一 多线程原子性
1.1 基本数据类型原子
atomicInteger, atomicLong,atomicBoolean
1.代码countdownlatch
package com.ljf.thread.atomic;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
class MyNumber
{
AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger();
public void addPlusPlus()
{
atomicInteger.getAndIncrement();
}
}
/**
* @ClassName: AtomicDemo
* @Description: TODO
* @Author: admin
* @Date: 2023/11/06 22:24:14
* @Version: V1.0
**/
public class AtomicDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyNumber myNumber = new MyNumber();
CountDownLatch ct=new CountDownLatch(10);
for(int k=1;k<=10;k++){
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for(int k=0;k<30;k++){
myNumber.addPlusPlus();
}
ct.countDown();
}
},String.valueOf(k)).start();
}
ct.await();
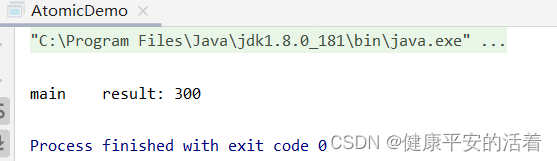
System.out.println("");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+"result: "+myNumber.atomicInteger.get());
}
}
结果:
1.2 原子数组类型
1.AtomicIntegerArray 2.AtomicLongArray 3. AtomicReferenceArray
1.3 引用数据类型
1.AtomicReference
2.AtomicStampedReference 携带版本号的引用类,解决修改过几次
3.AtomicMarkableReference 原子更新带有标记位 解决是否修改过 状态戳 true/false
1.4 字段级别原子更新
1.4.1 介绍作用
1.AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater 原子更新对象中int类型字段的值
2.AtomicLongFieldUpdater 原子更新对象中Long类型字段的值。
3.AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater 原子更新引用数据类型字段的值
目的:以一种线程安全的方式操作非线程安全的对象内的某些字段。更新的对象属性必须使用public volatile修饰符。因为对象的属性修改类型原子类都是抽象类,所有每次使用都必须使用静态方法newUpdate()方法创建一个更新器,并且需要设置想要更新的类和属性。
1.4.2 代码
1.4.2.1 原始锁的方式
1.原始锁方式
public class AtomicDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
CountDownLatch countDownLatch=new CountDownLatch(10);
PayInfo payInfo =new PayInfo();
for(int k=0;k<10;k++){
new Thread(()->{
try {
for (int m = 0; m < 1000; m++) {
payInfo.add();
//payInfo.transferMoney(payInfo);
}
}
catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
countDownLatch.countDown();
}
}).start();
}
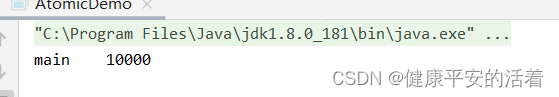
countDownLatch.await();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+payInfo.money);
}
}
资源类
public class PayInfo {
String bankName = "icbc";
int money = 0;
// public volatile int money = 0;
public synchronized void add(){
money++;
}
// AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater<PayInfo> atomicIntegerFieldUpdater=AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater.newUpdater(PayInfo.class,"money");
// public void transferMoney(PayInfo payInfo){
// atomicIntegerFieldUpdater.getAndIncrement(payInfo);
// }
}
3.结果
1.4.2.2 字段级别的更新
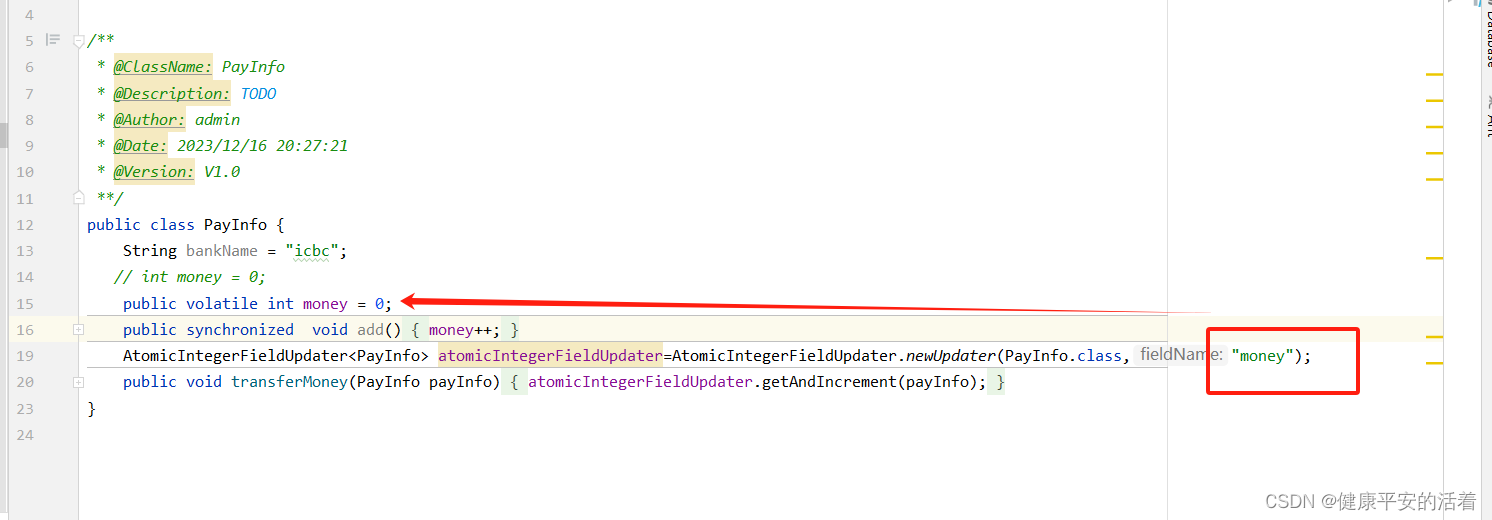
1.资源类
public class PayInfo {
String bankName = "icbc";
// int money = 0;
public volatile int money = 0;
public synchronized void add(){
money++;
}
AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater<PayInfo> atomicIntegerFieldUpdater=AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater.newUpdater(PayInfo.class,"money");
