BootLoader简介
一个嵌入式系统从软件角度来看可以分为三个层次:
- 引导加载程序
包括固化在固件(firmware)中的boot程序(可选),和bootloader两大部分 - Linux内核
特定于嵌入式平台的定制内核 - 文件系统
包括系统命令和应用程序
BootLoader就是在操作系统运行之前运行的一段小程序。通过这段小程序可以初始化硬件设备,从而将系统从硬件环境带到一个合适的状态,以便最终调用操作系统做好准备。
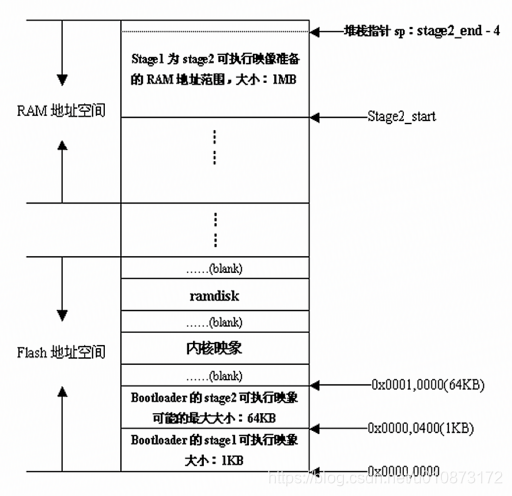
BootLoader的启动过程可分为单阶段(single-stage)和多阶段(multi-stage)两种,通常过阶段的BootLoader具有更复杂的功能,更好的可移植性,从固态存储设备上启动的BootLoader大多采用两阶段,即启动过程可以分为stage1和stage2:stage1完成初始化硬件,为stage2准备内存空间,并将stage2复制到内存中,设置堆栈,然后跳转到stage2.
stage1(汇编代码)通常包括以下步骤:
- 硬件设备初始化(主要是CPU内部寄存器)
- 为加载BootLoader的stage2准备RAM空间
- 拷贝BootLoader的stage2到RAM中
- 设置好堆栈(目的:为了运行c语言,创建环境)
- 跳转到stage2的c入口点
stage2通常包括以下步骤:
- 初始化本阶段要使用到的硬件设备
- 将内核映像和根文件系统映像从flash上读到RAM中
- 调用内核
U-boot简介
uboot是德国DENX小组开发的用于多种嵌入式CPU(MIPS、x86、ARM、XScale等)的BootLoader程序
uboot不仅支持嵌入式Linux系统的引导,还支持VxWorks,QNX等多种嵌入式操作系统。
uboot下载地址ftp://ftp.denx.de/pub/u-boot/
uboot源码目录结构如下
| 目录 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| board | 和开发板有关的文件。每一个开发板都以一个子目录出现在当前目录中,比如:SMDK2410,子目录中存放与开发板相关的文件 |
| common | 实现Uboot支持的命令 |
| cpu | 与特定cpu架构相关的代码 |
| doc | 文档目录 |
| drivers | Uboot支持的设备驱动程序都存放在该目录,比如各种网卡、支持CFI的flash、串口和USB等 |
| fs | 文件系统的支持 |
| include | 这个目录下的configs目录有与开发板相关的配置头文件 |
| net | 与网络协议相关 |
uboot的Makefile从功能上可以分为两个部分:
- 执行每种board相关的配置
- 编译生成uboot.bin文件
Uboot.bin的生成可以分为两步:
- 选择要使用的board:
$make mini2440_config(必须要经过移植的) - 编译生成u-boot.bin:
$make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-
常用命令
| 命令 | 说明 | 举例 |
|---|---|---|
| aaaaaaaaa | aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa | |
| help | 查看所有命令 | |
| printenv | 查看环境变量 | 参看某一个printenv 环境变量名 |
| setenv | 添加、修改、删除环境变量 | 添加:set name 123 ,修改:setenv name 456,删除:setenv name |
| saveenv | 保存环境变量 | |
| tftp | 通过网络下载文件 | **注意:使用tftp,需要先配置好网络:uboot>setenv ethaddr 12:34:56:78:91:bc uboot>setenv ipaddr 192.168.1.1 uboot>setenv serverip 192.168.1.254(tftp服务器的地址)**例:uboot>tftp 12000000 ulmage 把server(IP=环境变量中设置的serverip)中服务目录下的ulmage通过TFTP读入到0x12000000处 |
| md | 显示内存区的内容 | md [.b(单字节),.w(双字节), .l(四字节)] address, 例如:md .w 100000 |
