树的基础知识
树的定义:
- 树包含n(n ≥\ge≥ 0 )个节点,n = 0时称为空树。
- 在树的结构关系中,有且仅有一个节点没有前趋节点,这个节点称为树的根节点。
- 除根节点外,树中其他的节点有且仅有一个前趋节点,但可以有很多后继节点。如图,A为根节点。
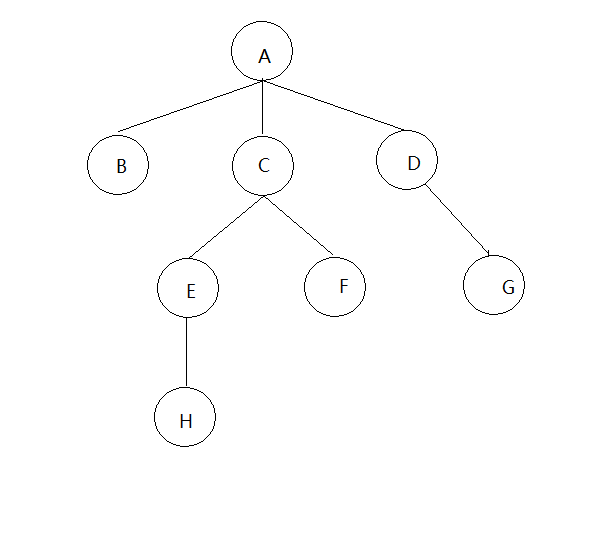
树的基本术语:
- 结点的度:每个节点具有的子树的个数(后继节点的个数)称为该节点的度;A的度为3,B的度为0。
- 树的度:树中所有节点的度的最大值;图中树的度为3。
- 分枝节点:度大于0的节点。
- 叶子节点:度为0的节点;如B、H、F、G。
- 孩子节点:一个节点的后继称为该节点的孩子节点;B为A的孩子节点。
- 父亲节点:一个节点的前趋称为该节点的父亲节点;A为B的父亲节点。
- 子孙节点:一个节点的所有子树中的节点称为该节点的子孙节点。
- 祖先节点:从树根节点到达某个节点的路径上所通过的所有节点称为该节点的祖先节点。
- 兄弟节点:具有相同父亲节点的节点;B、C、D为兄弟节点。
- 节点的层数:从上到下,根为第一层。
- 树的深度:树中节点的最大层数称为树的深度或高度;图中树深为4。
###二叉树的定义:二叉树是指树的度为2的有序树。左边的为左子树,右边的为右子树。
###如图所示:
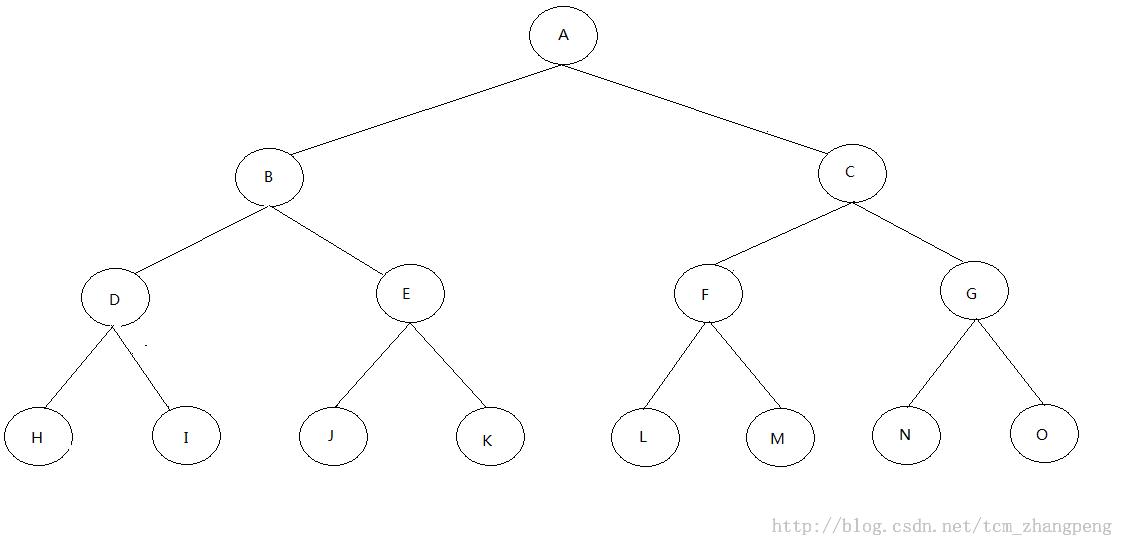
###二叉树的性质:
- 二叉树上叶子节点数等于度为2的节点数加1。
- 二叉树上第i层上最多有2i−12^{i - 1}2i−1个节点(i ≥\ge≥ 1)。
- 深度为h的二叉树最多有2h+1−12^{h+1} -12h+1−1个节点。
二叉树的遍历:
- 二叉树的先序遍历:先遍历根节点,再遍历左子树,再遍历右子树。
- 二叉树的中序遍历:先遍历左子树,再遍历根节点,再遍历右子树。
- 二叉树的后序遍历:先便利左子树,再遍历右子树,再遍历根节点。
- 二叉树的层次遍历:从上到下逐层遍历,根节点为第一层。
先序遍历为:A BDHIEJK - CFLMGNO
中序遍历为:HDIBJEK A LFMCNGO
后序遍历为:HIDJKEB - LMFNOGC A
层次遍历为:A BCDEFGHIJKLMNO
然后,建立二叉树。先序遍历、中序遍历、后序遍历、层次遍历。
Input:
ABDH##I##EJ##K##CFL##M##GN##O##
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
char data;
node *lchild,*rchild;
};
node *insert()//建立二叉树
{
char ch;
scanf("%c",&ch);
node *current;
if(ch=='#')
current=NULL;
else
{
current=new node;
current->data=ch;
current->lchild=insert();
current->rchild=insert();
}
return current;
}
void pre(node *root)//先序遍历
{
if (root)
{
printf("%c ",root->data);
pre(root->lchild);
pre(root->rchild);
}
}
void in(node *root)//中序遍历
{
if (root)
{
in(root->lchild);
printf("%c ",root->data);
in(root->rchild);
}
}
void post(node *root)//后序遍历
{
if (root)
{
post(root->lchild);
post(root->rchild);
printf("%c ",root->data);
}
}
void bfs(node *root)//层次遍历1
{
queue<node*>v;
v.push(root);
while (!v.empty())
{
root=v.front();
v.pop();
printf("%c ",root->data);
if (root->lchild!=NULL)
v.push(root->lchild);
if (root->rchild)
v.push(root->rchild);
}
}
// void bfs(node *root)//层次遍历2
// {
// if (root==NULL)
// {
// return ;
// }
// queue<node*>v;
// while (true)
// {
// if (root->lchild!=NULL)
// v.push(root->lchild);
// if (root->rchild!=NULL)
// v.push(root->rchild);
// printf("%c ",root->data);
// if (v.empty())
// break;
// root=v.front();
// v.pop();
// }
// }
int main()
{
node *root=insert();
printf("pre::\n");
pre(root);
printf("\nin::\n");
in(root);
printf("\npost::\n");
post(root);
printf("\nbfs\n");
bfs(root);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
二叉树的重建
- 已只二叉树的先序遍历和中序遍历,可重建二叉树;
- 已知二叉树的后序遍历和中序遍历,可重建二叉树;
