上篇runtime中我们了解到,虚拟 DOM是 Vue 在运行时,通过h函数获取到VNode对象,这里我们就来看下h函数是如何实现的
案例
首先引入h函数,之后通过h函数生成一个vnode对象,并将其打印
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<script src="../../dist/vue.global.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<script>
const { h } = Vue
debugger
const vnode = h(
'div',
{
class: 'test'
},
'hello render'
)
console.log(vnode)
</script>
</body>
</html>
h函数定义在packages/runtime-core/src/h.ts文件下:
可以看出h函数接收三个参数,当前type为div,propsOrChildren为{ class: 'test'},children 为hello render
createVNode方法
之后根据参数的长度不同走不同的判断逻辑,其核心是执行createVNode方法,实际执行的是_createVNode,该方法在packages/runtime-core/src/vnode.ts文件中:
export const createVNode = (
__DEV__ ? createVNodeWithArgsTransform : _createVNode
) as typeof _createVNode
function _createVNode(
type: VNodeTypes | ClassComponent | typeof NULL_DYNAMIC_COMPONENT,
props: (Data & VNodeProps) | null = null,
children: unknown = null,
patchFlag: number = 0,
dynamicProps: string[] | null = null,
isBlockNode = false
): VNode {
if (!type || type === NULL_DYNAMIC_COMPONENT) {
if (__DEV__ && !type) {
warn(`Invalid vnode type when creating vnode: ${type}.`)
}
type = Comment
}
// 是否是 vnode 通过 __v_isVNode 来判断
if (isVNode(type)) {
// createVNode receiving an existing vnode. This happens in cases like
// <component :is="vnode"/>
// #2078 make sure to merge refs during the clone instead of overwriting it
const cloned = cloneVNode(type, props, true /* mergeRef: true */)
if (children) {
normalizeChildren(cloned, children)
}
if (isBlockTreeEnabled > 0 && !isBlockNode && currentBlock) {
if (cloned.shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.COMPONENT) {
currentBlock[currentBlock.indexOf(type)] = cloned
} else {
currentBlock.push(cloned)
}
}
cloned.patchFlag |= PatchFlags.BAIL
return cloned
}
// class component normalization.
if (isClassComponent(type)) {
type = type.__vccOpts
}
// 2.x async/functional component compat
if (__COMPAT__) {
type = convertLegacyComponent(type, currentRenderingInstance)
}
// class & style normalization.
// class 和 style 的增强
if (props) {
// for reactive or proxy objects, we need to clone it to enable mutation.
props = guardReactiveProps(props)! // 解析 props
let { class: klass, style } = props // 结构 class 赋值给 klass, style
if (klass && !isString(klass)) {
props.class = normalizeClass(klass) // 增强 class
}
if (isObject(style)) {
// reactive state objects need to be cloned since they are likely to be
// mutated
if (isProxy(style) && !isArray(style)) {
style = extend({}, style)
}
props.style = normalizeStyle(style)
}
}
// encode the vnode type information into a bitmap
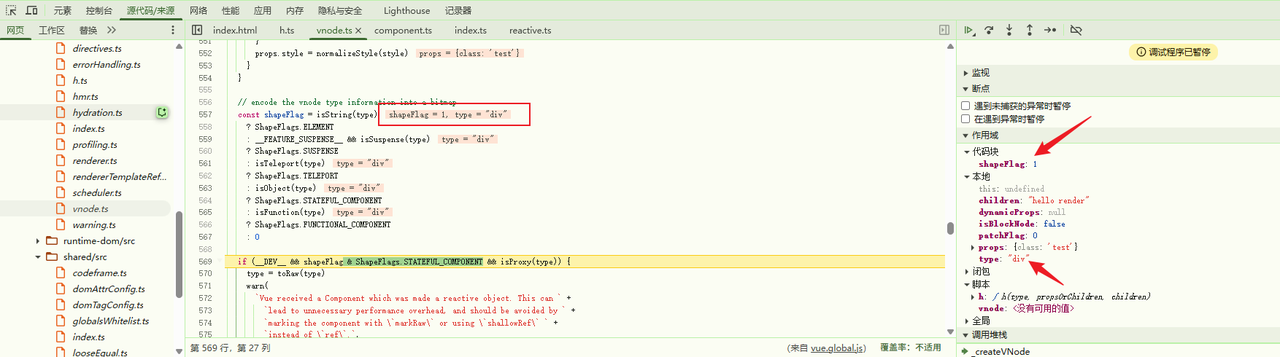
const shapeFlag = isString(type) // 根据 type 类型进行 shapeFlag 赋值 当前为 div 则 ShapeFlags.ELEMENT
? ShapeFlags.ELEMENT
: __FEATURE_SUSPENSE__ && isSuspense(type)
? ShapeFlags.SUSPENSE
: isTeleport(type)
? ShapeFlags.TELEPORT
: isObject(type)
? ShapeFlags.STATEFUL_COMPONENT
: isFunction(type)
? ShapeFlags.FUNCTIONAL_COMPONENT
: 0
