我用的是win10系统,想看linux系统下操作的请出门右转其他博主的文章。
一、安装rabbitmq
1.要安装RabbitMQ先必须安装erlang。 官网地址:http://www.erlang.org/downloads。选择wind 64位安装。
2.安装rabbitmq,官网地址:http://www.rabbitmq.com/download.html。
(1). rabbitmq在安装过程中需要特别注意 两个.erlang.cookie里面的内容必须一致。否则会一直报:
TCP connection succeeded but Erlang distribution failed
* suggestion: hostname mismatch?
* suggestion: is the cookie set correctly?
* suggestion: is the Erlang distribution using TLS?
一个在C:\Windows,这个文件夹下的.erlang.cookie。一个在C:\Users\sdc 这个文件夹下,
这两个文件里的内容必须一致。如果不一致或者你只发现了一个,就把另一个复制到那里就行了。
(2).安装rabbit好之后就可以在电脑的服务上看到rabbitmq了。我们还需要安装 rabbitmq management来在web上
对rabbit进行管理。
Program Files是rabbitmq默认的文件夹,在C:\Program Files\RabbitMQ Server\rabbitmq_server-3.6.9\sbin 处
运行shell命令
./rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_management 注意 前面的./。我的wind10不加 ./ 是会报错,安装失败的。
(3).安装成功之后,在浏览器输入http://127.0.0.1:15672/,输入默认用户名“guest”和默认密码"guest"就可以登录管理页面了。
二、springboot整合rabbitmq
1.在pom.xml里引入 下面代码spring-boot-starter-amqp。
- <dependency>
- <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
- <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
- </dependency>
2.不需要在启动类前加@EnableRabbit 和 新建 ConnectionFactory(),不需要。因为可以在propertires里配置rabbitmq的选项。
#rabbitmq
spring.rabbitmq.addresses=127.0.0.1:5672
spring.rabbitmq.username=wangjk
spring.rabbitmq.password=wangjk
spring.rabbitmq.publisher-confirms=true
spring.rabbitmq.virtual-host=/
spring.rabbitmq.listener.acknowledge-mode=manual为什么不用默认的用户名guest和密码,因为guest帐号只能用来在管理端,远程连接rabbitmq会被拒绝的。所以只好自己新建了一个用户,分配了管理员的权限。
至此,rabbitmq就算是整合到springboot里了。下面开始介绍在springboot中如何使用rabbitmq。
三、springboot中使用各种模式的rabbitmq
《rabbitmq实战》中说的rabbitmq 的5种模式
1.简单模式 2.工作队列模式 3.发布订阅模式 4.路由模式 5.主题模式
简单模式
其中1跟2只是消费者C是一个还是多个的问题,可以归纳到一起。简单发送模式看起来是没有用到交换机的,
类似于P -> Q -> C(C1,C2)的。一个生产者P发送消息到队列Q,一个或者多个消费者C接收。
我的P和C是写在两个springboot项目上的
producerClient的 Sender类代码。
package com.beltoo.producer.rabbitmq;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Sender {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
//简单发送队列
public static final String SIMPLE_QUEUE = "tea";
// 发布/订阅模式
public static final String FANOUT_EXCHANGE = "fanout_exchange";
//路由模式
public static final String DIRECT_EXCHANGE = "direct_exchange";
//主题模式
public static final String TOPIC_EXCHANGE = "topic_exchange";
/**
* 简单模式发送 String类型消息
* @param message
*/
public void send(String message) {
this.rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(SIMPLE_QUEUE,message);
}
/**
* 简单模式发送 Map类型消息
* @param message
*/
public void sendMapMessage(Map map) {
this.rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(SIMPLE_QUEUE,map);
}
/**
* 发布/订阅模式发送
* @param message
*/
public void psSend(String message) {
this.rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(FANOUT_EXCHANGE, "", message);
}
/**
* 路由模式发送
*
* @param message
*/
public void routingSend(String routingKey, String message) {
this.rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(DIRECT_EXCHANGE, routingKey, message);
}
/**
* 主题模式发送
*
* @param routingKey
* @param message
*/
public void topicSend(String routingKey, String message) {
this.rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(TOPIC_EXCHANGE, routingKey, message);
}
}
单独把简单发送模式的代码拿出来讲:
//简单发送队列
public static final String SIMPLE_QUEUE = "tea";
/**
* 简单模式发送 String类型消息
* @param message
*/
public void send(String message) {
this.rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(SIMPLE_QUEUE,message);
}
/**
* 简单模式发送 Map类型消息
* @param message
*/
public void sendMapMessage(Map map) {
this.rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(SIMPLE_QUEUE,map);
}rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(SIMPLE_QUEUE,message); 看看源码:
@Override
