1、作业内容的描述
基于Python库和机器学习实现对常见矿体(金矿,铜矿等)图像的自动识别
最终实现效果预览(这里给大家看一下最后的效果,觉得感兴趣的可以继续浏览下去):
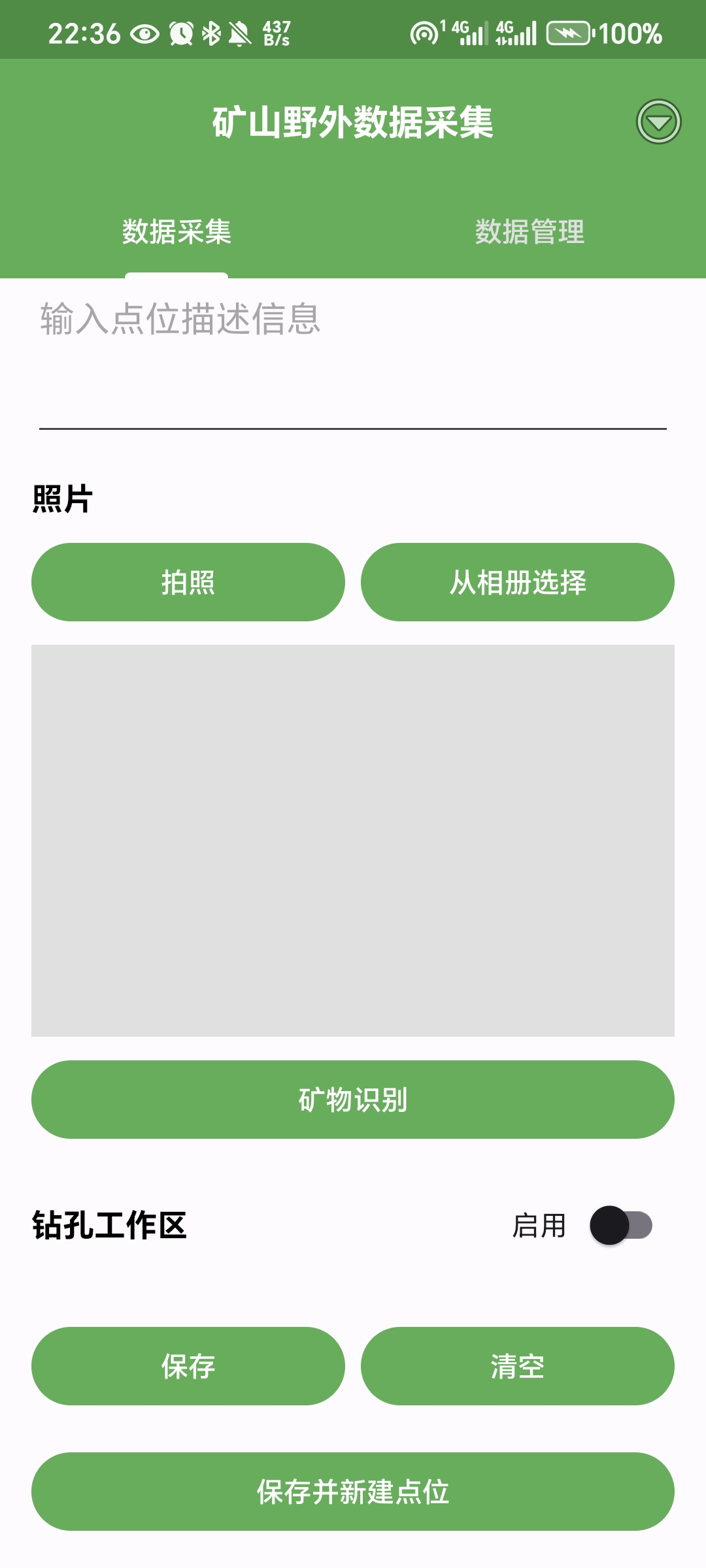
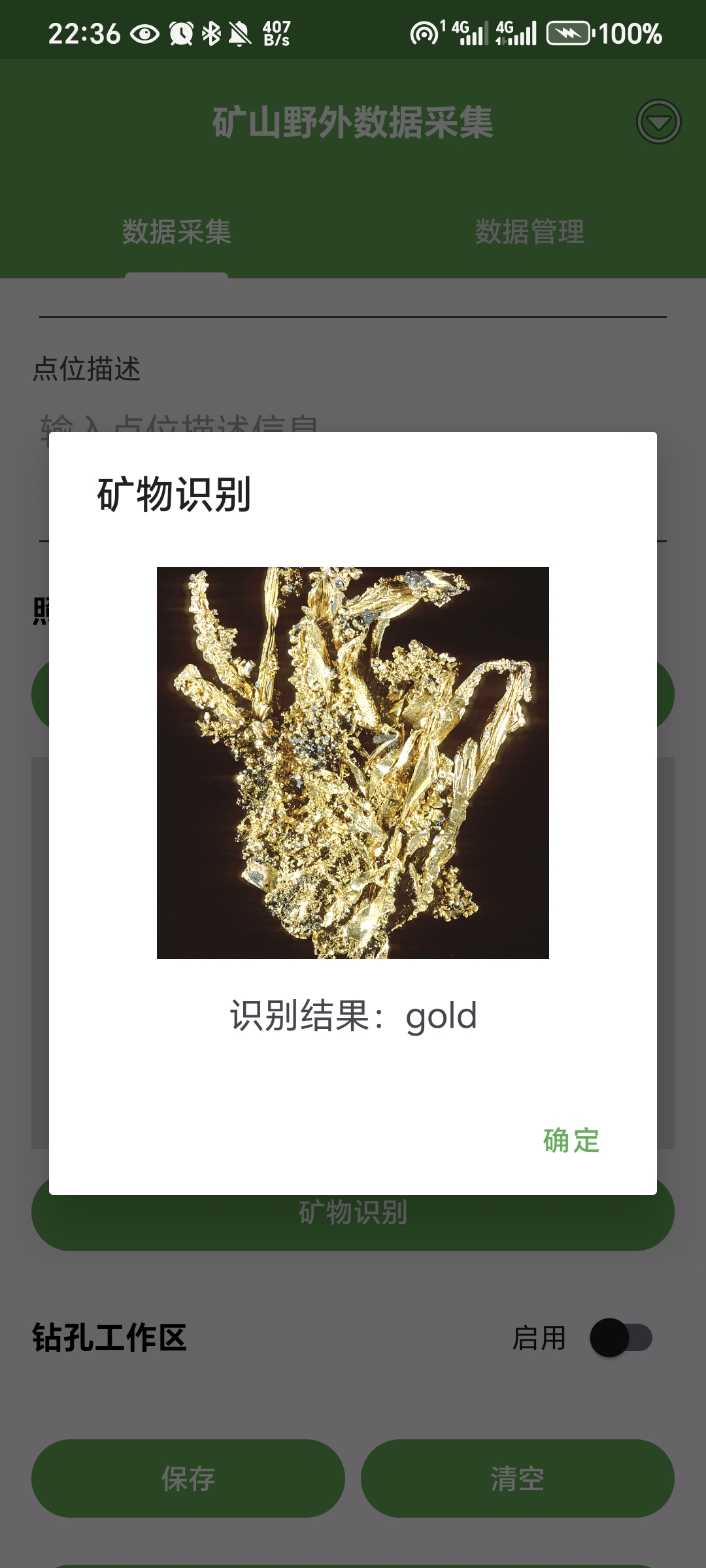
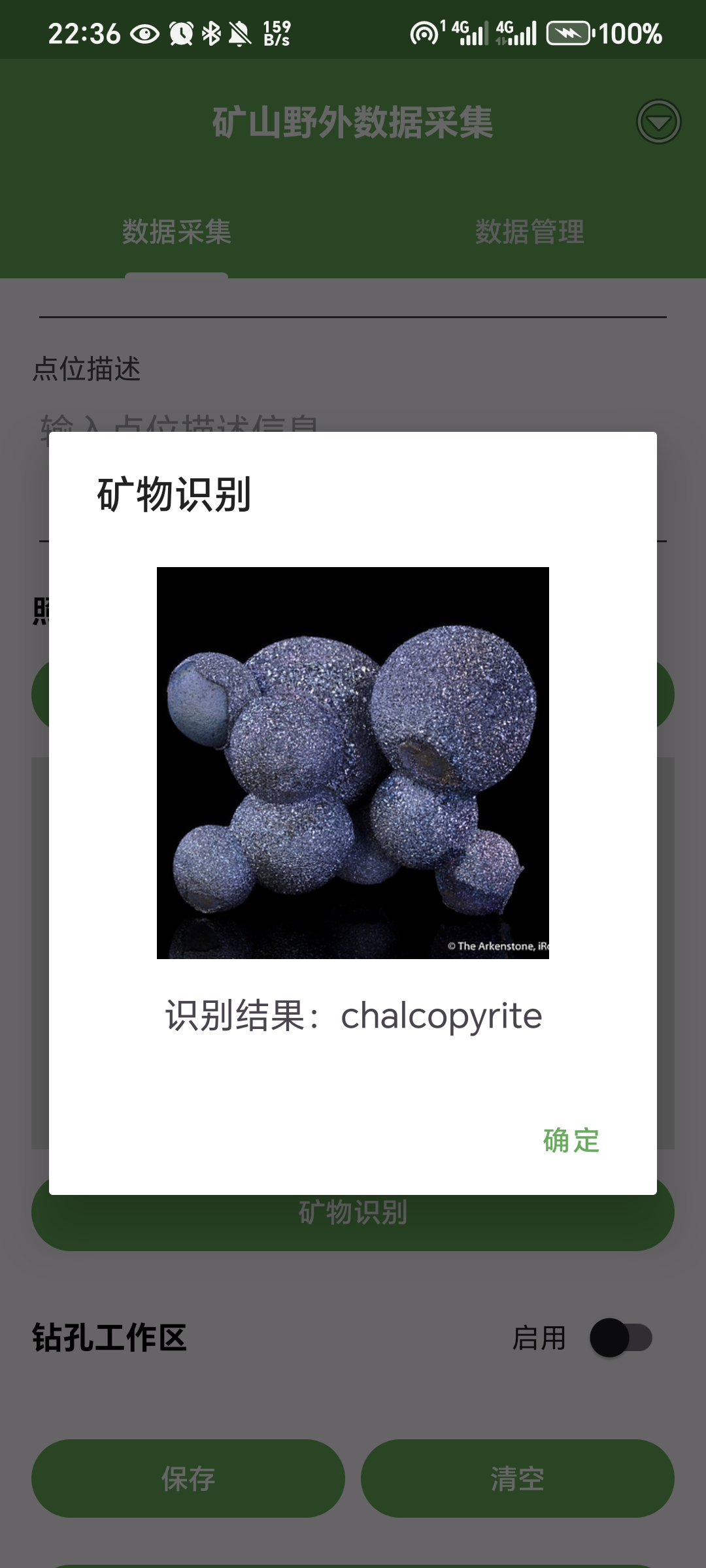
上面是集成在APP上的结果,中间用到的模型以及后端的搭建调用在后面分析
2、矿物图像数据来源介绍
这里训练模型用到的是从Mindat.org网站爬取的三类矿物数据:金矿(99张)、黄铜矿(113张)、斑铜矿(169张)。划分为训练集、验证集、测试集的比例分别为90.25%:4.75%:5%。
