什么是链表
链表是一种物理存储单元上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的。链表由一系列结点(链表中每一个元素称为结点)组成,结点可以在运行时动态生成。每个结点包括两个部分:一个是存储数据元素的数据域,另一个是存储下一个结点地址的指针域。
列表(也成为顺序表)和链表都是线性表,那他们有什么区别呢?从结构上来说,列表底层是通过数组来存储数据,需要申请空间,然后按照次序逐一存储,数据之间紧密贴合,数据之间联系是索引;链表每个节点只保留存储元素和下个节点指针,所以什么时候存数据就什么时候申请空间,数据之间联系是每个节点携带的指针。
- 空间利用率
从结构上就能看出列表的空间利用率比链表高,因为链表在存储数据的时候每次都只申请一个节点的空间,且空间的位置是随机的,这样便会产生很多空间碎片,一定程度上造成空间浪费;另外链表每个节点都至少带一个指针,所以链表申请空间的利用率也比列表低。
- 时间复杂度
因为列表底层是由数组实现的,访问元素,直接通过索引就能够获取元素,时间复杂度为 O(1),而链表需要遍历节点到指定位置,所以链表访问元素的时间复杂度为 O(n)。但是在删除和插入两种操作中,数组需要因为,因此时间复杂度为 O(n),而链表直接操作某个节点即可,因此时复杂度为O(1),因此,如何使用列表和链表可根据具体的业务场景进行选择。
-
若是业务场景查询操作比较多,但修改删除操作比较少,建议使用列表
-
若是业务场景修改删除操作比较多,但查询操作比较少,建议使用链表
最后阿导从其它地方找到一个表格进行总结,如下
| 比对项 | 链表 | 列表(数组) |
|---|---|---|
| 内存占用 | 不需要连续的内存空间 | 需要连续的内存空间 |
| 大小可变 | 可动态变化 | 数组大小固定,不能动态扩展 |
| 增删 | 较快,只需要修改前一个元素的指针即可 | 较慢,需要移动修改元素之后的所有元素 |
| 查询 | 较慢,只能遍历查找 | 较快,直接通过下标索引直接访问 |
| 访问方式 | 必须是顺序访问,不能随机访问 | 可随机访问其中的元素 |
| 空间使用 | 可以随意扩大 | 不能随意扩大 |
说完链表和列表的区别,在链表中常见的有单向链表,双向链表,下面逐一分析这三种链表。
单向链表
结构
private class Node<E> {
/**
* 元素
*/
private E e;
/**
* 下一个节点
*/
private Node<E> next;
}

单向链表结构体中包含存储数据区域的 e,和指向下一个节点的指针 next。
操作
新增元素:public boolean add(E e)

新增元素一般是将新增的元素添加到链表的尾部,一般这里面可以通过 size 来遍历至链表的最后一个元素,我这边根据判断每个元素下一个节点是否为空来判断是否是最后一个元素,这里面需要区别对待的是头节点,因为在操作类需要保留头节点信息。最后统计链表大小属性 size 加一。
插入元素:public boolean add(int index, E e)

插入元素,首先是需要判断插入的位置是否合法,然后找出插入的位置,插入元素需要注意的是后续指针区域的变化,这也是和列表中数组移位不相同的一点。最后统计链表大小属性 size 加一。
查询第一个匹配到的位置:public int indexOf(E e)
链表中访问元素必须是顺序访问,从头节点依次遍历,直到查询到目标元素或最后一个节点结束。
移除某个位置的节点:public E remove(int index)

移除某个位置的元素,第一步仍然需要判断移除的位置是否合法,然后找寻到移除位置,这里移除也不需要向数组那样移位,只需要处理移除的位置前后节点即可,这里需要注意的是头节点没有前驱节点。最后记得将统计链表大小的 size 减一。
移除链表上某个元素:public E remove(E e)
这里实现方式也比较多,第一种是通过遍历,进行匹配然后进行删除指定的位置信息,我这里的做法其实不建议使用,只是为了偷懒,先查询到位置,再移除该位置的元素。
修改指定位置的数据区域: public void set(int index, E e)
判断修改位置的合法性,然后找到位置直接修改元素即可。
判断元素是否存在: public boolean contains(E e)
这里可借助 indexOf 方法进行判断即可。
判断是否为空:public boolean isEmpty()
直接根据 size 是否为零进行判断。
获取指定位置的数据:public E getData(int index)
判断位置合法性,然后依次遍历到该位置取出数据区域的数据即可。
获取链表大小:public int size()
直接返回统计链表大小属性 size。
转换成数组:public Object[] toArray()
通过遍历赋值到数组并返回。
重写 toString 方法:public String toString()
通过连接符进行形象表示链式结构。
清空链表:public void clear()
将头节点置为空,统计链表大小的属性 size 置为 0。
示例
package com.dao.datastructure.list;
/**
* 链表
*
* @author 阿导
* @CopyRight 万物皆导
* @Created 2019-11-18 19:28:00
*/
public class DaoLinkedList<E> {
/**
* 节点内部类
*
* @author 阿导
* @time
* @copyRight 万物皆导
*/
private class Node<E> {
/**
* 元素
*/
private E e;
