数据结果课程设计(题目抄袭自某牛逼985高校)。
课程编号:0521733B 课程性质:必修
程序设计与算法训练课程设计报告

院 系: 计算机与信息系
班 级:
姓 名:
学 号:
指导教师:
选题名称: 二值图像数字水印技术实践
2019 年 1 月 20 日 至 2019 年 5 月 5 日
目录
一、 实验概述
1.1 课程设计题目
题目要求对给定的一种简单的二值图像的数字水印算法编程实现。
1.2 课程设计目的
对数字水印技术建立一定的认识,能建立位矩阵、位向量等 ADT,并能用这些 ADT 完成给定二值图像数字水印的嵌入和抽取。
1.3 系统主要内容与功能
1.3.1 设计内容
具体包括以下内容:
(1)图像的读取与保存,及相应的矩阵和向量的运算;
(2)二值图像水印算法的实现;
(3)软件的界面和接口设计,信号发送和槽位的设计;
(4)软件鲁棒性分析、算法鲁棒性分析和相关总结。
1.3.2 设计功能
(1)设计合理的数据结构,编程实现算法;
(2)给定测试图片,按照指定的 bmp 格式,保存于外存中。
1.3.3 系统类图
| watermark |
| QString array2byte(byteArray &array); QString array2str(byteArray &array); byteArray byte2Array(QString &number); byteArray decodeImg(uchar* buffer, uchar* dst, const int width, const int height, const int length); uchar* edgeExtract(uchar* buffer, const int width, const int height); byteArray encode(byteArray src, byteArray key); byteArray generateKey(const int length); byteArray img2Array(QString &dir); uchar* readBmp(const char *bmpName, int& bmpWidth, int& bmpHeight); byteArray str2Array(QString &str); uchar* substract(uchar* buffer1, uchar* buffer2, const int size); uchar* translation(uchar* buffer, const int width, const int height, int x_off, int y_off); uchar* watermarkImg(uchar* buffer, uchar* edge, const int size, byteArray code); bool savebmp(const char* filename, uchar* buffer, const u_int32_t height, const u_int32_t width); |
| BITMAPINFODEADER BMIH; BITMAPFILEHEADER BMFH; int biWidth; int biHeight; int biBitCount; int lineByte; RGBQUAD* pColorTable; |

| MainWindow |
| Q_OBJECT |
| explicit MainWindow(QWidget *parent = 0); ~MainWindow(); |
| void on_pushButtonBrowse_clicked(); void on_lineEdit_textChanged(const QString &arg1); void on_pushButtonEncode_clicked(); void on_pushButtonDecode_clicked(); |
| Ui::MainWindow *ui; QPixmap image;
byteArray key; uchar* dst; |
表 1.1 系统类图
1.3.4 属性和方法定义
| 类名 | 成员类型 | 类型 | 成员名 | 描述 |
| watermark | 属性 | BITMAPINFODEADER | BMIH | BMP图像信息头 |
| BITMAPFILEHEADER | BMFH | BMP图像文件头 | ||
| int | biWidth | BMP图像宽 | ||
| int | biHeight | BMP图像高 | ||
| int | biBitCount | 图像类型,每像素位数 | ||
| int | lineByte | 图像数据每行字节数 | ||
| RGBQUAD* | pColorTable | BMP图像调色板信息 | ||
| 方法 | QString | array2byte | 秘钥序列转换为二进制信息 | |
| QString | array2str | 秘钥序列转换为字符串 | ||
| byteArray | byte2Array | 二进制信息转秘钥序列 | ||
| byteArray | decodeImg | 使用水印秘钥编码原图 | ||
| uchar* | edgeExtract | 获得从buffer提取到的边缘图像,用作添加水印位置的参考 | ||
| byteArray | encode | 使用秘钥序列加密二进制 | ||
| byteArray | generateKey | 生成秘钥序列 | ||
| uchar* | readBmp | 读取BMP图片 | ||
| byteArray | str2Array | 字符串转换为秘钥序列 | ||
| uchar* | substract | 获得buffer1和buffer2相减得到的结果 | ||
| uchar* | translation | 获得原buffer图像右移x_off个单位,下移y_off个单位后得到的图像 | ||
| uchar* | watermarkImg | 由边缘图像和原图获得水印编码后的图像 | ||
| bool | savebmp | 保存编码水印信息的图像 | ||
| MainWindow | 属性 | Ui::MainWindow* | ui | 维护图形界面 |
| QPixmap | image | 维护读入的BMP图像 | ||
| byteArray | key | 秘钥序列 | ||
| uchar* | dst' | 维护编码水印的目标图像 | ||
| 方法 | 无 | MainWindow(QWidget *parent = 0) | 构造函数,初始化界面 | |
| 无 | ~MainWindow() | 析构函数,释放内存(Ui) | ||
| 槽位 | void | on_pushButtonBrowse_clicked() | 浏览、选择图像 | |
| void | on_lineEdit_textChanged(const QString &arg1) | 修改水印信息 | ||
| void | on_pushButtonEncode_clicked() | 水印信息编码BMP图像 | ||
| void | on_pushButtonDecode_clicked() | 解码水印BMP图像,获取水印信息 |
表 1.2 属性和方法定义
1.3.5 实验环境与工具
(1)操作系统:Ubuntu 16.04 LTS;
(2)开发工具:Qt、Qt Creator;
(3)实现语言:C++。
二、 实验原理
2.1 图像水印技术简述
随着互联网和信息技术的快速发展,近年来数字内容的未授权获取,传输,操纵和分发的问题变得越来越严重。信息安全研究引
起了人们的广泛关注。除了一般采用的数字加密算法之外,近年来用于信息安全的影像视觉算法包括光学图像加密、认证和水印算
法被广泛地研究和应用起来。影像视觉信息安全算法通常拥有并行高速处理和多维能力的优势。信息隐藏技术,即图像水印技术,也
称隐写技术是一种隐蔽性地改变载波信号以嵌入隐藏消息,即水印信号的技术。可以对各种各样类别的信号执行信息隐藏,其中包括
但不限于:音频信号、图像信号和视频信号。信息隐藏技术(图像水印技术)允许将特定的信息加入到需要保护的媒体信息中,加入的
信息一般为具有特定意义的内容,如版权所有者信息、发行标志、特定代码等。而图像水印技术也因而成为了数字图像处理专业当
下或未来重要的研究领域,在知识产权的保护等方面有着广泛的应用前景。为了确保大规模在线分发的多媒体内容的版权和知识产
权,我们需要通过有效的保护来控制分发和传播,控制来自盗版用户或未经授权普通用户的恶意操纵和恶意拷贝传播。
为了提高效率,水印需要良好的隐蔽性,并且拥有嵌入高容量和有效载荷,能够在确保有效载荷的安全传输的同时,对最常见的图像处理(恶意或非恶意)进行鲁棒性处理。此外水印技术还有以下的特点:
(1)水印后的主图像不应存在显著地信息损坏和分辨率降低;
(2)水印应具有在主图像中良好的隐蔽性,即不可见性,一般用图像的峰值信噪比 (PSNR) 与结构相似形(SSIM)来描述;
(3)水印应具有良好的鲁棒性,不易从主图像中被损坏。水印应可以承受不同类型的信息损坏打击,例如 JPEG 压缩、裁剪、旋
转、缩放、噪声、滤波运算和模糊运算。应该特别指出,该特点仅适用于一部分鲁棒性极好的水印算法中;
(4)未经授权的用户/盗版用户应很难非法访问到该水印信息。
2.2 图像处理技术简述
在图像水印技术实现时,需要大量运用到图像处理知识和技术。数字图像处理(Digital Image Processing)是通过计算机对图像
进行去除噪声、增强、复原、分割、提取特征等处理的方法和技术。数字图像处理(Digital Image Processing)又称为计算机图像
处理,它是指将图像信号转换成数字信号并利用计算机对其进行处理的过程。数字图像处理的产生和迅速发展主要受三个因素的影
响:一是计算机的发展;二是数学的发展(特别是离散数学理论的创立和完善);三是广泛的农牧业、林业、环境、军事、工业和医学等
方面的应用需求的增长。
在图像水印技术中,本着不损坏原有图像质量的原则,该算法需要对图像快速的读写能力、对分块图像稳定和鲁棒的运算能力,
以及优秀的边缘提取能力。
2.3 Qt 及 Qt Creator
Qt 是一个跨平台的 C++图形用户界面应用程序框架。它为应用程序开发者提供建立艺术级图形用户界面所需的所有功能。
它是完全面向对象的,很容易扩展,并且允许真正的组件编程。
作为一个优秀的 C++框架,由于其优秀的信号与槽机制,Qt 被广泛地应用于软件编写中。本次课程设计将采用 Qt 和 Qt
Creator 作为程序界面的编写工具。
2.4 相关算法简介
数字图像水印算法是将一段信息附加在图像上的算法,其中被附加信息的图像被称为主机图像(host image),简称主图像。根据
水印算法的鲁棒性,水印算法可以分为鲁棒/稳健的水印算法(robust watermarking)和脆弱的水印算法(fragilewatermarking),其中绝
