一 传统IO
1.1 传统IO的客户端
public class IOClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Socket socket = new Socket("localhost", 7001);
String fileName = "d:/test-file/P2PR203702_2021-06-29 09-33-26 186.txt";
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(fileName);
DataOutputStream dataOutputStream = new DataOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream());
byte[] buffer = new byte[4096];
long readCount;
long total = 0;
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
while ((readCount = inputStream.read(buffer)) >= 0) {
total += readCount;
dataOutputStream.write(buffer);
}
System.out.println("发送总字节数: " + total + ", 耗时: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime));
dataOutputStream.close();
socket.close();
inputStream.close();
}
}
1.2 传统IO的服务端
public class IOServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(7001);
while (true) {
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
DataInputStream dataInputStream = new DataInputStream(socket.getInputStream());
try {
byte[] byteArray = new byte[4096];
while (true) {
int readCount = dataInputStream.read(byteArray, 0, byteArray.length);
System.out.println("readCount:"+readCount);
if (-1 == readCount) {
break;
}
String content=new String(byteArray,0,readCount);
System.out.println("content:"+content);
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
1.3 调试结果
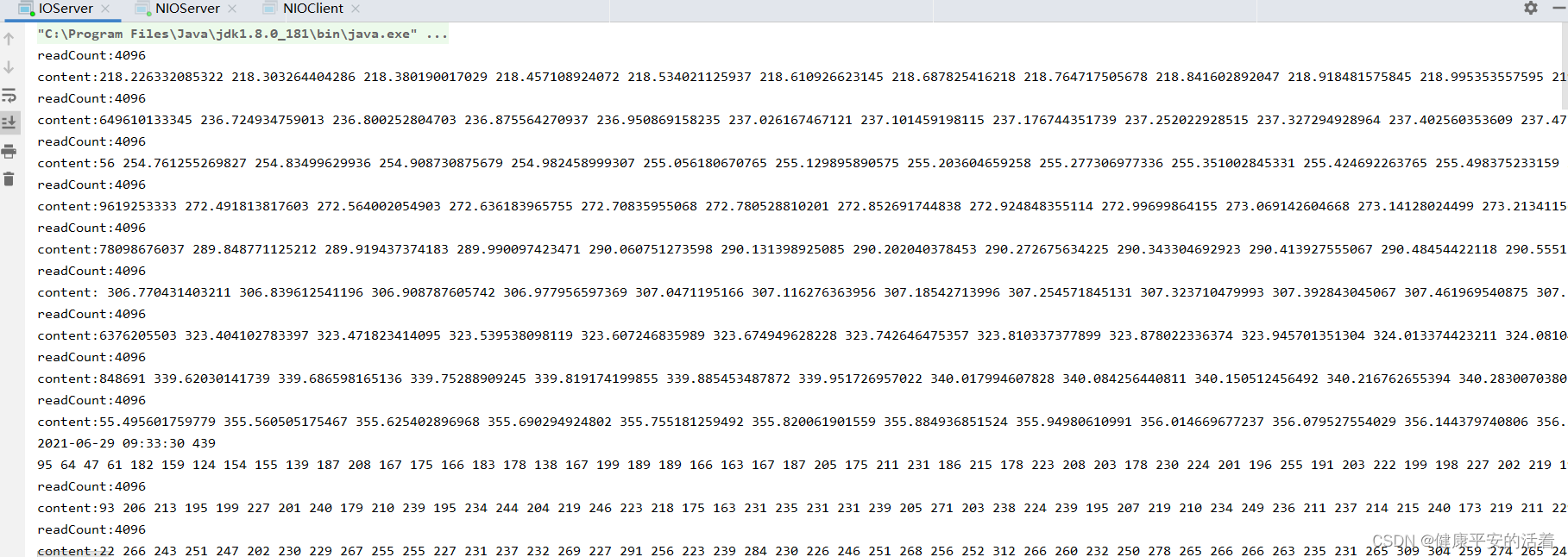
二 Nio实现此功能
2.1 NIO客户端
public class NIOClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 7002));
String filename = "d:/test-file/P2PR203702_2021-06-29 09-33-26 186.txt";
//得到一个文件channel
FileChannel fileChannel = new FileInputStream(filename).getChannel();
//准备发送
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
//在linux下一个transferTo 方法就可以完成传输
//在windows 下 一次调用 transferTo 只能发送8m , 就需要分段传输文件, 而且要主要
//传输时的位置 =》 课后思考...
//transferTo 底层使用到零拷贝
long transferCount = fileChannel.transferTo(0, fileChannel.size(), socketChannel);
System.out.println("发送的总的字节数 =" + transferCount + " 耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime));
//关闭
fileChannel.close();
}
}
2.2 NIO服务端
输出内容:System.out.println("from 客户端:"+new String(byteBuffer.array()));
public class NIOServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InetSocketAddress address = new InetSocketAddress(7002);
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
ServerSocket serverSocket = serverSocketChannel.socket();
serverSocket.bind(address);
//创建buffer
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(4096);
while (true) {
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
int readcount = 0;
while (-1 != readcount) {
try {
readcount = socketChannel.read(byteBuffer);
System.out.println("from 客户端:"+new String(byteBuffer.array()));
}catch (Exception ex) {
// ex.printStackTrace();
break;
}
//
byteBuffer.rewind(); //倒带 position = 0 mark 作废
}
}
}
}
2.3 结果






 本文探讨了传统IO与NIO在Java中客户端与服务端的实现,包括使用FileInputStream/OutputStream与SocketChannel/FileChannel进行文件读写,并比较了两者在性能和操作上的差异。NIO通过`transferTo`和`ByteBuffer`展示了零拷贝的优势。
本文探讨了传统IO与NIO在Java中客户端与服务端的实现,包括使用FileInputStream/OutputStream与SocketChannel/FileChannel进行文件读写,并比较了两者在性能和操作上的差异。NIO通过`transferTo`和`ByteBuffer`展示了零拷贝的优势。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