if (__DEV__ && shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.STATEFUL_COMPONENT && isProxy(type)) {
type = toRaw(type)
warn(
`Vue received a Component which was made a reactive object. This can ` +
`lead to unnecessary performance overhead, and should be avoided by ` +
`marking the component with `markRaw` or using `shallowRef` ` +
`instead of `ref`.`,
`\nComponent that was made reactive: `,
type
)
}
return createBaseVNode(
type,
props,
children,
patchFlag,
dynamicProps,
shapeFlag,
isBlockNode,
true
)
}
这里isVNode(type)通过判断type是否是 VNode,我们来看下isVNode方法:
export function isVNode(value: any): value is VNode {
return value ? value.__v_isVNode === true : false
}
主要通过__v_isVNode属性来判断是否是VNode,之后再判断props即传入的{ class: 'test'},对class 、style增强,这块我们放到之后来讨论
接着又对shapeFlag赋值,当前type为 string 类型,此时被赋值为ShapeFlags.ELEMENT即等于1,最后将处理好的type、props、children、shapeFlag等参数传入createBaseVNode方法中
_createVNode方法核心:
- 对
class、style增强 - 对
shapeFlag标记赋值
对shapeFlag标记赋值
接着再看下createBaseVNode方法:
function createBaseVNode(
type: VNodeTypes | ClassComponent | typeof NULL_DYNAMIC_COMPONENT,
props: (Data & VNodeProps) | null = null,
children: unknown = null,
patchFlag = 0,
dynamicProps: string[] | null = null,
shapeFlag = type === Fragment ? 0 : ShapeFlags.ELEMENT,
isBlockNode = false,
needFullChildrenNormalization = false
) {
const vnode = {
__v_isVNode: true,
__v_skip: true,
type,
props,
key: props && normalizeKey(props),
ref: props && normalizeRef(props),
scopeId: currentScopeId,
slotScopeIds: null,
children,
component: null,
suspense: null,
ssContent: null,
ssFallback: null,
dirs: null,
transition: null,
el: null,
anchor: null,
target: null,
targetAnchor: null,
staticCount: 0,
shapeFlag,
patchFlag,
dynamicProps,
dynamicChildren: null,
appContext: null
} as VNode
if (needFullChildrenNormalization) {
normalizeChildren(vnode, children) // 创建子节点
// normalize suspense children
if (__FEATURE_SUSPENSE__ && shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.SUSPENSE) {
;(type as typeof SuspenseImpl).normalize(vnode)
}
} else if (children) {
// compiled element vnode - if children is passed, only possible types are
// string or Array.
vnode.shapeFlag |= isString(children)
? ShapeFlags.TEXT_CHILDREN
: ShapeFlags.ARRAY_CHILDREN
}
// validate key
if (__DEV__ && vnode.key !== vnode.key) {
warn(`VNode created with invalid key (NaN). VNode type:`, vnode.type)
}
// track vnode for block tree
if (
isBlockTreeEnabled > 0 &&
// avoid a block node from tracking itself
!isBlockNode &&
// has current parent block
currentBlock &&
// presence of a patch flag indicates this node needs patching on updates.
// component nodes also should always be patched, because even if the
// component doesn't need to update, it needs to persist the instance on to
// the next vnode so that it can be properly unmounted later.
(vnode.patchFlag > 0 || shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.COMPONENT) &&
// the EVENTS flag is only for hydration and if it is the only flag, the
// vnode should not be considered dynamic due to handler caching.