public void transferMoney(PayInfo payInfo){
atomicIntegerFieldUpdater.getAndIncrement(payInfo);
}
}
2.代码
public class AtomicDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
CountDownLatch countDownLatch=new CountDownLatch(10);
PayInfo payInfo =new PayInfo();
for(int k=0;k<10;k++){
new Thread(()->{
try {
for (int m = 0; m < 1000; m++) {
//payInfo.add();
payInfo.transferMoney(payInfo);
}
}
catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
countDownLatch.countDown();
}
}).start();
}
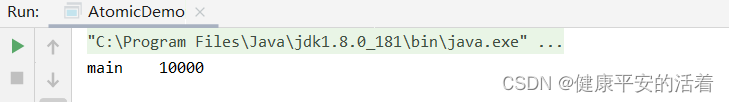
countDownLatch.await();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+payInfo.money);
}
}
3.结果
1.5 LongAdder与LongAccumlator
1.5.1 介绍
LongAdder 只能用来计算加法,且从零开始计算。
LongAccumulator提供了自定义的函数操作。
1.5.2 代码
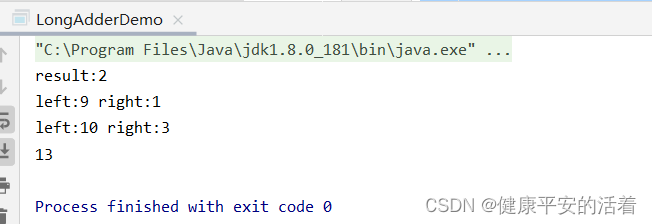
public class LongAdderDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LongAdder longAdder=new LongAdder();
longAdder.increment();
longAdder.increment();
System.out.println("result:"+longAdder.toString());
LongAccumulator longAccumulator = new LongAccumulator(new LongBinaryOperator()
{
@Override
public long applyAsLong(long left, long right)
{
System.out.println("left:"+left+" right:"+right);
return left + right;
}
},9);
longAccumulator.accumulate(1);//1
longAccumulator.accumulate(3);//4
System.out.println(longAccumulator.get());
}
}
结果:
1.6 四种原子操作计数的比较
1.代码
package com.ljf.thread.atomic;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.LongAccumulator;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.LongAdder;
/**
* @ClassName: Clik
* @Description: TODO
* @Author: admin
* @Date: 2023/12/24 10:51:07
* @Version: V1.0
**/
public class Clik {
int number = 0;
public synchronized void clickBySynchronized()
{
number++;
}
AtomicLong atomicLong = new AtomicLong(0);
public void clickByAtomicLong()
{
atomicLong.getAndIncrement();
}
LongAdder longAdder = new LongAdder();
public void clickByLongAdder()
{
longAdder.increment();
}
LongAccumulator longAccumulator = new LongAccumulator((x, y) -> x + y,0);
public void clickByLongAccumulator()
{
longAccumulator.accumulate(1);
}
}
2.调用类
package com.ljf.thread.atomic;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
/**
* @ClassName: AccumulatorCompareDemo
* @Description: TODO
* @Author: admin
* @Date: 2023/12/24 10:51:51
* @Version: V1.0
**/
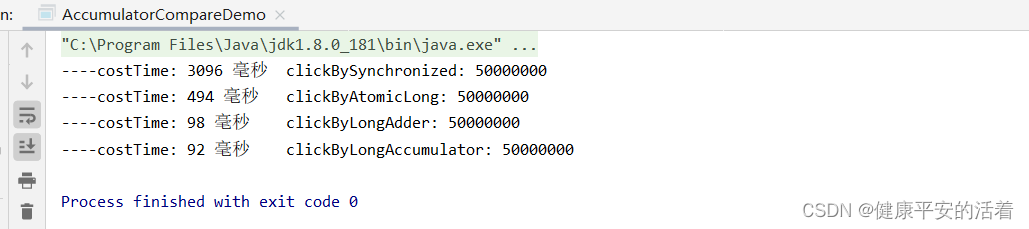
public class AccumulatorCompareDemo {
public static final int _1W = 10000;
public static final int threadNumber = 50;
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
long startTime;
long endTime;
Clik clik=new Clik();
CountDownLatch countDownLatch1 = new CountDownLatch(threadNumber);
CountDownLatch countDownLatch2 = new CountDownLatch(threadNumber);
CountDownLatch countDownLatch3 = new CountDownLatch(threadNumber);
CountDownLatch countDownLatch4 = new CountDownLatch(threadNumber);