网站展示:
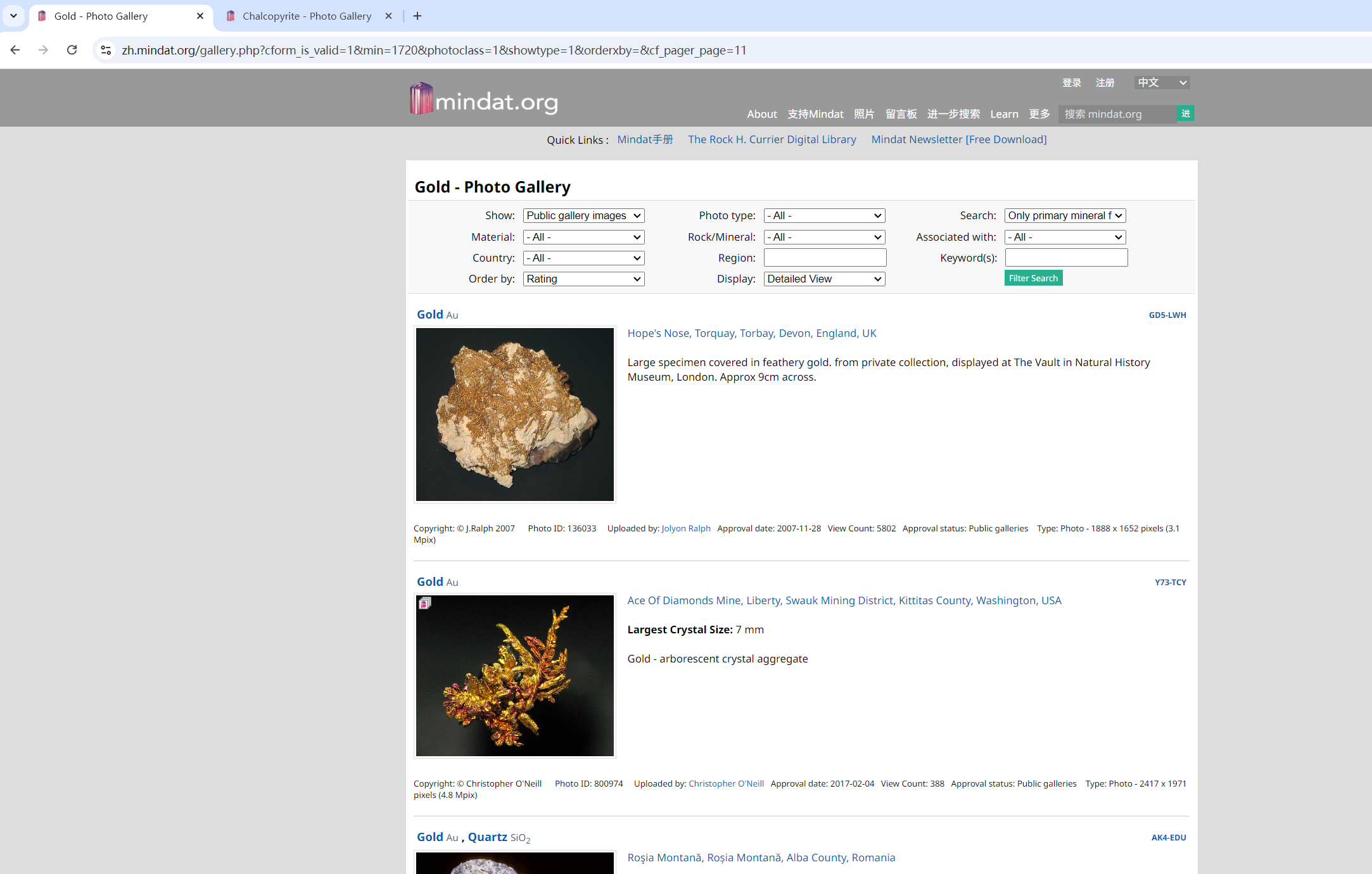
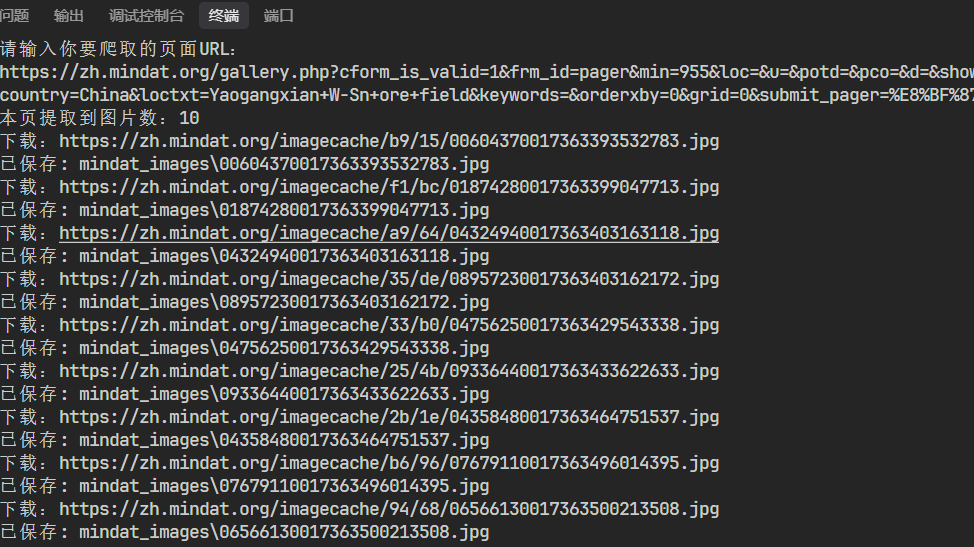
爬取日志:
爬取图片的代码:
(刚开始爬取的时候想要自动翻页爬取图片,但是发现这个网站有人机验证,所以最后采用每次爬取一页的图片,然后人为的翻页,当然如果碰到https://zh.mindat.org/gallery.php?cform_is_valid=1&min=1720&photoclass=1&showtype=1&orderxby=&cf_pager_page=12这种网站格式,就可以写个自增控制cf_pager_page=12来开多个界面进行爬取了)
import undetected_chromedriver as uc
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
import time
import os
import random
save_dir = "mindat_images"
os.makedirs(save_dir, exist_ok=True)
def get_image_links(soup):
imgs = []
for img in soup.find_all("img"):
src = img.get("src")
if src and "imagecache" in src:
if src.startswith("/"):
src = "https://zh.mindat.org" + src
imgs.append(src)
return imgs
def download_image(url, save_dir):
for _ in range(3): # 最多重试3次
try:
headers = {
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/114.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
}
resp = requests.get(url, headers=headers, timeout=10)
if resp.status_code == 200:
filename = os.path.join(save_dir, url.split("/")[-1])
with open(filename, "wb") as f:
f.write(resp.content)
print(f"已保存: {filename}")
return
else:
print(f"图片无法访问,状态码:{resp.status_code}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"下载失败: {url},原因: {e},重试中...")
