目录
1.2 方案2 使用sycnchronized+wait+notify
一 场景1 交替执行
1.1 方案1使用completablefuture
1.代码
package com.ljf.thread.jiaoti;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
/**
* @ClassName: main
* @Description: TODO
* @Author: admin
* @Date: 2024/12/10 20:25:15
* @Version: V1.0
**/
public class JTctf {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int k=1;k<10;k++) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("我是线程t1");
}
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
t1.join();
System.out.println("我是线程t2");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
});
Thread t3 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
t2.join();
System.out.println("我是线程t3");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
});
CompletableFuture completableFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
t1.start();
}).thenRun(() -> {
t2.start();
}
).thenRun(() -> {
t3.start();
});
}
}
}
2.结果:
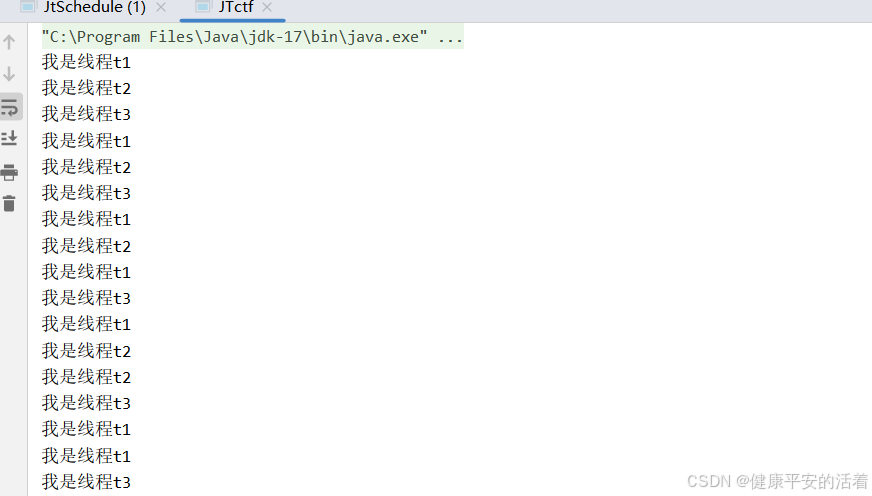
1.2 方案2 使用sycnchronized+wait+notify
1.代码
package com.ljf.thread.jiaoti;
/**
* @ClassName: JT
* @Description: https://blog.51cto.com/mouday/11443720
* @Author: admin
* @Date: 2024/12/10 20:08:40
* @Version: V1.0
**/
public class JT {
private static String flag="A";
private static Object obj =new Object();
public static void main(String args[]){
for (int k=1;k<10;k++) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (obj) {
while (!"A".equals(flag)) {//不等于A时
try {
// System.out.println("不等于A时,当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 等待....");
obj.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
//等于A时
System.out.println("线程A...");
flag = "B";
obj.notifyAll();
}
}
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (obj) {
while (!"B".equals(flag)) {//不等于B时
try {
// System.out.println("不等于B时,当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 等待....");
obj.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
//等于A时
System.out.println("线程B...");
flag = "C";
obj.notifyAll();
}
}
});
Thread t3 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (obj) {
while (!"C".equals(flag)) {//不等于C时
try {
// System.out.println("不等于C时,当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 等待....");
obj.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
//等于C时
System.out.println("线程C...");
flag = "A";
obj.notifyAll();
}
}
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
//System.out.println("====");
}
}
}
2.结果
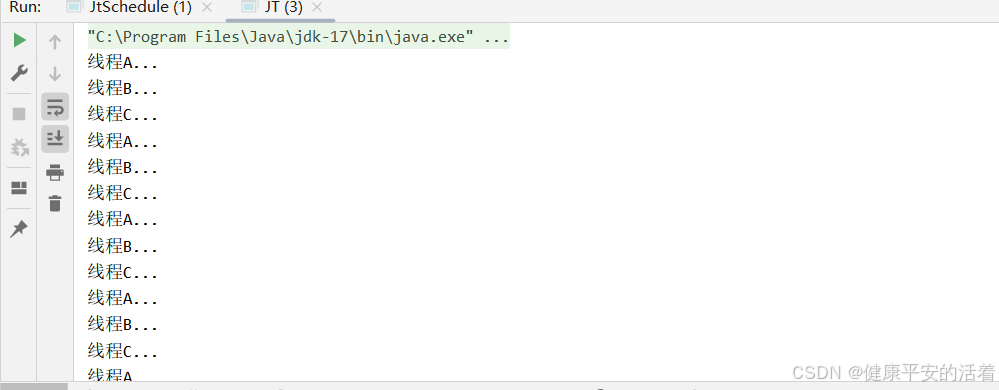
二 场景2 同时执行
2.1 使用countdownlatch
1.代码
package com.ljf.thread.tongshi;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
/**
* @ClassName: TS
* @Description: TODO
* @Author: admin
* @Date: 2024/12/10 20:38:54
* @Version: V1.0
**/
public class TS {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);
ExecutorService es = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
es.submit(()->{
try {
countDownLatch.await();
System.out.println("线程A"+System.currentTimeMillis());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
});
es.submit(()->{
try {
countDownLatch.await();
System.out.println("线程B"+System.currentTimeMillis());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
});
es.submit(()->{
try {
countDownLatch.await();
System.out.println("线程C"+System.currentTimeMillis());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
});
countDownLatch.countDown();
es.shutdown();
}
}
2.结果
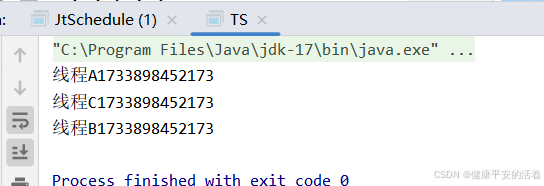
三 场景3 顺序执行
3.1 使用join
1.代码