vnode.patchFlag !== PatchFlags.HYDRATE_EVENTS
) {
currentBlock.push(vnode)
}
if (__COMPAT__) {
convertLegacyVModelProps(vnode)
defineLegacyVNodeProperties(vnode)
}
return vnode
}
该方法首先定义了一个vnode对象,属性__v_isVNode标记为该对象是否为VNode对象。由于当前needFullChildrenNormalization默认传入的是true,所以直接执行normalizeChildren(vnode, children)方法来创建子节点,再来看下normalizeChildren方法:
export function normalizeChildren(vnode: VNode, children: unknown) {
let type = 0
const { shapeFlag } = vnode // 当前shapeFlag 是 1 children是字符串
// children 为 undefined 或 null
if (children == null) {
children = null
} else if (isArray(children)) { // 是否是数组
type = ShapeFlags.ARRAY_CHILDREN
} else if (typeof children === 'object') { // 是否是对象
if (shapeFlag & (ShapeFlags.ELEMENT | ShapeFlags.TELEPORT)) {
// Normalize slot to plain children for plain element and Teleport
const slot = (children as any).default
if (slot) {
// _c marker is added by withCtx() indicating this is a compiled slot
slot._c && (slot._d = false)
normalizeChildren(vnode, slot())
slot._c && (slot._d = true)
}
return
} else {
type = ShapeFlags.SLOTS_CHILDREN
const slotFlag = (children as RawSlots)._
if (!slotFlag && !(InternalObjectKey in children!)) {
// if slots are not normalized, attach context instance
// (compiled / normalized slots already have context)
;(children as RawSlots)._ctx = currentRenderingInstance
} else if (slotFlag === SlotFlags.FORWARDED && currentRenderingInstance) {
// a child component receives forwarded slots from the parent.
// its slot type is determined by its parent's slot type.
if (
(currentRenderingInstance.slots as RawSlots)._ === SlotFlags.STABLE
) {
;(children as RawSlots)._ = SlotFlags.STABLE
} else {
;(children as RawSlots)._ = SlotFlags.DYNAMIC
vnode.patchFlag |= PatchFlags.DYNAMIC_SLOTS
}
}
}
} else if (isFunction(children)) { // 是否是 函数
