注:本文为 “网络设备” 相关文章合辑。
机翻,未校。
Network Devices (Repeater, Hub, Bridge, NIC, Switch, Router and Gateway)
In this tutorial, you will learn about the concept of Network Devices (Repeater, Hub, Bridge, NIC, Switch, Router and Gateway). After reading this tutorial, you will get some basic idea about which device works on which layer, how it works, what are its advantages and disadvantages, etc.
在本教程中,您将了解网络设备(中继器、集线器、桥接器、网卡、交换机、路由器和网关)的概念。阅读本教程后,您将了解哪个设备在哪个层工作、它是如何工作的、它的优点和缺点是什么等的一些基本概念。
Roles of Network Devices 网络设备的角色
Generally, network devices are responsible for communication over a network. How the user will connect to the network, which path to choose to send the data, and to whom to send the data are the basic responsibilities of the network devices.
通常,网络设备负责通过网络进行通信。用户将如何连接到网络,选择以哪条路径发送数据,以及向谁发送数据是网络设备的基本职责。
- A network cannot be created without network devices. Each network device has its own responsibilities and functions.
没有网络设备,就无法创建网络。每个网络设备都有自己的职责和功能。 - Network devices operate in different layers, and they use different information needed for communication.
网络设备在不同的层中运行,它们使用通信所需的不同信息。
The figure below shows the different network devices that operate on different layers.
下图显示了在不同层上运行的不同网络设备。

As shown in the figure, different network devices operate on different layers on which they interpret different pieces of information.
如图所示,不同的网络设备在不同的层上运行,它们在其上解释不同的信息片段。
The network devices are as follows:
网络设备如下:
-
Repeater and Hub 中继器和集线器
-
Bridge, NIC, and Switch 网桥、网卡和交换机
-
Router 路由器
-
Firewall 防火墙
-
Gateway 网关
-
Client and Server 客户端和服务器
Repeater and Hub 中继器和集线器
Repeaters and hubs are physical layer devices. Both devices are used as connection devices at the physical layer. Let us understand these two devices one by one.
中继器和集线器是物理层设备。这两个设备都用作物理层的连接设备。让我们一一了解这两种设备。
Repeater: The repeater only works in the physical layer. Repeaters are used to regenerate weak signals.
中继器:中继器仅在物理层工作。中继器用于再生微弱信号。
-
When the sender sends a signal over a network, it travels a certain distance. There is a repeater between the sender and the receiver that receives the signal sent by the sender before it becomes weak or corrupted and reproduces the original bit pattern. After that, the repeater sends the newly created refresh signal to the receiver.
当发送者通过网络发送信号时,它会传播一定的距离。发送器和接收器之间有一个中继器,该中继器在发送器变弱或损坏之前接收发送器发送的信号,并再现原始位模式。之后,中继器将新创建的刷新信号发送到接收器。 -
When the cable covers a short distance, we split the cable into segments and install a repeater between the segments. The repeater performs the function of a two-port node.
当电缆覆盖一小段时,我们将电缆分成几段,并在两段之间安装中继器。中继器执行双端口节点的功能。 -
The main disadvantage of the repeater is that it forwards each frame received on the ports, as it has no filtering capability.
中继器的主要缺点是它转发端口上接收到的每个帧,因为它没有过滤功能。 -
Furthermore, the repeater is a regenerator, not an amplifier.
此外,中继器是再生器,而不是放大器。
The diagram below shows the functionality of the repeater on the network.
下图显示了中继器在网络上的功能。
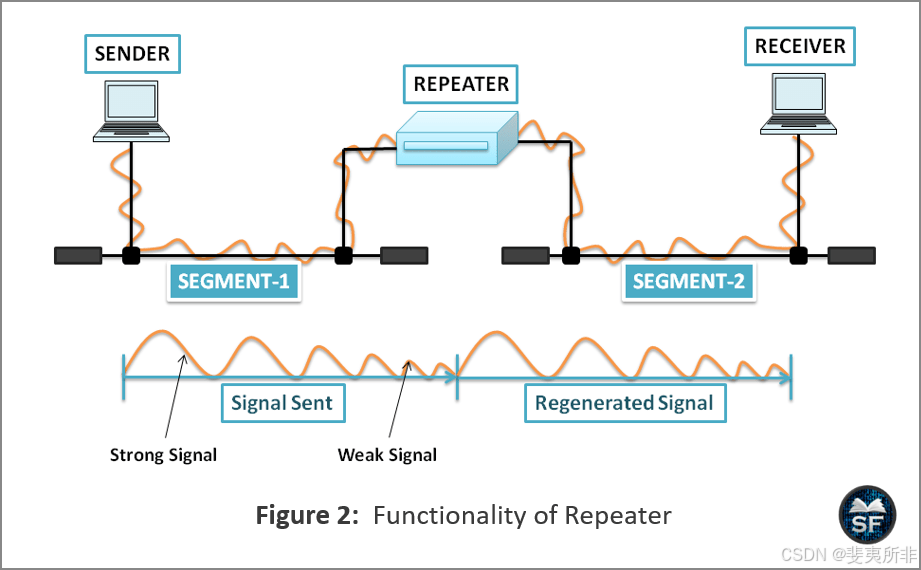
- As shown in the figure, there is a repeater between the sender and the receiver. When the sender sends a signal to the receiver, the signal strength starts decreasing during transmission.
如图所示,发送方和接收方之间有一个中继器。当发送者向接收器发送信号时,信号强度在传输过程中开始降低。 - The repeater receives the signal before the signal is too weak or corrupted, reproduces it, and sends it to the receiver.
中继器在信号太弱或损坏之前接收到信号,再现它,并将其发送到接收器。 - It also shows that the repeater does not connect two LANs, but it connects two segments, increasing the physical length of the LAN.
它还表明,中继器不连接两个局域网,而是连接两个段,增加了局域网的物理长度。
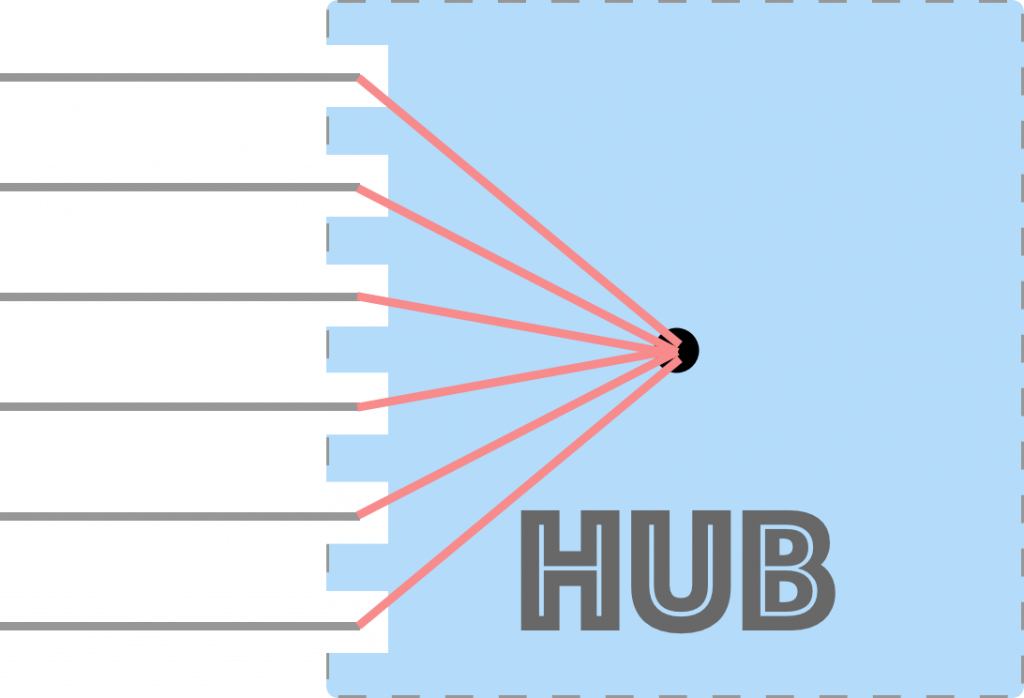
Hub: The hub operates at the physical layer and is the hardware-based device. The main difference between hub and repeater is that the repeater has two ports for two devices, whereas the hub has multiple ports (4 to 48). Hence, the hub is known as a multiport repeater.
集线器:集线器在物理层运行,是基于硬件的设备。集线器和中继器之间的主要区别在于,中继器有两个端口用于两个设备,而集线器有多个端口(4 到 48 个)。因此,该集线器被称为多端口中继器。
-
Hubs are used to form a star topology on a network that connects multiple devices.
集线器用于在连接多个设备的网络上形成星形拓扑。 -
If a cable is damaged during transmission, the hub can detect cable damage. This functionality is not present in the repeater.
如果电缆在传输过程中损坏,集线器可以检测到电缆损坏。中继器中不存在此功能。 -
If a device wants to communicate with another device and both are connected with the help of a hub, then the hub provides a forwarding feature to forward the message from one device to another. But it cannot filter messages because it is hardware-based. If one device sends a message to another device, the hub will broadcast the message to all devices connected to it.
如果一个设备想要与另一个设备通信,并且两个设备都在集线器的帮助下连接,则集线器提供转发功能,用于将消息从一个设备转发到另一个设备。但它无法过滤消息,因为它是基于硬件的。如果一台设备向另一台设备发送消息,集线器会将消息广播到连接到它的所有设备。 -
If more than one device transmits the signal to the hub, the collision occurs inside the hub.
如果多个设备将信号传输到集线器,则会在集线器内部发生冲突。 -
The CSMA/CD algorithm is not required for collision detection when the hub uses full-duplex mode over a point-to-point connection.
当集线器通过点对点连接使用全双工模式时,冲突检测不需要 CSMA/CD 算法。 -
Passive Hub and Active Hub are the two types of hubs.
被动集线器和主动集线器是两种类型的集线器。 -
Passive Hub: Passive Hub operates below the physical layer and is a connector that connects wires coming from different devices.
无源集线器:无源集线器在物理层以下运行,是一种连接器,用于连接来自不同设备的电线。 -
Active Hub: It works at the physical level. It is a multiport repeater and is used on the network to form the star topology.
Active Hub:它在物理级别工作。它是一个多端口中继器,在网络上用于形成星形拓扑。
The figure below shows the structure of the hub.
下图显示了轮毂的结构。

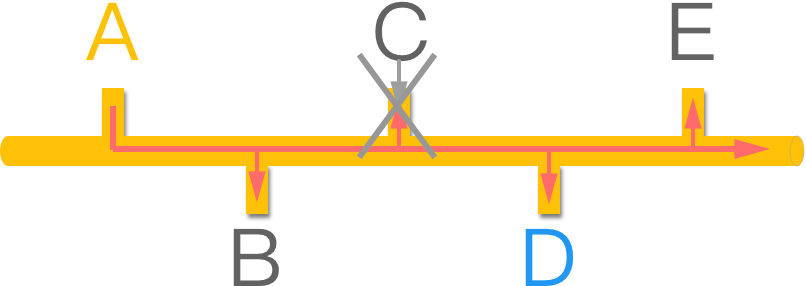
- As shown in the figure, five devices are connected to the hub. PC-1 wants to send data to PC-3, so it forwards to the hub. Hub is a hardware device, so it doesn’t understand IP or MAC addresses. It transmits data to all devices. So, we can say that hub does not provide filtering.
如图所示,有 5 台设备连接到集线器。PC-1 想要将数据发送到 PC-3,因此它转发到中心。Hub 是一种硬件设备,因此它无法识别 IP 或 MAC 地址。它将数据传输到所有设备。因此,我们可以说 hub 不提供过滤。 - In the second scenario, all devices simultaneously send data to the hub, so all data will collide and be lost.
在第二种情况下,所有设备同时向集线器发送数据,因此所有数据都会发生冲突并丢失。
Bridges, NIC, and Switches 网桥、网卡和交换机
Bridge, NIC, and Switch are data link layer devices. All three are important for the data link layer to function.
网桥、网卡和交换机是数据链路层设备。这三者对于数据链路层的运行都很重要。
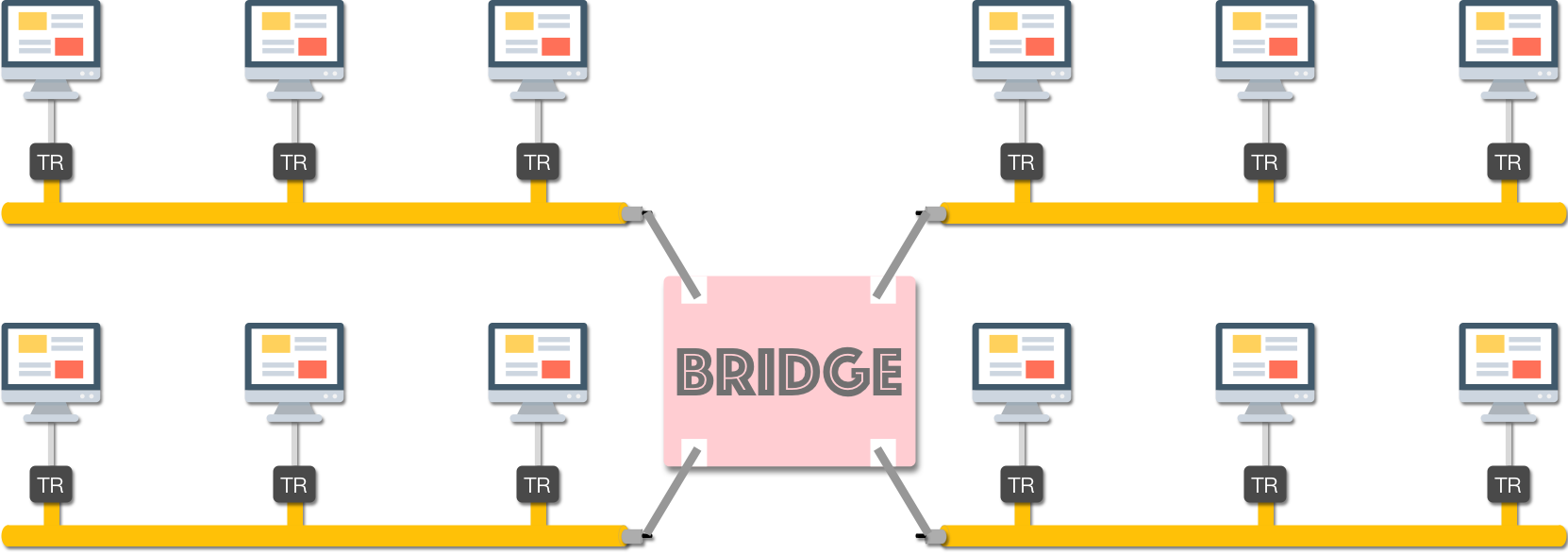
Bridge: The bridge is a hardware as well as software-based device and operates at both physical and data link layers. The bridge checks the MAC addresses of the source and destination in the data link layer, while in the physical layer, the bridge is used to reproduces signals.
桥接器:桥接器是一种基于硬件和软件的设备,在物理层和数据链路层都运行。桥接器在数据链路层检查源和目标的MAC地址,而在物理层中,桥接器用于再现信号。
- The bridge device acts as a bridge between two LANs and helps to connect them to transmit data with each other.
桥接设备充当两个局域网之间的桥梁,并帮助连接它们以相互传输数据。 - Bridge has filtering functionality. With the help of filtering, the bridge filters the MAC address of the destination and decides whether to transmit or drop the frame.
Bridge 具有过滤功能。在过滤的帮助下,桥接器过滤目的地的MAC地址,并决定是传输帧还是丢弃帧。
The diagram below shows the structure of the bridge.
下图显示了桥梁的结构。