public void convertAndSend(String routingKey, final Object object) throws AmqpException {
convertAndSend(this.exchange, routingKey, object, (CorrelationData) null);
}Controller 代码
package com.beltoo.producer.controller;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestHeader;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONArray;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import com.beltoo.producer.common.ResultUtils;
import com.beltoo.producer.entity.Book;
import com.beltoo.producer.entity.Result;
import com.beltoo.producer.rabbitmq.Sender;
import io.swagger.annotations.Api;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParam;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParams;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiOperation;
/**
* rabbitmq测试contronller
* @author wang
* @date 2018年4月3日
*/
@RestController
@Api(value="rabbitMqContronller",description="rabbitmq测试类")
public class RabbitMqContronller {
public static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RabbitMqContronller.class);
@Autowired
private Sender sender ;
@ApiOperation(value = "简单模式发送String消息",notes = "简单模式发送String消息" )
@ApiImplicitParams({
@ApiImplicitParam(name="Accept",value="接收属性",required=true,dataType="String",paramType="header",defaultValue="application/json"),
@ApiImplicitParam(name="Accept-Charset",value="接受字符集",required=true,dataType="String",paramType="header",defaultValue="utf-8"),
@ApiImplicitParam(name="Content-Type",value="内容类型",required=false,dataType="String",paramType="header",defaultValue="application/json")
})
@GetMapping("/rabbitmq/directsend/a")
public Result<?> sendStringMq( @RequestParam String message, @RequestHeader HttpHeaders headers){ //这里用于测试,key值可以自定义实现
try {
sender.send(message);
return ResultUtils.success(message);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
logger.error("mq发送消息失败:"+e.getMessage(), e);
}
return ResultUtils.error(1, "mq发送消息失败");
}
@ApiOperation(value = "简单模式发送Map消息",notes = "简单模式发送Map消息" )
@ApiImplicitParams({
@ApiImplicitParam(name="Accept",value="接收属性",required=true,dataType="String",paramType="header",defaultValue="application/json"),
@ApiImplicitParam(name="Accept-Charset",value="接受字符集",required=true,dataType="String",paramType="header",defaultValue="utf-8"),
@ApiImplicitParam(name="Content-Type",value="内容类型",required=false,dataType="String",paramType="header",defaultValue="application/json")
})
@GetMapping("/rabbitmq/directsend/b")
public Result<?> sendMapMq( @RequestParam String message, @RequestHeader HttpHeaders headers){ //这里用于测试,key值可以自定义实现
try {
Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("name", "蚂蚁上树");
map.put("age", "20");
sender.sendMapMessage(map);
return ResultUtils.success(map);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
logger.error("mq发送消息失败:"+e.getMessage(), e);
}
return ResultUtils.error(1, "mq发送消息失败");
}
@ApiOperation(value = "发布/订阅模式发送消息",notes = "发布/订阅模式发送消息" )
@ApiImplicitParams({
@ApiImplicitParam(name="Accept",value="接收属性",required=true,dataType="String",paramType="header",defaultValue="application/json"),
@ApiImplicitParam(name="Accept-Charset",value="接受字符集",required=true,dataType="String",paramType="header",defaultValue="utf-8"),
@ApiImplicitParam(name="Content-Type",value="内容类型",required=false,dataType="String",paramType="header",defaultValue="application/json")
})
@GetMapping("/rabbitmq/pssend")
public Result<?> sendPsMq( @RequestParam String message, @RequestHeader HttpHeaders headers){ //这里用于测试,key值可以自定义实现
try {
sender.psSend(message);
return ResultUtils.success(message);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
logger.error(" 发布/订阅模式下发送mq消息失败:"+e.getMessage(), e);
}