大多数的数字水印算法都属于前者。如上文所提到,鲁棒的水印在主图像受到攻击和扭曲时,仍能保持完整。由于鲁棒的水印很难从
主机图像中移除,因此常常用于保护版权;另一方面,脆弱的水印一般仅用于验证,即主机图像的完整性检查。完整的脆弱水印表示主
机图像处于其原始形式,并没有收到编辑、损坏或更改。在本次课程设计中,为了简洁起见,我们采用脆弱的水印算法。
经典的数字图像水印算法构建的系统包括双随机相位编码(DRPE)系统,离轴全息系统,相移全息系统,优化的仅相位掩模结构,
联合变换相关器(JTC),重影成像系统和 ptychography 系统,等等。它们在各自的领域都具有相当不错的效果。在本次课程设计中,
为了兼顾效率和效果,我们采用一种简单的二值图像数字水印算法,其基本思路如下:由于水印算法需要改变主机图像的像素值,从而
一定程度上改变主机图像的信息。而被改变像素值,因而保存着水印信息的像素点被称为隐藏点,它决定了隐藏了怎样的信息。而简
单的处理方法容易导致图像质量的下降,例如,在全白的图像块中插入一个黑色的噪声点。另一方面,隐藏点也应避免选取在图像中
的细线区域、直线边的中间像素、孤立像素等图像信息熵较大的点。由此,二值图像的数字水印嵌入算法的关键是隐藏点的选取,以
下是隐藏点的选取规则:
二值图像数据应隐藏域图像中黑/白色区域的边界上,但上述诸如细线区域等仍不适于隐藏数据的边界。因此隐藏点应具有以
下的特点:它是边界像素,并且不同时是左边界和右边界/上边界和下边界,以确保避免将信息隐藏在细线区域等。这需要一个优秀的
边界提取算法。
在隐藏点被确定后,水印信息应转换为二进制序列,并保存在隐藏点中。同理,因此所有可被转换为二进制序列的诸如文字信
号、音频信号、图像信号和视频信号,并可进行反转换的信号都可以作为该算法的水印信息。
在本次课程设计中,我们简单地以字符串信息和二进制序列信息为例,来保存相关的水印。值得一提的是,为了保证水印信息更
好地隐蔽,水印信息被加入前,需要用一段密钥进行加密,并在提取时,使用该密钥进行解密。
2.5 技术流程
本次课程设计采用的主要框架包括 C++与 Qt 等,其中 C++作为程序实现语言,Qt 作为软件实现框架,使用 C++中的指针工具作
为图像处理工具,BMP 图像的读写采用文件头信息解析模式。
本次编程是在 Ubuntu 16.04 LTS 上进行的,在该环境下,常用的图像解码工具包括 Qt 的 QPixMap 模块以及 OpenCV 库。其
中使用 C++进行 bmp 文件解码过程较为复杂,需要鲁棒的文件读写设计以及接口设计,同时,对于不同类型的文件需要不同的解码方
式,不广泛适用于.png,.img,.jpg,.giff 等等图像格式的使用,但减少了第三方库的利用。而 QPixMap 框架的引入对于文件数据对象的
空间开辟和释放过于频繁,降低了程序的效率,并需要引入标准模板库框架。作为对比,OpenCV 库拥有极高的鲁棒性、延展性和高
效性,但需要引入第三方库,软件打包较为复杂。在“尽量引入较少的第三方库”的原则下,我们采用了纯C++语言,根据 BMP 图像的特
点设计合理的数据结构进行编码、存储图像,以提高本软件的实用性。
本次课程设计的技术流程如下:首先设计并实现边缘信息提取的算法edgeExtract()函数,以确定隐藏点,再设计数字隐藏的算法
encodeImage()函数。在软件流程中,首先点击“浏览”按钮,选取二值图像,再输入需要加入的水印,最后点击“编码”按钮,则生成并显示
了附有水印信息的图像。该图像被保存在.pro 的 Qt 项目文件同名文件夹下,被命名为 encode.bmp。此外,对于已编码的
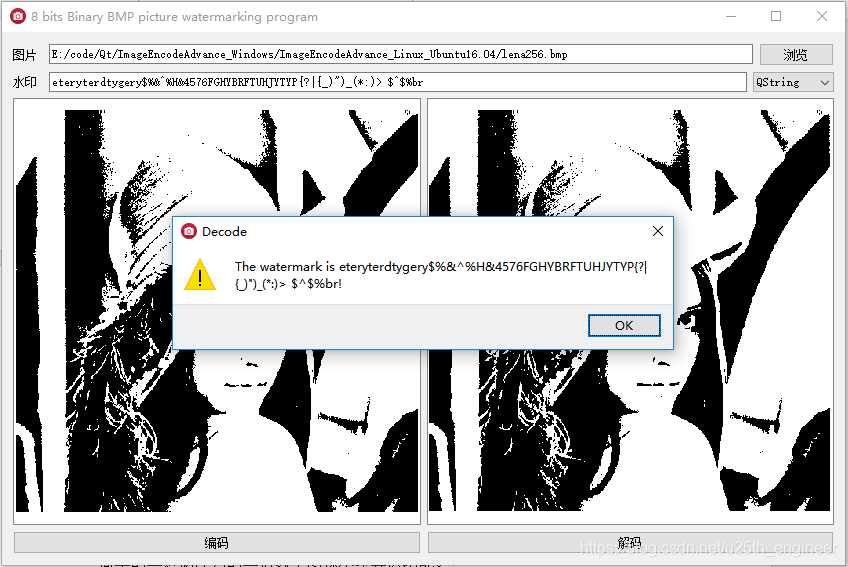
encode.bmp,点击“解码”按钮,会以对话框形式弹出被解码出的水印信息。
三、 实验结果
本次课程设计生成的软件结果如下:
软件打开后的界面如下,为避免用户每次打开软件后都需要输入水印,过于麻烦,本软件内置了水印二进制序列,如图3.1所示。
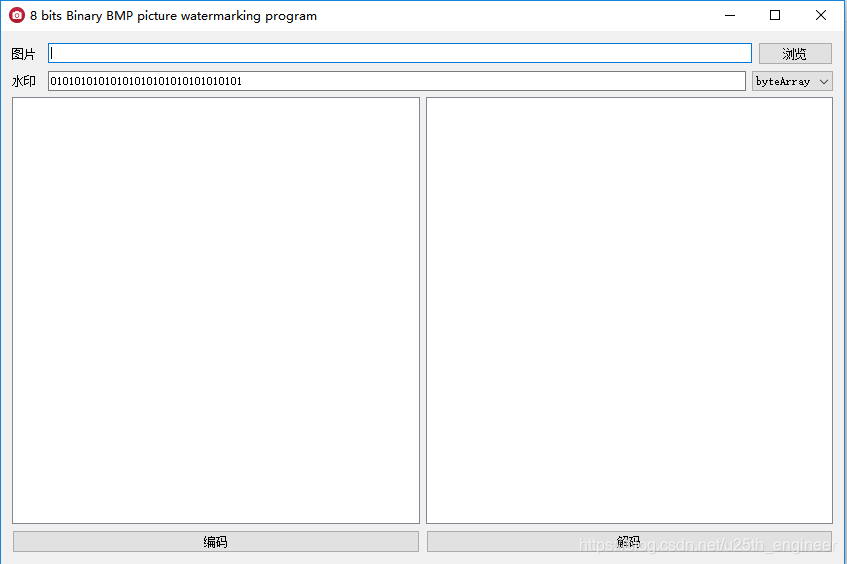
输入二值图像后,会被展示在软件中,如图3.2所示。
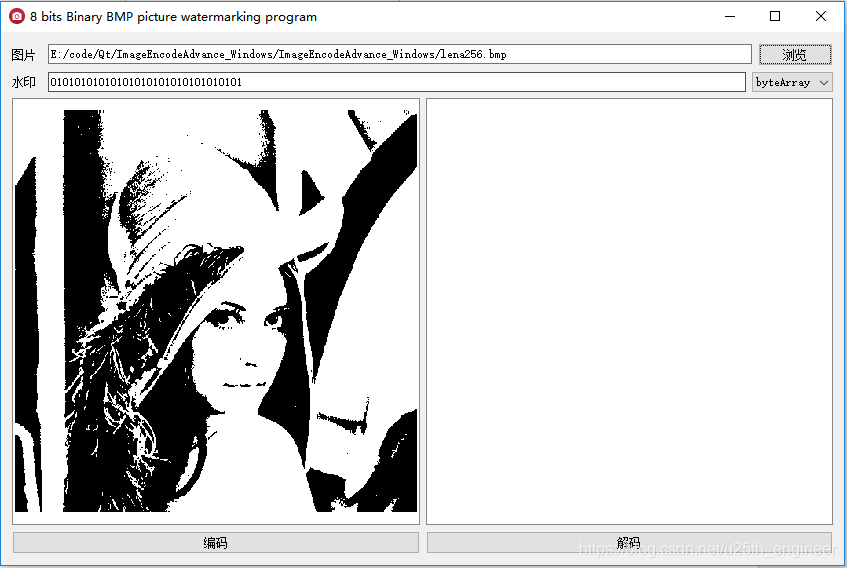
点击“编码”按钮后,生成编码图像,如图3.3所示。
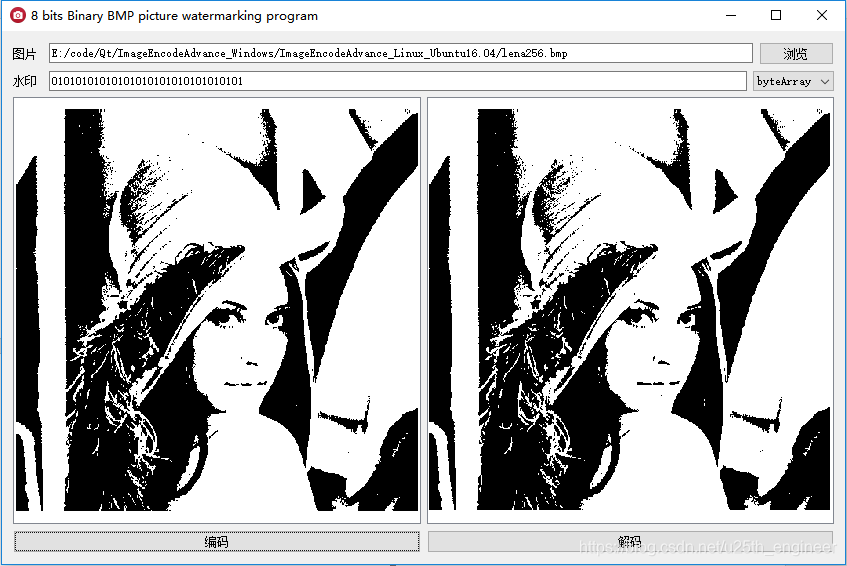
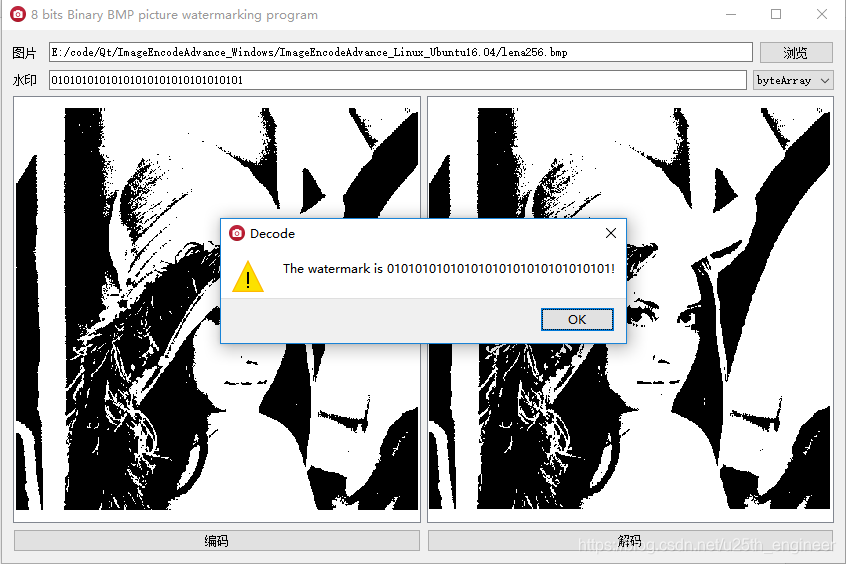
点击“解码”按钮,弹出水印信息,如图3.4所示。
本程序也支持字符串的水印编码,将水印附带的 comboBox 选取为“QString”,然后编码并解码后的结果,如图3.5所示。
四、 算法分析
本程序经过第三方测试发现并无 bug 存在,鲁棒性优秀,可以完整的实现简单的二进制序列的二值数字图像水印算法功能。
在第二章节中提到,优秀的水印算法拥有上述的四个特点: a.不改变原图信息;b.隐蔽性;c.鲁棒性;d.不可访问性。本报告将从这四个
角度评判该算法的性能。
1. 由第三章节的内容易见,该算法具有从肉眼中几乎无法分辨与原图像的区别,同时如表 3 所示,通过计算原图与被水印编码图
的峰值信噪比与结构相似比,两者均处于合理的置信区间,因而完美地符合了不改变原图信息和隐蔽性的原则;
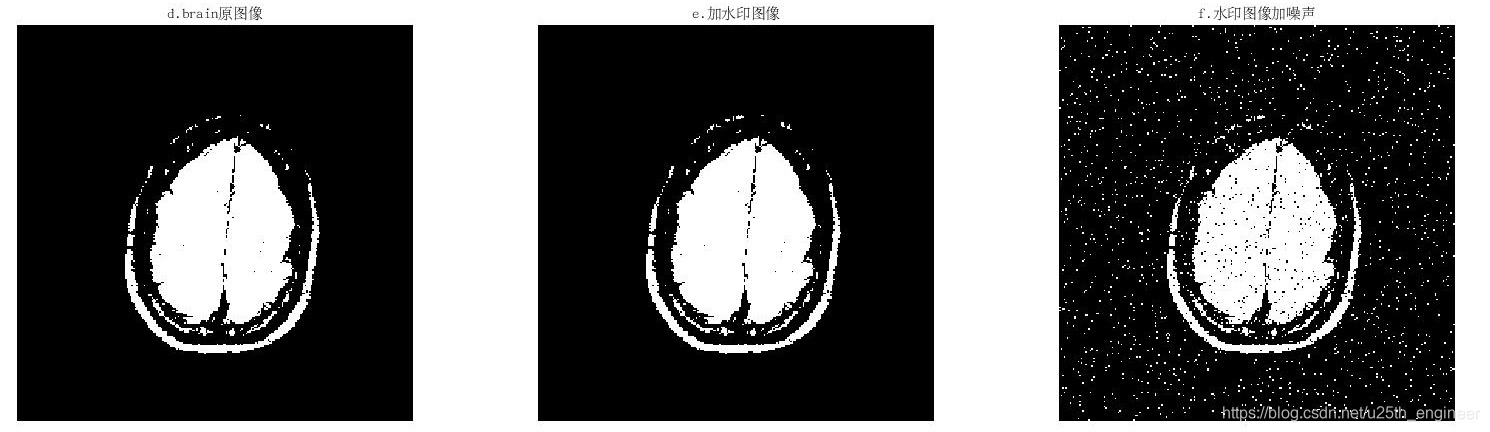
2. 该算法经过轻微地噪声扰动后就无法保存水印信息,如图 6 所示,因此鲁棒性极低,然而这符合脆弱的水印算法的特点,可以用
于验证图像的完整性;
3. 从 encode.bmp 和原图之间的差分影像可以轻易地获得加密后的二进制序列。但是由于有密钥的存在,无密钥的非授权用
户和盗版用户无法访问到原始水印的信息,具有不可访问性。关于不可访问性,在附录中有所展示。
| 对比 属性 | 原图与水印图 | 原图与加噪声水印图 | ||||
| Lena256 | brain | hippo | Lena256 | brain | hippo | |
| 峰值信噪比(PSNR) | 39.6375 | 27.5873 | 44.7908 | 13.7145 | 7.6078 | 13.621 |
| 结构相似性(SSIM) | 0.9999 | 0.9963 | 0.9998 | 0.4152 | 0.3125 | 0.3331 |
| 表 4.1 峰值信噪比与结构相似性实验数据 | ||||||
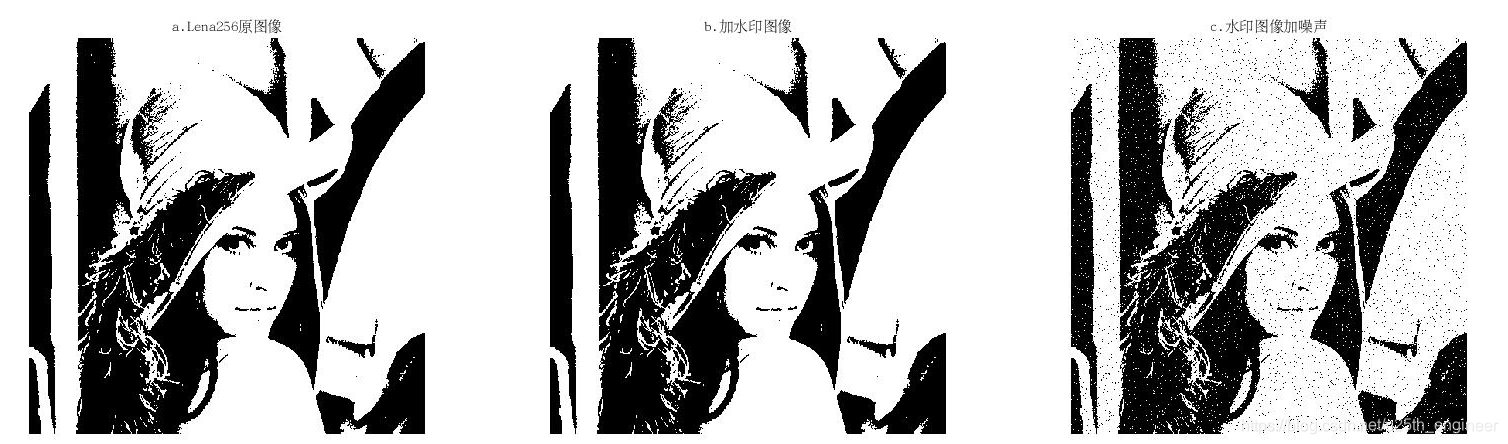


综上所述,本算法在效率极高的同时,完美地满足了优秀的脆弱水印算法的四个特点,同时保证了效果和效率。
五、 总结
在本次课程设计中,按照题目要求与提示,针对给定的二值图像数字水印算法完成了编程实现、算法分析与相关内容的简单介
绍。先将水印信息转换为二进制序列,然后,算法利用密钥对序列进行转换,从而降低了第三方获取水印的可能性。通过查阅有关资
料,对数字水印建立了一定的认识,并构建了位矩阵、位相量等 ADT。综述,本次课程设计完成了既定的各个要求。
附录(源代码与其他)
源代码
头文件 additional_utility.h:
#ifndef ADDDITIONAL_UTILITY_H
#define ADDDITIONAL_UTILITY_H
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
#include<QtCore>
#include<QMessageBox>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#pragma pack(2)// In the Linux environment
using byteArray = QVector<bool>;
//******************************************top******************************************************
//In the Linux environment
typedef struct BITMAPFILEHEADER
{
u_int16_t bfType;
u_int32_t bfSize;
u_int16_t bfReserved1;
u_int16_t bfReserved2;
u_int32_t bfOffBits;
}BITMAPFILEHEADER;
typedef struct BITMAPINFOHEADER
{
u_int32_t biSize;
u_int32_t biWidth;
u_int32_t biHeight;
u_int16_t biPlanes;
u_int16_t biBitCount;
u_int32_t biCompression;
u_int32_t biSizeImage;
u_int32_t biXPelsPerMeter;
u_int32_t biYPelsPerMeter;
u_int32_t biClrUsed;
u_int32_t biClrImportant;
struct BITMAPINFOHEADER &operator=( struct BITMAPINFOHEADER &BMIH )
{
biSize = BMIH.biSize;
biWidth = BMIH.biWidth;
biHeight = BMIH.biHeight;
biPlanes = BMIH.biPlanes;
biClrUsed = BMIH.biClrUsed;
biSizeImage = BMIH.biSizeImage;
biCompression = BMIH.biCompression;
biClrImportant = BMIH.biClrImportant;
biXPelsPerMeter = BMIH.biXPelsPerMeter;
biYPelsPerMeter = BMIH.biYPelsPerMeter;
//qDebug() << "214235423" << endl;
return *this;
}
}BITMAPINFODEADER;
typedef unsigned char BYTE;
typedef unsigned short WORD;
typedef unsigned int DWORD;
typedef long LONG;
typedef struct tagRGBQUAD
{
BYTE rgbBlue;
BYTE rgbGreen;
BYTE rgbRed;
BYTE rgbReserved;
}RGBQUAD;
typedef struct tagIMAGEDATA
{
BYTE blue;
BYTE green;//cancel the annotation by DFZ
BYTE red;//cancel the annotation by DFZ
}IMAGEDATA;
//********************************************bottom*******************************************
#endif // ADDDITIONAL_UTILITY_H
头文件 bmputil.h:
#ifndef BMPUTIL_H
#define BMPUTIL_H
#include "addditional_utility.h"
class watermark
{
public:
QString array2byte(byteArray &array);
QString array2str(byteArray &array);
byteArray byte2Array(QString &number);
byteArray decodeImg(uchar* buffer, uchar* dst, const int width, const int height, const int length);
uchar* edgeExtract(uchar* buffer, const int width, const int height);
byteArray encode(byteArray src, byteArray key);
byteArray generateKey(const int length);
byteArray img2Array(QString &dir);
uchar* readBmp(const char *bmpName, int& bmpWidth, int& bmpHeight);
byteArray str2Array(QString &str);
uchar* substract(uchar* buffer1, uchar* buffer2, const int size);
uchar* translation(uchar* buffer, const int width, const int height, int x_off, int y_off);
uchar* watermarkImg(uchar* buffer, uchar* edge, const int size, byteArray code);
bool savebmp(const char* filename, uchar* buffer, const u_int32_t height, const u_int32_t width);
private:
BITMAPINFODEADER BMIH;
BITMAPFILEHEADER BMFH;
int biWidth;
int biHeight;
int biBitCount;
int lineByte;
RGBQUAD* pColorTable;
protected:
};
#endif // BMPUTIL_H
头文件 mainwindow.h:
#ifndef MAINWINDOW_H
#define MAINWINDOW_H
#include <QMainWindow>
#include <QPixmap>
namespace Ui
{
class MainWindow;
}
using byteArray = QVector<bool>;
class MainWindow : public QMainWindow
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
explicit MainWindow(QWidget *parent = 0);
~MainWindow();
private slots:
void on_pushButtonBrowse_clicked();
void on_lineEdit_textChanged(const QString &arg1);
void on_pushButtonEncode_clicked();
void on_pushButtonDecode_clicked();
private:
Ui::MainWindow *ui;
QPixmap image;
byteArray key;
uchar* dst;
};
#endif // MAINWINDOW_H
源文件 additional_utility.cpp:
#include "addditional_utility.h"
源文件 bmputil.cpp:
#include "bmputil.h"
uchar* watermark::readBmp(const char *bmpName, int& bmpWidth, int& bmpHeight)
{
FILE *fp = fopen(bmpName, "rb");
if(fp == Q_NULLPTR)
{
QMessageBox::warning(Q_NULLPTR, "Error", "Error in Open File!");
return Q_NULLPTR;
}
// skip the fileheader
fseek(fp, sizeof(BITMAPFILEHEADER), SEEK_CUR);
// read the infoheader
//BITMAPINFOHEADER* head = new BITMAPINFOHEADER;
watermark WT;
//infohead = &(WT.BMIH);
BITMAPINFODEADER infohead = WT.BMIH;
fread(&infohead,sizeof(BITMAPINFOHEADER),1,fp);
//fread(infoHead, sizeof(BITMAPINFOHEADER), 1, fp);
bmpWidth = infohead.biWidth;
bmpHeight = infohead.biHeight;
biBitCount = infohead.biBitCount;
lineByte = (bmpWidth*biBitCount/8+3)/4*4;
//qDebug() << infohead.biSize << endl;
//qDebug() << infohead.biWidth << endl;
//qDebug() << infohead.biHeight << endl;
//qDebug() << infohead.biBitCount << endl;
if (biBitCount == 8)
{
pColorTable = new RGBQUAD[256];
fread(pColorTable, sizeof(RGBQUAD), 256, fp);
uchar* pBmpBuf = new uchar[ bmpWidth * bmpHeight ];
fread(pBmpBuf, sizeof(uchar), bmpWidth * bmpHeight, fp);
fclose(fp);
uchar* buffer = new uchar[bmpWidth * bmpHeight];
for(int i = 0; i < bmpHeight; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j<bmpWidth; j++)
{
if(pBmpBuf[(bmpHeight- i - 1)*bmpWidth + j] != 255 && pBmpBuf[(bmpHeight- i - 1)*bmpWidth + j] != 0)
{
QMessageBox::warning(Q_NULLPTR, "Error", "This is not a binary image!");
return Q_NULLPTR;
}
buffer[i*bmpWidth + j] = pBmpBuf[(bmpHeight- i - 1)*bmpWidth + j];
}
}
return buffer;
}
else
{
QMessageBox::warning(Q_NULLPTR, "Error", "Our program can only deal with 8-bit image!");
return Q_NULLPTR;
}
}
bool watermark::savebmp(const char* filename, uchar* buffer, const u_int32_t height, const u_int32_t width)
{
//RGBQUAD *pColorTable = new RGBQUAD;
if(buffer == Q_NULLPTR)
{
QMessageBox::warning(Q_NULLPTR, "Error", "The Buffer is nullptr!");
return false;
}
uchar* data = new uchar[height*width];
for(int i = 0; i < height; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j<width; j++)
{
data[i*width + j] = buffer[(height- i - 1)*width + j];
}
}
int colorTableSize = 1024;
BITMAPFILEHEADER fileHeader;
fileHeader.bfType = 0x4D42;
fileHeader.bfReserved1 = 0;
fileHeader.bfReserved2 = 0;
fileHeader.bfSize = sizeof(BITMAPFILEHEADER) + sizeof(BITMAPINFOHEADER) + colorTableSize + height*width;
fileHeader.bfOffBits = sizeof(BITMAPFILEHEADER) + sizeof(BITMAPINFOHEADER) + colorTableSize;
BITMAPINFOHEADER bitmapHeader = { 0 };
bitmapHeader.biSize = sizeof(BITMAPINFOHEADER);
//qDebug() << "In bool watermark::savebmp(const char* filename, uchar* buffer, const u_int32_t height, const u_int32_t width), height = " << height << endl;
//qDebug() << "In bool watermark::savebmp(const char* filename, uchar* buffer, const u_int32_t height, const u_int32_t width), width = " << width << endl;
//qDebug() << sizeof(BITMAPINFOHEADER) << endl;
bitmapHeader.biHeight = height;
bitmapHeader.biWidth = width;
bitmapHeader.biPlanes = 1;
bitmapHeader.biBitCount = 8;
bitmapHeader.biSizeImage = height*width;
bitmapHeader.biCompression = 0;