/**
* 下一个节点
*/
private Node<E> next;
private Node() {
this(null);
}
private Node(E e) {
this(e, null);
}
private Node(E e, Node<E> next) {
this.e = e;
this.next = next;
}
}
/**
* 头节点
*/
private Node head;
/**
* 节点数目
*/
private int size;
/**
* 构造方法
*
* @return
* @author 阿导
* @time 2019/11/19 :00
*/
public DaoLinkedList() {
this.head = null;
this.size = 0;
}
/**
* 添加元素
*
* @param e
* @return boolean
* @author 阿导
* @time 2019/11/19 :00
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
// 新节点
Node<E> newNode = new Node(e);
// 找到链表最尾部,然后插入结果即可(头节点比较特殊)
if (this.size == 0 && this.head == null) {
this.head = newNode;
} else {
// 临时遍历获取当前头节点
Node<E> next = this.head;
// 遍历直到尾节点
while (next.next != null) {
next = next.next;
}
// 将尾节点的下一个节点指向新节点
next.next = newNode;
}
// 节点大小加一
this.size++;
// 操作成功
return true;
}
/**
* 指定位置插入节点
*
* @param index
* @param e
* @return boolean
* @author 阿导
* @time 2019/11/19 :00
*/
public boolean add(int index, E e) {
// 判断插入的位置是否合法
this.indexOutOfBoundsException(index);
// 记录位置
int pox = 0;
// 获取头节点
Node<E> next = this.head;
// 记录上一个节点
Node<E> cur = null;
// 找到插入位置
while (pox++ < index) {
// 当前节点保存
cur = next;
// 下一节点
next = next.next;
}
//若是此种情况,则是头节点
if (cur == null) {
// 新节点的下一个节点是头节点
Node<E> newNode = new Node(e, this.head);
// 将头节点指向新节点
this.head = newNode;
} else {
// 新节点的下一个节点当前节点的下一个节点
Node<E> newNode = new Node(e, next);
// 当前节点指向新节点
cur.next = newNode;
}
// 节点大小加一
this.size++;
// 操作成功
return true;
}
/**
* 查询第一个匹配到的位置
*
* @return int
* @author 阿导
* @time 2019/11/19 :00
*/
public int indexOf(E e) {
// 记录位置
int pox = 0;
// 获取头节点
Node<E> cur = this.head;
// 遍历节点
while (cur != null) {
// 若查询到节点,则返回位置
if ((cur.e == null && e == null) || e != null && e.equals(cur.e)) {
return pox;
}
// 下个节点走起
cur = cur.next;
pox++;
}
// 表示未找到
return -1;
}
/**
* 移除某个位置的节点
*
* @param index
* @return E
* @author 阿导
* @time 2019/11/19 :00
*/
public E remove(int index) {
// 判断插入的位置是否合法
this.indexOutOfBoundsException(index);
// 记录位置
int pox = 0;
// 记录上一个节点
Node<E> cur = null;
// 获取头节点
Node<E> next = this.head;
// 找到插入位置
while (pox++ < index) {
// 当前节点保存
cur = next;
// 下一节点
next = next.next;
}
// 保留删除的节点
E e = (E) next.e;
if (cur == null) {
// 若是删除头节点,直接将头节点指向头节点的下一个节点即可
this.head = this.head.next;
} else {
// 当前节点下一个节点指向下一个节点的下一个节点
cur.next = next.next;
}
// 节点大小减一
this.size--;
return e;
}
/**
* 移除链表上某个元素
*
* @param e
* @return E
* @author 阿导
* @time 2019/11/19 :00
*/
public E remove(E e) {
int index = this.indexOf(e);
