CompletableFuture 是 Java 8 引入的一个强大的异步编程工具类,它实现了 Future 和 CompletionStage 接口。相比传统的 Future,CompletableFuture 提供了更丰富的功能来处理异步编程。
CompletableFuture 主要方法分类
1. 创建 CompletableFuture 对象
// 创建一个已完成的 CompletableFuture
CompletableFuture<String> completedFuture = CompletableFuture.completedFuture("Hello");
// 创建一个空的 CompletableFuture
CompletableFuture<Void> future = new CompletableFuture<>();
// 使用 supplyAsync 异步执行任务并返回结果
CompletableFuture<String> asyncFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// 模拟耗时操作
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
return "Result";
});
// 使用 runAsync 异步执行任务(无返回值)
CompletableFuture<Void> runFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
// 执行一些操作但不返回结果
System.out.println("Running async task");
});
2. 转换和组合结果
// thenApply - 转换结果
CompletableFuture<String> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Hello");
CompletableFuture<String> future2 = future1.thenApply(s -> s + " World");
// thenCompose - 组合多个 CompletableFuture(类似 flatMap)
CompletableFuture<String> future3 = future1.thenCompose(s ->
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> s + " Composed"));
// thenCombine - 组合两个 CompletableFuture 的结果
CompletableFuture<String> future4 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Hello");
CompletableFuture<String> future5 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "World");
CompletableFuture<String> combined = future4.thenCombine(future5, (s1, s2) -> s1 + " " + s2);
3. 处理完成和异常情况
// thenAccept - 处理完成后的结果(无返回值)
CompletableFuture<String> future6 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Hello");
future6.thenAccept(System.out::println);
// exceptionally - 处理异常
CompletableFuture<String> future7 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
if (Math.random() > 0.5) {
throw new RuntimeException("Error occurred");
}
return "Success";
}).exceptionally(throwable -> {
System.out.println("Caught exception: " + throwable.getMessage());
return "Default Value";
});
// handle - 同时处理正常结果和异常
CompletableFuture<String> future8 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
if (Math.random() > 0.5) {
throw new RuntimeException("Error occurred");
}
return "Success";
}).handle((result, throwable) -> {
if (throwable != null) {
System.out.println("Caught exception: " + throwable.getMessage());
return "Default Value";
}
return result;
});
4. 多个 CompletableFuture 的组合
// allOf - 等待所有 CompletableFuture 完成
CompletableFuture<String> future9 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Task 1");
CompletableFuture<String> future10 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Task 2");
CompletableFuture<String> future11 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Task 3");
CompletableFuture<Void> allFutures = CompletableFuture.allOf(future9, future10, future11);
allFutures.thenRun(() -> System.out.println("All tasks completed"));
// anyOf - 等待任一 CompletableFuture 完成
CompletableFuture<Object> anyFuture = CompletableFuture.anyOf(future9, future10, future11);
anyFuture.thenAccept(result -> System.out.println("First completed task result: " + result));
5. 超时控制
// orTimeout - 设置超时时间
CompletableFuture<String> future12 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(5000); // 模拟耗时操作
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
return "Delayed Result";
}).orTimeout(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS); // 2秒后超时
// completeOnTimeout - 超时时提供默认值
CompletableFuture<String> future13 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
return "Delayed Result";
}).completeOnTimeout("Default Value", 2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
6. 手动完成 CompletableFuture
// complete - 手动完成 CompletableFuture
CompletableFuture<String> future14 = new CompletableFuture<>();
future14.complete("Manual Result");
// completeExceptionally - 手动完成并抛出异常
CompletableFuture<String> future15 = new CompletableFuture<>();
future15.completeExceptionally(new RuntimeException("Manual Exception"));
// cancel - 取消任务
CompletableFuture<String> future16 = new CompletableFuture<>();
future16.cancel(false);
实际应用示例
以下是一个在机器人导航系统中使用 CompletableFuture 的实际示例:
public class RobotNavigationExample {
public void navigateToTarget(int targetId) {
// 创建一个 CompletableFuture 来监听导航状态
CompletableFuture<TaskStatusEvent> navigationFuture = new CompletableFuture<>();
// 注册监听器
EventNotifierBus.getInstance()
.listen(EventNotifier.ROBOT_RUN_STATUS.getEventKey(String.valueOf(targetId)),
navigationFuture);
// 设置超时处理
navigationFuture
.orTimeout(120, TimeUnit.MINUTES)
.thenAccept(event -> {
// 处理导航完成事件
System.out.println("Navigation completed with status: " + event.getStatus());
})
.exceptionally(throwable -> {
// 处理超时或异常
System.err.println("Navigation failed or timed out: " + throwable.getMessage());
return null;
