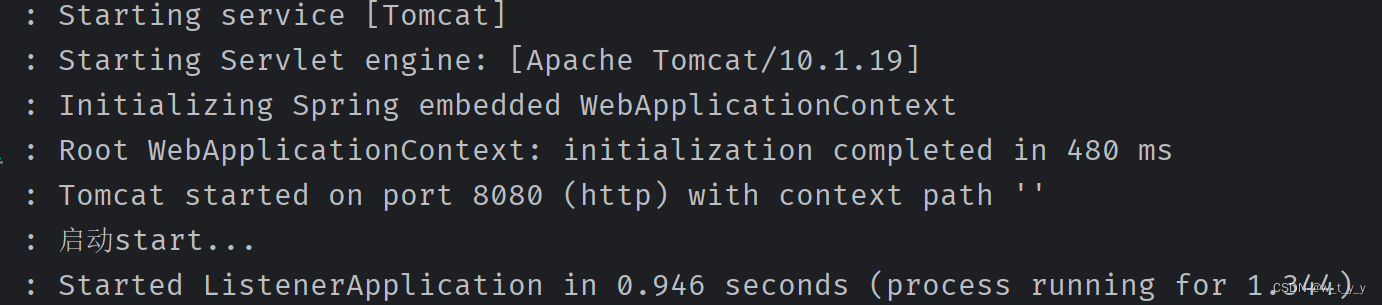
注意:有时会加个标志位,
@Slf4j
@Component
public class MyTask implements ApplicationListener<ContextRefreshedEvent> {
private static boolean aFlag = false;
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {
if (!aFlag) {
aFlag = true;
log.info("我已经监听到了");
}
}
}
因为web应用会出现父子容器,这样就会触发两次监听任务,所以需要一个标志位,保证监听任务(log.info(“我已经监听到了”))只会触发一次 。
2、自定义事件
如现在自定义一个注解,在controller接口加这个注解-->aop拦截获取相关信息,并触发事件监听-->在监听器中处理业务,如存储、发送mq等等。
(1)自定义注解
package com.listener.demo.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
// 声明注解作用于方法
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
// 声明注解运行时有效
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyLog {
String url() ;
String detail() ;
}
package com.listener.demo.controller;
import com.listener.demo.annotation.MyLog;
import com.listener.demo.dto.UserDTO;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@MyLog(url = "/user/add",
detail = "addUser")
@RequestMapping("/add")
public String add(UserDTO userDTO) {
return "add success";
}
@MyLog(url = "/user/update",detail = "updateUser")
@RequestMapping("/update")
public String update() {
return "update success";
}
}
(2)DTO:
package com.listener.demo.dto;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class UserDTO {
private String userName;
private String userAccount;
private Integer age;
}
package com.listener.demo.dto;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
@Builder
public class UserLogDTO {
private String url;
private String detail;
}
(3)aop:
package com.listener.demo.aop;
import com.listener.demo.annotation.MyLog;
import com.listener.demo.dto.UserLogDTO;
import com.listener.demo.event.MyLogEvent;
import jakarta.annotation.Resource;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.Signature;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
@Aspect
@Component
public class LogAspect {
@Resource
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Around(value = "@annotation(com.listener.demo.annotation.MyLog)")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
MethodSignature methodSignature = (MethodSignature) signature;
Method targetMethod = methodSignature.getMethod();
MyLog annotation = targetMethod.getAnnotation(MyLog.class);
//非AuthVerify权限类注解,放开
if (annotation == null) {
return joinPoint.proceed();
}
//触发listener
UserLogDTO userLogDTO = UserLogDTO.builder()
.detail(annotation.detail())
.url(annotation.url())
.build();
applicationContext.publishEvent(new MyLogEvent(userLogDTO));
return joinPoint.proceed();
}
}
(4)监听:
package com.listener.demo.event;
import com.listener.demo.dto.UserLogDTO;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent;
public class MyLogEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
public MyLogEvent(UserLogDTO log) {
super(log);
}
public UserLogDTO getSource() {
return (UserLogDTO) super.getSource();
}
}
package com.listener.demo.listener;
import com.listener.demo.dto.UserLogDTO;
import com.listener.demo.event.MyLogEvent;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Slf4j
@Component
public class MyListener implements ApplicationListener<MyLogEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(MyLogEvent event) {
UserLogDTO source = event.getSource();
log.info("监听到:url={},detail={}",source.getUrl(),source.getDetail());
//其他处理,比如存储日志
}
}
(5)测试:访问localhost:4444/listenerDemo/user/add?userName=zhangsan&userAccount=zs
控制台打印























 979
979

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