time.sleep(random.uniform(1, 3))
print(f"最终失败: {url}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
url = input("请输入你要爬取的页面URL:\n")
driver = uc.Chrome()
driver.get(url)
# 多段、随机距离滑动
total_height = driver.execute_script("return document.body.scrollHeight")
current_height = 0
while current_height < total_height:
step = random.randint(300, 800)
current_height += step
driver.execute_script(f"window.scrollTo(0, {current_height});")
time.sleep(random.uniform(0.8, 2.0))
total_height = driver.execute_script("return document.body.scrollHeight")
#time.sleep(random.uniform(3, 6))
html = driver.page_source
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, "html.parser")
img_links = get_image_links(soup)
print(f"本页提取到图片数:{len(img_links)}")
for img_url in img_links:
print(f"下载:{img_url}")
download_image(img_url, save_dir)
time.sleep(random.uniform(0.8, 2.0)) # 随机延时
driver.quit()
print("本页图片下载完成!请手动打开下一页,复制URL后重新运行本程序。")
3、模型的构建训练评估
3.1思路设计来源
这里刚开始找到的是一个开源代码和数据集
开源数据集展示矿物鉴定数据集![]() https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/asiedubrempong/minerals-identification-dataset下面是具体的内容 大家可以看看有没有自己需要的
https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/asiedubrempong/minerals-identification-dataset下面是具体的内容 大家可以看看有没有自己需要的
开源代码展示(这里原作者用的是ipynb写的 后面我把它转为py文件了 感兴趣的可以往后面看):
Mineral Classification![]() https://www.kaggle.com/code/saidrasidin/mineral-classification/notebook这是参考的原作者代码界面
https://www.kaggle.com/code/saidrasidin/mineral-classification/notebook这是参考的原作者代码界面
3.2 内容的转化
这里就不讲里面的一些原理了,包括里面的数据预处理,以及图像特征提取(里面有两个方法,一个是采用预定义好的vgg16模型,一个是自定义的cnn模型),然后还有自定义全连接层映射到我的数据上去,这里大家有兴趣研究的可以查看后面的源码学习使用。因为本作者也没有深入研究深度学习的原理,只知道他的过程和调用,所以这里就不误导大家了。下面是转化后的py文件内容:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# coding: utf-8
# # Load Library
from multiprocessing import freeze_support
import torch
from torchvision.datasets import ImageFolder
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torchvision import transforms
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
from torch.utils.data import random_split
from torchvision.utils import make_grid
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, SubsetRandomSampler
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
import time
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, classification_report
from collections import Counter
from torchvision import models
# 定义一些函数和类
def plot_dist(indexes, dataset):
count = Counter()
for i in indexes:
_, label = dataset[i]
count[target_label[label]] += 1
dist_2 = dict(sorted(count.items(), key=lambda kv: kv[1], reverse=True))
plt.bar(dist_2.keys(), dist_2.values())
plt.xticks(rotation=30)
plt.title('Data distribution'); plt.ylabel('count')
plt.show()
def fit(epochs, model, train_loader, val_loader, criterion, optimizer):
train_losses = []
test_losses = []
train_accu = []
val_accu = []
fit_time = time.time()
for e in range(epochs):
since = time.time()
running_loss = 0
train_acc = 0
for image, label in train_loader:
optimizer.zero_grad()
image = image.to(device); label = label.to(device);
output = model(image)
ps = torch.exp(output)
_, top_class = ps.topk(1, dim=1)
correct = top_class == label.view(*top_class.shape)
train_acc += torch.mean(correct.type(torch.FloatTensor))
loss = criterion(output, label)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
running_loss += loss.item()
else:
model.eval()
test_loss = 0
accuracy = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for image, label in val_loader:
image = image.to(device); label = label.to(device);
output = model(image)
loss = criterion(output, label)
ps = torch.exp(output)
_, top_class = ps.topk(1, dim=1)
correct = top_class == label.view(*top_class.shape)
accuracy += torch.mean(correct.type(torch.FloatTensor))
test_loss += loss.item()
train_losses.append(running_loss/len(train_loader))
test_losses.append(test_loss/len(val_loader))
train_accu.append(train_acc/len(train_loader))
val_accu.append(accuracy/len(val_loader))
model.train()