| mm | 修改内存,地址自动递增 | mm [.b, .w, .l] address, mm提供了一种互动修改存储器内容的方法。它会显示地址和当前值,然后提示用户输入。如果你没有输入任何值,只是按了一个回车,那么该地址的内容保持不变。如果想结束输入,则输入空格,然后回车 |
| protect | flash写保护,打开或关闭扇区写保护 | 用法:protect off all 关闭所有扇区的写保护 protect on all 打开所有扇区的写保护 protect off start end 关闭从start到end扇区的写保护(比如扇区0地址为0,扇区1地址为1000,则start为0,end为0fff)protect on start end 打开从start到end扇区的写保护 |
| erase | 擦除flash扇区 | 用法:erase start end 擦除从start到end的扇区,start为要擦除的第一各扇区的起始地址,end为要擦除的最后一个扇区的结束地址**(在使用cp命令向Nor型flash写入数据之前必须先使用erase命令擦除flash,因为nor flash按字节写入时,无法写入1,所以必须通过擦除来写入1)**例如:erase 30000 1effff |
| cp | 数据拷贝 | cp [.b, .w, .l] saddress daddress len,例如:cp.b 31000000 50000 d0000 将内存地址31000000 处的数据(长度为d0000)拷贝到地址50000 处 |
| go | 执行内存中的二进制代码,一个简单的跳转指令 | go addr [arg …]如果有参数可以加参数 |
| bootm | 执行内存中的二进制,与go相似,但bootm要求二进制代码有固定格式的文件头 | bootm [addr [arg …]] |
设置自动启动
=>setenv bootcmd tftp 12000000 ulmage ; bootm 12000000其实就是添加环境变量每多加一个;可以多加一条环境变量
uboot移植
板级设备的配置文件位于include/configs/<board_name>.h (board_name用相应的BOARD定义代替,例如smdk2410.h)
开始移植之前,首先要分析U-boot已经支持的开发板,选择出硬件配置最接近的开发板。选择的原则是,首先选择MCU相同的开发板,如果没有,则选择MPU相同的开发板。
移植u-boot的基本步骤如下:
-
在顶层Makefile中为开发板添加新的配置选项,使用已有的配置项目为例
smdk2410_config : unconfig
@./mkconfig $(@:_config=) arm arm920t smdk2410 NULL s3c24x0
参考上面2行,添加下面2行:
mini2440_config : unconfig
@./mkconfig $(@:_config=) arm arm920t mini2410 NULL s3c24x0
arm: CPU架构
arm920t: CPU类型,对应cpu/arm920t目录
mini2440:开发板型号,对应board/mini2440目录
NULL:开发者
s3c24x0:片上系统(SOC) -
在board目录中创建一个属于新开发板的目录,向目录中添加文件,并修改:
mkdir -p board/mini2440
cp -rf board/smdk2410/* board/mini2440 -
为开发板添加新的配置文件,先复制参考开发板的配置文件,再修改,例如:$cp include/configs/smdk2410.h include/configs/mini2440.h
-
选择板级配置
$make mini2440_config -
编译U-Boot
执行make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-命令,编译成功可以得到U-Boot映像。








 本文介绍了BootLoader的启动过程,包括单阶段和多阶段启动,并详细讲解了U-boot的起源、功能和源码目录结构。此外,还阐述了如何设置U-boot常用命令以及U-boot的移植步骤,包括配置选项、开发板目录创建和配置文件修改等。
本文介绍了BootLoader的启动过程,包括单阶段和多阶段启动,并详细讲解了U-boot的起源、功能和源码目录结构。此外,还阐述了如何设置U-boot常用命令以及U-boot的移植步骤,包括配置选项、开发板目录创建和配置文件修改等。
















 7515
7515

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