As shown in the figure, a bridge connects two different LANs to communicate. LAN-1 devices can send frames to LAN-2 via the bridge so that the bridge decides where to send the frame in LAN-2 according to the MAC address of the destination.
如图所示,一个网桥连接两个不同的局域网进行通信。LAN-1 设备可以通过网桥将帧发送到 LAN-2,以便网桥根据目标的 MAC 地址决定将帧发送到 LAN-2 中的哪个位置。
NIC (Network Interface Card): NIC stands for Network Interface Card and is used to connect devices to the network via media. Each NIC has a 48-bit number, known as a MAC address. The MAC address is designed in such a way that no two devices have the same NIC address to avoid collisions on the LAN.
NIC(网络接口卡):NIC代表网络接口卡,用于通过媒体将设备连接到网络。每个 NIC 都有一个 48 位数字,称为 MAC 地址。MAC 地址的设计方式是,没有两个设备具有相同的 NIC 地址,以避免 LAN 上的冲突。
-
Normally, NICs don’t know anything about IP addresses. They use the MAC address of the sender and receiver to send a frame.
通常,NIC 对 IP 地址一无所知。它们使用发送方和接收方的MAC地址来发送帧。 -
NIC is a hardware device that performs the operations of the data link layer as well as a physical layer.
NIC 是一种硬件设备,用于执行数据链路层和物理层的操作。
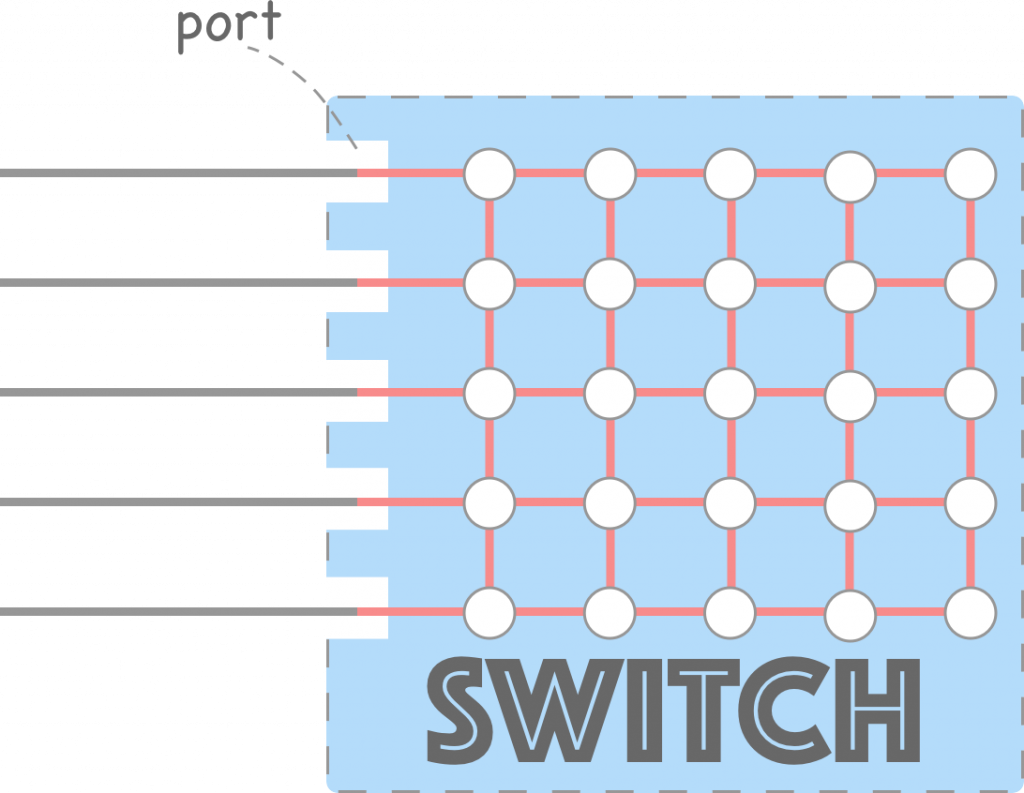
Switch: A switch is a bridge, but it has better performance than a bridge. Classic Ethernet used a bridge but then switched networks came, which become more popular these days. It looks like a hub.
交换机:交换机是桥接器,但它比桥接器具有更好的性能。经典以太网使用桥接器,但后来交换网络出现了,如今这种网络变得越来越流行。它看起来像一个中心。
-
Switches have multi-ports to which devices can be connected using twisted pair cables.
交换机具有多个端口,可以使用双绞线电缆将设备连接到这些端口。 -
Switches can be classified in two ways, layer-2 switches, and layer-3 switches. Layer-2 and Layer-3 switches are used at the data link layer and the network layer, respectively.
交换机可以分为二层交换机和三层交换机两种分类方式。二层交换机和三层交换机分别用于数据链路层和网络层。 -
Layer-2 switches allow better performance over the network than bridges, connecting multiple devices and making filtering decisions based on the MAC address of the frame it receives.
与网桥相比,第 2 层交换机在网络上提供更好的性能,可连接多个设备并根据其接收的帧的 MAC 地址做出过滤决策。 -
Layer-2 switches also have a buffer that holds frames until the switch detects the destination and has processed the frame.
第 2 层交换机还具有一个缓冲区,用于保存帧,直到交换机检测到目标并处理帧。 -
The layer-3 switch is used as a router at the network layer, which has faster processing power. It rapidly checks the address of the frame and finds the MAC address from the table, if available.
三层交换机在网络层充当路由器,处理能力更快。它会快速检查帧的地址,并从表中查找 MAC 地址(如果可用)。
The figure below explains the connection of hosts through a switch in the same LAN.
下图说明了通过同一局域网中的交换机连接主机。

