(转)(改编)自https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/effervescence/article/details/81236076
E. Store
time limit per test
2 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Natasha was already going to fly back to Earth when she remembered that she needs to go to the Martian store to buy Martian souvenirs for her friends.
It is known, that the Martian year lasts ????xmax months, month lasts ????ymax days, day lasts ????zmax seconds. Natasha also knows that this store works according to the following schedule: 2 months in a year were selected: ??xl and ??xr (1≤??≤??≤????1≤xl≤xr≤xmax), 2 days in a month: ??yl and ??yr (1≤??≤??≤????1≤yl≤yr≤ymax) and 2 seconds in a day: ??zl and ??zr (1≤??≤??≤????1≤zl≤zr≤zmax). The store works at all such moments (month ?x, day ?y, second ?z), when simultaneously ??≤?≤??xl≤x≤xr, ??≤?≤??yl≤y≤yr and ??≤?≤??zl≤z≤zr.
Unfortunately, Natasha does not know the numbers ??,??,??,??,??,??xl,xr,yl,yr,zl,zr.
One Martian told Natasha: "I went to this store (?+?)(n+m) times. ?n times of them it was opened, and ?m times — closed." He also described his every trip to the store: the month, day, second of the trip and whether the store was open or closed at that moment.
Natasha can go to the store ?k times. For each of them, determine whether the store at the time of the trip is open, closed, or this information is unknown.
Input
The first line contains 66 integers ????xmax, ????ymax, ????zmax, ?n, ?m, ?k (1≤????,????,????≤1051≤xmax,ymax,zmax≤105, 1≤?≤1051≤n≤105, 0≤?≤1050≤m≤105, 1≤?≤1051≤k≤105) — number of months in a year, days in a month, seconds in a day, times when the store (according to a Martian) was opened, when it was closed and Natasha's queries.
The ?i-th of the next ?n lines contains 33 integers ??xi, ??yi, ??zi (1≤??≤????1≤xi≤xmax, 1≤??≤????1≤yi≤ymax, 1≤??≤????1≤zi≤zmax) — month, day and second of ?i-th time, when the store, according to the Martian, was opened.
The ?i-th of the next ?m lines contains 33 integers ??xi, ??yi, ??zi (1≤??≤????1≤xi≤xmax, 1≤??≤????1≤yi≤ymax, 1≤??≤????1≤zi≤zmax) — month, day and second of ?i-th time, when the store, according to the Martian, was closed.
The ?i-th of the next ?k lines contains 33 integers ??xi, ??yi, ??zi (1≤??≤????1≤xi≤xmax, 1≤??≤????1≤yi≤ymax, 1≤??≤????1≤zi≤zmax) — month, day and second of ?i-th Natasha's query.
Output
If the Martian was mistaken and his information about when the store is open and when it is closed is inconsistent, print a single line "INCORRECT" (without quotes).
Otherwise, print the first line "CORRECT" (without quotes). Next output ?k lines: in ?i-th of them, output an answer to ?i-th Natasha's query: "OPEN" (without quotes), if the store was opened at the moment of this query, "CLOSED" (without quotes), if it was closed, or "UNKNOWN" (without quotes), if this information can not be determined on the basis of available data.
Examples
input
Copy
10 10 10 3 1 3 2 6 2 4 2 4 6 4 6 9 9 9 3 3 3 10 10 10 8 8 8
output
Copy
CORRECT OPEN CLOSED UNKNOWN
input
Copy
10 10 10 1 1 1 2 5 7 2 5 7 8 9 10
output
Copy
INCORRECT
Note
Consider the first test case.
There are 1010 months in a year, 1010 days in a month, and 1010 seconds in a day.
The store was opened in 33 moments:
- month 22, day 66, second 22;
- month 44, day 22, second 44;
- month 66, day 44, second 66.
The store was closed at the time: month 99, day 99, second 99.
Queries:
- month 33, day 33, second 33 — open ("OPEN") (since the store opens no later than month 22, day 22, second 22 and closes no earlier than in month 66, day 66, second 66);
- month 1010, day 1010, second 1010 — closed ("CLOSED") (since it is closed even in the month 99, day 99, second 99);
- month 88, day 88, second 88 — unknown ("UNKNOWN") (because the schedule in which the store is open at this moment exists, and the schedule in which the store is closed at this moment exists as well).
In the second test case, the store was closed and opened at the same time — contradiction ("INCORRECT").