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 1; i <=threadNumber; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int j = 1; j <=100 * _1W; j++) {
clik.clickBySynchronized();
}
} finally {
countDownLatch1.countDown();
}
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
countDownLatch1.await();
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("----costTime: "+(endTime - startTime) +" 毫秒"+"\t clickBySynchronized: "+clik.number);
//
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 1; i <=threadNumber; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int j = 1; j <=100 * _1W; j++) {
clik.clickByAtomicLong();
}
} finally {
countDownLatch2.countDown();
}
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
countDownLatch2.await();
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("----costTime: "+(endTime - startTime) +" 毫秒"+"\t clickByAtomicLong: "+clik.number);
//
//
//
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 1; i <=threadNumber; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int j = 1; j <=100 * _1W; j++) {
clik.clickByLongAdder();
}
} finally {
countDownLatch3.countDown();
}
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
countDownLatch3.await();
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("----costTime: "+(endTime - startTime) +" 毫秒"+"\t clickByLongAdder: "+clik.number);
//
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 1; i <=threadNumber; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int j = 1; j <=100 * _1W; j++) {
clik.clickByLongAccumulator();
}
} finally {
countDownLatch4.countDown();
}
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
countDownLatch4.await();
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("----costTime: "+(endTime - startTime) +" 毫秒"+"\t clickByLongAccumulator: "+clik.number);
}
}
1.7 logAdder为何比atomic要快
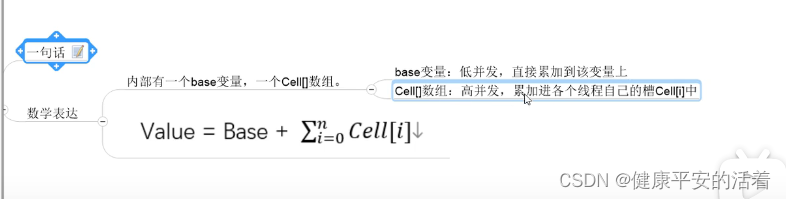
1.logadder的基本思想是分散热点,将value值分散到一个cell数组中,不同线程会命中到数组的不同槽中,各个线程只对自己槽中的那个值进行cas操作,这样热点就被分散了,冲突的概率就小很多,如果要获取真正的long值,只要将各个槽中的变量值累加。
sum()会根据所有cell数组中的value和base累加作为返回值,核心的思想就是将之前的AtomicLog的一个value的更新压力分散到多个value中去。从而降级更新热点。
概述:内部有一个base变量,一个cell[i]数组,最终结果=base+所有cell[i]数组和。
1.8 logAdder的源码
1.最初无竞争时只更新base;
2.如果更新base失败后,首次新建一个cell[]数组
3.当多个线程竞争同一个cell比较激烈时,可能就要对cell[]扩容。

1.9 总结
| 名称 | 原理 | 场景 | 缺陷 |
| AtomciLong | cas+自旋+incrementAndGet | 低并发下的全局计算;保证在并发下的计算的正确性 | 自旋会成为瓶颈。n个线程cas操作线程的值,每次只有一个修改成功,n-1个失败,失败不停自旋,大量失败自旋,一下子cpu就打高了。 |
| LongAdder | cas+base+Cell数组分散;空间换时间分散了热点数据 | 高并发下的全局计算 | sum求和后还有计算线程修改结果的话,最后结果不够准确 |





 本文详细介绍了Java中多线程环境下的原子性操作,包括基本数据类型原子、数组类型原子、引用数据类型的原子引用和字段级别原子更新,以及LongAdder、LongAccumulator的使用和它们与AtomicLong的区别。重点讨论了并发场景下原子操作的性能和优化策略。
本文详细介绍了Java中多线程环境下的原子性操作,包括基本数据类型原子、数组类型原子、引用数据类型的原子引用和字段级别原子更新,以及LongAdder、LongAccumulator的使用和它们与AtomicLong的区别。重点讨论了并发场景下原子操作的性能和优化策略。
















 1007
1007

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








