C++ Boost库:简介和第一个示例程序
C++ Boost库:数值转换 lexical_cast
C++ Boost库:字符串格式化 format
C++ Boost库:字符串string_algo
C++ Boost库:字符串算法string_algo
C++ Boost库:类型推导BOOST_AUTO/BOOST_TYPEOF
C++ Boost库:分词处理库 tokenizer
C++ Boost库:windows下编译Boost库
C++ Boost库:日期时间库 date_time
C++ Boost库:智能指针scoped_ptr
C++ Boost库:数组智能指针 scoped_array
C++ Boost库:共享所有权的智能指针 shared_ptr
C++ Boost库:工厂函数 make_shared
C++ Boost库:共享有权的数组智能指针shared_array
C++ Boost库:弱引用智能指针 weak_ptr
C++ Boost库:禁止拷贝 nocopyable
C++ Boost库:计时器 timer
C++ Boost库:普通数组array
C++ Boost库:散列容器 unordered_set、unordered_multiset
C++ Boost库:散列容器 unordered_map、unordered_multimap
C++ Boost库:双向映射容器 bimap
C++ Boost库:环形缓冲区 circular_buffer
C++ Boost库:动态多维数组 multi_array
C++ Boost库:使用property_tree解析XML和JSON
C++ Boost库:简化循环 BOOST_FOREACH
C++ Boost库:随机数库 Random
C++ Boost库:引用库 ref
C++ Boost库:绑定库 bind
C++ Boost库:线程库 thread 跨平台多线程
C++ Boost库:互斥量 mutex
1. 简介
shared_ptr是可以共享所有权的指针。如果有多个shared_ptr共同管理同一个对象时,只有这些 shared_ptr全部与该对象分离之后,被管理的对象才会被释放,使用需要包含头文件:
#include <boost/shared_ptr.hpp>
注:c++11标准中std::shared_ptr与 boost::shared_ptr功能相似。
shared_ptr使用引用计数,每一个shared_ptr的拷贝都指向相同的内存;每关联一次,内部的引用计数加1。
2. shared_ptr示例代码
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<boost/shared_ptr.hpp>
using namespace boost;
class A
{
public:
A()
{
cout << "构造A类对象!" << endl;
}
~A( )
{
cout << "析构A类对象!" << endl;
}
int m_a;
};
int main()
{
boost::shared_ptr<A> p1(new A);//引用计数为1
//此时唯一管理A的内存
cout << p1.unique() << " , " << p1.use_count() << endl;
//此时, p1,p2同时管理A的内存
boost::shared_ptr<A> p2( p1); //拷贝构造,引用计数+1
cout << p2.unique() << " , " << p2.use_count() << endl;
boost::shared_ptr<A> p3;
p3 = p2;//赋值运算符 引用计数+1
cout << p1.unique() << " , " << p1.use_count() << endl;
//3个智能指针指向同一地址
cout << p1.get() << " , " << p2.get() << " , " << p3.get() << " , " << endl;
//手动分离管理权
p1.reset();// 引用计数-1
cout << p2.unique() << " , " << p2.use_count() << endl;
cout << p3.unique() << " , " << p3.use_count() << endl;
p2.reset();// 引用计数-1
cout << p3.unique() << " , " << p3.use_count() << endl;
p3.reset();//引用计数-1 ,此时,全部放弃了管理权,A内存就会释放
cout << "结束!" << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
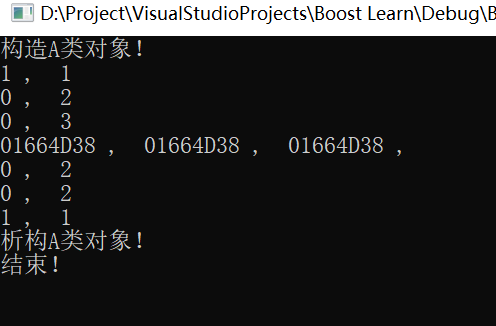
3. shared_ptr使用陷阱
- 陷阱1:
shared_ptr不能引用栈内存
int a = 100;
// 不能引用栈内存
boost::shared_ptr<int > p(&a);//运行时出错
cout << p.use_count() << endl;
- 陷阱2:
shared_ptr不能多次引用同一原始指针,否则同一内存会被delete多次
int a = 100;
// 不能引用栈内存
boost::shared_ptr<int > p(&a);//运行时出错
cout << p.use_count() << endl;
- 陷阱3:
shared_ptr循环引用导致内存泄露
int a = 100;
// 不能引用栈内存
boost::shared_ptr<int > p(&a);//运行时出错
cout << p.use_count() << endl;
- 陷阱4:
shared_ptr管理的内存必须是new出来的
int a = 100;
// 不能引用栈内存
boost::shared_ptr<int > p(&a);//运行时出错
cout << p.use_count() << endl;
示例代码:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<boost/shared_ptr.hpp>
using namespace boost;
class B;//类的前置声明
class A
{
public:
A()
{
cout << "构造A类对象!" << endl;
}
~A( )
{
cout << "析构A类对象!" << endl;
}
boost::shared_ptr<B> m_pb; //指向B的内存
};
class B
{
public:
B()
{
cout << "构造B类对象!" << endl;
}
~B()
{
cout << "析构B类对象!" << endl;
}
boost::shared_ptr<A> m_pa;////指向A的内存
};
int main()
{
//陷阱1,不要把栈内存地址赋给 scoped_ptr, scoped_array, shared_ptr
/* int a = 100;
boost::shared_ptr<int > p(&a);//运行时出错
cout << p.use_count() << endl;
//陷阱2,shared_ptr不能多次引用同一原始指针,否则同一内存会被delete多次
A *pA = new A;
boost::shared_ptr<A> p1(pA);
cout << p1.use_count() << endl;
//boost::shared_ptr<A> p2(pA); //这里p2并不知道p1的存在
boost::shared_ptr<A> p2(p1);//正确写法
cout << p2.use_count() << endl;
//p1 p2在对象析构时,会各自delete pA,从而报错
//陷阱3:shared_ptr循环引用导致内存泄露。
boost::shared_ptr<A> pA(new A);
boost::shared_ptr<B> pB(new B);
cout << pA.use_count() << " , " << pB.use_count() << endl;
pA->m_pb = pB;// 此刻 ,pB指向的内存引用计数为2
pB->m_pa = pA;//此刻 ,pA指向的内存引用计数为2
cout << pA.use_count() << " , " << pB.use_count() << endl;
//此刻,pA,pB都析构时,都只会将引用计数-1, 各自剩余引用计数为1,则不会释放
//从而导致A,B内存泄漏
*/
//陷阱4: shared_ptr管理的内存必须是new出来的
A *pA = (A *)malloc(sizeof(A));
boost::shared_ptr<A> p(pA); //这样肯定有问题的
getchar();
return 0;
}





 本文详细介绍了C++ Boost库中的shared_ptr概念,包括示例代码和常见陷阱,如不能引用栈内存、引用循环引用等。通过实例演示了如何正确使用shared_ptr避免内存问题。
本文详细介绍了C++ Boost库中的shared_ptr概念,包括示例代码和常见陷阱,如不能引用栈内存、引用循环引用等。通过实例演示了如何正确使用shared_ptr避免内存问题。

















 6249
6249