As shown in the figure, switches are used to connect multiple devices on the same LAN. Switches have multi-ports to which each device connects with a twisted pair cable. It supports Ethernet standards such as Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet.
如图所示,交换机用于连接同一局域网上的多个设备。交换机具有多个端口,每个设备都通过双绞线电缆连接到这些端口。它支持以太网标准,例如快速以太网和千兆以太网。
Router and its Functions 路由器及其功能
A router is a hardware and software-based device, like a switch. It works at the network layer and forwards the packets on the network based on the IP address.
路由器是一种基于硬件和软件的设备,如交换机。它工作在网络层,根据IP地址在网络上转发数据包。
-
The router is a device that helps to connect a LAN to the Internet.
路由器是一种有助于将 LAN 连接到 Internet 的设备。 -
When the router receives a frame from the device, it de-encapsulates the frame and finds the IP packet. Then, the router examines the IP packet, which stores the destination IP address. Based on the IP address of the destination, it decides path, re-encapsulates the frame in WAN format, and sends it to the next device or destination for further processing.
当路由器从设备接收到帧时,它会解封装该帧并找到 IP 数据包。然后,路由器检查存储目标 IP 地址的 IP 数据包。根据目标的 IP 地址,它确定路径,以 WAN 格式重新封装帧,并将其发送到下一个设备或目的地进行进一步处理。 -
The router understands both versions of IP that are IPv4 (32-bit) and IPv6 (128-bit).
路由器可识别 IPv4(32 位)和 IPv6(128 位)的 IP 版本。 -
Router finds a route to send packets and creates a routing table according to IP address. It ensures the optimal path for sending packets from sender to receiver.
Router找到发送数据包的路由,并根据IP地址创建路由表。它确保了将数据包从发送方发送到接收方的最佳路径。
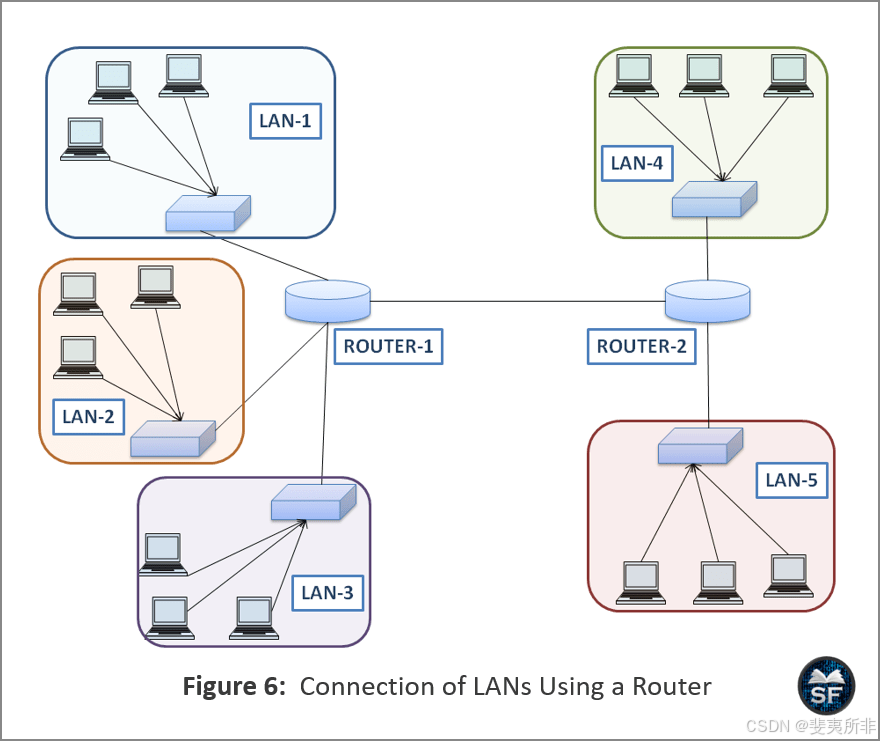
The diagram below explains the connection of LANs using a router.
下图说明了使用路由器连接LAN的方法。
-
As shown in the figure, the router helps the various LANs to connect to the Internet. In the above figure, 3 LANs are connected to Router-1, and Router-1 is connected to Router-2, which is live on a network.
如图所示,路由器帮助各种局域网连接到Internet。在上图中,3 个 LAN 连接到 Router-1,Router-1 连接到 Router-2,Router-2 在网络上处于活动状态。 -
So that, if a LAN connected to Router-1 wants to send data to a LAN connected to Router-2, sends the packet to the router, and the router will forward the packet through the interface.
这样,如果连接到Router-1的LAN想要向连接到Router-2的LAN发送数据,则将数据包发送到路由器,路由器将通过接口转发数据包。
Firewall and Its Types 防火墙及其类型
A firewall is a device that ensures the security of a LAN. A firewall protects the LAN by filtering out bad and good packets and prevents unwanted packets from entering the LAN.
防火墙是确保局域网安全的设备。防火墙通过过滤掉坏数据包和好数据包来保护 LAN,并防止不需要的数据包进入 LAN。
- A firewall protects users or organizations from external threats by preventing unwanted traffic from entering the internal network.
防火墙通过阻止不需要的流量进入内部网络来保护用户或组织免受外部威胁。 - A firewall is located between two or more networks, which prevents unauthorized access.
防火墙位于两个或多个网络之间,可防止未经授权的访问。 - The network administrator enforces a specific policy for a server called a demilitarized zone server (DMZ server), which is located outside the internal network so that it can access the internal network, even if the network is protected by a firewall.
网络管理员对称为“隔离区服务器”(DMZ 服务器)的服务器强制实施特定策略,该服务器位于内部网络外部,以便可以访问内部网络,即使网络受防火墙保护也是如此。
The figure below shows the firewall topology.
下图显示了防火墙拓扑。
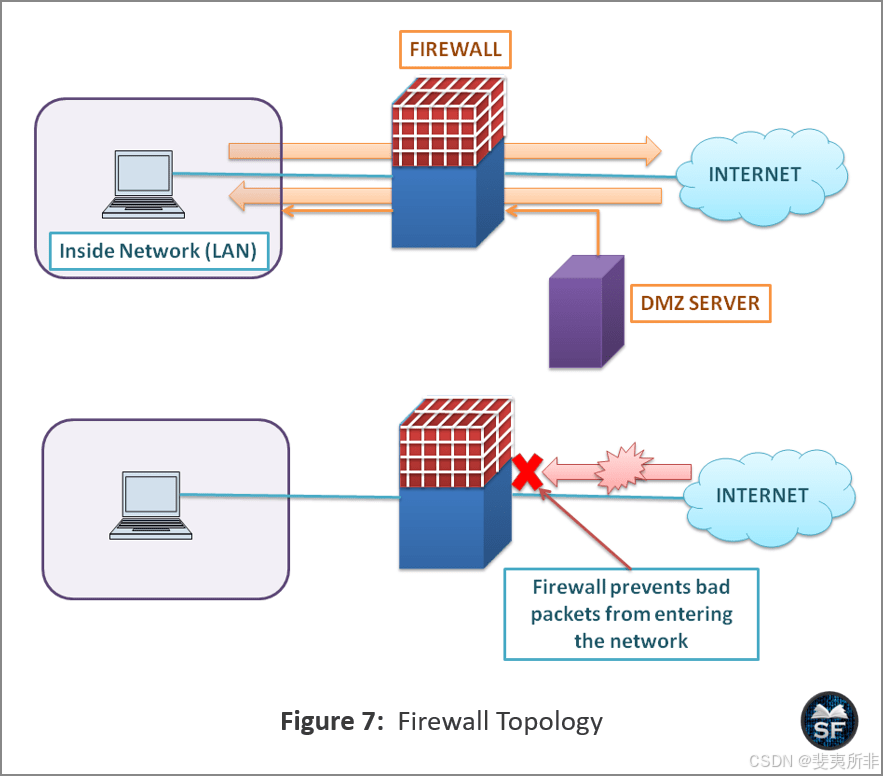
- As shown in the figure, LAN is protected by a firewall. The firewall blocked external traffic from accessing the resources of LAN.
如图所示,局域网受到防火墙的保护。防火墙阻止了外部流量访问 LAN 的资源。 - Also, the DMZ server can access LAN because it is configured by the network administrator and has implemented a specific policy.
此外,DMZ 服务器可以访问 LAN,因为它由网络管理员配置并已实施特定策略。
Four types of firewalls are as follows:
四种类型的防火墙如下:
-
IP or MAC-based filtering: Firewall filters packets based on IP and MAC address.
基于 IP 或 MAC 的过滤:防火墙根据 IP 和 MAC 地址过滤数据包。 -
Port-based filtering: The firewall checks the port number and denies the device if the port number is not allowed to access the internal network.
基于端口的过滤:防火墙会检查端口号,如果不允许端口号访问内部网络,则拒绝设备。 -
URL Filtering: Filter by browser URL or specific keywords.
URL 过滤:按浏览器URL或特定关键字过滤。 -
Stateful Packet Inspection (SPI): Filter attacks such as Denial of Service (DoS).
状态数据包检测 (SPI):过滤拒绝服务 (DoS) 等攻击。
Transport Gateways and Application Gateways 传输网关和应用程序网关
We can consider the gateway as a computer. A computer that operates on all layers of the OSI reference model. Gateway works at Transport Layer and Application Layer. Devices using different models for communication can be connected using gateways.
我们可以将网关视为一台计算机。在 OSI 参考模型的所有层上运行的计算机。网关工作在传输层和应用层。使用不同型号进行通信的设备可以使用网关进行连接。
Transport Gateways: A transport gateway connects two devices that use different connection-oriented protocols.
传输网关:传输网关连接使用不同面向连接的协议的两个设备。
-
It helps the device to communicate with the TCP/IP model using a connection-oriented protocol such as TCP or SCTP.
它帮助设备使用面向连接的协议(如 TCP 或 SCTP)与 TCP/IP 模型进行通信。 -
The transport gateway receives packets from the network layer and copies them from one connection to another. It copies in such a way that the packet format can be understood by the communicating devices.
传输网关接收来自网络层的数据包,并将它们从一个连接复制到另一个连接。它以这样一种方式进行复制,即通信设备可以理解数据包格式。
Application Gateways: The application gateway works at the application layer on which the user is interacting. The user generates the data, and the application gateway receives it. Upon receiving the data, the application gateway understands the format and translates it into another format if necessary.
应用程序网关:应用程序网关在用户交互的应用程序层工作。用户生成数据,应用程序网关接收数据。收到数据后,应用程序网关会理解该格式,并在必要时将其转换为另一种格式。
- For example, an image file is formatted in PNG, or JPEG, or TIFF, etc. The Video file is formatted in MP4, MKV, etc.
例如,图像文件的格式为 PNG、JPEG 或 TIFF 等。视频文件采用 MP4、MKV 等格式。 - Another example of formatting is email messages, in which the application gateway translates Internet messages into SMS messages to make them compatible with mobile phones.
格式化的另一个示例是电子邮件消息,其中应用程序网关将 Internet 消息转换为 SMS 消息,以使其与移动电话兼容。 - It also filters out unwanted application-layer messages that are not necessary and provides security.
它还可以过滤掉不需要的应用层消息,并提供安全性。
Client and Server 客户端和服务器
Client-server is a common and one of the most used mechanisms on the network. Client and server are network devices in which the client sends a request and the server gives a response.
客户端-服务器是网络上一种常见且最常用的机制之一。客户端和服务器是网络设备,其中客户端发送请求,服务器提供响应。
Client: A client is a computer that wants to access the Internet’s resources from the server. It generates the request and sends it to the server.
客户端:客户端是想要从服务器访问 Internet 资源的计算机。它生成请求并将其发送到服务器。
Server: A server is a network device that provides services to the client in the form of a response when a request is received from the client.
服务器:服务器是一种网络设备,当从客户端收到请求时,它以响应的形式向客户端提供服务。
- The server only provides the services that the client requests. It does not send security information to the client.
服务器仅提供客户端请求的服务。它不会向客户端发送安全信息。 - Both the client and the server use key mechanisms for authentication so that the server can authenticate to the client that it is authorized to use the services of the Internet.
客户端和服务器都使用密钥机制进行身份验证,以便服务器可以向客户端验证它有权使用 Internet 服务的权限。
The diagram below explains the client and server mechanism.
下图说明了客户端和服务器机制。
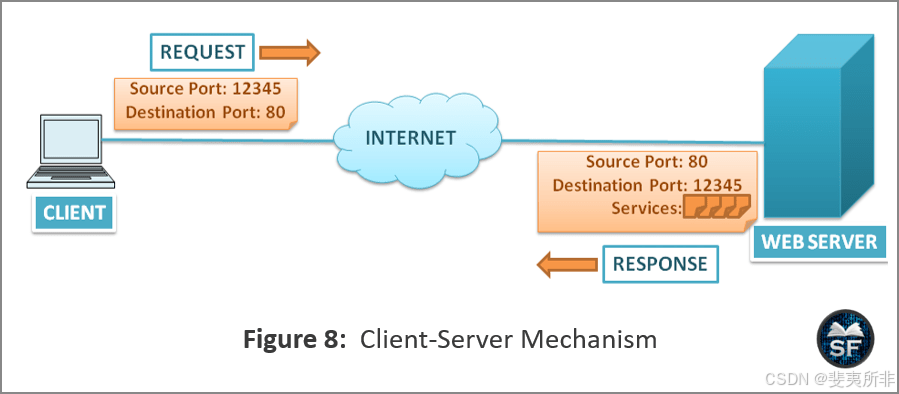
- As shown in the figure, the client wants to access the webpage from the server. So, it will generate a port number randomly from its side. In this case, the port number of the sender is 12345, which is generated randomly.
如图所示,客户端希望从服务器访问该网页。因此,它将从其一侧随机生成一个端口号。在这种情况下,发送方的端口号是12345,这是随机生成的。 - The client adds the destination port 80 in the TCP header, as the 80-port number is used for the HTTP request. After adding port number 80 as the destination, the client will send the TCP segment to the server as a request.
客户端在 TCP 标头中添加目标端口 80,因为 80 端口号用于 HTTP 请求。将端口号 80 添加为目标后,客户端会将 TCP 段作为请求发送到服务器。 - The server will identify the port number and assign the web services to the client as per port number 80 as a response.
服务器将识别端口号,并根据端口号 80 将 Web 服务分配给客户端作为响应。
Topology of Network Devices 网络设备的拓扑
We learned about network devices like hubs, bridges, switches, routers, gateways, firewalls, and NICs, etc. Now let’s understand the working of network devices together.
我们了解了网络设备,如集线器、网桥、交换机、路由器、网关、防火墙和 NIC 等。现在让我们一起了解网络设备的工作原理。
The diagram below explains the topology of various network devices.
下图说明了各种网络设备的拓扑结构。
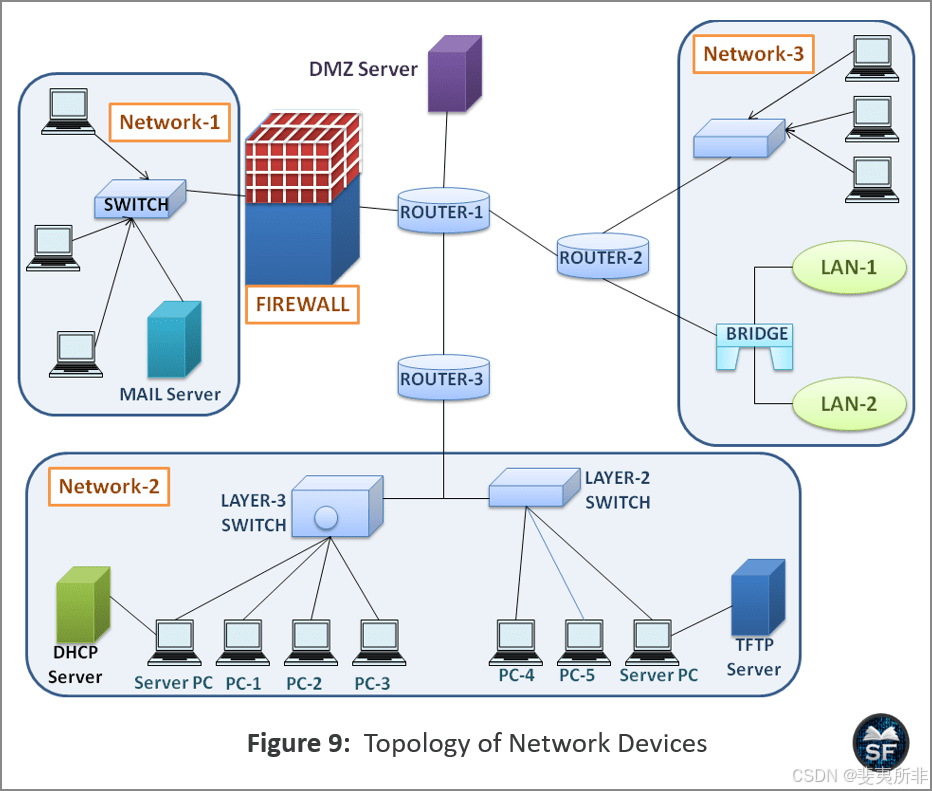
- As shown in the figure, all the devices in the LAN are connected through media to the switch port using NIC. The LAN is connected to the router so that the router connects the LAN to the live internet.
如图所示,局域网中的所有设备都通过媒体连接到使用网卡的交换机端口。LAN连接到路由器,以便路由器将LAN连接到实时Internet。 - LAN-1 is protected by a firewall, and the firewall is connected to the router that is connected to the DMZ server. Here, the firewall is used for filtering purposes and prevents bad packets from entering the internal network. However, the DMZ server can access LAN-1, which is protected by a firewall because the network administrator has applied specific policies to it.
LAN-1 受防火墙保护,防火墙连接到连接到 DMZ 服务器的路由器。在这里,防火墙用于过滤目的,并防止不良数据包进入内部网络。但是,DMZ 服务器可以访问 LAN-1,LAN-1 受防火墙保护,因为网络管理员已对其应用特定策略。 - All LANs are interconnected and can communicate with each other. For example, PC-1 in Network-2 wants to send data to PC-5, PC-1 transmits the data to Layer-3 Switch, Layer 3 Switch will forward the frame to Layer-2 Switch, and finally, Layer-2 Switch will forward the frame to PC-5.
所有局域网都是互连的,可以相互通信。例如,Network-2中的PC-1希望向PC-5发送数据,PC-1将数据传输到Layer-3交换机,Layer 3交换机将帧转发到Layer-2交换机,最后,Layer-2交换机将帧转发到PC-5。
Key Points to Remember 要记住的关键点
Here is the list of key points we need to remember about “Network Devices”.
以下是我们需要记住的有关“网络设备”的关键点列表。
- Network devices operate in different layers, and they use different information needed for communication.
网络设备在不同的层中运行,它们使用通信所需的不同信息。 - Repeater, Hub, Bridge, NIC, Switch, Router, Firewall, Gateway, Client, and Server are the network devices used on a network for communication.
中继器、集线器、网桥、网卡、交换机、路由器、防火墙、网关、客户端和服务器是网络上用于通信的网络设备。 - Repeaters and hubs are physical layer devices. Repeaters are used to regenerate weak signals. The hub is known as a multiport repeater.
中继器和集线器是物理层设备。中继器用于再生微弱信号。该集线器称为多端口中继器。 - Bridge, NIC, and Switch are data link layer devices. The bridge device acts as a bridge between two LANs and helps to connect them to transmit data with each other.
Bridge、NIC 和 Switch 是数据链路层设备。桥接设备充当两个局域网之间的桥梁,并帮助连接它们以相互传输数据。 - Switches can be classified in two ways, layer-2 switches, and layer-3 switches. Layer-2 and Layer-3 switches are used at the data link layer and the network layer, respectively.
交换机可以分为二层交换机和三层交换机两种分类方式。二层交换机和三层交换机分别用于数据链路层和网络层。 - A router is a hardware and software-based device, like a switch. It works at the network layer and forwards the packets on the network based on the IP address.
路由器是一种基于硬件和软件的设备,如交换机。它工作在网络层,根据IP地址在网络上转发数据包。 - A firewall protects the LAN by filtering out bad and good packets and prevents unwanted packets from entering the LAN.
防火墙通过过滤掉坏数据包和好数据包来保护 LAN,并防止不需要的数据包进入 LAN。 - Gateway works at Transport Layer and Application Layer. Devices using different models for communication can be connected using gateways.
网关工作在传输层和应用层。使用不同型号进行通信的设备可以使用网关进行连接。
Network Devices (Hub, Repeater, Bridge, Switch, Router, Gateways and Brouter)
网络设备(集线器、中继器、网桥、交换机、路由器、网关和路由器)
Last Updated : 09 Dec, 2024
Network devices are physical devices that allow hardware on a computer network to communicate and interact with each other. Network devices like hubs, repeaters, bridges, switches, routers, gateways, and brouters help manage and direct data flow in a network. They ensure efficient communication between connected devices by controlling data transfer, boosting signals, and linking different networks. Each device serves a specific role, from simple data forwarding to complex routing between networks. In this article, we are going to discuss different types of network devices in detail.
网络设备是允许计算机网络上的硬件相互通信和交互的物理设备。集线器、中继器、网桥、交换机、路由器、网关和路由器等网络设备有助于管理和指导网络中的数据流。它们通过控制数据传输、增强信号和链接不同的网络来确保连接设备之间的有效通信。每个设备都扮演着特定的角色,从简单的数据转发到网络之间的复杂路由。在本文中,我们将详细讨论不同类型的网络设备。
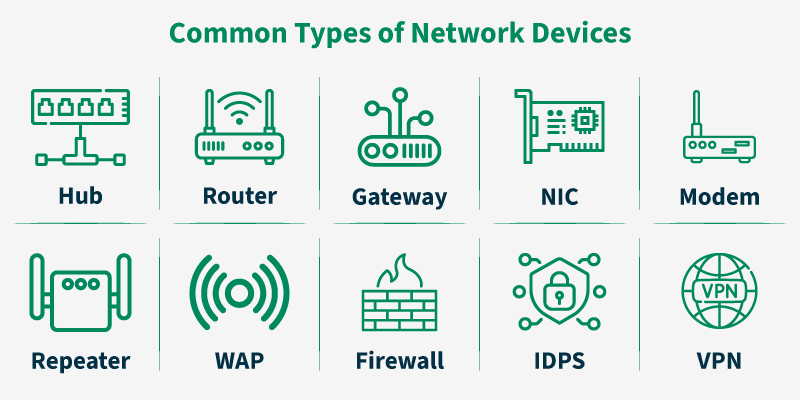
Types of Network Devices
网络设备的类型
Functions of Network Devices
网络设备的功能
- Network devices help to send and receive data between different devices.
网络设备有助于在不同设备之间发送和接收数据。 - Network devices allow devices to connect to the network efficiently and securely.
网络设备允许设备高效、安全地连接到网络。 - Network devices Improve network speed and manage data flow better.
网络设备 提高网络速度并更好地管理数据流。 - It protect the network by controlling access and preventing threats.
它通过控制访问和防止威胁来保护网络。 - Expand the network range and solve signal problems.
扩展网络范围并解决信号问题。
Common Types of Networking Devices and Their Uses
常见的网络设备类型及其用途
Network devices work as a mediator between two devices for transmission of data, and thus play a very important role in the functioning of a computer network. Below are some common network devices used in modern networks:
网络设备充当两个设备之间的中介,用于数据传输,因此在计算机网络的运行中起着非常重要的作用。以下是现代网络中使用的一些常见网络设备:
- Access Point 接入点
- Modems 调制解调器
- Firewalls 防火墙
- Repeater 中继 器
- Hub 集线器
- Bridge 桥
- Switch 交换机
- Routers 路由器
- Gateway 网关
- Brouter 路由器
- NIC 网卡