// 未查询到不做任何处理,直接返回
if (index == -1) {
return e;
}
// 移除元素
remove(index);
// 直到所有的元素都删除
return remove(e);
}
/**
* 修改内容
*
* @author 阿导
* @time 2019/11/20 :00
* @param index
* @param e
* @return void
*/
public void set(int index, E e) {
// 判断插入的位置是否合法
this.indexOutOfBoundsException(index);
// 记录位置
int pox = 0;
Node<E> cur = this.head;
// 查找指定位置
while (pox++ < index) {
cur = cur.next;
}
// 替换元素
cur.e = e;
}
/**
* 重写 toString
*
* @author 阿导
* @time 2019/11/20 :00
* @return java.lang.String
*/
@Override
public String toString() {
// 声明结果
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
// 当前节点
Node<E> cur = this.head;
// 遍历节点
while (cur != null) {
// 获取当前节点元素
sb.append(cur.e);
// 是否需要连接符号
if (cur.next != null) {
sb.append("->");
}
// 指针指向下一个节点
cur = cur.next;
}
// 返回结果
return sb.toString();
}
/**
* 判断元素是否存在
*
* @param e
* @return boolean
* @author 阿导
* @time 2019/11/19 :00
*/
public boolean contains(E e) {
return this.indexOf(e) > -1;
}
/**
* 判断是否为空
*
* @return boolean
* @author 阿导
* @time 2019/11/19 :00
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.size == 0;
}
/**
* 查找指定位置的数据
*
* @param index
* @return E
* @author 阿导
* @time 2019/11/19 :00
*/
public E getData(int index) {
this.indexOutOfBoundsException(index);
// 记录位置
int pox = 0;
Node<E> cur = this.head;
// 查找指定位置
while (pox++ < index) {
cur = cur.next;
}
return cur.e;
}
/**
* 转换成数组
*
* @return E[]
* @author 阿导
* @time 2019/11/19 :00
*/
public Object[] toArray() {
// 存储结果
Object[] obj = new Object[this.size];
// 获取头节点
Node<E> cur = this.head;
// 记录位置
int pox = 0;
// 遍历节点
while (cur != null) {
// 获取元素
obj[pox++] = cur.e;
// 指向下一个节点
cur = cur.next;
}
// 返回结果
return obj;
}
/**
* 获取链表大小
*
* @return int
* @author 阿导
* @time 2019/11/19 :00
*/
public int size() {
return this.size;
}
/**
* 清空链表
*
* @author 阿导
* @time 2019/11/20 :00
* @return void
*/
public void clear(){
this.head = null;
this.size=0;
}
/**
* 判断是否越界
*
* @param index
* @return void
* @author 阿导
* @time 2019/11/19 :00
*/
private void indexOutOfBoundsException(int index) {
if (index >= this.size || index < 0) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("位置越界!!!");
}
}
}
双向链表
结构
private class Node<E> {
/**
* 节点元素
*/
private E e;
/**
* 上一个节点
*/
private Node<E> pre;
/**
* 下一个节点
*/
private Node<E> next;
}
双向链表最基本的结构有三个,分别是存储数据的 e,指向上一个节点 pre,以及指向下一个节点的 next。

操作
新增元素:public boolean add(E e)

双向链表相比较单向链表能更快的添加新的元素,因为双向链表会存储尾节点,所以直接替换尾节点即可,这里主要注意的是第一个节点进来如何处理,新节点前驱节点和后续节点怎么处理。最后统计链表大小属性 size 加一。
插入元素:public boolean add(int index, E e)
