转载自 Qt-PySide2-Primer,年代久远,PySide2 无法在新版本的 Python 中运行,建议替换为 PySide6,原文的代码仍可使用。
QML布局
QML可以使用x、y、z三个属性设置对象的位置,其中z更大的对象覆盖更小的对象。直接使用这些属性既不方便也不美观,通常使用布局功能来设置对象的位置。
在QML中有三种常用的布局工具:锚、定位器、布局管理器。
使用锚进行布局
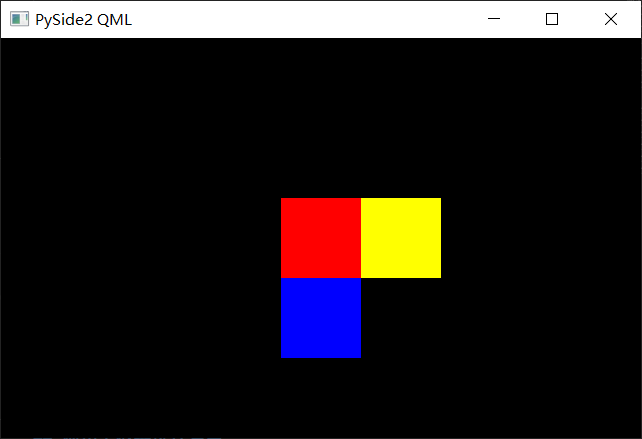
锚(anchors)是所有可视对象的父类Item的属性,用来标记不同对象直接的相关关系。
import QtQuick 2.13
import QtQuick.Window 2.13
Window {
id: mainWindow
visible: true // 是否可见,请注意默认值是false不可见
width: 640
height: 400
title: qsTr("PySide2 QML")
Rectangle {
color: "black"
anchors.fill: parent // 填满父对象
}
Rectangle {
id: red // id为red,可以在任何地方通过red操作这个对象
width: 80 // 宽80
height: 80 // 高80
color:"red" // 红色
anchors.centerIn: parent // 与父对象中心对齐
}
Rectangle {
width: 80
height: 80
color:"yellow"
anchors.top : red.top // 上边沿和red的上边沿对齐,即y相同
anchors.left : red.right // 左边沿和red的右边沿对齐
}
Rectangle {
width: 80
height: 80
color:"blue"
anchors.top : red.bottom // 上边沿和red的下边沿对齐
anchors.left : red.left // 左边沿和red的左边沿对齐,即x相同
}
}
使用定位器进行布局
定位器有四个:Row(行定位器)、Column(列定位器)、Grid(栅格定位器)、Flow(流式定位器)。
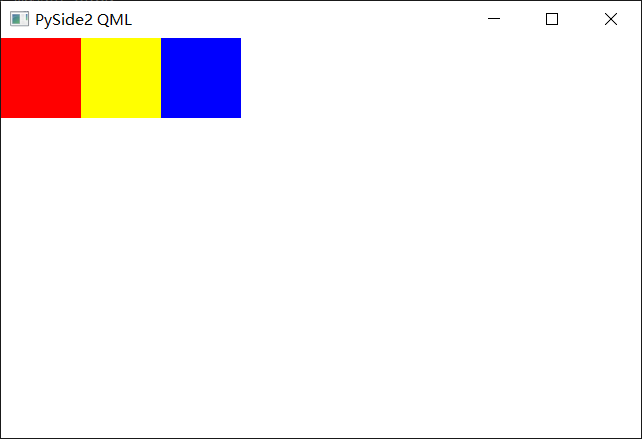
Row
- Row定位器将子对象横着排成一行
import QtQuick 2.13
import QtQuick.Window 2.13
Window {
id: mainWindow
visible: true // 是否可见,请注意默认值是false不可见
width: 640
height: 400
title: qsTr("PySide2 QML")
// 行定位器
Row {
Rectangle {
width: 80 // 宽80
height: 80 // 高80
color:"red" // 红色
}
Rectangle {
width: 80
height: 80
color:"yellow"
}
Rectangle {
width: 80
height: 80
color:"blue"
}
}
}