- 已知二叉树的先序遍历和后序遍历不能重建二叉树,因为无法确定左子树和右子树,所以重建所得二叉树不唯一。
####1.后序遍历 +++ 中序遍历 ↦\mapsto↦ 重建二叉树:
- 递归创建,后序遍历的最后一个节点即为根节点root。每次先取出后序遍历的最后一个节点ch=last[len-1],然后在中序遍历的序列中查找while(ch!=mid[index]),找到后就为根节点申请内存,将值赋给根节点。然后就递归创建左子树、右子树。
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
struct node
{
char data;
node *lchild,*rchild;
};
///中序+后序->二叉树
void re(char *last,char *mid,node *&root,int len)///node *&root根节点的引用作为形参
{
if (len==0)//创建完成后返回
{
root=NULL;
return ;
}
int index=0;
char ch=last[len-1];//取出后序遍历序列的最后一个节点,即为根节点root
while (mid[index]!=ch)//在中序遍历序列中查找根节点root
{
index++;
}
root=new node;
root->data=mid[index];
re(last,mid,root->lchild,index);//递归创建左子树
re(last+index,mid+index+1,root->rchild,len-index-1);//递归创建右子树
}
void pre(node *root)
{
if (root)
{
printf("%c",root->data);
pre(root->lchild);
pre(root->rchild);
}
}
void del(node *root)
{
if (root==NULL)
return ;
del(root->lchild);
del(root->rchild);
free(root);
}
int main()
{
char last[30],mid[30];
while (scanf("%s%s",last,mid)!=EOF)
{
node *root=NULL;
int len=strlen(last);
re(last,mid,root,len);
pre(root);
printf("\n");
del(root);
}
return 0;
}
####2.先序遍历+++中序遍历 ↦\mapsto↦ 重建二叉树:
- 递归创建,先序遍历的第一个节点即为根节点root。每次先取出先序遍历的第一个节点ch=first[0],然后在中序遍历的序列中查找while(ch!=mid[index]),找到后就为根节点申请内存,将值赋给根节点。然后就递归创建左子树、右子树。
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
struct node
{
char data;
node *lchild,*rchild;
};
//先序遍历+中序遍历->二叉树
void re(char *first,char *mid,node *&root,int len)
{
if (len==0)
{
root=NULL;
return ;
}
int index=0;
char ch=first[0];
while (ch!=mid[index])
{
index++;
}
root=new node;
root->data=mid[index];
re(first+1,mid,root->lchild,index);
re(first+index+1,mid+index+1,root->rchild,len-index-1);
}
void post(node *root)
{
if (root)
{
post(root->lchild);
post(root->rchild);
printf("%c",root->data);
}
}
void del(node *root)
{
if (root==NULL)
{
return ;
}
del(root->lchild);
del(root->rchild);
free(root);
}
int main()
{
char first[33],mid[33];
while(scanf("%s%s",first,mid)!=EOF)
{
node *root=NULL;
int len=strlen(first);
re(first,mid,root,len);
post(root);
puts("");
del(root);
}
return 0;
}
####PS:引自考研大纲解析38页:
树的深度是↓从根节点开始(其深度为1)自顶向下逐层累加的。
树的高度是↑从叶节点开始(其高度为1)自底向上逐层累加的。
虽然树的深度和高度一样,但是具体到树的某个节点,其深度和高度是不一样的。 我的理解是:非根非叶结点的深度是从根节点数到它的,高度是从叶节点数到它的。
int FindTreeDeep(BinTree BT)
{
int deep=0;
if(BT)
{
int lchilddeep=FindTreeDeep(BT->lchild);
int rchilddeep=FindTreeDeep(BT->rchild);
deep=lchilddeep>=rchilddeep?lchilddeep+1:rchilddeep+1;
}
return deep;
}
























 464
464

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