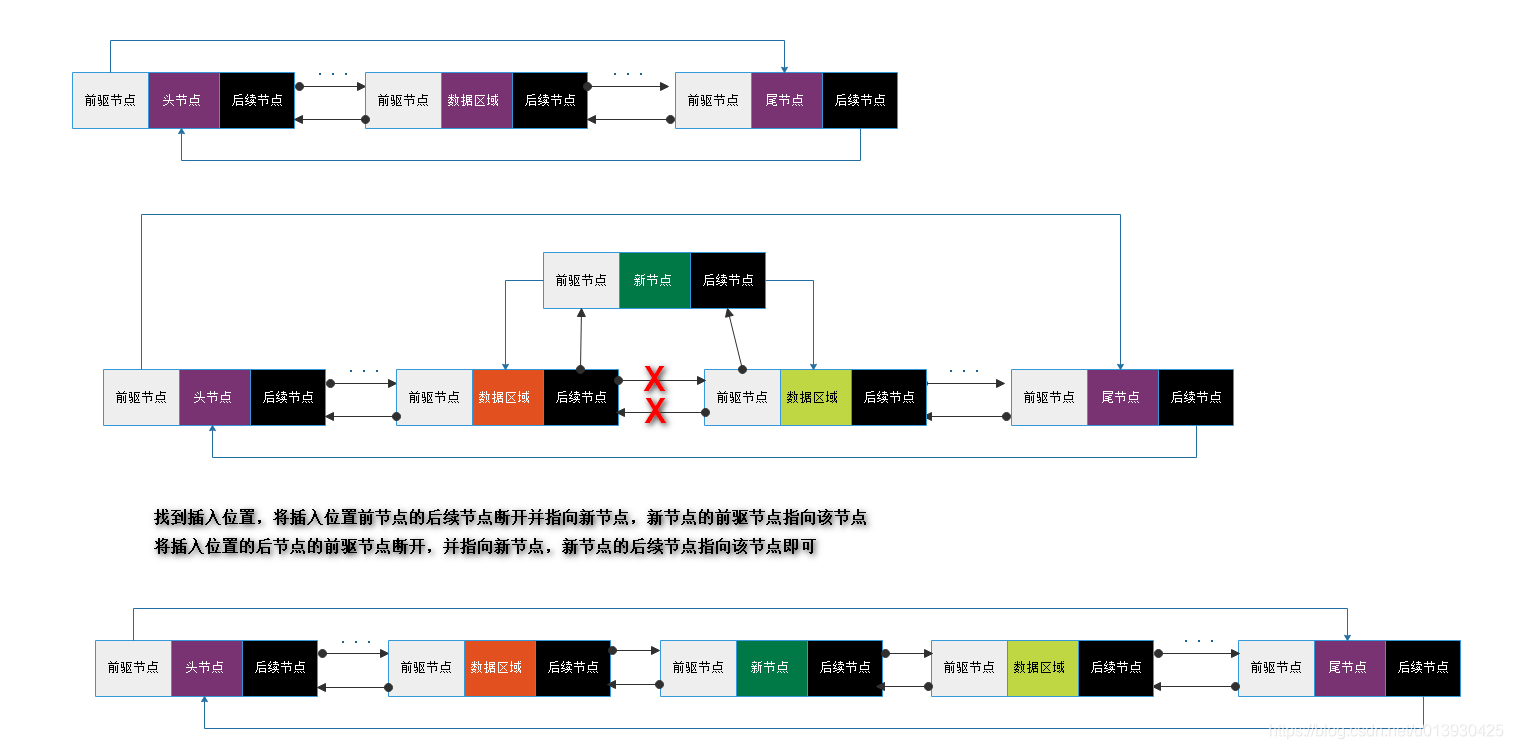
插入元素,首先是需要判断插入的位置是否合法,然后找出插入的位置,这里相对单向节点可以根据插入位置离头尾节点距离一定程度上减少遍历次数,这里依旧注意的是插入头节点的情况,最后要处理好新节点和旧节点的指针指向。最后统计链表大小属性 size 加一。
查询第一个匹配到的位置:public int indexOf(E e)
可以同时从头节点和尾节点,双向查找,谁最先查到相同的元素,先返回谁的序列位置
移除某个位置的节点:public E remove(int index)

移除某个位置的元素,第一步仍然需要判断移除的位置是否合法,不过这里需要注意的是移除的元素是否是最后一个元素,另外是否是头节点或者尾节点,最后需要处理好每个节点的指针指向。最后记得将统计链表大小的 size 减一。
移除链表上某个元素:public E remove(E e)
这里实现和单向链表类似。
修改指定位置的数据区域: public void set(int index, E e)
判断修改位置的合法性,然后找到位置直接修改元素即可。
判断元素是否存在: public boolean contains(E e)
这里可借助 indexOf 方法进行判断即可。
判断是否为空:public boolean isEmpty()
直接根据 size 是否为零进行判断。
获取指定位置的数据:public E getData(int index)
判断位置合法性,然后找到位置取出数据区域的数据即可。
获取链表大小:public int size()
直接返回统计链表大小属性 size。
转换成数组:public Object[] toArray()
通过遍历赋值到数组并返回。
重写 toString 方法:public String toString()
通过连接符进行形象表示链式结构。
清空链表:public void clear()
将头尾节点置为空,统计链表大小的属性 size 置为 0。
示例
package com.dao.datastructure.list;
/**
* 双向链表
*
* @author 阿导
* @CopyRight 万物皆导
* @Created 2019-11-19 15:27:00
*/
public class DaoDoubleLinkedList<E> {
private class Node<E> {
/**
* 节点元素
*/
private E e;
/**
* 上一个节点
*/
private Node<E> pre;
/**
* 下一个节点
*/
private Node<E> next;
public Node() {
}
public Node(E e) {
this.e = e;
}
public Node(E e, Node<E> pre, Node<E> next) {
this.e = e;
this.pre = pre;
this.next = next;
}
}
/**
* 节点
*/
private Node<E> head;
/**
* 尾节点
*/
private Node<E> foot;
/**
* 大小
*/
private int size;
/**
* 构造方法
*
* @return
* @author 阿导
* @time 2019/11/19 :00
*/
public DaoDoubleLinkedList() {
this.head = null;
this.foot = null;
this.size = 0;
}
/**
* 添加元素
*
* @param e
* @return boolean
* @author 阿导
* @time 2019/11/19 :00
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
// 找到链表最尾部,然后插入结果即可(头节点比较特殊)
if (this.size == 0 && this.head == null && this.foot == null) {
// 新节点
Node<E> newNode = new Node(e);
// 头尾节点都是本身
this.head = newNode;
this.foot = newNode;
this.head.next = this.foot;
this.head.pre = this.foot;
} else {
// 新节点,前驱指针指向头部,后续指针指向尾节点
Node<E> newNode = new Node(e, this.foot, this.head);
// 尾节点的后续指针指向新节点
this.foot.next = newNode;
// 头节点的前驱指针指向新节点
this.head.pre = newNode;
// 新节点为尾节点
this.foot = newNode;
}
// 节点大小加一
this.size++;
// 操作成功
return true;
}
/**
* 指定位置插入节点
*
* @param index
* @param e
* @return boolean
* @author 阿导
* @time 2019/11/19 :00
*/
public boolean add(int index, E e) {
// 判断插入的位置是否合法
this.indexOutOfBoundsException(index);
// 记录位置
int pox = 0;
// 获取最多访问次数
int n = this.size/ 2;
// 获取头节点
Node<E> next = this.head;
// 记录上一个节点
