目录
1. 数据集构建
2. LLava网络结构
3. 源码分析
4. 资料
LLava使用视觉编码器(CLIP-VIT)和大语言模型(LLama)构建多模态大模型,通过GPT-4生成的数据样本进行指令微调.
一. 数据集构建
利用GPT-4生成样本,具体步骤如下:
将图像以Caption(描述性标题)和Bounding boxes(边界框)的形式输入给GPT-4,结合特定的prompt,生成3中类型的instruction-following(指令跟随)样本:Conversation(对话), Detailed description(详细描述)和Complex reasoning(复杂推理), 如下图所示:

二. LLava网络结构
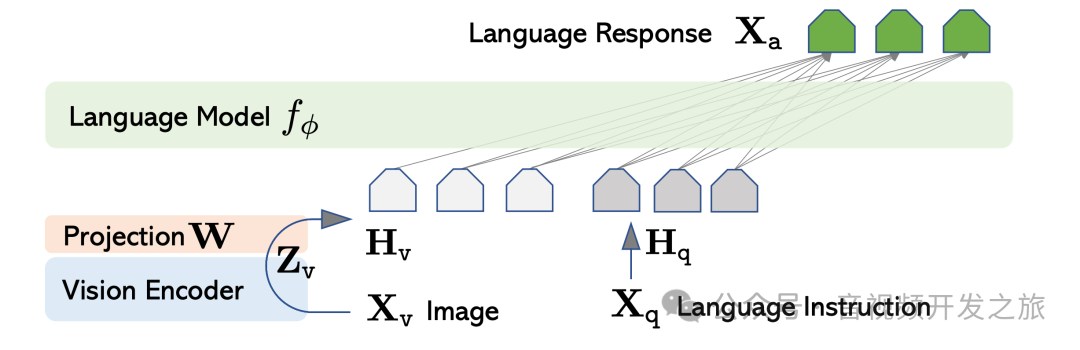
llava网络结构有3部分组成:视觉编码器(Vision Encoder),投影层(Projection W) 和大语言模型(Language Model)
视觉编码器使用预训练的CLIP-VIT编码器,输入图像输出视觉特征Z_v
投影层,通过一个可训练的投影矩阵W 将图像特征转换为语言Embeding H_v,使得视觉特征能够与语言特征的Embeding空间兼容.
转换公式如下
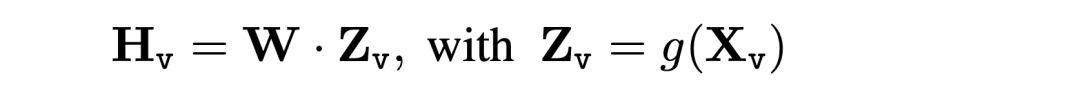
然后将视觉Embeding H_v和文本Embeding H_q 拼接在一起, 输入给LLM,生成X_a
LLava的使用两个阶段的方式来进行训练
第一阶段:预训练 frozen(冻结)视觉编码器(CLIP-VIT)和大语言模型,从CC3M数据中过滤595K图像-文本对,只训练Project W权重
第二阶段:微调, 只冻结视觉编码器权重,更新Project和LLM大模型的权重
三. 源码解析
3.1 基本使用
class LLavaModel():def __init__(self):self.model_path = "llava-v1.5-7b"#model_name=llava-v1.5-7bself.model_name=get_model_name_from_path(self.model_path)self.tokenizer, self.model, self.image_processor, self.context_len = load_pretrained_model(model_path=self.model_path,model_base=None,model_name=self.model_name,load_4bit=True)self.prompt = "What are the things I should be cautious about when I visit here?"def inference_image(self,image_file):args = type('Args', (), {"model_name": self.model_name,"query": self.prompt,"image_file": image_file,"sep": ",","temperature": 0,"top_p": None,"num_beams": 1,"max_new_tokens": 512})()return inference_model(args,self.tokenizer, self.model, self.image_processor, self.context_len)
3.2 模型加载
def load_pretrained_model(model_path, model_base, model_name, load_8bit=False, load_4bit=False, device_map="auto", device="cuda", use_flash_attn=False, **kwargs):kwargs = {"device_map": device_map, **kwargs}if load_8bit:kwargs['load_in_8bit'] = Trueelif load_4bit:#int4量化,降低显存占用kwargs['load_in_4bit'] = Truekwargs['quantization_config'] = BitsAndBytesConfig(load_in_4bit=True,bnb_4bit_compute_dtype=torch.float16,bnb_4bit_use_double_quant=True,bnb_4bit_quant_type='nf4')else:kwargs['torch_dtype'] = torch.float16#Flash Attention,是一种用于提高注意力机制效率的技术,用来减少计算复杂度和内存占用,同时保持或提高模型性能if use_flash_attn:kwargs['attn_implementation'] = 'flash_attention_2'# Load LLaVA modeltokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_path, use_fast=False)model = LlavaLlamaForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_path,low_cpu_mem_usage=True,**kwargs)image_processor = None#len(tokenizer):32000model.resize_token_embeddings(len(tokenizer))#config中配置的vision_tower,比如这里是:clip-vit-large-patch14-336vision_tower = model.get_vision_tower()vision_tower.load_model(device_map=device_map)image_processor = vision_tower.image_processorcontext_len = 2048return tokenizer, model, image_processor, context_len
3.3 推理流程
def inference_model(args,tokenizer, model, image_processor, context_len):model_name = args.model_nameqs = DEFAULT_IMAGE_TOKEN + "\n"conv_mode = "llava_v1""""根据不同模型,有不同的映射模板,例如:llava_v1对应的配置如下:conv_llava_v1 = Conversation(system="A chat between a curious human and an artificial intelligence assistant. ""The assistant gives helpful, detailed, and polite answers to the human's questions.",roles=("USER", "ASSISTANT"),version="v1",messages=(),offset=0,sep_style=SeparatorStyle.TWO,sep=" ",sep2="</s>",)"""conv = conv_templates[conv_mode].copy()#下面两行代码添加的messages=[['USER', '<image>\n'], ['ASSISTANT', None]]conv.append_message(conv.roles[0], qs)conv.append_message(conv.roles[1], None)#prompt为:"A chat between a curious human and an artificial