FILE *fp = fopen(filename, "wb");
//qDebug() << "OK! line 154 " << endl;
if(fp == Q_NULLPTR)
{
QMessageBox::warning(Q_NULLPTR, "Error", "Error in Save File!");
//qDebug() << "OK! line 156 " << endl;
return false;
}
else
{
fwrite(&fileHeader, sizeof(BITMAPFILEHEADER), 1, fp);
//qDebug() << "OK! line 162 " << endl;
fwrite(&bitmapHeader, sizeof(BITMAPINFOHEADER), 1, fp);
//qDebug() << "OK! line 164 " << endl;
//qDebug() << "pColorTable address = " << pColorTable << endl;
fwrite(pColorTable, sizeof(RGBQUAD), 256, fp);
delete pColorTable;
//qDebug() << "OK! line 168 " << endl;
fwrite(data, height*width, 1, fp);
delete []data;
//qDebug() << "OK! line 171 " << endl;
fclose(fp);
//qDebug() << "OK! line 173 " << endl;
return true;
}
}
// generate keyArray
byteArray watermark::generateKey(const int length)
{
byteArray res;
for(int i = 0; i<length; i++)
{
if(double(qrand())/RAND_MAX > 0.5)
{
res.append(true);
}
else
{
res.append(false);
}
}
return res;
}
//获得原buffer图像右移x_off个单位,下移y_off个单位后得到的图像
uchar* watermark::translation(uchar* buffer, const int width, const int height, int x_off, int y_off)
{
uchar* res = new uchar[width*height];
for(int i = 0; i<height; i++)
{
for(int j = 0;j<width; j++)
{
if(i-x_off < 0 || j-y_off < 0)
{
res[i*width + j] = 0;
}
else
{
res[i*width + j] = buffer[(i - x_off)*width + (j - y_off)];
}
}
}
return res;
}
// 获得buffer1和buffer2相减得到的结果
uchar* watermark::substract(uchar* buffer1, uchar* buffer2, const int size)
{
uchar* res = new uchar[size];
for(int i = 0; i<size; i++)
{
res[i] = buffer1[i] > buffer2[i] ? buffer1[i] - buffer2[i] : 0;
}
return res;
}
// 获得从buffer提取到的边缘图像,用作添加水印位置的参考
uchar* watermark::edgeExtract(uchar* buffer, const int width, const int height)
{
uchar* BL = substract(translation(buffer, width, height, 1, 0), buffer, width*height);
uchar* BR = substract(translation(buffer, width, height, -1, 0), buffer, width*height);
uchar* BT = substract(translation(buffer, width, height, 0, 1), buffer, width*height);
uchar* BB = substract(translation(buffer, width, height, 0, -1), buffer, width*height);
uchar* B1 = new uchar[height*width];
for(int i = 0; i<height*width; i++)
{
BL[i] = BL[i]/255;
BR[i] = BR[i]/255;
BT[i] = BT[i]/255;
BB[i] = BB[i]/255;
int lr = BL[i] + BR[i];
int tb = BT[i] + BB[i];
int b = lr + tb;
B1[i] = 0;
if((b == 1) ||(b == 2 && lr != 2 && tb != 2))
{
B1[i] = 1;
}
}
uchar* res = new uchar[height*width];
for(int i = 0; i<height; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j<width; j++)
{
res[i*width + j] = B1[i*width + j] * 255;
if(B1[i*width + j])
{
int sum1 = 0, sum2 = 0;
for(int a = -1; a<2; a++)
{
if(a + i <0 || a+ i >= height)
{
continue;
}
for(int b = -1; b<2; b++)
{
if(b +j <0 || b+j>=width)
{
continue;
}
sum1 += buffer[(a + i) *width + (b + j)]/255;
sum2 += B1[(a + i) *width + (b + j)];
}
}
if(sum1 == sum2)
{
res[i*width + j] = 0;
}
}
}
}
return res;
}
// 由边缘图像和原图获得水印编码后的图像
uchar* watermark::watermarkImg(uchar* buffer, uchar* edge, const int size, byteArray code)
{
uchar* res = new uchar[size];
for(int i = 0; i<size; i++)
{
res[i] = buffer[i];
}
int count = 0;
for(int i = 0; i<size; i++)
{
if(edge[i]==255)
{
res[i] = 255*code[count++];
if(count == code.length())
{
return res;
}
}
}
QMessageBox::warning(Q_NULLPTR, "Error", "The image is too small to contain such a code!");
return Q_NULLPTR;
}
byteArray watermark::decodeImg(uchar* buffer, uchar* dst, const int width, const int height, const int length)
{
uchar* edge = edgeExtract(buffer, width, height);
byteArray res;
for(int i = 0; i<width*height; i++)
{
if(edge[i] == 255)
{
res.append(dst[i]);
if(length == res.length())
{
return res;
}
}
}
QMessageBox::warning(Q_NULLPTR, "Error", "The image is too small to contain such a code!");
return byteArray();
}
byteArray watermark::byte2Array(QString &number)
{
byteArray res;
for(auto byte : number)
{
if(byte == '1')
{
res.append(true);
}
else if(byte == '0')
{
res.append(false);
}
else
{
QMessageBox::warning(nullptr, "Error", "Error in byte2Array: Charater else than 0 and 1!\nThe application will be forced to abort.");
throw EXIT_FAILURE;
}
}
return res;
}
byteArray watermark::str2Array(QString &str)
{
QString num;
for(auto character : str)
{
int i = character.unicode();
QString ele = QString::number(i, 2);
for(int j = 0;j<8-ele.length();j++)
{
num += '0';
}
num += QString::number(i, 2);
}
qDebug()<<num;
return byte2Array(num);
}
byteArray watermark::img2Array(QString &dir)
{
Q_UNUSED(dir);
QString str = "01010101010101010101010101010101";
//return byte2Array(QString("01010101010101010101010101010101"));
return byte2Array(str);
}
QString watermark::array2byte(byteArray &array)
{
QString res;
for(auto ele:array)
{
if(ele)
{
res.append('1');
}
else
{
res.append('0');
}
}
return res;
}
QString watermark::array2str(byteArray &array)
{
QString res;
for(int i = 0 ; i<array.length(); i+=8)
{