Access Point
An access point in networking is a device that allows wireless devices, like smartphones and laptops, to connect to a wired network. It creates a Wi-Fi network that lets wireless devices communicate with the internet or other devices on the network. Access points are used to extend the range of a network or provide Wi-Fi in areas that do not have it. They are commonly found in homes, offices, and public places to provide wireless internet access.
网络中的接入点是一种允许无线设备(如智能手机和笔记本电脑)连接到有线网络的设备。它创建一个 Wi-Fi 网络,允许无线设备与互联网或网络上的其他设备进行通信。接入点用于扩展网络范围或在没有 Wi-Fi 的区域提供 Wi-Fi。它们常见于家庭、办公室和公共场所,以提供无线互联网接入。
Modems
Modems is also known as modulator/demodulator is a network device that is used to convert digital signal into analog signal of different frequencies and transmits these signal to a modem at the receiving location. These converted signals can be transmitted over the cable systems, telephone lines, and other communication mediums. A modem is also used to convert analog signal back into digital signal. Modems are generally used to access internet by customers of an Internet Service Provider (ISP).
调制解调器也称为调制器/解调器,是一种网络设备,用于将数字信号转换为不同频率的模拟信号,并将这些信号传输到接收位置的调制解调器。这些转换后的信号可以通过电缆系统、电话线和其他通信介质传输。调制解调器还用于将模拟信号转换回数字信号。调制解调器通常由 Internet 服务提供商 (ISP) 的客户用于访问 Internet。
Types of Modems
There are four main types of modems:
调制解调器有四种主要类型:
- DSL Modem : Uses regular phone lines to connect to the internet but it is slower compared to other types.
DSL 调制解调器:使用普通电话线连接到互联网,但与其他类型的电话相比,它的速度较慢。 - Cable Modem : Sends data through TV cables, providing faster internet than DSL.
电缆调制解调器:通过电视电缆发送数据,提供比 DSL 更快的互联网。 - Wireless Modem : Connects devices to the internet using Wi-Fi relying on nearby Wi-Fi signals.
无线调制解调器:使用 Wi-Fi 将设备连接到互联网,具体取决于附近的 Wi-Fi 信号。 - Cellular Modem : Connects to the internet using mobile data from a cellular network not Wi-Fi or fixed cables.
蜂窝调制解调器:使用来自蜂窝网络的移动数据(而不是 Wi-Fi 或固定电缆)连接到互联网。
Firewalls
A firewall is a network security device that monitors and controls the flow of data between your computer or network and the internet. It acts as a barrier, blocking unauthorized access while allowing trusted data to pass through. Firewalls help protect your network from hackers, viruses, and other online threats by filtering traffic based on security rules. Firewalls can be physical devices (hardware), programs (software), or even cloud-based services, which can be offered as SaaS, through public clouds, or private virtual clouds.
防火墙是一种网络安全设备,用于监视和控制您的计算机或网络与 Internet 之间的数据流。它充当屏障,阻止未经授权的访问,同时允许受信任的数据通过。防火墙通过根据安全规则过滤流量,帮助保护您的网络免受黑客、病毒和其他在线威胁的侵害。防火墙可以是物理设备(硬件)、程序(软件),甚至是基于云的服务,它们可以通过公共云或私有虚拟云作为 SaaS 提供。
Repeater
A repeater operates at the physical layer. Its main function is to amplify (i.e., regenerate) the signal over the same network before the signal becomes too weak or corrupted to extend the length to which the signal can be transmitted over the same network. When the signal becomes weak, they copy it bit by bit and regenerate it at its star topology connectors connecting following the original strength. It is a 2-port device.
中继器在物理层运行。它的主要功能是在信号变得太弱或损坏以致无法延长信号在同一网络上传输的长度之前,通过同一网络放大(即重新生成)信号。当信号变弱时,他们一点一点地复制它,并在其星形拓扑连接器处按照原来的强度连接它。它是一个 2 端口设备。
Hub
A hub is a multiport repeater. A hub connects multiple wires coming from different branches, for example, the connector in star topology which connects different stations. Hubs cannot filter data, so data packets are sent to all connected devices. In other words, the collision domain of all hosts connected through Hub remains one. Also, they do not have the intelligence to find out the best path for data packets which leads to inefficiencies and wastage.
集线器是多端口中继器。集线器连接来自不同分支的多根电线,例如,连接不同工作站的星形拓扑连接器。Hub 无法过滤数据,因此数据包将发送到所有连接的设备。 换句话说,通过 Hub 连接的所有主机的冲突域保持一个。 此外,他们没有智能来找出数据包的最佳路径,这会导致效率低下和浪费。
Types of Hub
-
Active Hub: These are the hubs that have their power supply and can clean, boost, and relay the signal along with the network. It serves both as a repeater as well as a wiring center. These are used to extend the maximum distance between nodes.
有源集线器: 这些是有电源的集线器,可以与网络一起清洁、增强和中继信号。它既用作中继器,也用作布线中心。这些用于扩展节点之间的最大距离。 -
Passive Hub: These are the hubs that collect wiring from nodes and power supply from the active hub. These hubs relay signals onto the network without cleaning and boosting them and can’t be used to extend the distance between nodes.
无源集线器:这些是从节点收集布线并从主动集线器收集电源的集线器。这些集线器将信号中继到网络上,而无需清理和提升它们,并且不能用于延长节点之间的距离。 -
Intelligent Hub: It works like an active hub and includes remote management capabilities. They also provide flexible data rates to network devices. It also enables an administrator to monitor the traffic passing through the hub and to configure each port in the hub.
智能集线器 :它的工作方式类似于活动 Hub,并包含远程管理功能。它们还为网络设备提供灵活的数据速率。它还使管理员能够监控通过集线器的流量,并配置集线器中的每个端口。
Bridge
A bridge operates at the data link layer. A bridge is a repeater, with add on the functionality of filtering content by reading the MAC addresses of the source and destination. It is also used for interconnecting two LANs working on the same protocol. It typically connects multiple network segments and each port is connected to different segment. The exact number of ports depends on the type of bridge and design, but it usually has at least two ports for basic functionality.
网桥在数据链路层运行。网桥是一个中继器,具有通过读取源和目标的 MAC 地址来过滤内容的功能。它还用于互连使用同一协议的两个 LAN。它通常连接多个网段,每个端口连接到不同的网段。端口的确切数量取决于网桥的类型和设计,但它通常至少有两个端口用于基本功能。
Types of Bridges
-
Transparent Bridges: These are the bridge in which the stations are completely unaware of the bridge’s existence i.e. whether or not a bridge is added or deleted from the network, reconfiguration of the stations is unnecessary. These bridges make use of two processes i.e. bridge forwarding and bridge learning.
透明网桥:这些是站点完全不知道网桥存在的网桥,即无论是否在网络中添加或删除网桥,都不需要重新配置站点。这些桥使用两个过程,即桥转发和桥学习。 -
Source Routing Bridges: In these bridges, routing operation is performed by the source station and the frame specifies which route to follow. The host can discover the frame by sending a special frame called the discovery frame, which spreads through the entire network using all possible paths to the destination.
源路由网桥:在这些网桥中,路由操作由源站执行,帧指定要遵循的路由。主机可以通过发送一个称为发现帧的特殊帧来发现该帧,该帧使用所有可能的路径传播到整个网络到目的地。
Switch 交换机
A switch is a multiport bridge with a buffer and a design that can boost its efficiency(a large number of ports imply less traffic) and performance. A switch is a data link layer device. The switch can perform error checking before forwarding data, which makes it very efficient as it does not forward packets that have errors and forward good packets selectively to the correct port only. In other words, the switch divides the collision domain of hosts, but the broadcast domain remains the same.
交换机是一种具有缓冲区和设计(可以提高其效率(大量端口意味着较少的流量)和性能的多端口桥接器。交换机是数据链路层设备。交换机可以在转发数据之前执行错误检查,这使其非常高效,因为它不会转发有错误的数据包,而是仅选择性地将正常数据包转发到正确的端口。 换句话说,交换机划分了主机的冲突域,但广播域保持不变。
Types of Switch 交换机类型
-
Unmanaged Switches: These switches have a simple plug-and-play design and do not offer advanced configuration options. They are suitable for small networks or for use as an expansion to a larger network.
非管理型交换机:这些交换机具有简单的即插即用设计,不提供高级配置选项。它们适用于小型网络或用作大型网络的扩展。 -
Managed Switches: These switches offer advanced configuration options such as VLANs, QoS, and link aggregation. They are suitable for larger, more complex networks and allow for centralized management.
管理型交换机:这些交换机提供高级配置选项,例如 VLAN、QoS 和链路聚合。它们适用于更大、更复杂的网络,并允许集中管理。 -
Smart Switches: These switches have features similar to managed switches but are typically easier to set up and manage. They are suitable for small- to medium-sized networks.
智能交换机:这些交换机具有类似于管理型交换机的功能,但通常更易于设置和管理。它们适用于中小型网络。 -
Layer 2 Switches: These switches operate at the Data Link layer of the OSI model and are responsible for forwarding data between devices on the same network segment.
第 2 层交换机:这些交换机在 OSI 模型的数据链路层运行,负责在同一网段上的设备之间转发数据。 -
Layer 3 switches: These switches operate at the Network layer of the OSI model and can route data between different network segments. They are more advanced than Layer 2 switches and are often used in larger, more complex networks.
第 3 层交换机:这些交换机在 OSI 模型的网络层运行,可以在不同的网段之间路由数据。它们比第 2 层交换机更先进,通常用于更大、更复杂的网络。 -
PoE Switches : These switches have Power over Ethernet capabilities, which allows them to supply power to network devices over the same cable that carries data.
PoE 交换机:这些交换机具有以太网供电功能,这使它们能够通过传输数据的同一根电缆为网络设备供电。 -
Gigabit switches: These switches support Gigabit Ethernet speeds, which are faster than traditional Ethernet speeds.
千兆交换机:这些交换机支持千兆以太网速度,比传统以太网速度更快。 -
Rack-Mounted Switches: These switches are designed to be mounted in a server rack and are suitable for use in data centers or other large networks.
机架式交换机:这些交换机设计为安装在服务器机架中,适用于数据中心或其他大型网络。 -
Desktop Switches: These switches are designed for use on a desktop or in a small office environment and are typically smaller in size than rack-mounted switches.
桌面交换机:这些交换机专为在桌面或小型办公环境中使用而设计,通常比机架式交换机的尺寸小。 -
Modular Switches : These switches have modular design, which allows for easy expansion or customization. They are suitable for large networks and data centers.
模块化交换机:这些交换机采用模块化设计,可轻松扩展或定制。它们适用于大型网络和数据中心。
Router 路由器
A router is a device like a switch that routes data packets based on their IP addresses. The router is mainly a Network Layer device. Routers normally connect LANs and WANs and have a dynamically updating routing table based on which they make decisions on routing the data packets. The router divides the broadcast domains of hosts connected through it.
路由器是一种类似于交换机的设备,它根据数据包的 IP 地址路由数据包。路由器主要是网络层设备。路由器通常连接 LAN 和 WAN,并有一个动态更新的路由表,它们根据该表来决定路由数据包。路由器划分通过它连接的主机的广播域。
Gateway 网关
A gateway, as the name suggests, is a passage to connect two networks that may work upon different networking models. They work as messenger agents that take data from one system, interpret it, and transfer it to another system. Gateways are also called protocol converters and can operate at any network layer. Gateways are generally more complex than switches or routers.
网关,顾名思义,是连接两个网络的通道,这两个网络可能适用于不同的网络模型。他们充当信使代理,从一个系统获取数据,对其进行解释,然后将其传输到另一个系统。网关也称为协议转换器,可以在任何网络层运行。网关通常比交换机或路由器更复杂。
Brouter 路由器
It is also known as the bridging router is a device that combines features of both bridge and router. It can work either at the data link layer or a network layer. Working as a router, it is capable of routing packets across networks and working as the bridge, it is capable of filtering local area network traffic.
它也被称为桥接路由器,是一种结合了网桥和路由器功能的设备。它可以在数据链路层或网络层工作。作为路由器,它能够跨网络路由数据包,并作为桥梁,它能够过滤局域网流量。
NIC 网卡
NIC or network interface card is a network adapter that is used to connect the computer to the network. It is installed in the computer to establish a LAN. It has a unique id that is written on the chip, and it has a connector to connect the cable to it. The cable acts as an interface between the computer and the router or modem. NIC card is a layer 2 device which means that it works on both the physical and data link layers of the network model.
NIC 或网络接口卡是用于将计算机连接到网络的网络适配器。它安装在计算机中以建立 LAN。 它有一个写在芯片上的唯一 ID,并且有一个连接器来连接电缆。该电缆充当计算机与路由器或调制解调器之间的接口。NIC 卡是第 2 层设备,这意味着它可以在网络模型的物理层和数据链路层上工作。
Conclusion 结论
In conclusion, different types of network devices play essential roles in keeping a network running smoothly and securely. Devices like routers, switches, modems, and access points help connect devices, manage data traffic, and ensure efficient communication. Firewalls add a layer of security, while other tools extend the network’s reach or make it easier to manage. Each device has a specific function, but together they create a reliable and secure network environment for both personal and business use.
总之,不同类型的网络设备在保持网络平稳和安全运行方面发挥着至关重要的作用。路由器、交换机、调制解调器和接入点等设备有助于连接设备、管理数据流量并确保高效通信。防火墙增加了一层安全性,而其他工具则扩展了网络的范围或使其更易于管理。每个设备都有特定的功能,但它们共同为个人和企业使用创造了一个可靠且安全的网络环境。
Frequently Asked Questions on Network Devices – FAQ’s 有关网络设备的常见问题 – 常见问题解答
Why do we need network devices? 为什么需要网络设备?
Network devices are necessary to connect computers, manage data traffic, extend internet access, and ensure secure and efficient communication within a network.
网络设备对于连接计算机、管理数据流量、扩展 Internet 访问以及确保网络内安全高效的通信是必需的。
What does a modem do? 调制解调器有什么作用?
A modem connects your network to the internet by converting data between digital signals (used by devices) and analog signals (used by the internet provider).
调制解调器通过在数字信号(由设备使用)和模拟信号(由 Internet 提供商使用)之间转换数据来将您的网络连接到 Internet。
What is the difference between a switch and a hub? 交换机和集线器有什么区别?
A switch sends data only to the specific device that needs it, while a hub sends data to all connected devices, which can slow down the network.
交换机仅将数据发送到需要它的特定设备,而集线器将数据发送到所有连接的设备,这可能会减慢网络速度。
中继器 (Repeater)、集线器 (Hub)、桥接器 (Bridge)、交换器 (Switch) 原理与介绍
发表于 2018-06-12 郑中胜
理解网络设备的关键在于:
厘清这些设备运作的网络层级,与其解决的问题。
笔者很欣赏《Computer Network 5th by Andrew》中的设备分层表,其综合 OSI 与 TCP/IP 的参考模型,具有良好的职责划分:
[注]:图中仅为简易情况,不包含如 L3,4 交换器等设备。
本篇将依此模型,逐层介绍以下常见设备:中继器、集线器、桥接器、交换器。
传统以太网路
在讨论网络装置之前,需要了解以太网路 (Ethernet)。以太网路可说是过去 30 年来最广泛使用的“有线区/广域网络”技术。一般所说的网络线,即为用于乙太网络的“RJ45 接头+无遮蔽式双绞线 (UTP)”。