intelligence assistant. The assistant gives helpful, detailed, and polite answers to the human's questions. USER: <image>\n ASSISTANT:"prompt = conv.get_prompt()image_files = image_parser(args)#这里其实使用Image.open(image_file).convert('RGB'),convert('RGB')的作用是统一颜色模式,确保数据的一致性和兼容性images = load_images(image_files)image_sizes = [x.size for x in images]#图像处理器,是一些常规的裁剪 反转 归一化等处理images_tensor = process_images(images,image_processor,model.config).to(model.device, dtype=torch.float16)"""把prompt转为输入Embedingeg:"A chat between a curious human and an artificial intelligence assistant. The assistant gives helpful, detailed, and polite answers to the human's questions. USER: <image>\n ASSISTANT:'""转为tensor([[ 1, 319, 13563, 1546, 263, 12758, 5199, 322, 385, 23116,21082, 20255, 29889, 450, 20255, 4076, 8444, 29892, 13173, 29892,322, 1248, 568, 6089, 304, 278, 5199, 29915, 29879, 5155,29889, 3148, 1001, 29901, 29871, -200, 29871, 13, 319, 1799,9047, 13566, 29901]], device='cuda:7')"""input_ids = (tokenizer_image_token(prompt, tokenizer, IMAGE_TOKEN_INDEX, return_tensors="pt").unsqueeze(0).cuda())with torch.inference_mode():#进行内容理解,model为:LlavaLlamaForCausalLM生成outputEmbedingoutput_ids = model.generate(input_ids,images=images_tensor,image_sizes=image_sizes,do_sample=True if args.temperature > 0 else False,temperature=args.temperature,top_p=args.top_p,num_beams=args.num_beams,max_new_tokens=args.max_new_tokens,use_cache=True,)#把token解码为str 输出outputs = tokenizer.batch_decode(output_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)[0].strip()return outputs
3.4 图像嵌入和文本嵌入的融合
LlavaMetaForCausalLM#prepare_inputs_labels_for_multimodal 将图像的嵌入(embedding)与文本的嵌入结合起来,形成一个统一的输入,并最终传递给大模型(例如 LLaMA)进行因果语言建模任务的推理
class LlavaLlamaForCausalLM(LlamaForCausalLM, LlavaMetaForCausalLM):@torch.no_grad()def generate(self,inputs: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,images: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,image_sizes: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,**kwargs,) -> Union[GenerateOutput, torch.LongTensor]:position_ids = kwargs.pop("position_ids", None)attention_mask = kwargs.pop("attention_mask", None)if "inputs_embeds" in kwargs:raise NotImplementedError("`inputs_embeds` is not supported")if images is not None:(inputs,position_ids,attention_mask,_,inputs_embeds,_) = self.prepare_inputs_labels_for_multimodal(inputs,position_ids,attention_mask,None,None,images,image_sizes=image_sizes)else:inputs_embeds = self.get_model().embed_tokens(inputs)return super().generate(position_ids=position_ids,attention_mask=attention_mask,inputs_embeds=inputs_embeds,**kwargs)
四. 资料
论文Visual Instruction Tuning(LLaVA):https://arxiv.org/abs/2304.08485
论文Improved Baselines with Visual Instruction Tuning(LLaVA-1.5):https://arxiv.org/abs/2310.03744
LLaVA: https://github.com/haotian-liu/LLaVA
LLaVA-NeXT:https://github.com/LLaVA-VL/LLaVA-NeXT
微软LLaVa模型论文笔记:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/625723805
多模态大模型LLaVA https://blog.51cto.com/u_16600817/10098069
详解多模态大模型:LLaVA+LLaVA1.5+LLaVA-Med https://posts.careerengine.us/p/65bf9ba51fb10327d7178303
Emo Visual Data 表情包视觉数据集 https://hyper.ai/datasets/32012
多模态大模型LLaVA模型讲解 https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1nw4m1S7nZ
训练LLava模型(数据集构建,基于Trainer的训练框架搭建):https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Si421v7j1
感谢你的阅读
接下来我们继续学习输出AI相关内容,欢迎关注公众号“音视频开发之旅”,一起学习成长。
欢迎交流


























 538
538

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