});
}
public CompletableFuture<String> performMultipleTasks() {
// 并行执行多个任务
CompletableFuture<String> task1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> fetchDataFromService1());
CompletableFuture<String> task2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> fetchDataFromService2());
CompletableFuture<String> task3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> fetchDataFromService3());
// 等待所有任务完成并组合结果
return CompletableFuture.allOf(task1, task2, task3)
.thenApply(v -> {
try {
return task1.get() + ", " + task2.get() + ", " + task3.get();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
});
}
private String fetchDataFromService1() {
// 模拟从服务1获取数据
return "Data from Service 1";
}
private String fetchDataFromService2() {
// 模拟从服务2获取数据
return "Data from Service 2";
}
private String fetchDataFromService3() {
// 模拟从服务3获取数据
return "Data from Service 3";
}
}
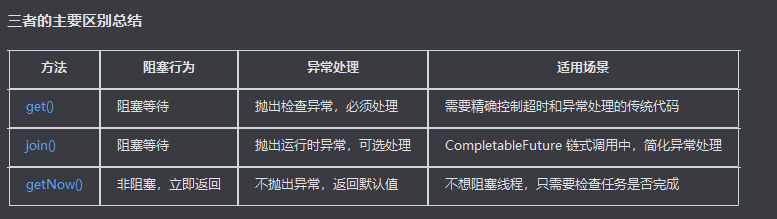
1. get() 方法
public T get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException
public T get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException
特点:
阻塞当前线程直到计算完成
如果任务已完成,立即返回结果
如果任务未完成,阻塞等待直到完成
可以设置超时时间(第二个重载版本)
抛出检查异常(InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException)
示例:
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000); // 模拟耗时操作
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
return "Result";
});
try {
// 阻塞等待结果
String result = future.get();
System.out.println("Result: " + result);
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 带超时的版本
try {
String result = future.get(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println("Result: " + result);
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException | TimeoutException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
2. join() 方法
public T join()
特点:
阻塞当前线程直到计算完成
如果任务已完成,立即返回结果
如果任务未完成,阻塞等待直到完成
不需要处理检查异常(只抛出未检查异常 RuntimeException)
当 CompletableFuture 内部发生异常时,会将异常包装成 CompletionException 抛出
示例:
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
return "Result";
});
// 不需要 try-catch 处理检查异常
String result = future.join();
System.out.println("Result: " + result);
// 处理异常情况
CompletableFuture<String> failedFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
throw new RuntimeException("Something went wrong");
});
try {
String result2 = failedFuture.join(); // 会抛出 CompletionException
} catch (CompletionException e) {
System.out.println("Caught exception: " + e.getCause().getMessage());
}
3. getNow(T valueIfAbsent) 方法
public T getNow(T valueIfAbsent)
特点:
非阻塞方法,立即返回
如果任务已完成,返回计算结果
如果任务未完成,立即返回传入的默认值 valueIfAbsent
不会抛出异常(即使任务内部有异常,也会返回默认值)
示例
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(5000); // 模拟长时间运行的任务
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
return "Result";
});
// 任务未完成,立即返回默认值
String result1 = future.getNow("Default Value");
System.out.println("Result1: " + result1); // 输出: Result1: Default Value
// 等待一段时间后再次检查
try {
Thread.sleep(6000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
// 任务已完成,返回实际结果
String result2 = future.getNow("Default Value");
System.out.println("Result2: " + result2); // 输出: Result2: Result
public class NavigationService {
public void waitForNavigationResult() {
CompletableFuture<TaskStatusEvent> future = new CompletableFuture<>();
// 注册监听器等操作...
// 使用 join() 等待结果(在实际代码中)
try {
TaskStatusEvent result = future.orTimeout(120, TimeUnit.MINUTES).join();
handleNavigationResult(result);
} catch (CompletionException e) {
System.err.println("Navigation failed: " + e.getCause().getMessage());
}
}
public void checkNavigationProgress() {
CompletableFuture<TaskStatusEvent> future = new CompletableFuture<>();
// 注册监听器等操作...
// 使用 getNow() 检查进度而不阻塞
TaskStatusEvent currentStatus = future.getNow(null);
if (currentStatus != null) {
System.out.println("Current navigation status: " + currentStatus.getStatus());
} else {
System.out.println("Navigation still in progress...");
}
}
public void waitForNavigationResultWithTraditionalApproach() {
CompletableFuture<TaskStatusEvent> future = new CompletableFuture<>();
// 注册监听器等操作...
// 使用 get() 等待结果
try {
TaskStatusEvent result = future.get(120, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
handleNavigationResult(result);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
System.err.println("Interrupted while waiting for navigation");
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
System.err.println("Navigation failed: " + e.getCause().getMessage());
} catch (TimeoutException e) {
System.err.println("Navigation timed out");
}
}
private void handleNavigationResult(TaskStatusEvent result) {
System.out.println("Navigation completed with status: " + result.getStatus());
}
}




















 315
315

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