children = { default: children, _ctx: currentRenderingInstance }
type = ShapeFlags.SLOTS_CHILDREN
} else {
children = String(children) // 此时 'hello render'
// force teleport children to array so it can be moved around
if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.TELEPORT) {
type = ShapeFlags.ARRAY_CHILDREN
children = [createTextVNode(children as string)]
} else {
type = ShapeFlags.TEXT_CHILDREN
}
}
vnode.children = children as VNodeNormalizedChildren
// 9 按位或赋值 vnode.shapeFlag |= type 等同于 vnode.shapeFlag = vnode.shapeFlag | type
vnode.shapeFlag |= type
}
该方法接收两个参数,一个是定义的vnode对象,一个是children即hello render。之后再从vnode对象中解构出shapeFlag,即当前 string 类型为 1,根据children类型不同对children、type和 shapeFlag重新赋值
由于当前children为 string 类型,执行children = String(children),此时children为hello render,并将其vnode.children = children重新赋值。type = ShapeFlags.TEXT_CHILDREN 即 type 为 8
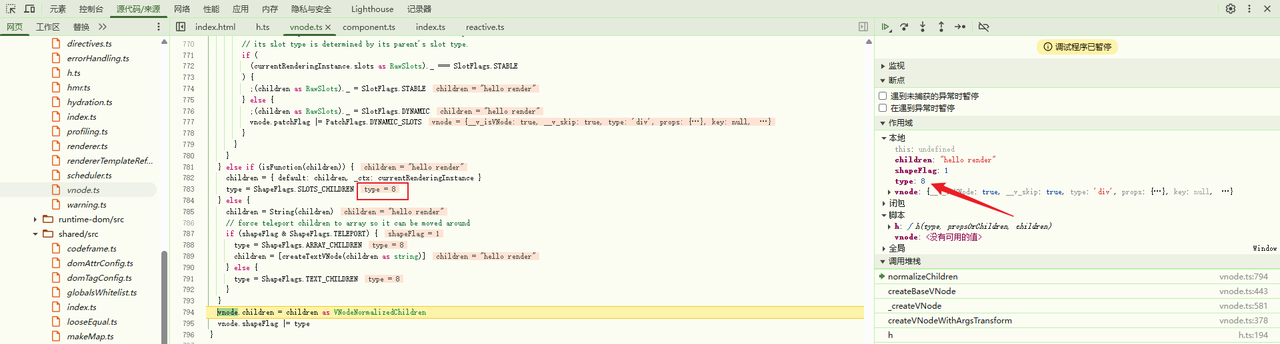
最后对 vnode.shapeFlag |= type 按或位赋值即为 9
这里拓展下 |= 按或位赋值,vnode.shapeFlag |= type 等同于 vnode.shapeFlag = vnode.shapeFlag | type。当前 vnode.shapeFlag = 8,type = 1,转为二进制:
// type = 1
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000001
// shapeFlag = 8
00000000 00000000 00000000 00001000
// 或 就是通过上下 ↕ 比较,如果上下是 0 则是 0,上下是 0 和 1 则是 1
// 结果是 9
00000000 00000000 00000000 00001001
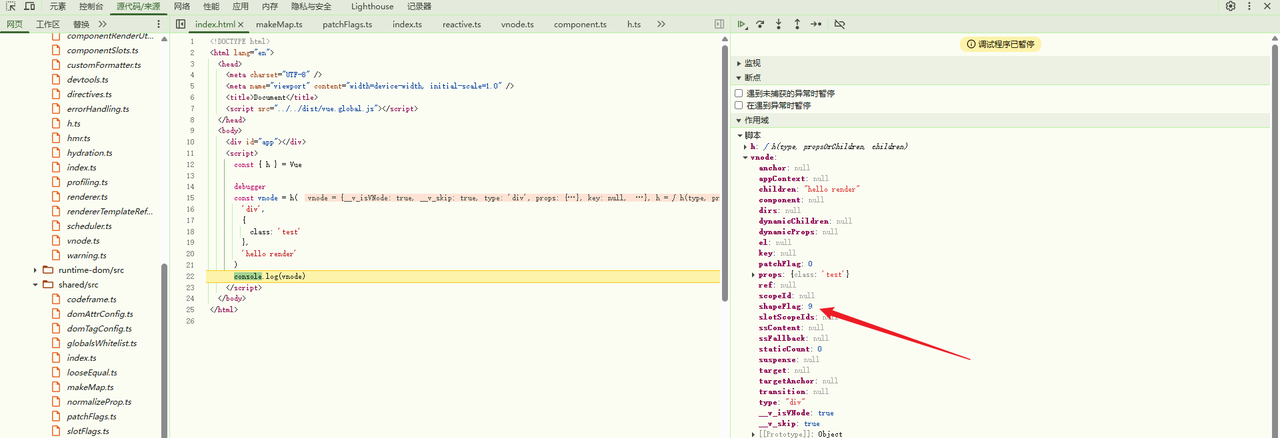
所以此时计算后的 vnode.shapeFlag = 9,之后 createBaseVNode 执行完毕返回 vnode 对象,至此 h 函数执行完毕,打印 vnode 对象:
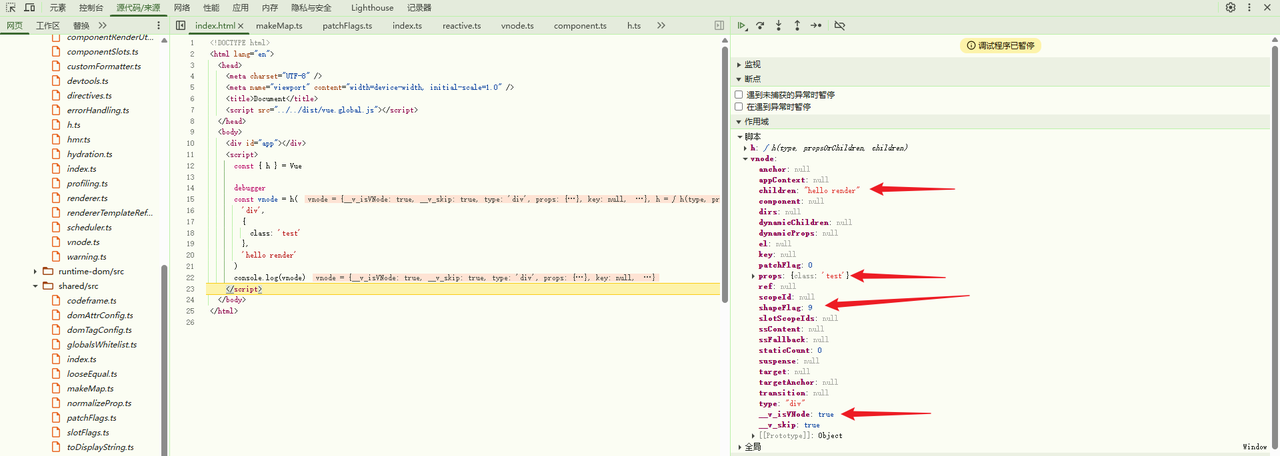
对class、style增强
我们再回过来看下 h 函数如何对 class style 增强的,该逻辑在 _createVNode 方法中:
function _createVNode(
type: VNodeTypes | ClassComponent | typeof NULL_DYNAMIC_COMPONENT,
props: (Data & VNodeProps) | null = null,
children: unknown = null,
patchFlag: number = 0,
dynamicProps: string[] | null = null,
isBlockNode = false
): VNode {
// 省略
// class & style normalization.