int num = array[i + 7] + array[i + 6]*2 + array[i + 5]*4 + array[i + 4]*8 +
array[i + 3]*16 + array[i + 2]*32 + array[i + 1]*64 + array[i + 0]*128;
res.append(char(num));
}
return res;
}
// encode byteArray with keyArray
byteArray watermark::encode(byteArray src, byteArray key)
{
byteArray res;
if(src.length() != key.length())
{
qDebug()<< "The length of keyArray and srcArray doesn't match! ";
return byteArray();
}
for(int i = 0; i < src.length(); i++)
{
res.append(src[i] ^ key[i]);
}
return res;
}
/*
BITMAPINFODEADER &watermark::operator=(BITMAPINFODEADER& BMIH)
{
if( &((*this).BMIH) == &BMIH )
return (*this).BMIH;
BMIH.biSize = (*this).BMIH.biSize;
BMIH.biWidth = (*this).BMIH.biWidth;
BMIH.biHeight = (*this).BMIH.biHeight;
BMIH.biPlanes = (*this).BMIH.biPlanes;
BMIH.biClrUsed = (*this).BMIH.biClrUsed;
BMIH.biSizeImage = (*this).BMIH.biSizeImage;
BMIH.biCompression = (*this).BMIH.biCompression;
BMIH.biClrImportant = (*this).BMIH.biClrImportant;
BMIH.biXPelsPerMeter = (*this).BMIH.biXPelsPerMeter;
BMIH.biYPelsPerMeter = (*this).BMIH.biYPelsPerMeter;
qDebug() << "214235423" << endl;
//return (*this).BMIH;
return BMIH;
}
*/
源文件 mainwindow.cpp:
#include "mainwindow.h"
#include "ui_mainwindow.h"
#include <QtCore>
#include <QFile>
#include <QFileDialog>
#include <QMessageBox>
#include "bmputil.h"
//#include "bmputil.cpp"
MainWindow::MainWindow(QWidget *parent) :
QMainWindow(parent),
ui(new Ui::MainWindow)
{
ui->setupUi(this);
image = QPixmap();
QStringList bands = QStringList() << "QString" << "byteArray";
ui->comboBoxWaterMark->setModel(new QStringListModel(bands));
ui->comboBoxWaterMark->setCurrentIndex(1);
ui->lineEditWaterMark->setText("01010101010101010101010101010101");
}
MainWindow::~MainWindow()
{
delete ui;
}
void MainWindow::on_pushButtonBrowse_clicked()
{
auto file = QFileDialog::getOpenFileName(this, tr("Append selected images"));
ui->lineEdit->setText(file);
}
void MainWindow::on_lineEdit_textChanged(const QString &arg1)
{
Q_UNUSED(arg1);
watermark WT;
if(QFileInfo(ui->lineEdit->displayText()).exists())
{
int height, width;
uchar* buffer = WT.readBmp(ui->lineEdit->displayText().toStdString().data(), width, height);
if(buffer)
{
QPixmap img = QPixmap::fromImage(QImage(buffer, width, height, QImage::Format_Grayscale8));
QGraphicsScene *scene = new QGraphicsScene;
scene->addPixmap(img);
ui->graphicsViewPrevious->setScene(scene);
ui->graphicsViewPrevious->show();
ui->graphicsViewPrevious->fitInView(img.rect(), Qt::KeepAspectRatio);
}
}
}
void MainWindow::on_pushButtonEncode_clicked()
{
byteArray code;
watermark WT;
if(ui->comboBoxWaterMark->currentIndex() == 1)
{
QRegExp regx("[0-1]+$");
QValidator *validator = new QRegExpValidator(regx, this );
ui->lineEditWaterMark->setValidator( validator );
QString str1 = ui->lineEditWaterMark->text();
code = WT.byte2Array(str1);
delete validator;
}
else
{
QRegExp regx(".+\n");
QValidator *validator = new QRegExpValidator(regx, this );
ui->lineEditWaterMark->setValidator( validator );
QString str2 = ui->lineEditWaterMark->text();
//code = str2Array(ui->lineEditWaterMark->text());
code = WT.str2Array(str2);
delete validator;
}
key = WT.generateKey(code.length());
int width, height;
uchar* buffer = WT.readBmp(ui->lineEdit->displayText().toStdString().data(), width, height);
uchar* edge = WT.edgeExtract(buffer, width, height);
dst = WT.watermarkImg(buffer, edge, width*height, WT.encode(code, key));
//imwrite("encode.bmp", dst*255);
image = QPixmap::fromImage(QImage(dst, width, height, QImage::Format_Grayscale8));
QGraphicsScene *scene = new QGraphicsScene;
scene->addPixmap(image);
ui->graphicsViewAfter->setScene(scene);
ui->graphicsViewAfter->show();
ui->graphicsViewAfter->fitInView(image.rect(), Qt::KeepAspectRatio);
//WT.saveBmp(dst);
//qDebug() << "In void MainWindow::on_pushButtonEncode_clicked(), height = " << height << endl;
//qDebug() << "void MainWindow::on_pushButtonEncode_clicked(), width = " << width << endl;
WT.savebmp("encode.bmp", dst, height, width);
}
void MainWindow::on_pushButtonDecode_clicked()
{
int width, height;
watermark WT;
uchar* buffer = WT.readBmp(ui->lineEdit->displayText().toStdString().data(), width, height);
byteArray code = WT.encode(WT.decodeImg(buffer, dst, width, height, key.length()), key);
if(ui->comboBoxWaterMark->currentIndex() == 1)
{
QMessageBox::warning(this, "Decode", "The watermark is " + WT.array2byte(code)+"!");
}
if(ui->comboBoxWaterMark->currentIndex() == 0)
{
QMessageBox::warning(this, "Decode", "The watermark is " + WT.array2str(code)+"!");
}
}
源文件 main.cpp:
#include "mainwindow.h"
#include <QApplication>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QApplication a(argc, argv);
MainWindow w;
w.setWindowTitle("8 bits Binary BMP picture watermarking program");
w.show();
return a.exec();
}
配置文件 my_app.rc:
IDI_ICON1 ICON DISCARDABLE t14.ico工程文件 ImageEncodeAdvance.pro:
#-------------------------------------------------
#
# Project created by QtCreator 2019-02-03T14:45:42
#
#-------------------------------------------------
QT += core gui
greaterThan(QT_MAJOR_VERSION, 4): QT += widgets
TARGET = ImageEncodeAdvance
TEMPLATE = app
# The following define makes your compiler emit warnings if you use
# any feature of Qt which has been marked as deprecated (the exact warnings
# depend on your compiler). Please consult the documentation of the
# deprecated API in order to know how to port your code away from it.
DEFINES += QT_DEPRECATED_WARNINGS
# You can also make your code fail to compile if you use deprecated APIs.
# In order to do so, uncomment the following line.
# You can also select to disable deprecated APIs only up to a certain version of Qt.
#DEFINES += QT_DISABLE_DEPRECATED_BEFORE=0x060000 # disables all the APIs deprecated before Qt 6.0.0
#INCLUDEPATH += $$PWD/opencv/include
INCLUDEPATH += /usr/local/include \
/usr/local/include/opencv4 \
/usr/local/include/opencv4/opencv2
#LIBS += $$PWD/opencv/lib/opencv_world320.lib
LIBS += /usr/local/lib/libopencv_calib3d.so.4.0.1 \
/usr/local/lib/libopencv_core.so.4.0.1 \
/usr/local/lib/libopencv_features2d.so.4.0.1 \
/usr/local/lib/libopencv_flann.so.4.0.1 \
/usr/local/lib/libopencv_highgui.so.4.0.1 \
/usr/local/lib/libopencv_imgcodecs.so.4.0.1 \
/usr/local/lib/libopencv_imgproc.so.4.0.1 \
/usr/local/lib/libopencv_ml.so.4.0.1 \
/usr/local/lib/libopencv_objdetect.so.4.0.1 \
/usr/local/lib/libopencv_photo.so.4.0.1 \
/usr/local/lib/libopencv_stitching.so.4.0.1 \
/usr/local/lib/libopencv_videoio.so.4.0.1 \
/usr/local/lib/libopencv_video.so.4.0.1
SOURCES += \
main.cpp \
mainwindow.cpp \
bmputil.cpp \
addditional_utility.cpp
HEADERS += \
mainwindow.h \
bmputil.h \
addditional_utility.h
FORMS += \
mainwindow.ui
TARGET = "The Binary BMP Picture watermarking Program"
RC_FILE = my_app.rc
测试用图(256*256,8 位 BMP 二值图像):

其他
在这里简要说明一下程序所编码水印的不可访问性。由数字水印的稳健性可知,数字水印必须难以被除去 , 如果只知道部分数
字水印信息 , 那么试图除去或破坏数字水印将导致严重降质或不可用;又由数字水印的安全性知,数字水印的信息应是安全的 , 难以
篡改或伪造。由此推论,当以第三方途径解析带数字水印图像时,结果必然错误。
bmp 图像的组成格式部分为: bmp 文件头 (14 bytes) + 位图信息头 (40bytes) + 调色板 ( 由颜色索引数决定 ) + 位图数据 ( 由
图像尺寸决定 ) ,而设计题目要求处理的格式的为二值 bmp 图像,获取其 RGB 值是方便的。
基于以上观点,我采用以下方法证明设计中程序所编码难以篡改与不可访问:
(1 )若二值 bmp 图像未加水印,则可以通过读取原图的 RGB 像素矩阵另存为新图,其与原图像具有相同的性质,可以访问;
(2 )若二值 bmp 图像添加了数字水印,则无法通过读取原图的 RGB 像素矩阵将其还原,所得图像不具有访问性。
实验代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <fstream>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#pragma pack(2)
using namespace std;
typedef struct BITMAPFILEHEADER
{
u_int16_t bfType;
u_int32_t bfSize;
u_int16_t bfReserved1;
u_int16_t bfReserved2;
u_int32_t bfOffBits;
}BITMAPFILEHEADER;
typedef struct BITMAPINFOHEADER
{
u_int32_t biSize;
u_int32_t biWidth;
u_int32_t biHeight;
u_int16_t biPlanes;
u_int16_t biBitCount;
u_int32_t biCompression;
u_int32_t biSizeImage;
u_int32_t biXPelsPerMeter;
u_int32_t biYPelsPerMeter;
u_int32_t biClrUsed;
u_int32_t biClrImportant;
}BITMAPINFODEADER;
class OperateBMP
{
public:
int readBmp();
int saveBmp();
void work();
void compareBMP();
~OperateBMP();
private:
BITMAPFILEHEADER BMFH;
BITMAPINFODEADER BMIH;
int biWidth; //图像宽
int biHeight; //图像高
int biBitCount; //图像类型,每像素位数
unsigned char *pBmpBuf; //存储图像数据
int lineByte; //图像数据每行字节数
string originFileName_string;
string newFileName_string;
const char *originFileName_char;
const char *newFileName_char;
string pictureName_without_type;
//string resultName_string;
char *resultName_char;
int lengthOfResultName_char;
string compareResult;
};
OperateBMP::~OperateBMP()
{
/*
delete pBmpBuf;
delete originFileName_char;
delete newFileName_char;
delete resultName_char;
*/
}
int OperateBMP::readBmp()
{
FILE *fp;
cout << "Please input the name of the origin BMP file:" << endl;
cin >> originFileName_string;
originFileName_char = new char[ originFileName_string.length() ];
originFileName_char = originFileName_string.c_str();
if( (fp = fopen(originFileName_char,"rb")) == NULL) //以二进制的方式打开文件
{
cout<<"The file "<<originFileName_char<<"was not opened"<<endl;
return -1;
}