package com.ljf.thread.shunxu;
/**
* @ClassName: JtJoin
* @Description: TODO
* @Author: admin
* @Date: 2024/12/10 17:11:36
* @Version: V1.0
**/
public class SxJoin {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("我是线程t1");
}
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
t1.join();
System.out.println("我是线程t2");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
});
Thread t3 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
t2.join();
System.out.println("我是线程t3");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}2.执行结果
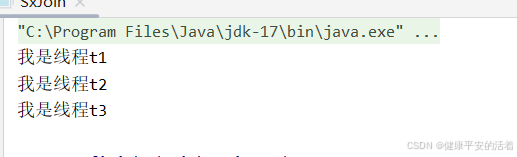
3.2 使用countdownlatch
1.代码
package com.ljf.thread.shunxu;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
/**
* @ClassName: SxCountD
* @Description: https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/ply78SKIiA0Ru0CzYqlWrQ
* @Author: admin
* @Date: 2024/12/10 19:41:16
* @Version: V1.0
**/
public class SxCountD {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CountDownLatch cd1 = new CountDownLatch(0);
CountDownLatch cd2 = new CountDownLatch(1);
CountDownLatch cd3 = new CountDownLatch(1);
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Work(cd1,cd2),"t1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(new Work(cd2,cd3),"t2");
Thread t3 = new Thread(new Work(cd3,cd3),"t3");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}
public class Work implements Runnable{
CountDownLatch ct1;
CountDownLatch ct2;
public Work(CountDownLatch ct1, CountDownLatch ct2) {
this.ct1 = ct1;
this.ct2 = ct2;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
ct1.await();
System.out.println("线程:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
finally {
ct2.countDown();
}
}
}2.结果
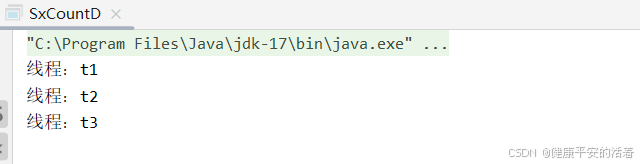
3.3 使用单例线程池
1.代码
package com.ljf.thread.shunxu;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
/**
* @ClassName: JtSchedule
* @Description: TODO
* @Author: admin
* @Date: 2024/12/10 17:19:35
* @Version: V1.0
**/
public class SxSchedule {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("我是线程t1");
}
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("我是线程t2");
}
});
Thread t3 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("我是线程t3");
}
});
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
executorService.submit(t1);
executorService.submit(t2);
executorService.submit(t3);
executorService.shutdown();
}
}
2.执行结果
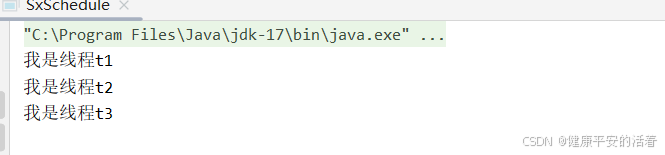
3.4 使用单例线程池
1.代码
package com.ljf.thread.shunxu;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
/**
* @ClassName: SxCompletefutureable
* @Description: TODO
* @Author: admin
* @Date: 2024/12/10 17:27:24
* @Version: V1.0
**/
public class SxCompletefutureable {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int k = 1; k < 10; k++) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("我是线程t1");
}
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
t1.join();
System.out.println("我是线程t2");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
});
Thread t3 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
t2.join();
System.out.println("我是线程t3");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
});
CompletableFuture ct1 = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
t1.start();
});
ct1.thenRun(() -> {
t2.start();
}).thenRun(() -> {
t3.start();
});
}
}
}
2.结果
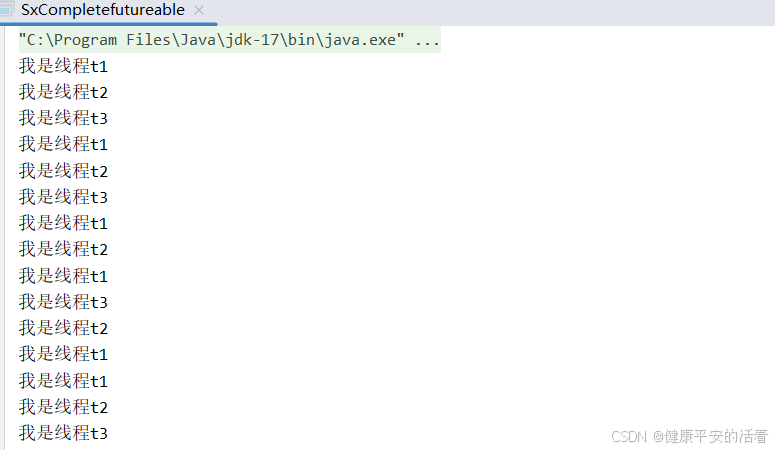






















 288
288

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