return ResultUtils.error(101, "发布/订阅模式下发送mq消息失败");
}
/*
* 路由模式发送mq
*/
@ApiOperation(value = "路由模式发送消息",notes = "路由模式发送消息" )
@ApiImplicitParams({
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "message",value="要传送的消息jsonArray",required = true,dataType = "String" , paramType ="body"),
@ApiImplicitParam(name="Accept",value="接收属性",required=true,dataType="String",paramType="header",defaultValue="application/json"),
@ApiImplicitParam(name="Accept-Charset",value="接受字符集",required=true,dataType="String",paramType="header",defaultValue="utf-8"),
@ApiImplicitParam(name="Content-Type",value="内容类型",required=false,dataType="String",paramType="header",defaultValue="application/json")
})
@PostMapping(value = "/rabbitmq/routingsend" ,produces ="application/json;charset=UTF-8")
public Result<?> sendRoutingMq( @RequestBody String message, @RequestHeader HttpHeaders headers){ //这里用于测试,key值可以自定义实现
JSONArray jsonArray = JSON.parseArray(message);
if(jsonArray == null || jsonArray.size() <= 0) {
return ResultUtils.error(102, "请输入有效message参数");
}
try {
jsonArray.forEach(( json ) -> sender.routingSend("order",JSONObject.toJSONString(json)));
return ResultUtils.success(message);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
logger.error(" 路由模式下发送mq消息失败:"+e.getMessage(), e);
}
return ResultUtils.error(101, "路由模式下发送mq消息失败");
}
/*
* 主题模式发送mq
*/
@ApiOperation(value = "主题模式发送消息",notes = "主题模式发送消息" )
@ApiImplicitParams({
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "message",value="要传送的消息jsonArray",required = true,dataType = "String" , paramType ="body"),
@ApiImplicitParam(name="Accept",value="接收属性",required=true,dataType="String",paramType="header",defaultValue="application/json"),
@ApiImplicitParam(name="Accept-Charset",value="接受字符集",required=true,dataType="String",paramType="header",defaultValue="utf-8"),
@ApiImplicitParam(name="Content-Type",value="内容类型",required=false,dataType="String",paramType="header",defaultValue="application/json")
})
@PostMapping(value = "/rabbitmq/topicsend" ,produces ="application/json;charset=UTF-8")
public Result<?> sendTopicMq( @RequestBody String message, @RequestHeader HttpHeaders headers){ //这里用于测试,key值可以自定义实现
JSONArray jsonArray = JSON.parseArray(message);
if(jsonArray == null || jsonArray.size() <= 0) {
return ResultUtils.error(102, "请输入有效message参数");
}
try {
jsonArray.forEach(( json ) -> sender.topicSend("user.add",JSONObject.toJSONString(json)));
return ResultUtils.success(message);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
logger.error(" 主题模式下发送mq消息失败:"+e.getMessage(), e);
}
return ResultUtils.error(101, "主题模式下发送mq消息失败");
}
}
C端监听器代码:
package com.beltoo.customer.rabbitmq;
import java.util.Map;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.messaging.handler.annotation.Payload;
@Configuration
@RabbitListener(queues = "tea")
public class Listener {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Listener.class);
/**
* 简单发送模式
* @return
*/
@Bean
public Queue teaQueue() {
return new Queue("tea",true);
}
@RabbitHandler
public void process(@Payload String message) {
logger.info("Listener收到String类型mq消息:" + message );
}
// @RabbitListener(queues = "tea")
@RabbitHandler
public void process1(@Payload Map map) {
logger.info("Listener收到Map类型mq消息:" + map );
}
}
在类上 加
@Configuration
@RabbitListener(queues = "tea")
说明这个类是配置类,这个rabbit监听器监听name 为 tea 的消息队列。
@RabbitHandler是对不同类型的消息进行处理(知道为什么写了两个不同的Sender方法了吗)
@Payload有效载荷,即消息的有用部分。这个注解不加也没问题。
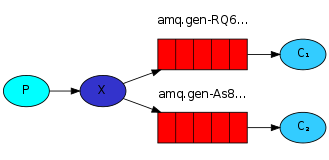
发布/订阅模式(Publish/Subscribe)
P Sender
// 发布/订阅模式
public static final String FANOUT_EXCHANGE = "fanout_exchange";
/**
* 发布/订阅模式发送
* @param message
*/
public void psSend(String message) {