题意
有一个国家,他们每一年有xmaxxmax月,每月有ymaxymax天,每天有zmaxzmax秒。这个国家的商店的时间表是这样排的:在一年中选出两个月:xl,xr(1≤xl≤xr≤xmax)xl,xr(1≤xl≤xr≤xmax),在一个月中选出两天:yl,yr(1≤yl≤yr≤ymax)yl,yr(1≤yl≤yr≤ymax),在每天中选出两秒:zl,zr(1≤zl≤zr≤zmax)zl,zr(1≤zl≤zr≤zmax)。商店在第xx月,第yy天,第zz秒(xl≤x≤xr,yl≤y≤yr,zl≤z≤zr)(xl≤x≤xr,yl≤y≤yr,zl≤z≤zr)会开门。现在有一个人,想去商店买东西,但是他并不知道准确的xl,xr,yl,yr,zl,zrxl,xr,yl,yr,zl,zr,他知道有n(1≤n≤105)n(1≤n≤105)个时间点,商店是开门的,有m(1≤m≤105)m(1≤m≤105)个时间点,商店是不开门的。
(1)(1)你的第一个任务是判断他的信息是否有错误,有错误输出INCORRECT,并跳过第二个任务;如果正确,输出CORRECT,继续执行第二个任务。
(2)(2)之后他给出k(1≤k≤105)k(1≤k≤105)个时间点,问你能不能确定这个时间点商店是否开门。如果开门,输出OPEN;如果不开门,输出CLOSE;如果不确定输出UNKNOWN。分析
这道题在比赛的时候并没有时间想,因为前面的题由于自己的智障花掉了太多时间。赛后想想发现其实也不是特别难。
首先因为商店开门的时间其实可以转化为一个长方体,而知道商店开门的时间点就是在三维坐标系中位于这个长方体中的一个点,而商店关门的时间则是不在这个长方体中的一个点。询问就是给出一个点,问你这个点是否一定在长方形内部。
我们先将原来给出的商店开门的时间构造成一个原长方体。对于一次询问,如果这个点在原长方体内,那么这个时间点商家一定是开门的。对于剩下的点,我们先将这个点假设为可以开门的点,那么我们可以扩大这个长方体。如果这个长方体扩大后发现没有任何一个关门的时间点在这个长方体内的话,那么是有可能开门的也有可能关门的,输出UNKNOWN。那么剩下的点就一定是关门的时间点了。这样可以将这个问题转化为三维数点的问题。对于这个问题我写的是二维线段树,然后里面那一维动态开点,然而应该也可以用KD-tree,或CDQ分治来做。
---------------------
作者:Effervescence
来源:优快云
原文:https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/effervescence/article/details/81236076
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请附上博文链接!
有两行想了好久 :
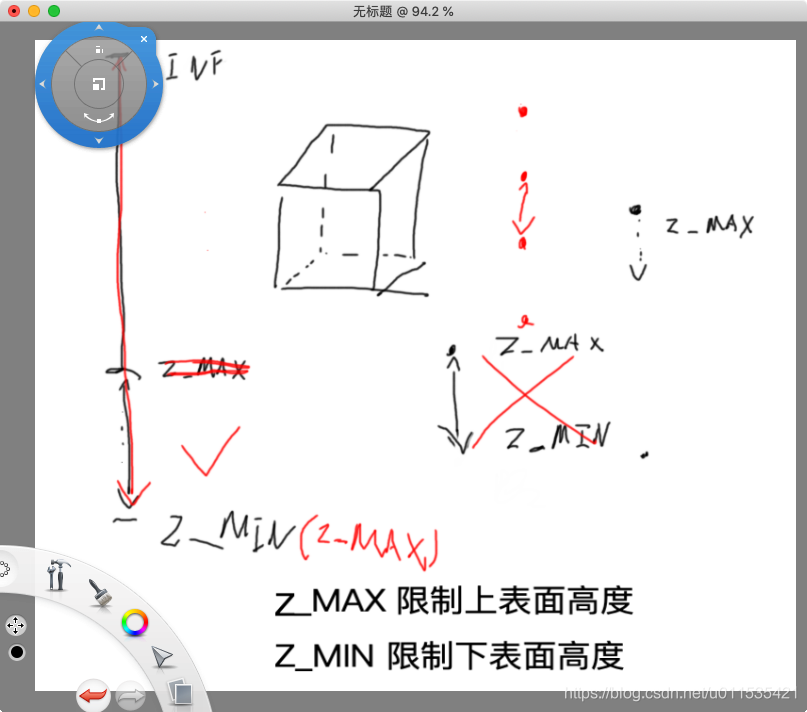
if (z_i >= open_z_l) node[cur].z_max = min(node[cur].z_max, z_i);
if (z_i <= open_z_r) node[cur].z_min = max(node[cur].z_min, z_i);
为什么要这个条件限制,见下图
然后就是二维线段树点修改区间查询,还卡内存 666
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 1e6+6e6;
int x_max, y_max, z_max, n, m, k, x_i, y_i, z_i,
open_x_l, open_y_l, open_z_l, open_x_r, open_y_r, open_z_r,
cnt_node = 1;
struct Node{
int lc, rc, z_max, z_min;
}node[MAXN];
const int MAXX = 4e5+55;
int y_tree_start[MAXX];
int node_z_max, node_z_min;
void update_y(int &cur, int l, int r, int y_i, int z_i){
if (!cur) {
cur = cnt_node++;
node[cur].z_max = z_max + 1;
node[cur].z_min = 0;
}
// important 上面的点
if (z_i >= open_z_l) node[cur].z_max = min(node[cur].z_max, z_i);
if (z_i <= open_z_r) node[cur].z_min = max(node[cur].z_min, z_i);
if (l == r) return;
int mid = l+r>>1;
if (y_i <= mid) update_y(node[cur].lc, l, mid, y_i, z_i);
if (y_i > mid) update_y(node[cur].rc, mid+1, r, y_i, z_i);
}
void update_x(int cur, int l, int r, int x_i, int y_i, int z_i){
update_y(y_tree_start[cur], 1, y_max, y_i, z_i);
if (l == r) return;
int mid = l+r>>1;
if (x_i <= mid) update_x(cur<<1, l, mid, x_i, y_i, z_i);
if (x_i > mid) update_x(cur<<1|1, mid+1, r, x_i, y_i, z_i);