Node<E> cur = this.foot;
// 若是离头节点比较近
if (index < n) {
while (pox++ < index) {
// 当前节点保存
cur = next;
// 下一节点
next = next.next;
}
} else {
while (pox++ < this.size - index) {
// 下一节点
next = cur;
// 当前节点保存
cur = cur.pre;
}
}
//若是此种情况,则是头节点
if (cur == null) {
// 若插入的是头节点
Node<E> newNode = new Node(e, this.foot, this.head);
// 当头节点前驱指针指向新节点
this.head.pre = newNode;
// 尾节点的后续指针指向新节点
this.foot.next = newNode;
// 新节点作为头节点
this.head = newNode;
} else {
// 新节点,下一个节点指向 next,上一个节点指向 cur
Node<E> newNode = new Node(e, cur, next);
// 当前节点后续指针指向新节点
cur.next = newNode;
// 下一个节点前驱指针指向新节点
next.pre = newNode;
}
// 节点大小加一
this.size++;
// 操作成功
return true;
}
/**
* 查询离头或根节点最近的节点
*
* @return int
* @author 阿导
* @time 2019/11/19 :00
*/
public int indexOf(E e) {
// 记录位置
int pox = 0;
// 获取头节点
Node<E> curNext = this.head;
Node<E> curPre = this.foot;
// 获取最多访问次数
int n = (this.size + 1) / 2;
// 遍历节点
while (pox < n) {
// 若查询到节点,则返回位置
if ((curNext.e == null && e == null) || e != null && e.equals(curNext.e)) {
return pox;
}
if ((curPre.e == null && e == null) || e != null && e.equals(curPre.e)) {
return this.size - pox - 1;
}
// 下个节点走起
curNext = curNext.next;
curPre = curPre.pre;
pox++;
}
// 表示未找到
return -1;
}
/**
* 移除某个位置的节点
*
* @param index
* @return E
* @author 阿导
* @time 2019/11/19 :00
*/
public E remove(int index) {
// 判断插入的位置是否合法
this.indexOutOfBoundsException(index);
// 获取最多访问次数
int n = this.size / 2;
// 记录位置
int pox = 0;
// 记录上一个节点
Node<E> curPre = this.foot;
// 获取头节点
Node<E> curNext = this.head;
// 若是离头节点比较近
if (index < n) {
while (pox++ < index) {
curPre = curNext;
curNext = curNext.next;
}
} else {
while (pox++ < this.size - index) {
curNext = curPre;
curPre = curPre.pre;
}
}
// 保留删除的节点
E e = curNext.e;
// 若是头节点
if (curNext.equals(this.head)) {
// 若是删除头节点,直接将头节点指向头节点的下一个节点即可
if (this.size == 1) {
this.head = null;
this.foot = null;
} else {
this.head = this.head.next;
this.head.pre = this.foot;
this.foot.next = this.head;
}
} else if (curNext.equals(this.foot)) {
e = curPre.e;
// 若是尾节点
this.foot = this.foot.pre;
this.foot.next = this.head;
this.head.pre = this.foot;
} else {
curPre.next = curNext.next;
curNext.next.pre = curPre;
}
// 节点大小减一
this.size--;
return e;
}
/**
* 移除链表上某个元素
*
* @param e
* @return E
* @author 阿导
* @time 2019/11/19 :00
*/
public E remove(E e) {
int index = this.indexOf(e);
// 未查询到不做任何处理,直接返回
if (index == -1) {
return e;
}
// 移除元素
remove(index);
// 直到所有的元素都删除
return remove(e);
}
/**
* 修改内容
*
* @param index
* @param e
* @return void