this.rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(FANOUT_EXCHANGE, "", message);
}rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(FANOUT_EXCHANGE, "", message);第二个参数 routingKey是空的。
Controller里代码 和简单模式的在一起。
P 的监听器 代码 :
package com.beltoo.customer.rabbitmq;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.FanoutExchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* 发布/订阅模式监听器
* @author wang
* @date 2018年4月3日
*/
@Configuration
public class PSListener {
public static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(PSListener.class);
public static final String PS_QUEUE_1 = "ps_queue_1";
public static final String PS_QUEUE_2 = "ps_queue_2";
public static final String FANOUT_EXCHANGE = "fanout_exchange";
@Bean
public Queue psQueue1() {
return new Queue(PS_QUEUE_1, true);
}
@Bean
public Queue psQueue2() {
return new Queue(PS_QUEUE_2, true);
}
@Bean
public FanoutExchange fanoutExchange() {
return new FanoutExchange(FANOUT_EXCHANGE);
}
@Bean
public Binding fanoutBinding1() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(psQueue1()).to(fanoutExchange());
}
@Bean
public Binding fanoutBinding2() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(psQueue2()).to(fanoutExchange());
}
/**
* 发布/订阅模式接收
*
* @param message
*/
@RabbitListener(queues = PS_QUEUE_1)
public void psReceive1(String message) {
System.out.println(PS_QUEUE_1 + "接收消息:" + message);
logger.info(PS_QUEUE_1 + "接收消息:" + message);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = PS_QUEUE_2)
public void psReceive2(String message) {
System.out.println(PS_QUEUE_2 + "接收消息:" + message);
logger.info(PS_QUEUE_2 + "接收消息:" + message);
}
}我的项目中都是在消费者端的监听器中声明并创建交换器和队列的,其实这样不安全。因为生产者将消息发布到交换器后,而这个交换器并没有绑定队列的话,这些消息就会丢失。所以最好的方法在生产者和消费者两端都声明交换器和队列。因为new Queue()在发现队列已经创建的情况下,什么都不做并且返回已经存在的 队列。
监听器中创建两个 队列 psQueue1和psQueue2,两个fanout类型交换机 fanoutExchange1和 fanoutExchange2。并且把psQueue1绑定到fanoutExchange1上。psQueue2绑定到fanoutExchange2.绑定时没有指明bindingKey
如果有多个C端都有Q绑定这个X的话,所有的Q都会收到传递的这个M的复制。
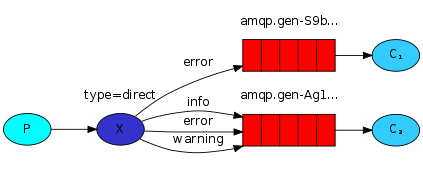
路由模式(Routing)
/**
* 路由模式发送
*
* @param message
*/
public void routingSend(String routingKey, String message) {
this.rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(DIRECT_EXCHANGE, routingKey, message);
}package com.beltoo.customer.rabbitmq;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.DirectExchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* 路由模式监听器
* @author wang
* @date 2018年4月4日
*/
@Configuration
public class RoutingListener {
public static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RoutingListener.class);
public static final String ROUTING_QUEUE_1 = "routing_queue_1";
public static final String ROUTING_QUEUE_2 = "routing_queue_2";
public static final String DIRECT_EXCHANGE = "direct_exchange";
@Bean
public Queue routingQueue1() {
return new Queue(ROUTING_QUEUE_1, true);
}
@Bean
public Queue routingQueue2() {
return new Queue(ROUTING_QUEUE_2, true);
}
@Bean
public DirectExchange directExchange() {
return new DirectExchange(DIRECT_EXCHANGE);
}
@Bean
public Binding directBinding1() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(routingQueue1()).to(directExchange()).with("user");
}
@Bean
public Binding directBinding2() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(routingQueue2()).to(directExchange()).with("order");
}
/**
* 路由模式接收
*
* @param message
*/
@RabbitListener(queues = ROUTING_QUEUE_1 )
public void routingReceive1(String message) {
System.out.println( ROUTING_QUEUE_1 + "接收路由模式消息:" + message);
logger.info(ROUTING_QUEUE_1 + "接收路由模式消息:" + message);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = ROUTING_QUEUE_2 )
public void routingReceive2(String message) {