此标准最初订于 1983 年 IEEE 802.3,历经多个附加标准后,从最初的 10 Mbit/s 发展至如今的 400 Gbit/s 太位元以太网。
的确,这里的“G”表示千兆,意味着一秒钟能下载 46.57 GiB 的档案。
在理解现今的以太网路技术之前,让我们追溯到 30 年前。
总线拓朴 (Bus Topology)
传统以太网路多采用 总线拓扑 (Bus Topology):

将一同轴电缆布于建筑物内,并通过收发器 (transceiver) 将多台主机连接至此主干网络。其简单、成本低的特性,在当时迅速得到广泛应用。
若节点 A 欲发送以太网路讯框 (封包) 给节点 D,只需在讯框的目的位址 (destination address) 字段,填上节点 D 的 MAC 位址。
然而,由于共享介质的原因,传统以太网路以广播 (broadcast) 方式进行传输。尽管节点 A 只是想发送讯框给节点 D,线路上的所有节点也都会收到。这不仅存在安全性问题,还带来了许多其他问题(稍后讨论):
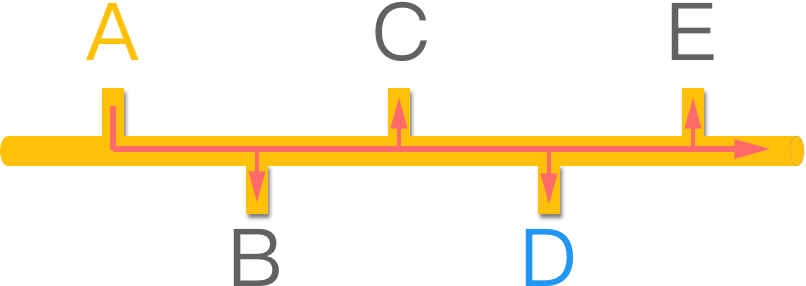
例如,若节点 C 想拦截经过的封包,只需通过以下指令 (Linux) 开启 混杂模式 (promiscuous mode),就能监控甚至修改讯框内容:
ifconfig 界面名称 promisc
本节重点:
目的位址仅为“逻辑上”的目的描述,不代表实体上的‘传输方式’。
根据不同底层技术,单播位址可能以点对点传输,也可能以广播传输。
[注]
系统通常会默认关闭混杂模式,以避免处理原本应被忽略的封包。可以通过以下指令关闭混杂模式:
ifconfig 界面名称 -promisc
中继器 (Repeater)
由于“讯号衰减和时序”的问题,每个版本的以太网路都对不同缆线的最大长度有限制。为了支持大型的局域网,此时会使用“讯号放大器”——中继器 (Repeater)。
中继器也称为增益器、转发器,是实体层 (Physical layer) 设备,用于双向接收、调整、放大讯号,并将其传到另一端的缆线上,从而改善讯号衰减问题,扩展缆线总长度。

此外,中继器也广泛应用于电话系统、无线网络等。例如,若家中 3G/4G 讯号较差,可能会安装一台双频 ICS 中继器:

Photo courtesy of 展连.
又或者家中/办公室隔间多、面积大,导致 Wi-Fi 讯号不佳,最简单的方法是安装一台 Wi-Fi 延伸器 (e.g., ASUS RP-N12):

Photo courtesy of ASUS.
[注 1]:现今许多网络设备都已内置中继器功能。
[注 2]:市面上用铝罐自制的‘Wi-Fi 放大器’,属于“集波器”而非中继器(无讯号放大功能)。
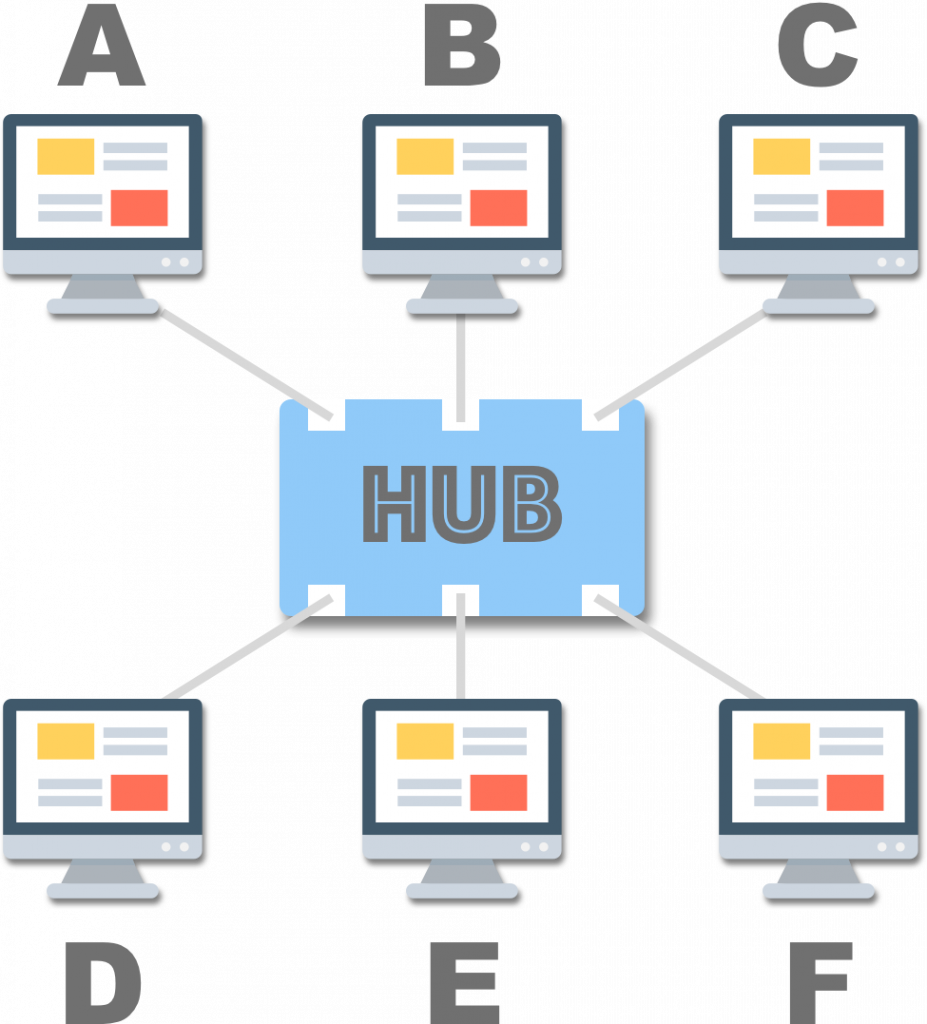
集线器 (Hub)
尽管传统以太网路布线简单,但为日后维护带来了诸多不便。于是,实体层设备——集线器 (Hub) 应运而生,用于整合主机,有些集线器还提供了 中继器 (repeater) 的功能,称为主动式集线器。

Photo courtesy of Wiki.
集线器基于中央节点 (central node) 的概念,新增主机只需将网络线插到连接埠 (port) 上,移除主机也只需拔掉线,这使得网络扩展和设备维护更加容易。这种布线模式称为 星状拓朴 (star topology):
然而:
集线器 (Hub) 并不像想象中那么强大,它已逐渐被淘汰,原因将在下文提及。
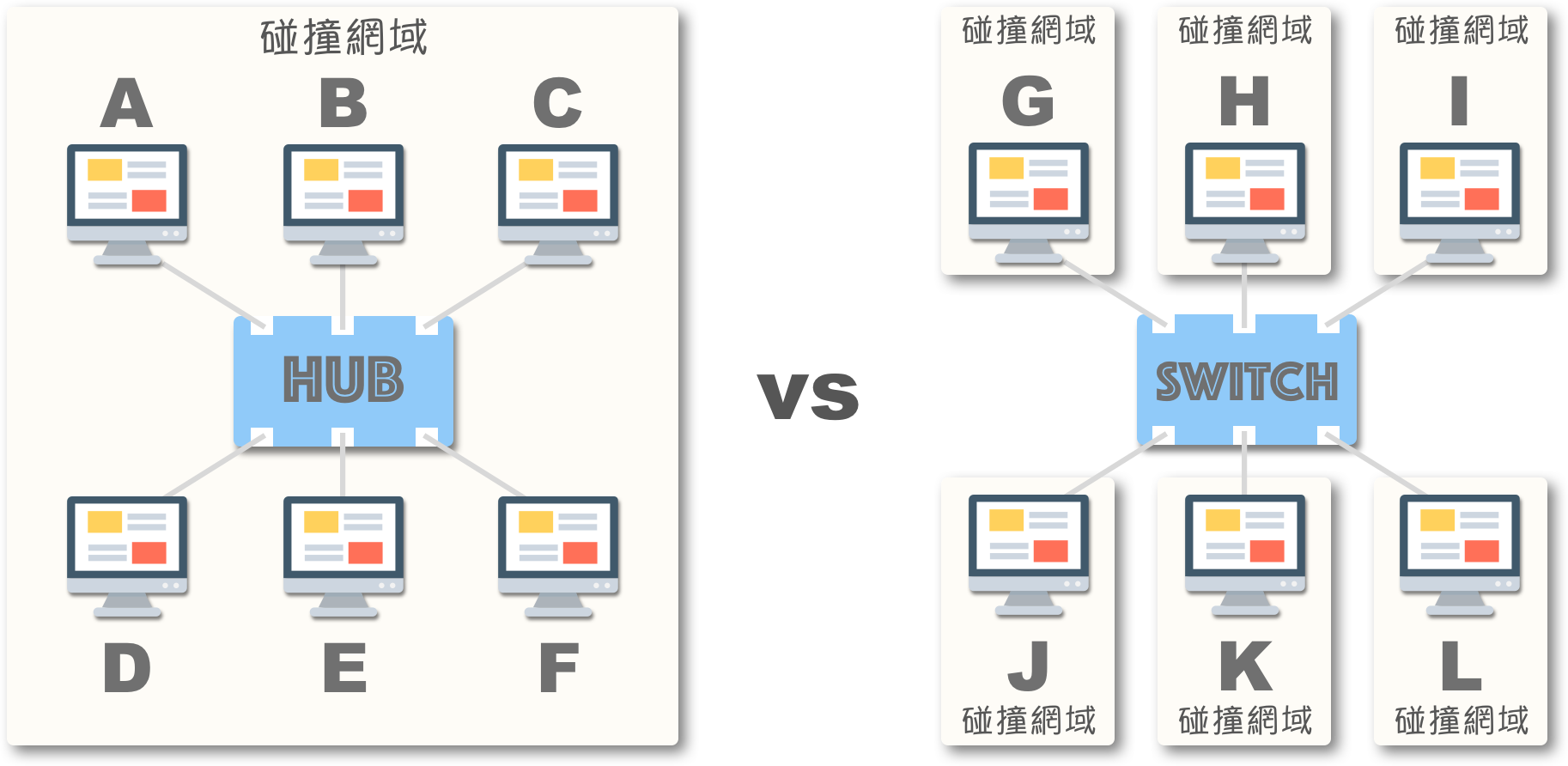
碰撞网域 (Collision Domain)
还记得前几节提到的 总线拓朴 吗?传统以太网路中多台主机共享相同介质,因此以广播 (broadcast) 方式进行传输。尽管节点 A 只是想发送讯框 (封包) 给节点 D,线路上的所有节点也都会收到:
此时,若节点 C 也发送讯框,由于广播 (broadcast) 的原因,会与节点 A 的讯框发生碰撞 (collision),结果是讯号被干扰而产生错误。
这就好比一群人在“同一个房间”同时发言,只会导致混乱。其中,这个“房间”被称为——碰撞网域 (Collision Domain):
使用 星状拓朴 的集线器 (Hub) 也存在问题,它就像将电路焊接在内部一样,因此集线器上的所有节点都位于同一碰撞网域 (房间),碰撞 (collision) 从同轴电缆转移到了集线器内部:
基于以上原因,集线器以太网被认为是实体上的“伪”星状拓朴,逻辑上仍属于总线拓朴 (bus topology)。
[注]:碰撞网域在乙太网路中也称为网段 (Segment),准确来说是 Layer 1 (Network) Segment。
载波感测多重存取/碰撞侦测 (CSMA/CD)
由于存在碰撞 (collision) 的问题,需要一种方式来协调设备间的通信,确保不打断对方、不垄断发言权,例如举手获取发言权、轮流发言等。
在传统以太网路中,这些“协调”标准都规定在资料链接层 (data link layer) 的子层——媒介存取控制 (media access control, MAC) 或称媒体存取控制,所采用的方法是 1-Persistent 式 载波感测多重存取/碰撞侦测 (CSMA/CD)。
[注]:此处 media 是“介质”的意思,并非“影音多媒体”。
1-Persistent CSMA,简单来说就是“先听后发”:
主机在发送讯框前,先检测媒介是否正在被使用 (有人在说话),若否,则立即发送;否则,持续检测直到媒介闲置 (idle) 后再发送。
由于存在“传导延迟”,载波感测能力有限,CSMA 无法完全避免碰撞发生,只能尽量降低碰撞率。因此,传统以太网路还配备了碰撞侦测 (CD):
持续检测媒介是否发生碰撞,若检测到碰撞,就中止传输并发送一个 48 bit 的壅塞讯号,通知其他节点已发生碰撞,最后,利用 二元指数倒退算法 等待合适的时
交换式以太网路
显然,CSMA/CD 只是一种治标不治本的方法,不仅速度慢、浪费带宽,还带来了布线上的诸多限制。
既然碰撞是由于“节点们都位于同一‘房间’(碰撞网域)”引起的,那么一个直观的解决办法是:
“尽量”让每个节点有独立的空间!
这个想法推动了以太网路的重大进步,促成了 1995 年的 高速以太网路 (Fast Ethernet),也为现代的 太位元以太网 (Terabit Ethernet) 奠定了坚实的基础。
桥接器 (Bridge)
在以太网路的演进过程中,首先出现的是桥接器 (bridge),当时主要用于连接多个总线拓朴的传统以太网路,形成一个大型以太网路。划分区段的主要目的是分割碰撞网域,从而减少碰撞概率,提高平均带宽。
图中,共有四个碰撞网域 (一个区域网路):
那么,为什么不多增加几个连接埠,将碰撞领域划分得更细呢?
不久之后,多埠桥接器 (multiport bridge) 被称为交换器 (switch),因此桥接器 (bridge) 与交换器 (switch) 常常被视为等同的设备:
 Cisco MS225-48 交换器
Cisco MS225-48 交换器
Andrew Tanenbaum 曾指出:
交换器是“现代桥接器”的另一个名称,它们之间的差异更多体现在行销方面而非技术层面。
从 IEEE 文件中可以了解到,规范上主要使用“桥接器”这一术语,而实际设备大多称为“交换器”。
交换器 (Switch)
交换器 (switch) 也称为网络交换器 (以区别于电话交换器),是位于资料链接层 (data link layer)[注 1] 的设备,是交换式以太网路的核心。其目的是在连接埠之间转发讯框,在构建大型区网时,可以通过交换器连接各个设备。
根据是否提供管理、监控、设置 (configure) 等功能,交换器可分为:网管型交换器 (managed switch) 与 非网管型交换器 (unmanaged switch)。