* @author 阿导
* @time 2019/11/20 :00
*/
public void set(int index, E e) {
// 判断插入的位置是否合法
this.indexOutOfBoundsException(index);
// 获取最多访问次数
int n = (this.size + 1) / 2;
// 记录位置
int pox = 0;
Node<E> cur = this.head;
// 若是离头节点比较近
if (index < n) {
while (pox++ < index) {
cur = cur.next;
}
} else {
cur = this.foot;
while (pox++ < this.size - index - 1) {
cur = cur.pre;
}
}
// 替换元素
cur.e = e;
}
/**
* 重写 toString
*
* @return java.lang.String
* @author 阿导
* @time 2019/11/20 :00
*/
@Override
public String toString() {
// 声明结果
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
// 当前节点
Node<E> cur = this.head;
// 遍历节点
while (!cur.equals(this.foot)) {
// 获取当前节点元素
sb.append(cur.e);
// 是否需要连接符号
sb.append("->");
// 指针指向下一个节点
cur = cur.next;
}
sb.append(this.foot.e);
// 返回结果
return sb.toString();
}
/**
* 判断元素是否存在
*
* @param e
* @return boolean
* @author 阿导
* @time 2019/11/19 :00
*/
public boolean contains(E e) {
return this.indexOf(e) > -1;
}
/**
* 判断是否为空
*
* @return boolean
* @author 阿导
* @time 2019/11/19 :00
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.size == 0;
}
/**
* 查找指定位置的数据
*
* @param index
* @return E
* @author 阿导
* @time 2019/11/19 :00
*/
public E getData(int index) {
this.indexOutOfBoundsException(index);
// 记录位置
int pox = 0;
Node<E> cur = this.head;
// 查找指定位置
while (pox++ < index) {
cur = cur.next;
}
return cur.e;
}
/**
* 转换成数组
*
* @return E[]
* @author 阿导
* @time 2019/11/19 :00
*/
public Object[] toArray() {
// 存储结果
Object[] obj = new Object[this.size];
// 获取头节点
Node<E> cur = this.head;
// 记录位置
int pox = 0;
// 遍历节点
while (cur != null) {
// 获取元素
obj[pox++] = cur.e;
// 指向下一个节点
cur = cur.next;
}
// 返回结果
return obj;
}
/**
* 获取链表大小
*
* @return int
* @author 阿导
* @time 2019/11/19 :00
*/
public int size() {
return this.size;
}
/**
* 清空链表
*
* @author 阿导
* @time 2019/11/20 :00
* @return void
*/
public void clear(){
this.head = null;
this.foot = null;
this.size = 0;
}
/**
* 判断是否越界
*
* @param index
* @return void
* @author 阿导
* @time 2019/11/19 :00
*/
private void indexOutOfBoundsException(int index) {
if (index >= this.size || index < 0) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("位置越界!!!");
}
}
}
结束语
作为一个java 从业者,我们需要了解的是 LinkedList,查看源码即可知道,节点的定义和我这里面说的双向链表一致,所以它也是一个双向链表,一般面试官都喜欢问的话题就是拿它和顺序表进行对比,也就是 ArrayList(通过数组实现),他们都实现了 List 和 Collection 接口,具体类图如下所示,他们的区别在本文开篇基本已阐述,此处不再赘述。

不知各位看官对链表是否有一定的了解,如有疑问,欢迎留言,如有不当之处,请多多包涵和指教!
























 563
563

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