System.out.println( ROUTING_QUEUE_2 + "接收路由模式消息:" + message);
logger.info(ROUTING_QUEUE_2 + "接收路由模式消息:" + message);
}
}
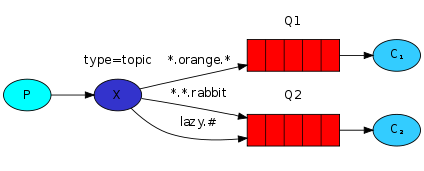
主题模式(Topic)
P端Sender代码
/**
* 主题模式发送
*
* @param routingKey
* @param message
*/
public void topicSend(String routingKey, String message) {
this.rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(TOPIC_EXCHANGE, routingKey, message);
}C端Lisenter代码:
package com.beltoo.customer.rabbitmq;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.TopicExchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.messaging.handler.annotation.Payload;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
/**
* 主题模式监听器
* @author wang
* @date 2018年4月4日
*/
@Configuration
public class TopicListenter {
public static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RoutingListener.class);
public static final String TOPIC_QUEUE_1 = "topic_queue_1";
public static final String TOPIC_QUEUE_2 = "topic_queue_2";
public static final String TOPIC_EXCHANGE = "topic_exchange";
public static final String TOPIC_ROUTINGKEY1 = "user.*";
public static final String TOPIC_ROUTINGKEY2 = "order.#";
@Bean
public TopicExchange topicExchange() {
return new TopicExchange(TOPIC_EXCHANGE);
}
@Bean
public Queue topicQueue1() {
//第二个参数 是durable 队列持久化
return new Queue(TOPIC_QUEUE_1,true);
}
@Bean
public Queue topicQueue2() {
//第二个参数 是durable 队列持久化
return new Queue(TOPIC_QUEUE_2,true);
}
@Bean
public Binding topicBinding1() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQueue1()).to(topicExchange()).with(TOPIC_ROUTINGKEY1);
}
@Bean
public Binding topicBinding2() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQueue2()).to(topicExchange()).with(TOPIC_ROUTINGKEY2);
}
/**
* 主题模式接收
*
* @param message
*/
@RabbitListener(queues = TOPIC_QUEUE_1)
public void topicReceive1(@Payload String message, Message mes, Channel channel) throws IOException {
channel.basicAck(mes.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
System.out.println(TOPIC_QUEUE_1 + "接收消息:" + mes.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag() + message);
logger.info(TOPIC_QUEUE_1 + "接收消息id为:" + mes.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag() + "内容为: "+ message);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = TOPIC_QUEUE_2)
public void topicReceive2(@Payload String message, Message mes, Channel channel) throws IOException {
channel.basicAck(mes.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
System.out.println(TOPIC_QUEUE_2 + "接收消息:" + mes.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag() + message);
logger.info(TOPIC_QUEUE_2 + "接收消息id为" + mes.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag() + "内容为: "+ message);
}
}
四、rabbitmq中交换机Exchange的类型
fanout、direct、topic在前面讲发布模式的已经讲到了。
还有headers类型没讲:
五、ACK 消息的确认机制
@RabbitListener(queues = TOPIC_QUEUE_1)
public void topicReceive1(@Payload String message, Message mes, Channel channel) throws IOException {
channel.basicAck(mes.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
System.out.println(TOPIC_QUEUE_1 + "接收消息:" + mes.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag() + message);
logger.info(TOPIC_QUEUE_1 + "接收消息id为:" + mes.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag() + "内容为: "+ message);
}方法里多了 两个参数
Message mes, Channel channel
好了,以前都是用的activemq,最近项目里因为有用到rabbitmq,才去看了《rabbitmq实战》和网上的博文,发现要不是linux环境下的,要不没有一篇文章能讲的很细。在练习过程中经常出现错误。所以就记录下来,供大家交流。如果有什么问题,可以联系我的邮箱673748314@qq.com。








 本文详细介绍RabbitMQ在Spring Boot中的安装、配置与使用方法,并深入探讨简单模式、工作队列模式、发布订阅模式、路由模式及主题模式的具体实现。
本文详细介绍RabbitMQ在Spring Boot中的安装、配置与使用方法,并深入探讨简单模式、工作队列模式、发布订阅模式、路由模式及主题模式的具体实现。
















 962
962

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