Column
- Column定位器将子对象竖着排成一列
import QtQuick 2.13
import QtQuick.Window 2.13
Window {
id: mainWindow
visible: true // 是否可见,请注意默认值是false不可见
width: 640
height: 400
title: qsTr("PySide2 QML")
// 列定位器
Column {
Rectangle {
width: 80 // 宽80
height: 80 // 高80
color:"red" // 红色
}
Rectangle {
width: 80
height: 80
color:"yellow"
}
Rectangle {
width: 80
height: 80
color:"blue"
}
}
}

Gird
- Grid定位器根据设定的行数与列数,将子对象从左到右、从上到下依次排列
import QtQuick 2.13
import QtQuick.Window 2.13
Window {
id: mainWindow
visible: true // 是否可见,请注意默认值是false不可见
width: 640
height: 400
title: qsTr("PySide2 QML")
// 栅格定位器
Grid {
rows: 2 // 2行
columns: 3 // 3列
Rectangle {
width: 80 // 宽80
height: 80 // 高80
color:"red" // 红色
}
Rectangle {
width: 80
height: 80
color:"yellow"
}
Rectangle {
width: 80
height: 80
color:"blue"
}
Rectangle {
width: 80
height: 80
color:"orange"
}
Rectangle {
width: 80
height: 80
color:"green"
}
Rectangle {
width: 80
height: 80
color:"purple"
}
}
}

Flow
- Flow定位器将子对象从左到右依次排列,当自身宽度不足以放下下一个子对象时换行
import QtQuick 2.13
import QtQuick.Window 2.13
Window {
id: mainWindow
visible: true // 是否可见,请注意默认值是false不可见
width: 640
height: 400
title: qsTr("PySide2 QML")
// 流式定位器
Flow {
anchors.fill: parent //填满父对象(即窗口)
Rectangle {
width: 240 // 宽
height: 80 // 高
color:"red"
}
Rectangle {
width: 160
height: 80
color:"yellow"
}
Rectangle {
width: 160
height: 80
color:"blue"
}
Rectangle {
width: 320
height: 80
color:"orange"
}
Rectangle {
width: 160
height: 80
color:"green"
}
Rectangle {
width: 400
height: 80
color:"purple"
}
}
}

使用布局管理器进行布局
布局管理器有三个:RowLayout、ColumnLayout、GridLayout
- 需要加载Layouts模块
import QtQuick.Layouts 1.13 - 布局管理器和定位器类似,区别在于布局管理器处理可定位元素的位置以外,还能调节元素的大小。
import QtQuick 2.13
import QtQuick.Window 2.13
import QtQuick.Layouts 1.13
Window {
id: mainWindow
visible: true // 是否可见,请注意默认值是false不可见
width: 640
height: 400
title: qsTr("PySide2 QML")
// 列布局管理器
ColumnLayout {
anchors.fill: parent
// 行布局管理器
RowLayout {
Layout.fillWidth: true // 宽度填满布局
Layout.fillHeight: true // 高度填满布局
Rectangle {
Layout.fillWidth: true
Layout.fillHeight: true
color: "red"
}
Rectangle {
Layout.fillWidth: true
Layout.fillHeight: true
color: "yellow"
}
Rectangle {
Layout.fillWidth: true
Layout.fillHeight: true
color: "blue"
}
}
// 行布局管理器
RowLayout {
Layout.fillWidth: true // 宽度填满布局
Layout.fillHeight: true // 高度填满布局
Rectangle {
Layout.fillWidth: true
Layout.fillHeight: true
color: "orange"
}
Rectangle {
Layout.fillWidth: true
Layout.fillHeight: true
color: "green"
}
Rectangle {
Layout.fillWidth: true
Layout.fillHeight: true
color: "purple"
}
}
}
}
























 1098
1098

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