Photo courtesy of D-Link.
可以看到,小型交换器 (非网管型) 与 集线器 (hub ) 外观相似度约为 87%,然而,它们的内部结构完全不同,交换器的所有连接埠都是独立处理的,逻辑示意图如下:
这样设计的目的是:
使每个连接埠 (port) 成为独立的碰撞网域 (房间)。
[注 1]:此处指 Layer 2 Switch。
消除碰撞
由于交换器中每个连接埠都是一个独立的碰撞网域,它就像社区管理员一样,根据讯框的目的位址查表后将讯框送往指定的连接埠。例如 (实际上还包括 VLAN 等字段,稍后讨论):
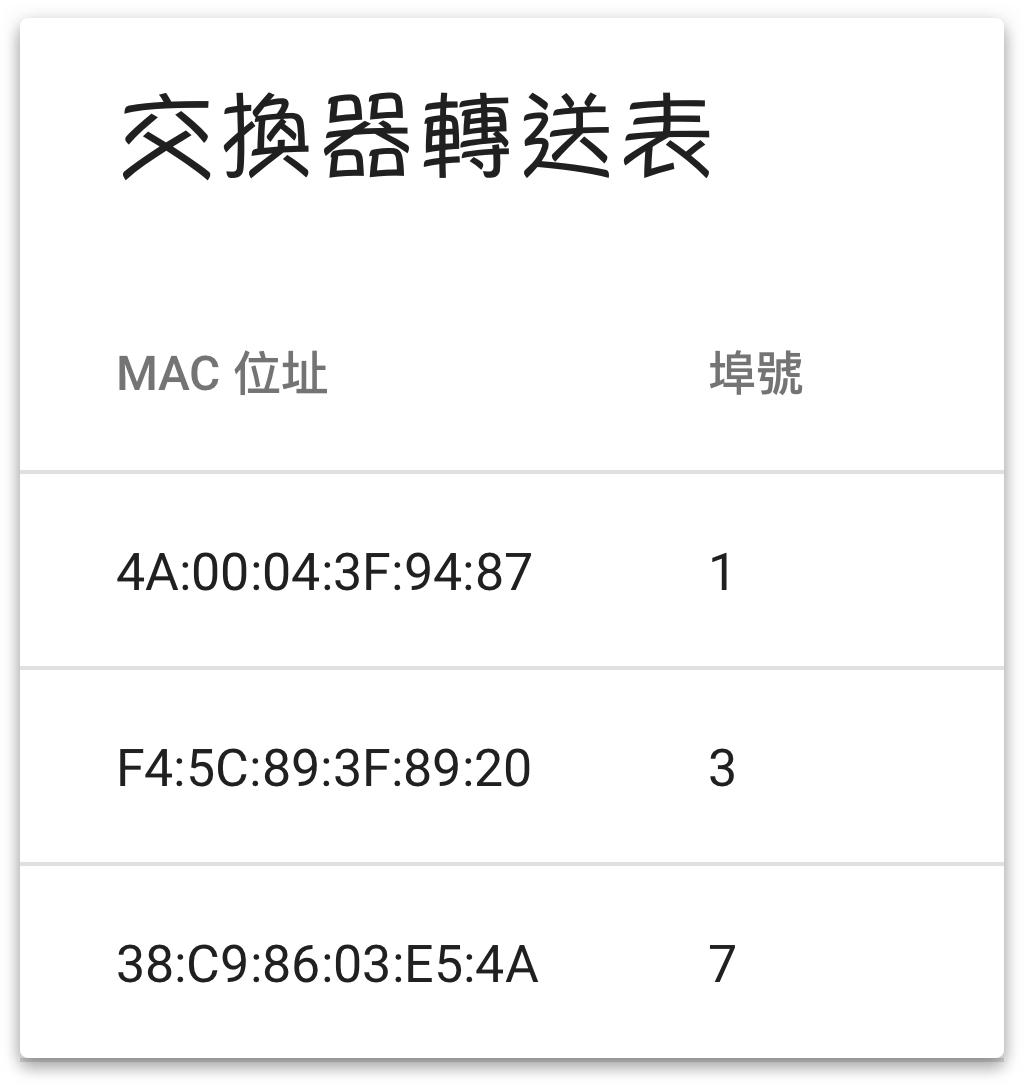
这意味着不再需要 CSMA/CD 机制_ (因为不会发生碰撞),每台主机可以随时发送/接收 (全双工),从而大大提高了平均带宽。
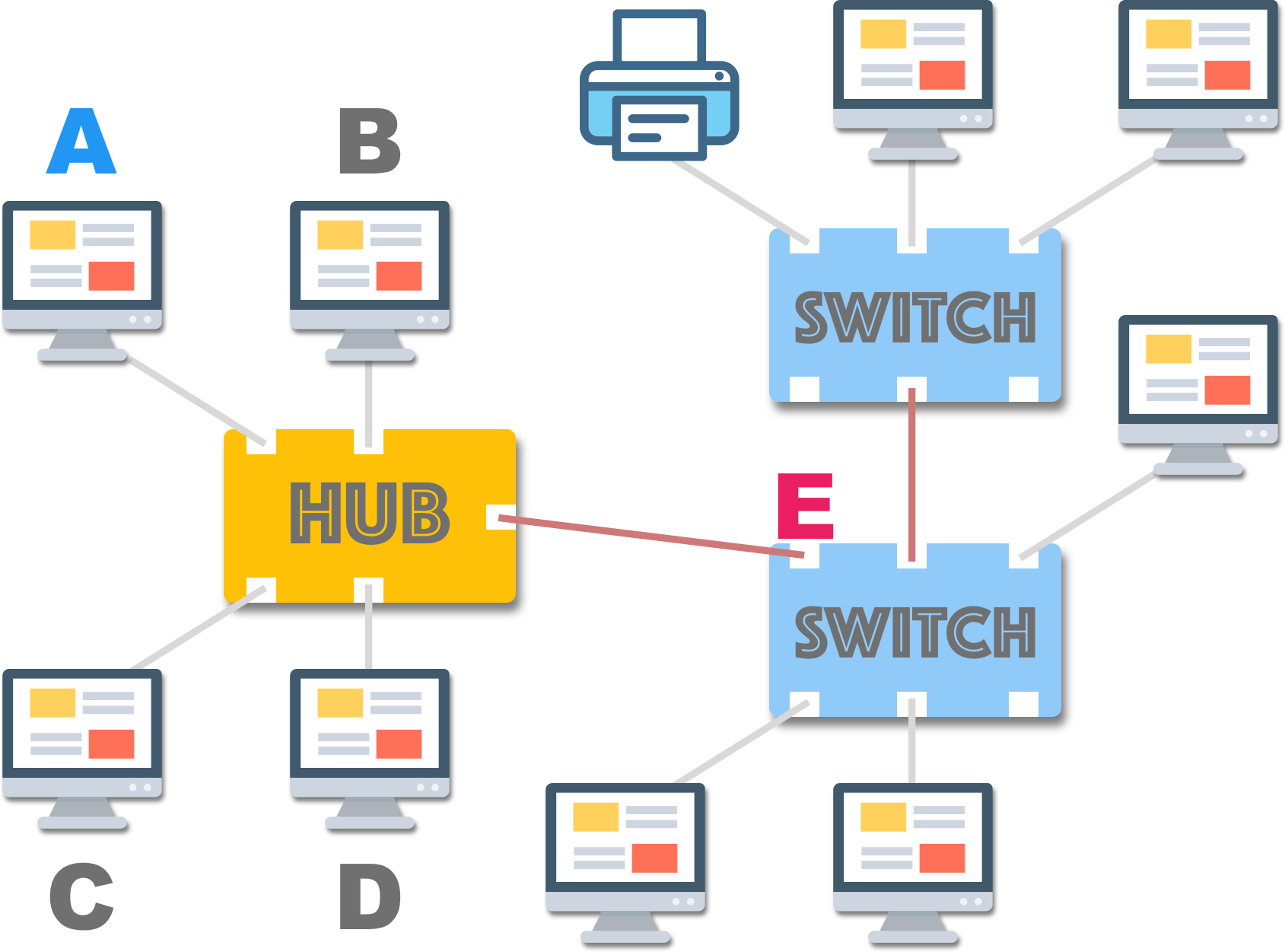
例如,节点 A 向节点 E 发送讯框,若使用集线器,节点 B, C, D, E, F 都会收到;而若节点 G 向节点 K 发送讯框,使用交换器时,只有节点 K 会收到。这不仅提高了传输效率,还增强了安全性。
然而,在很多情况下,集线器的“广播”特性更便于进行故障排除。幸运的是,大多数网管型交换器具备 Port Mirroring 功能,方便监控流量。
过滤 (filtering)
交换器并非只连接电脑主机,还可能连接其他交换器、路由器甚至集线器。当节点 A 欲发送讯框给节点 D 时,若使用集线器,连接埠 E 也会意外收到一份讯框:
如前所述,交换器会根据讯框的目的位址查表,将讯框送往指定的连接埠。然而,当讯框的来源与目的位址位于相同的埠号时,说明节点 A 与节点 D 位于同一区段,此时交换器不会转发该讯框,而是将其忽略、丢弃,这一功能称为——过滤 (filtering)。
注意:
交换器能够实现这一点,是因为它是资料链接层设备 (不同于集线器),它能够识别讯框,因此损坏的讯框也会被过滤掉。
因此,大部分网管型交换器还具备安全性与服务品质的存取控制清单 (ACL)。通过安全性 ACL 查表 (e.g., TCAM),可以限制特定的 MAC 位址、连接埠与通讯协定等;或依据服务品质 (QoS) ACL,为不同讯框赋予不同的优先权,以便优先转发。
学习 (learning)
目前我们假设交换器能够通过转送表 (forwarding table) 得知所有目的位址的埠号,实际上,交换器一开始并不知晓这些信息。
传统交换器的转送表是静态的,需要手动建立表格来维护位址信息,显然这种方式效率低下,不仅需要频繁修改,还容易出错。

因此,现今的交换器大多采用动态表格策略 (e.g., CAM):表格最初为空,每当有讯框进入交换器时,就记录其来源位址与连接埠,此功能称为——学习 (learning)。
当交换器欲转发讯框时,便查询表格中是否有该目的位址的对应埠号条目。若有,则直接转发至该连接埠;否则,将采取 洪泛算法 (flooding algorithm):
复制讯框并传送到“除了来源埠以外”的“所有连接埠”。
[注]:暂不考虑 VLAN (稍后提及)。
此种情形称为单播洪泛 (unicast flood):
是指交换器 (switch) 将单播讯框视为广播讯框的潜在无意行为。
单播洪泛 (unicast flood) 本质上仍是单播,若下一个接收到洪泛讯框的交换器知道目的位址的埠号,即可直接进行点对点转送,这点与广播 (broadcast) 截然不同。
[注]
网管型交换器通常还是会提供静态 MAC 位址设定,以支持其他网络规划需求 (e.g., 无法学习到的 MAC 位址),例如 Cisco 的 mac address-table static 指令。
广播网域 (Broadcast Domain)
需要明确的是,以太网路标准主要位于实体层及资料链接层,上述所有的“来源/目的位址”皆是 MAC 位址,而非网络层的 IP 位址。理解这一点对于清晰区分网络装置至关重要!