// class 和 style 的增强
if (props) {
// for reactive or proxy objects, we need to clone it to enable mutation.
props = guardReactiveProps(props)! // 解析 props
let { class: klass, style } = props // 结构 class 赋值给 klass, style
if (klass && !isString(klass)) {
props.class = normalizeClass(klass) // 增强 class
}
if (isObject(style)) {
// reactive state objects need to be cloned since they are likely to be
// mutated
if (isProxy(style) && !isArray(style)) {
style = extend({}, style)
}
props.style = normalizeStyle(style)
}
}
// 省略
return createBaseVNode(
type,
props,
children,
patchFlag,
dynamicProps,
shapeFlag,
isBlockNode,
true
)
}
结合一下案例进行分析:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<script src="../../dist/vue.global.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<script>
const { h, render } = Vue
// <div :class="{ red: true }">增强的 class</div>
debugger
const vnode = h(
'div',
{
class: {
red: true
}
},
'增强的 class'
)
render(vnode, document.querySelector('#app'))
</script>
</body>
</html>
可以看出 { class: klass, style } = props 对 props 解构,并将 class 赋值给 klass,如果存在 klass 且不为 string 类型,则执行 props.class = normalizeClass(klass),对其 props.class 重新赋值。我们再看下 normalizeClass 方法:
export function normalizeClass(value: unknown): string {
let res = ''
// 是字符串 直接赋值
if (isString(value)) {
res = value
} else if (isArray(value)) {
// 是数组 则递归迭代再拼接
for (let i = 0; i < value.length; i++) {
const normalized = normalizeClass(value[i])
if (normalized) {
res += normalized + ' '
}
}
} else if (isObject(value)) {
// 是对象 则 for in 再拼接返回
for (const name in value) {
if (value[name]) {
res += name + ' '
}
}
}
return res.trim()
}
根据 value 类型,如果是字符串则直接返回;如果是数组则递归迭代再拼接返回;如果是对象则迭代再拼接返回。由于当前 value 是对象 { red: true },所以此时的 res 为 red:
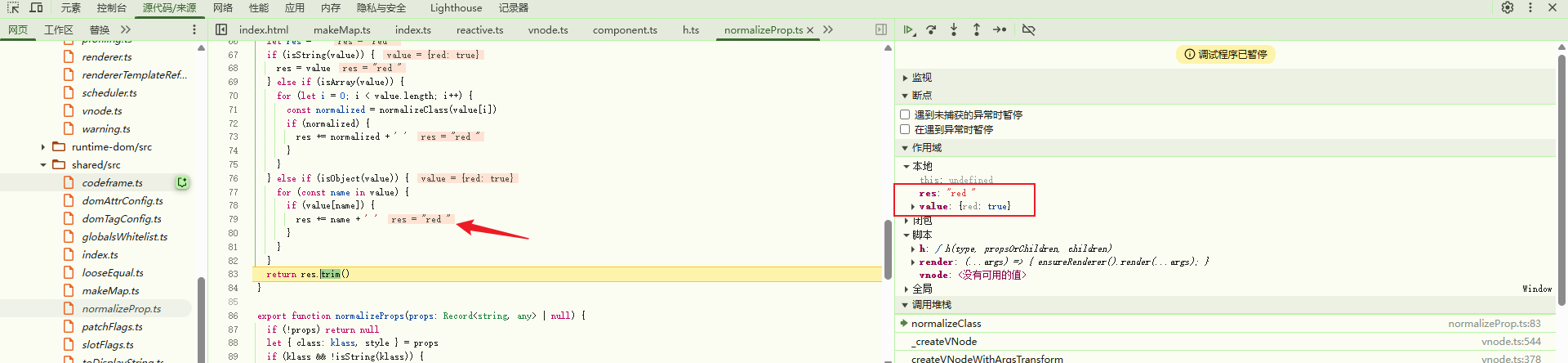
最终的结果:

总结
1)createVNode 核心是处理 shapeFlag 赋值,之后在 createBaseVNode 中又通过 shapeFlag 和 type 根据按位或运算,重新对 shapeFlag 赋值
2)h 函数本质上是对四个属性处理 children、props、shapeFlag、type 和 class style 的增强





















 2919
2919

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