}
bool query_y(int cur, int l, int r, int qy_min, int qy_max, int qz_min, int qz_max){
if (!cur) return 1;
if (qy_min<=l && r<=qy_max){
//printf("qz_min = %d qz_max = %d node[cur].z_min = %d node[cur].z_max = %d\n",
// qz_min, qz_max, node[cur].z_min, node[cur].z_max);
return qz_min > node[cur].z_min && qz_max < node[cur].z_max;
}
int mid = l+r>>1, retr = 1;
if (qy_min <= mid) retr &= query_y(node[cur].lc, l, mid, qy_min, qy_max, qz_min, qz_max);
if (qy_max > mid) retr &= query_y(node[cur].rc, mid+1, r, qy_min, qy_max, qz_min, qz_max);
return retr;
}
// retrun if it's unknown
bool query_x(int cur, int l, int r, int qx_min, int qx_max, int qy_min, int qy_max, int qz_min, int qz_max){
if (qx_min<=l && r<=qx_max){
return query_y(y_tree_start[cur], 1, y_max, qy_min, qy_max, qz_min, qz_max);
}
int mid = l+r>>1, retr = 1;
if (qx_min <= mid) retr &= query_x(cur<<1, l, mid, qx_min, qx_max, qy_min, qy_max, qz_min, qz_max);
if (qx_max > mid) retr &= query_x(cur<<1|1, mid+1, r, qx_min, qx_max, qy_min, qy_max, qz_min, qz_max);
return retr;
}
int main(){
scanf("%d%d%d%d%d%d", &x_max, &y_max, &z_max, &n, &m, &k);
open_x_l = x_max; open_y_l = y_max; open_z_l = z_max;
for (int i=0; i<n; i++){
scanf("%d%d%d", &x_i, &y_i, &z_i);
open_x_l = min(open_x_l, x_i);
open_x_r = max(open_x_r, x_i);
open_y_l = min(open_y_l, y_i);
open_y_r = max(open_y_r ,y_i);
open_z_l = min(open_z_l, z_i);
open_z_r = max(open_z_r, z_i);
}
//printf("%d %d %d %d %d %d", open_x_l ,open_x_r, open_y_l, open_y_r, open_z_l, open_z_r);
for (int i=0; i<m; i++){
scanf("%d%d%d", &x_i, &y_i, &z_i);
if (open_x_l <= x_i && x_i <= open_x_r && open_y_l <= y_i && y_i <= open_y_r
&& open_z_l <= z_i && z_i <= open_z_r){
puts("INCORRECT");
return 0;
}
update_x(1, 1, x_max, x_i, y_i, z_i);
}
puts("CORRECT");
for (int i=0; i<k; i++){
scanf("%d%d%d", &x_i, &y_i, &z_i);
if (open_x_l <= x_i && x_i <= open_x_r && open_y_l <= y_i && y_i <= open_y_r
&& open_z_l <= z_i && z_i <= open_z_r){
puts("OPEN");
continue;
}
if (query_x(1, 1 ,x_max, min(x_i, open_x_l), max(x_i, open_x_r),
min(y_i, open_y_l), max(y_i, open_y_r),
min(z_i, open_z_l), max(z_i, open_z_r)) ){
puts("UNKNOWN");
}
else {
puts("CLOSED");
}
}
}








 本文探讨了一个三维数点问题,通过构建长方体模型和利用二维线段树来解决商店开门时间判断的难题。介绍了如何使用线段树进行点修改和区间查询,以确定特定时间点商店是否开门。
本文探讨了一个三维数点问题,通过构建长方体模型和利用二维线段树来解决商店开门时间判断的难题。介绍了如何使用线段树进行点修改和区间查询,以确定特定时间点商店是否开门。
















 558
558

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