if(fseek(fp,sizeof(BITMAPFILEHEADER),SEEK_CUR)) //跳过BITMAPFILEHEADE
{
cout<<"跳转失败"<<endl;
return -1;
}
fread(&BMIH,sizeof(BITMAPINFOHEADER),1,fp); //从fp中读取BITMAPINFOHEADER信息到infoHead中,同时fp的指针移动
biWidth = BMIH.biWidth;
biHeight = BMIH.biHeight;
biBitCount = BMIH.biBitCount;
lineByte = (biWidth*biBitCount/8+3)/4*4; //lineByte必须为4的倍数
//24位bmp没有颜色表,所以就直接到了实际的位图数据的起始位置
pBmpBuf = new unsigned char[lineByte * biHeight];
fread(pBmpBuf,sizeof(char),lineByte * biHeight,fp);
fclose(fp); //关闭文件
//delete fp;
return 0;
}
int OperateBMP::saveBmp()
{
FILE *fp;
newFileName_char = new char[ originFileName_string.length() + 4 ];
newFileName_string = "New_" + originFileName_string;
newFileName_char = newFileName_string.c_str();
int pos = originFileName_string.find(".bmp");
pictureName_without_type = originFileName_string.erase( pos, 4 );
//cout << pictureName_without_type << endl;
if( (fp = fopen(newFileName_char,"wb") )== NULL) //以二进制写入方式打开
{
cout<<"打开失败!"<<endl;
return -1;
}
//设置BITMAPFILEHEADER参数
BMFH.bfType = 0x4D42;
BMFH.bfSize = sizeof(BITMAPFILEHEADER) + sizeof(BITMAPINFOHEADER) + lineByte * biHeight;
BMFH.bfReserved1 = 0;
BMFH.bfReserved2 = 0;
BMFH.bfOffBits = sizeof(BITMAPFILEHEADER) + sizeof(BITMAPINFOHEADER);
fwrite(&BMFH,sizeof(BITMAPFILEHEADER),1,fp);
//设置BITMAPINFOHEADER参数
BMIH.biSize = 40;
BMIH.biWidth = biWidth;
BMIH.biHeight = biHeight;
BMIH.biPlanes = 1;
BMIH.biBitCount = biBitCount;
BMIH.biCompression = 0;
BMIH.biSizeImage = lineByte * biHeight;
BMIH.biXPelsPerMeter = 0;
BMIH.biYPelsPerMeter = 0;
BMIH.biClrUsed = 0;
BMIH.biClrImportant = 0;
//写入
fwrite(&BMIH,sizeof(BITMAPINFOHEADER),1,fp);
fwrite(pBmpBuf,sizeof(char),lineByte * biHeight,fp);
fclose(fp); //关闭文件
return 0;
}
void OperateBMP::work()
{
if(-1 == readBmp())
cout<<"readfile error!"<<endl;
//输出图像的信息
cout<<"Width = "<<biWidth<<" Height = "<<biHeight<<" biBitCount="<<biBitCount<<endl;
string TXT = "imageData_" + originFileName_string + ".txt"; //15
const char *TXT_char = TXT.c_str();
resultName_char = new char[ 15 + originFileName_string.length() ];
strcpy( resultName_char, TXT_char );
lengthOfResultName_char = 15 + originFileName_string.length();
ofstream outfile(TXT_char,ios::in | ios::trunc);
if(!outfile)
{
cout<<"open error"<<endl;
return ;
}
int count = 0;
//图像数据信息是从左下角按行开始存储的
for(int i = 0; i < biHeight; i++ )
{
for(int j = 0; j < biWidth; j++ )
{
for(int k = 0; k < 3; k++ )
{
int temp = *(pBmpBuf + i * lineByte + j + k);
count++;
outfile<<temp<<" ";
if(count % 8 == 0)
{
outfile<<endl;
}
}
}
}
cout<<"总的像素数:"<<count / 3<<endl;
newFileName_string = "_" + originFileName_string;
newFileName_char = new char[ newFileName_string.length() ];
newFileName_char = newFileName_string.c_str();
saveBmp();
return ;
}
void OperateBMP::compareBMP()
{
OperateBMP OBMP1, OBMP2;
OBMP1.work();
OBMP2.work();
char *fileName1, *fileName2;
fileName1 = new char[OBMP1.lengthOfResultName_char];
strcpy(fileName1, OBMP1.resultName_char );
fileName2 = new char[OBMP2.lengthOfResultName_char];
strcpy( fileName2, OBMP2.resultName_char );
FILE *fp1 = fopen( fileName1, "r" ), *fp2 = fopen( fileName2, "r" );
int arr1[10], arr2[10], firstRow, firstColumn;
int length = 0;
long long cnt = 0;
compareResult = OBMP1.pictureName_without_type + "_With_" + OBMP2.pictureName_without_type + "_Comparing_Result.txt";
char *resultTXT = new char[ compareResult.length() ];//compareResultLength.c_str();
strcpy( resultTXT, compareResult.c_str() );
freopen( resultTXT, "w", stdout );
while( ( fscanf( fp1, "%d %d %d %d %d %d %d %d \n", &arr1[0], &arr1[1], &arr1[2], &arr1[3], &arr1[4], &arr1[5], &arr1[6], &arr1[7] ) != EOF ) && ( fscanf( fp2, "%d %d %d %d %d %d %d %d \n", &arr2[0], &arr2[1], &arr2[2], &arr2[3], &arr2[4], &arr2[5], &arr2[6], &arr2[7] ) != EOF ) )
{
length ++;
for( int i = 0; i < 7; i ++ )
{
if( arr1[i] != arr2[i] )
{
cnt ++;
cout << "NO " << cnt << " difference:" << endl;
cout << "row = " << length << ", " << "column = " << i + 1 << endl;
printf( "In file %s\narr1[%d][%d] = %d\nIn file %s\narr2[%d][%d] = %d\n\n", fileName1,length, i + 1, arr1[i], fileName2, length, i + 1, arr2[i] );
//break;
//return 0;
