我们使用数组时,通常使用下标运算符([])来索引数组的特定元素,但我们常用的自定义类型(结构struct,类class,枚举enum等)却不像数组那样有内置的下标运算符,所以我们需要重载下标运算符[].
目录结构:
├── ~/cpp/ # C++ 项目主目录
│ ├── StudentGrade.h # StudentGrade类头文件
│ ├── GradeMap.h # GradeMap类实现
│ ├── GradeMap.cpp # GradeMap类实现
│ └── main.cpp # 主程序文件
└── README.md # 项目说明文档
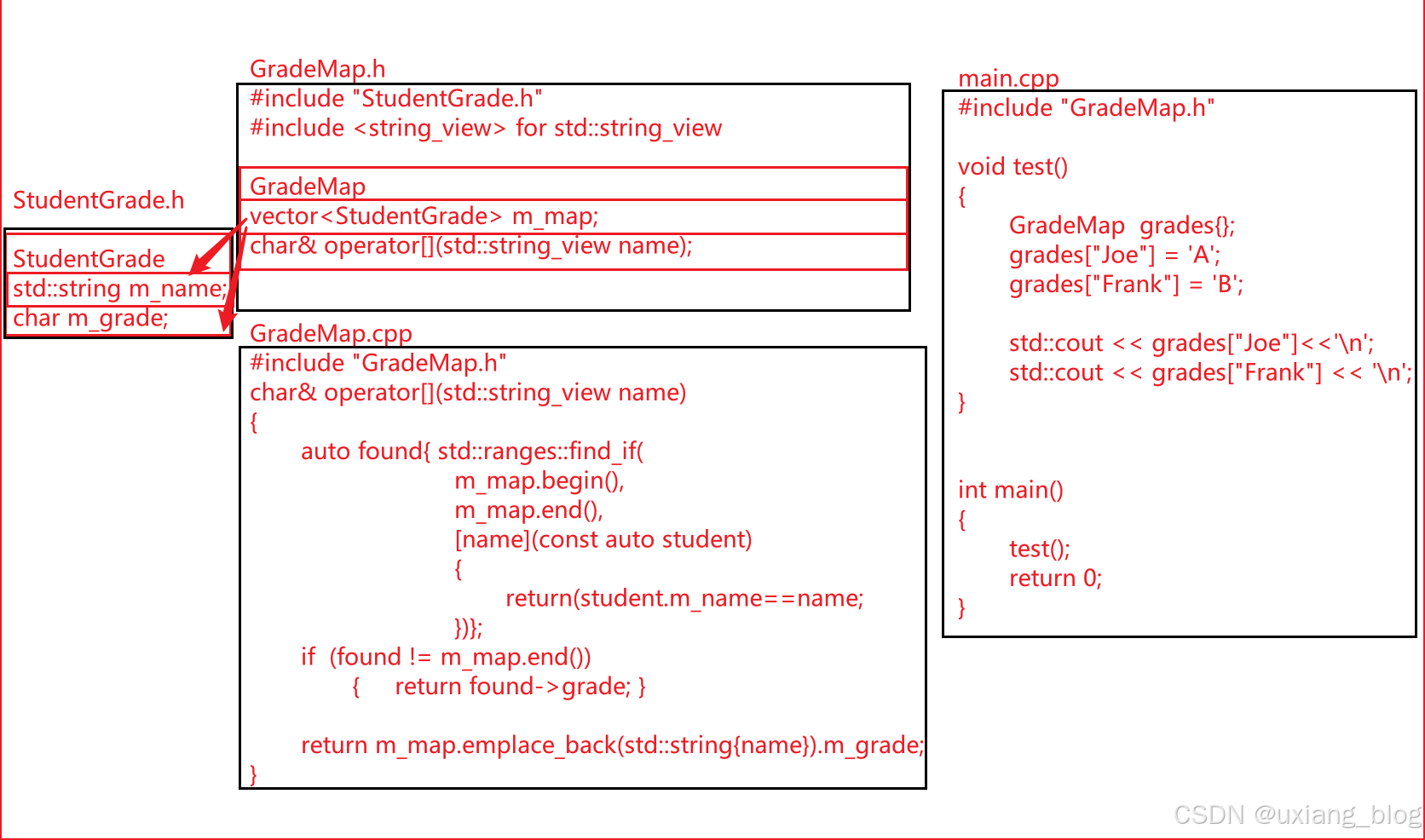
注意:这个为伪代码,用于梳理逻辑. lamda表达式处为const auto& student
实现目的
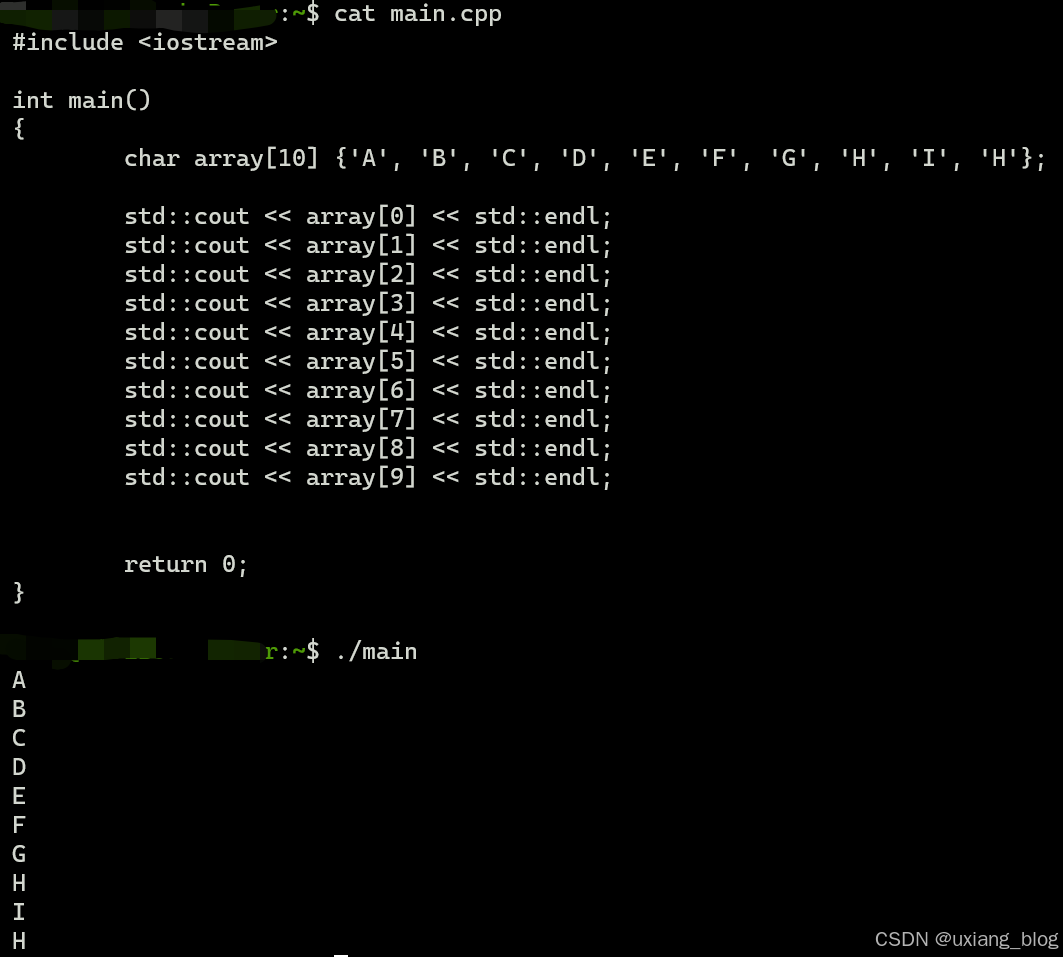
就像数组那样, 当我们访问array的下标arrary[i]时,就能得到它所对应的值.
源文件
StudentGrade.h
#ifndef STUDENTGRADE_H
#define STUDENTGRADE_H
#include <string>
struct StudentGrade
{
std::string m_name{};
char m_grade{};
}; #endif
GradeMap.h
#ifndef GRADEMAP_H
#define GRADEMAP_H
#include "StudentGrade.h"
#include <vector>
#include <string_view>
class GradeMap
{
private:
std::vector<StudentGrade> m_map{};
public:
GradeMap() = default;
GradeMap(const std::vector<StudentGrade>& map)
:m_map{ map }
{}
char& operator[](std::string_view name);
};
#endif
此处我用std::string_view name,而没有用std::string name,是因为std::string为了解决初始化(或复制)开销过大的问题,C++17 引入了std::string_view(位于 <string_view> 标头中)。它提供了对现有字符串(C 样式字符串、或其他)std::string_view的只读访问,而无需进行复制。
GradeMap.cpp
#include "GradeMap.h"
#include <string>
char& GradeMap::operator[](std::string_view name)
{
auto found{ std::ranges::find_if(m_map.begin(), m_map.end(),