而 MAC 位址. 并非只有单播位址 (unicast address),还包括广播位址 (broadcast address) 以及群播位址 (multicast address)。
例如,当节点 A 欲传送讯框给同一区网的所有装置时,仅需在讯框的目的位址字段填入 ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff (广播位址)。若节点之间能够通过广播进行通信,则称它们位于相同的广播网域 (Broadcast Domain):
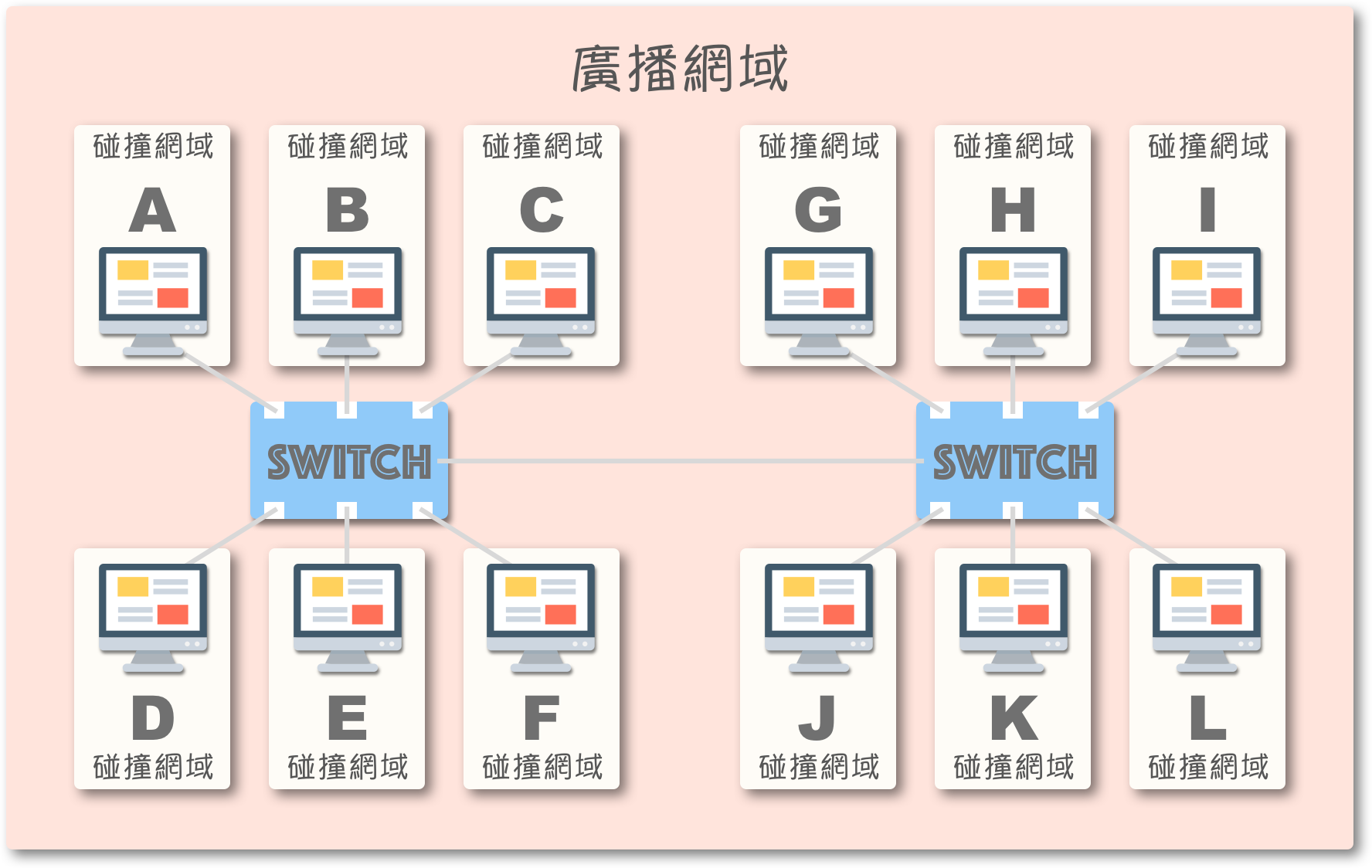
(由于位于同一广播网域,节点 B 至节点 L 皆会收到讯框)
[注]
广播网域是交换器可直接转送讯框的领域,又称为 Layer 2 Segment。
广播风暴 (Broadcast Storm)
尽管交换器 (Switch) 能够分割碰撞网域 (每个节点一个独立空间),但若节点们位于相同的广播网域 (broadcast domain) (社区),它们都将被迫处理并丢弃未知目的单播 (洪泛) 讯框,以及广播、群播讯框。
若讯框数量过多,将导致整个区网性能下降,极端情况下甚至可能使网络瘫痪,这种情形称为——广播风暴。
广播风暴 (broadcast storm) 通常是由于交换器之间的连接存在循环、并联所导致。不过,这并不一定意味着拓扑方式错误,相反,企业在实际应用中常常需要这些冗余链接,以防止主交换器故障造成损失。
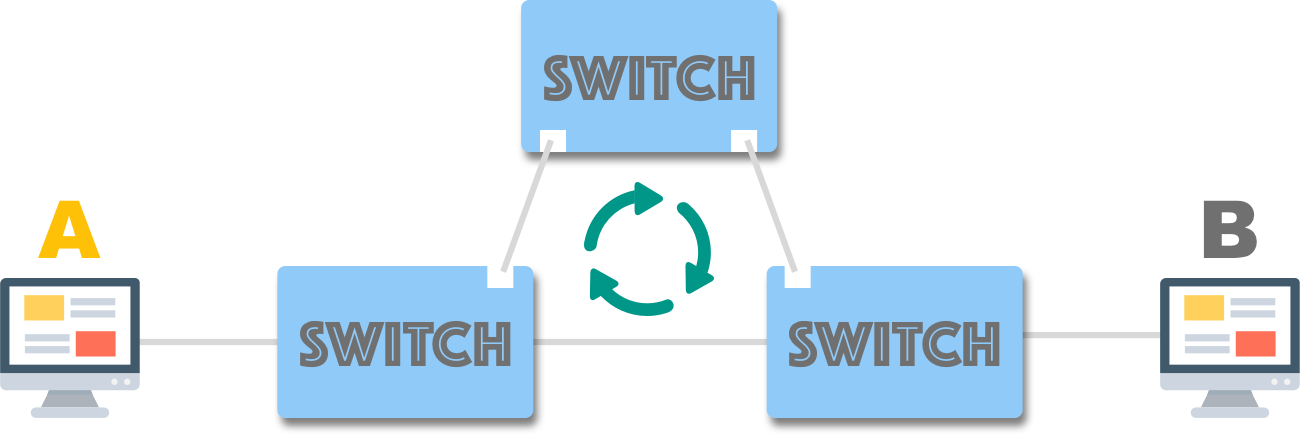
为避免交换器链接存在循环(loop),导致讯框被无限复制、转发,Radia Perlman 于 1985 年发明了著名的生成树协定 (Spanning Tree Protocol, STP)。随后,IEEE 引入了 RSTP (802.1w) 以及 MSTP (802.1s),以缩短 STP 的收敛时间 (convergence time)。
事先预防桥接循环 (bridge loop),比在循环形成后再去解决它更为有效。 — David Hucaby
这些协定使得我们能够安全地配置冗余机制:它们能够预先检测到循环,并停用导致循环的冗余链接 (封锁埠),确保仅在设备故障或拓扑结构改变时启用。
然而,如果使用的是非网管型交换器,最好仔细检查拓扑结构 。无论如何,都要移除导致桥接循环的网络线,否则可能会导致电脑运行异常。
如果使用的是网管型交换器,并且能够确保不会产生循环,也建议直接停用 ®STP,以避免不必要的网络延迟。
何谓局域网路 (Local Area Network)
讨论了这么多,局域网路 (LAN) 的定义究竟是什么呢?
如同大数据 (Big Data)、成长骇客 (Growth Hacking) 等流行术语 (Buzzword),实际上,局域网路 (LAN) 或广域网络 (WAN) 都没有严格精确的定义与划分。
局域网路 (LAN) 通常以“地理范围”来定义,例如一个住宅、办公室或大楼。显然,这种定义并不严谨,存在模糊性。
试想,若同一办公室内的两个部门被设置为永远无法直接通信,它们还能被称为区网吗?

Photo courtesy of Cisco.
幸好,Cisco 网络专家 Wendell Odom 给出了局域网路一个狭义但具体的定义:
一个局域网路 (LAN) 是由相同广播网域内的所有装置所组成。
A LAN consists of all devices in the same broadcast domain.
这一定义有助于我们清晰地描述交换器 (Switch) 的行为,也便于介绍下述的虚拟局域网路 (Virtual LAN)。本系列文章也将以此作为“局域网路”一词的定义。
虚拟局域网路 (VLAN)
到目前为止,我们只讨论了“实体”的网络拓扑模式。然而在实际应用中,企业可能需要根据部门划分、流量管理等来划分局域网路 (LAN) ,以体现企业组织架构,而非单纯基于建筑物内的实体设备配置。
如果每次都需要根据组织变化调整实体机器布线,这将带来极大的不便。幸运的是,虚拟局域网路 (VLAN) 技术能够对区网中的设备进行逻辑分组,帮助企业更好地进行网络管理:
VLAN 的基本设置相对简单,只需根据埠号或 MAC 来分配 VLAN ID ,其中 1 号 ID 为预设 VLAN 。出于安全考虑,通常不会将其分配给普通主机:
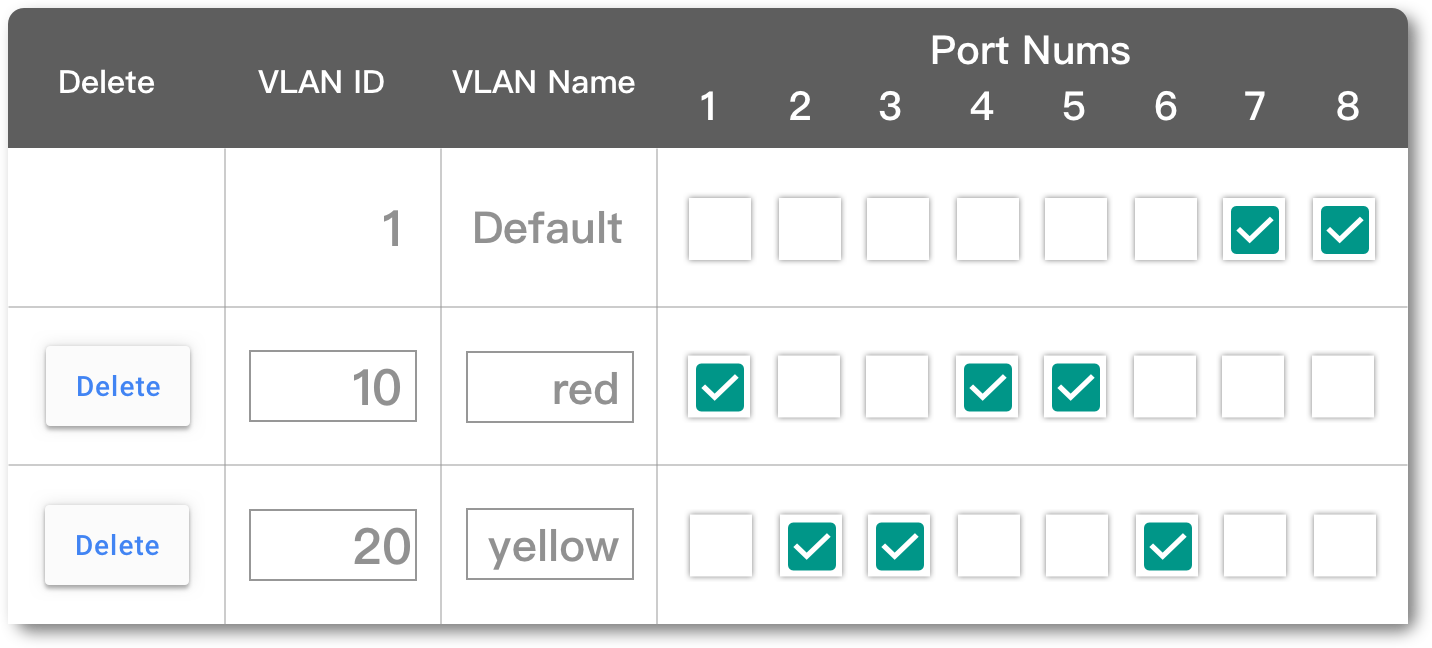
[注]:Cisco Switch 可通过 switchport access vlan {vlan-id} 指令进行设置。
切割广播网域
在前面介绍的实体拓扑中,我们看到“连接至相连交换器的设备,皆位于相同的广播网域”,这意味着随着工作站数量的增加,整个区网的广播讯框也会增多,导致效率下降 :