}
}
}
delete fileName1;
delete fileName2;
if( cnt == 0 )
{
cout << "These two pictures come to one!" << endl;
}
delete fp1;
delete fp2;
delete resultTXT;
}
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
OperateBMP OBMP;
OBMP.compareBMP();
return 0;
}
实验结果
选取的 3 张图的原图、程序解析原图复制的图像,以及水印编码后的图像、程序解析被编码图复制的图像,如2至图13所
示。
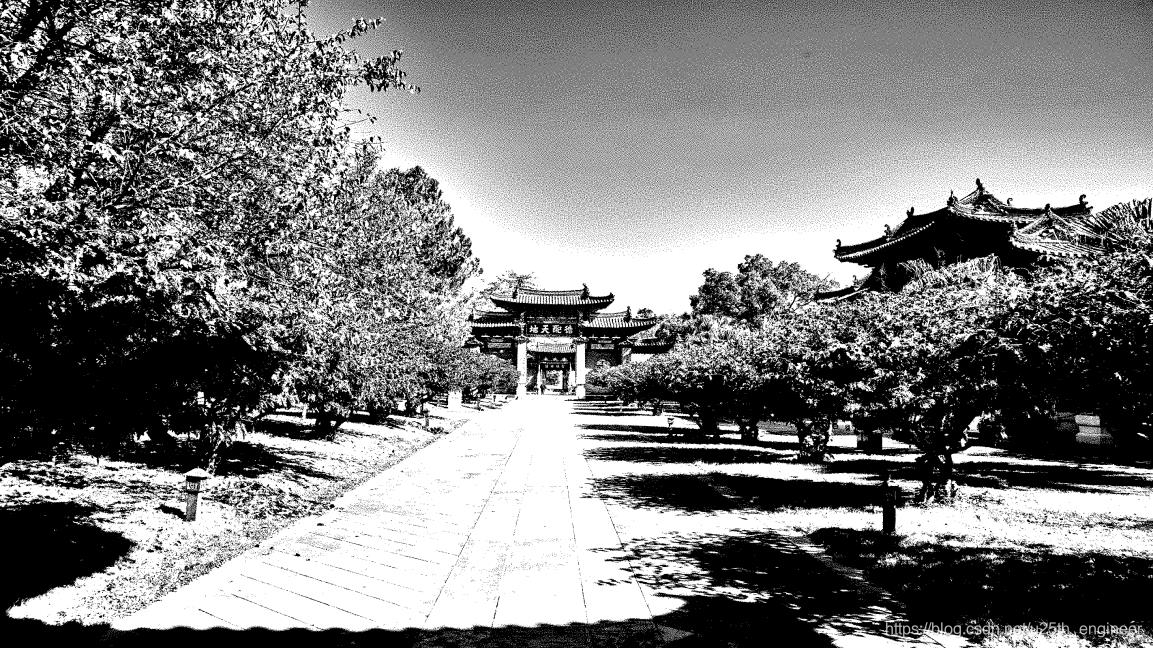
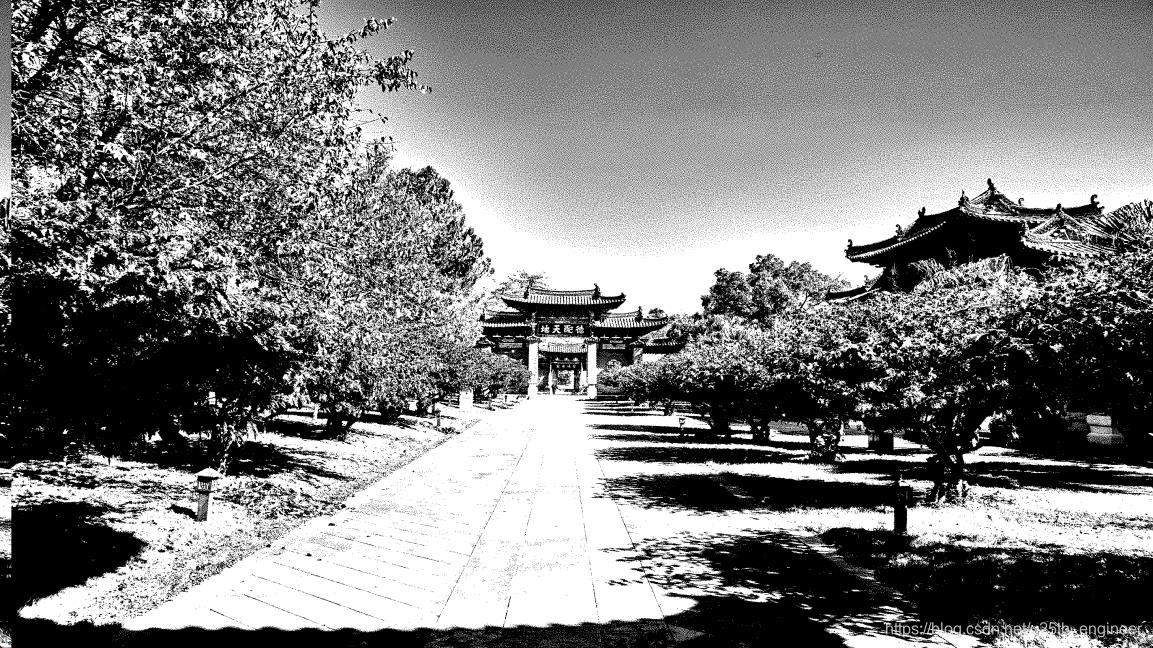
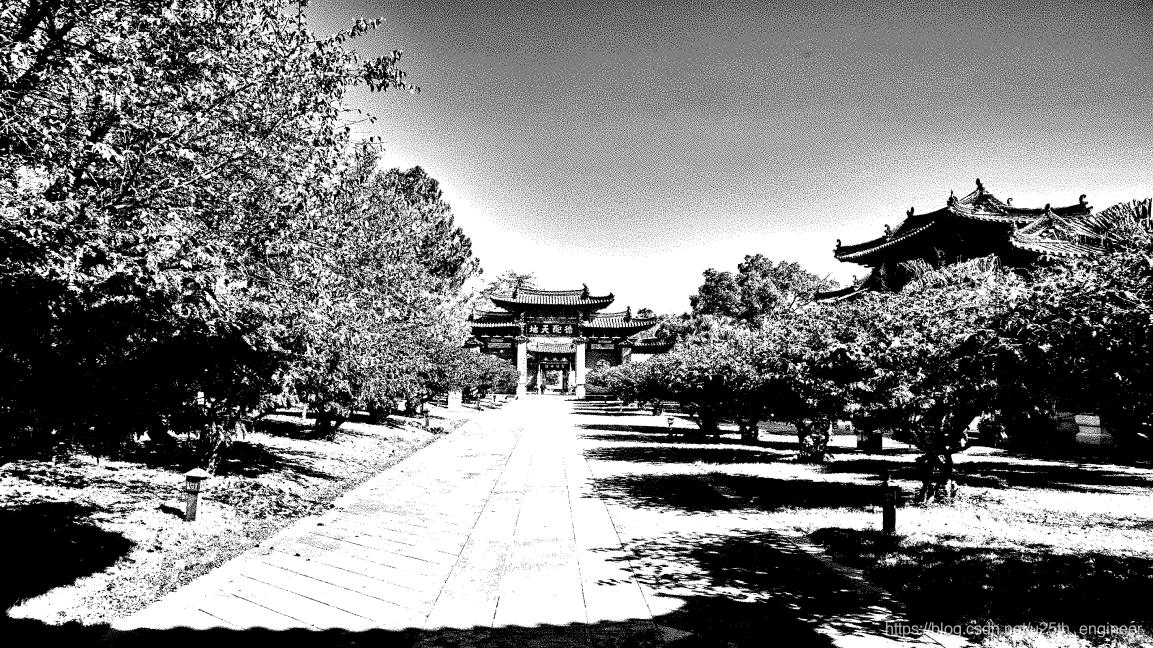
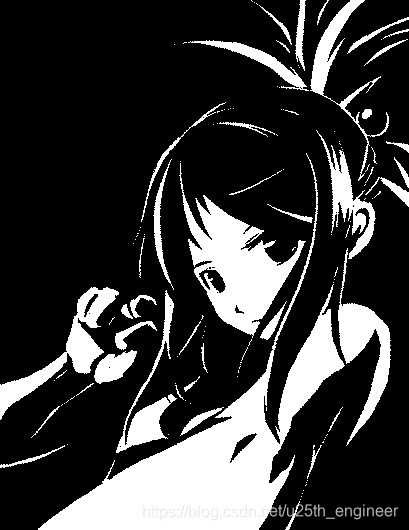
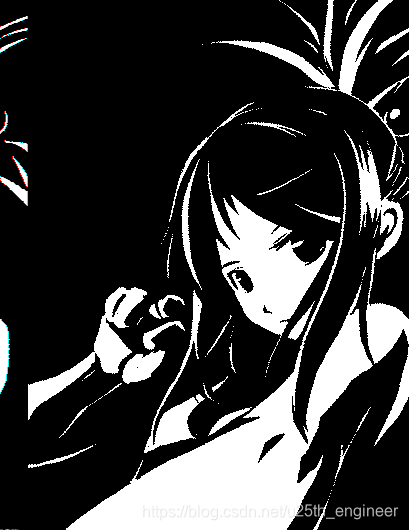
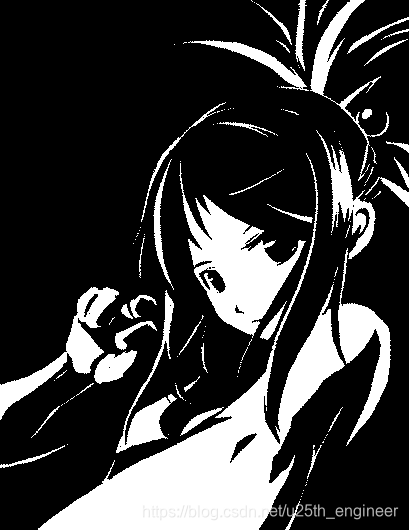









实验结论:
综合上述判定方法与结果,原报告中设计的算法编码的二值图像数字水印具有安全性与稳健性。显然被水印编码图像与原图
像,无法产生人类视觉明显的差别,因此符合隐蔽性。
计算图像的 PSNR 与 SSIM 所用 matlab 代码:
clc;
close all;
path1 = '/home/u25th_engineer/lena256.bmp';
path2 = '/home/u25th_engineer/lena256_encode.bmp';
path3 = '/home/u25th_engineer/lena256_encode_noise.bmp';
X = imread(path1);
Y = imread(path2);
%KKK = filter2( fspecial('sobel'), Y );
%X1 = mat2gray(Y)
%Z=X1;
Z = imnoise(Y, 'salt & pepper');%添加椒盐噪声,也可以改成其他噪声
%Z = imnoise(Y,'gaussian',0.1,0.004);
imwrite( Z, path3 );
%A = fspecial('average',3); %生成系统预定义的3X3滤波器
figure;
subplot(1, 3, 1); imshow(X); title('a.Lena256原图像');
subplot(1, 3, 2); imshow(Y); title('b.加水印图像');
subplot(1, 3, 3); imshow(Z); title('c.水印图像加噪声');
X = double(X);
Y = double(Y);
D = Y - X;
MSE = sum(D(:).*D(:)) / numel(Y);%均方根误差MSE
d = 0;
e = 0;
file_name = path1;
cover_object = double(imread(file_name));
Mc = size(cover_object, 1); %原图像行数
Nc = size(cover_object, 2); %原图像列数
file_name = path2;
watermarked_image = double(imread(file_name));
%计算信噪比
for i = 1 : Mc
for j = 1 : Nc
a(i, j) = cover_object(i, j) ^ 2;
b(i, j) = cover_object(i, j) - watermarked_image(i, j);
d = d + a(i, j);
e = e + b(i, j) ^ 2;
end
end
PSNR = 10 * log10(d / e);
MAE = mean(mean(abs(D)));%平均绝对误差
w = fspecial('gaussian', 11, 1.5); %window 加窗
K(1) = 0.01;
K(2) = 0.03;
L = 255;
Y = double(Y);
X = double(X);
C1 = (K(1)*L) ^ 2;
C2 = (K(2)*L) ^ 2;
w = w/sum(sum(w));
ua = filter2(w, Y, 'valid');%对窗口内并没有进行平均处理,而是与高斯卷积,
ub = filter2(w, X, 'valid'); % 类似加权平均
ua_sq = ua.*ua;
ub_sq = ub.*ub;
ua_ub = ua.*ub;
siga_sq = filter2(w, Y.*Y, 'valid') - ua_sq;
sigb_sq = filter2(w, X.*X, 'valid') - ub_sq;
sigab = filter2(w, Y.*X, 'valid') - ua_ub;
ssim_map = ((2*ua_ub + C1).*(2*sigab + C2))./((ua_sq + ub_sq + C1).*(siga_sq + sigb_sq + C2));
MSSIM = mean2(ssim_map);
display(MSE);%均方根误差MSE
display(PSNR);%峰值信噪比
display(MAE);%平均绝对误差
display(MSSIM);%结构相似性SSIM
%display(d);
%display(e);
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
X = double(X);
Y = double(Z);
D = Y - X;
MSE1 = sum(D(:).*D(:)) / numel(Y);%均方根误差MSE
d = 0;
e = 0;
file_name = path1;
cover_object = double(imread(file_name));
Mc = size(cover_object, 1); %原图像行数
Nc = size(cover_object, 2); %原图像列数
file_name = path3;
watermarked_image = double(imread(file_name));
%计算信噪比
for i = 1 : Mc
for j = 1 : Nc
a(i, j) = cover_object(i, j) ^ 2;
b(i, j) = cover_object(i, j) - watermarked_image(i, j);
d = d + a(i, j);
e = e + b(i, j) ^ 2;
end
end
PSNR1 = 10 * log10(d / e);
MAE1 = mean(mean(abs(D)));%平均绝对误差
w = fspecial('gaussian', 11, 1.5); %window 加窗
K(1) = 0.01;
K(2) = 0.03;
L = 255;
Y = double(Y);
X = double(X);
C1 = (K(1)*L) ^ 2;
C2 = (K(2)*L) ^ 2;
w = w/sum(sum(w));
ua = filter2(w, Y, 'valid');%对窗口内并没有进行平均处理,而是与高斯卷积,
ub = filter2(w, X, 'valid'); % 类似加权平均
ua_sq = ua.*ua;
ub_sq = ub.*ub;
ua_ub = ua.*ub;
siga_sq = filter2(w, Y.*Y, 'valid') - ua_sq;
sigb_sq = filter2(w, X.*X, 'valid') - ub_sq;
sigab = filter2(w, Y.*X, 'valid') - ua_ub;
ssim_map = ((2*ua_ub + C1).*(2*sigab + C2))./((ua_sq + ub_sq + C1).*(siga_sq + sigb_sq + C2));
MSSIM1 = mean2(ssim_map);
display(MSE1);%均方根误差MSE
display(PSNR1);%峰值信噪比
display(MAE1);%平均绝对误差
display(MSSIM1);%结构相似性SSIM
%display(d);
%display(e);








 本文是程序设计与算法训练课程设计报告,围绕二值图像数字水印技术展开。介绍了课程设计目的、系统内容与功能,阐述图像水印和处理技术原理,采用 Qt 和 C++实现算法,给出技术流程、实验结果,分析算法性能,证明水印安全性与稳健性。
本文是程序设计与算法训练课程设计报告,围绕二值图像数字水印技术展开。介绍了课程设计目的、系统内容与功能,阐述图像水印和处理技术原理,采用 Qt 和 C++实现算法,给出技术流程、实验结果,分析算法性能,证明水印安全性与稳健性。
















 12
12

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