[name](const auto& student){ // this is lambda that captures name from the surronding scope
return (student.m_name == name);// so we can use name here
})};
if (found != m_map.end())
{
return found->m_grade;
}
// emplace_back version (C++20 onward)
// StudentGrade is an aggregate and emplace_back only works with aggregates as of C++20
return m_map.emplace_back(std::string{name}).m_grade;
// push_back version (C++17 or older)
// m_map.push_back(StudentGrade{std::string{name}});
// return m_map.back().grade;
}
return m_map.emplace_back(std::string{name}).m_grade;
其作用是在vector容器的第二个元素,也就是SudentGrade::grade,添加一个元素.并没有用到obj.push_back()和obj.back()的组合,原因是push_back()的开销太大了,详情如下:
// push_back 的方式:
StudentGrade temp(name, ’ '); // 1. 创建临时对象
m_map.push_back(temp); // 2. 拷贝到容器
// 或者
m_map.push_back(StudentGrade(name, ’ ')); // 创建临时对象再移动
// emplace_back 的方式:
m_map.emplace_back(name, ’ '); // 直接在容器内存中构造,无临时对象
main.cpp
#include "StudentGrade.h"
#include "GradeMap.h"
#include <iostream>
void class_implement_test()
{
GradeMap grades{};
grades["Joe"] = 'A';
grades["Frank"] = 'B';
std::cout << "Joe has a grade of " << grades["Joe"] << '\n';
std::cout << "Frank has a grade of " << grades["Frank"] << '\n';
}
int main()
{
class_implement_test();
return 0;
}
功能演示






















 569
569

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