(图中,每台主机都需要处理、丢弃未知目的单播 (洪泛) 讯框,以及广播、群播讯框)
而 VLAN 赋予了交换器切割广播网域的功能:
一个 VLAN 即是一个广播网域。
[注]:不要忘记局域网路的 定义_!
也就是说,同一 VLAN 的成员只能收到彼此的广播,不同 VLAN 的成员则无法接收。(包括上述的单播洪泛也只会在同一 VLAN 中传播)
此外,由于交换器的任务是将同一局域网路中的讯框转发到对应的连接埠,而“不同 VLAN”的成员处于不同的 (虚拟) 局域网路,它们无法通过交换器直接通信,只能借助外部设备或第三层以上的交换器:
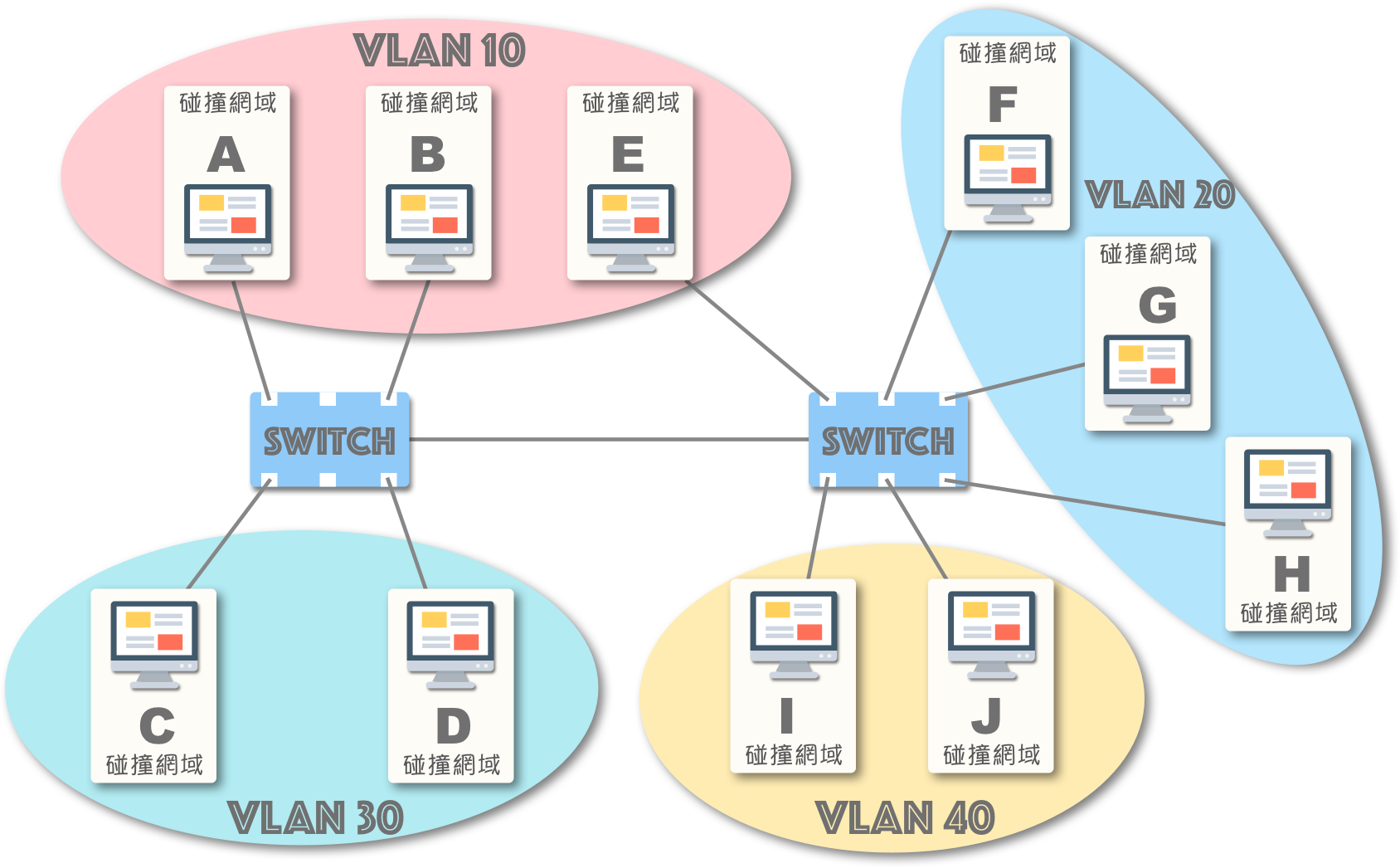
如上图 VLAN 10 中,节点 A 若发送广播讯框,只有节点 B 与节点 E 会收到,且节点 A 无法与其他节点 (C, D, F~J) 进行直接通信。
这种 VLAN 配置适用于同一部门 (A,B,E) 但分散在不同办公室的场景 。
VLAN 能有效地控制广播流量范围,提高整体网络效率,并确保局域网路的安全性和可维护性。
切割广播网域虽然能够在一定程度上隔离和缓解广播风暴,但对于桥接循环所引发的广播风暴,这只是一种治标不治本的方法。
当然,这一切都基于良好的 VLAN 部署。如果 VLAN 配置不当,使得 VLAN 跨越多层级,甚至影响到企业的核心交换器,只会导致广播流量扩散,消耗带宽,降低整体性能 。
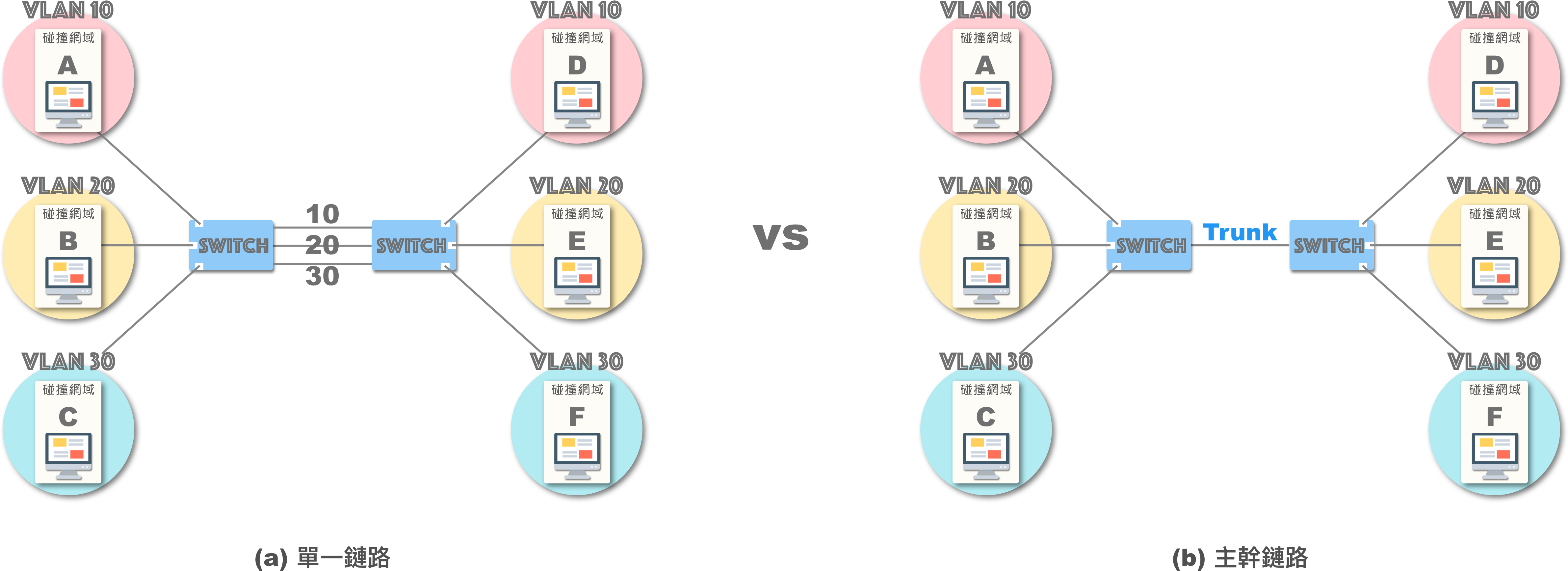
主干 (Trunking)
传统交换器构建“跨交换器”的 VLAN 较为复杂。若要连接 3 个 VLAN ,就需要连接 3 条网络线到对应的埠号 (图 a)。
幸运的是,如今的网管型交换器都具备主干链路 (Trunk Link):
交换器转送讯框时加上 VLAN 标签,接收方交换器解读并移除标签 (确保讯框相容性),从而通过单一主干链路构建多个 VLAN (e.g., 802.1Q)。
此外,Trunk 对于交换器与路由器的连接也非常便捷!它允许使用一条主干链路,支持所有 VLAN 流量进出路由器 (Router),这种设计也称为单臂路由 (router-on-a-stick):
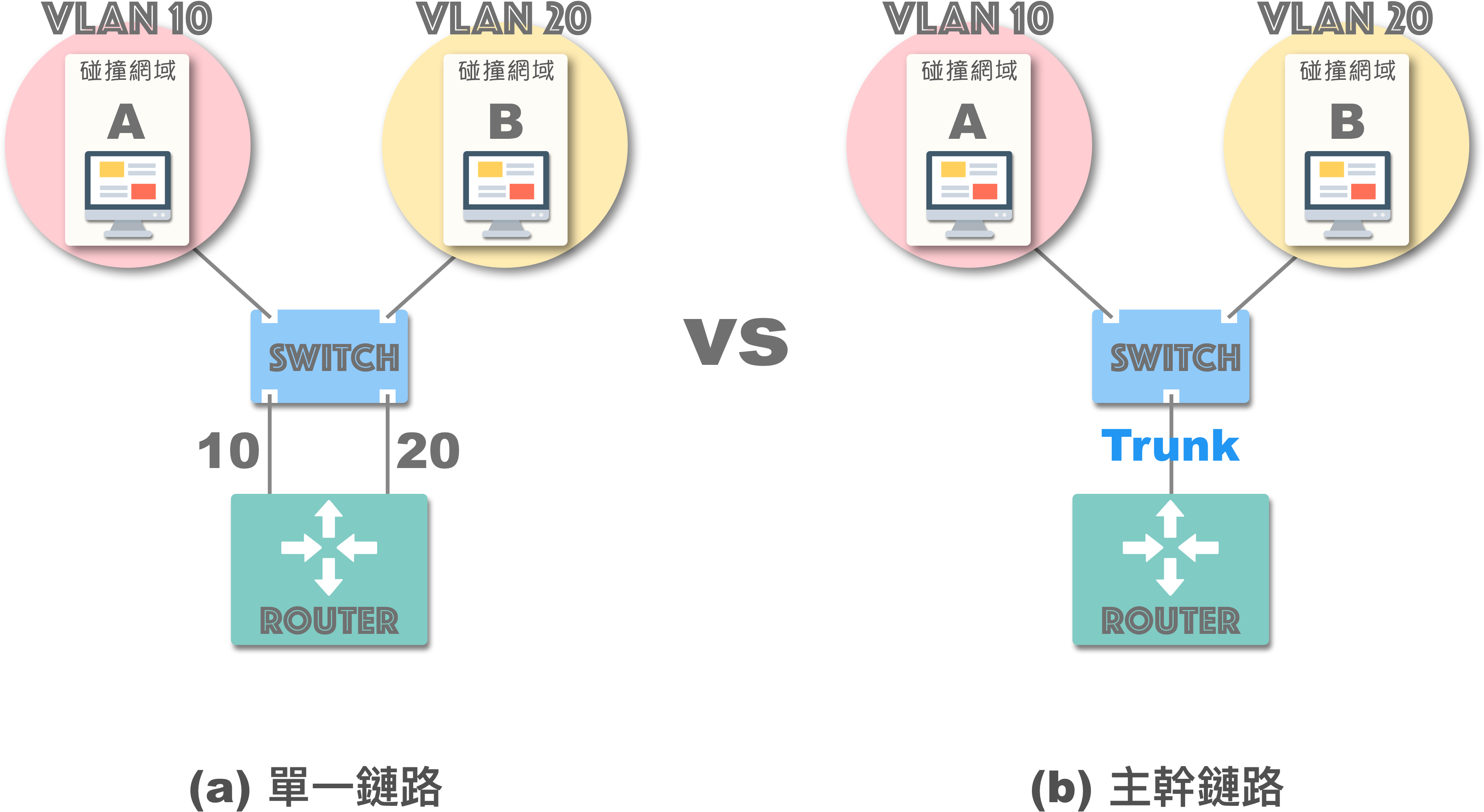
使用 VLAN Trunk 时,务必确认连接埠之间是否开启 Trunk 模式,实际中许多错误案例都是由于 Trunking 状态不一致导致的。
VLAN 交换器
最后综合上述内容,示例说明常见的 VLAN 交换器转送逻辑。当一单播讯框抵达交换器:
- 首先,依据讯框正确性、存取控制清单 (ACL)、生成树协定状态进行过滤 (filtering),并确定讯框转送的优先权、服务等级 (搭配入境伫列)。
- 接着,需要确认来源 VLAN ID 。若是一般存取接口的连接埠,就根据 VLAN 设定查询 ID ;若是 Trunk 接口,则根据 VLAN 标签获取 ID 。
- 转送表根据来源位址、连接埠号 (接口)、VLAN ID 进行学习 (新增/更新)。
- 根据目的位址以及来源 VLAN ID 查表,以确定转送接口 (搭配出境伫列)。若存在对应条目,则将讯框转发至该接口;否则:
将讯框从所有相同 VLAN 埠且未被生成树协定封锁埠洪泛出。
总结
本篇主要探讨了同一 局域网路_ 内的通信,并通过以太网路的演进阐述了相关设备的原理。然而,在大部分应用开发中,通常只涉及到 TCP/IP ,而非底层的 MAC Address。
这正是协定堆叠带来的优势 (详见 依赖倒置原则_):
针对接口进行设计,而非关注底层实现。
不过,若要构建稳定可靠的大型网络系统,只有深入了解底层原理,才能合理设计架构、提升性能。曾有开发者在编写 Socket 时,甚至无法区分 public, private IP ,最终导致无法建立连接 。
via:
-
Network Devices (Repeater, Hub, Bridge, NIC, Switch, Router and Gateway)
https://www.sanfoundry.com/computer-network-devices-repeater-hub-bridge-nic-switch-router-and-gateway/ -
Network Devices (Hub, Repeater, Bridge, Switch, Router, Gateways and Brouter) - Last Updated : 09 Dec, 2024
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/network-devices-hub-repeater-bridge-switch-router-gateways/ -
中繼器、集線器、橋接器、交換器 原理與介紹 - 發表於 2018-06-12 鄭 中勝
https://notfalse.net/66/repeater-hub-bridge-switch





















 1924
1924

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