print("Epoch: {}/{}.. ".format(e+1, epochs),
"Train Loss: {:.3f}.. ".format(running_loss/len(train_loader)),
"Test Loss: {:.3f}.. ".format(test_loss/len(val_loader)),
"Train Accuracy: {:.3f}.. ".format(train_acc/len(train_loader)),
"Test Accuracy: {:.3f}.. ".format(accuracy/len(val_loader)),
"Time: {:.2f}s" .format((time.time()-since)))
history = {'train_loss' : train_losses, 'val_loss': test_losses,
'train_accuracy': train_accu, 'val_accuracy':val_accu}
print('Total time: {:.2f} m' .format((time.time()- fit_time)/60))
return history
def save_model(model, optim, fpath):
checkpoint = {'model' : model,
'state_dict': model.state_dict(),
'optim' : optim.state_dict()
}
torch.save(checkpoint, fpath)
#load model
def load_model(fpath, inference=True, map_location=None):
"""
安全地加载PyTorch模型
Args:
fpath (str): 模型文件路径
inference (bool): 是否用于推理模式
map_location: 设备映射,如'cpu'或'cuda'
Returns:
model: 加载的模型
"""
try:
# 如果没有指定map_location,自动检测
if map_location is None:
map_location = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
# 添加VGG模型到安全全局变量列表
try:
from torch.serialization import add_safe_globals
from torchvision.models.vgg import VGG
add_safe_globals([VGG])
except ImportError:
print("警告:无法导入add_safe_globals,使用标准加载方式")
# 方法1:使用torch.load的安全加载方式
try:
# 新版本PyTorch的安全加载方式,明确指定weights_only=False
check = torch.load(fpath, map_location=map_location, weights_only=False)
except (AttributeError, TypeError):
# 兼容旧版本PyTorch
check = torch.load(fpath, map_location=map_location)
# 检查checkpoint格式
if not isinstance(check, dict):
raise ValueError("模型文件格式不正确,应该是字典格式")
# 获取模型
if 'model' in check:
model = check['model']
else:
raise ValueError("模型文件中没有找到'model'键")
# 加载状态字典
if 'state_dict' in check:
model.load_state_dict(check['state_dict'])
else:
print("警告:模型文件中没有找到'state_dict',模型参数可能未正确加载")
# 设置模型模式
if inference:
for param in model.parameters():
param.requires_grad = False
model.eval()
else:
model.train()
print(f"模型成功加载到设备: {map_location}")
return model
except FileNotFoundError:
print(f"错误:找不到模型文件 {fpath}")
raise
except Exception as e:
print(f"加载模型时发生错误: {str(e)}")
raise
# 备用方法:如果需要加载自定义类,可以使用这个函数
def load_model_with_custom_classes(fpath, custom_classes=None, inference=True, map_location=None):
"""
加载包含自定义类的模型
Args:
fpath (str): 模型文件路径
custom_classes (list): 自定义类列表
inference (bool): 是否用于推理模式
map_location: 设备映射
Returns:
model: 加载的模型
"""
try:
if map_location is None:
map_location = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
# 添加自定义类到安全列表
if custom_classes:
try:
from torch.serialization import add_safe_globals
add_safe_globals(custom_classes)
except ImportError:
print("警告:无法导入add_safe_globals,使用标准加载方式")
# 添加VGG模型到安全全局变量列表
try:
from torch.serialization import add_safe_globals
from torchvision.models.vgg import VGG
add_safe_globals([VGG])
except ImportError:
print("警告:无法导入add_safe_globals,使用标准加载方式")
# 使用weights_only=False来加载完整模型
try:
check = torch.load(fpath, map_location=map_location, weights_only=False)
except (AttributeError, TypeError):
check = torch.load(fpath, map_location=map_location)
if not isinstance(check, dict):
raise ValueError("模型文件格式不正确")
model = check['model']
if 'state_dict' in check:
model.load_state_dict(check['state_dict'])
if inference:
for param in model.parameters():
param.requires_grad = False
model.eval()
else:
model.train()
print(f"模型成功加载到设备: {map_location}")
return model
except Exception as e:
print(f"加载模型时发生错误: {str(e)}")
raise
def plot_loss(history, n_epoch):
epoch = [x for x in range(1, n_epoch+1)]
plt.plot(epoch, history['train_loss'], label='Train_loss')
plt.plot(epoch, history['val_loss'], label='val_loss')
plt.title('Loss per epoch')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.xlabel('epoch')
plt.legend();
plt.show()
def plot_accuracy(history, n_epoch):
epoch = [x for x in range(1, n_epoch+1)]
plt.plot(epoch, history['train_accuracy'], label='Train_accuracy')
plt.plot(epoch, history['val_accuracy'], label='val_accuracy')
plt.title('accuracy per epoch')
plt.ylabel('accuracy')
plt.xlabel('epoch')
plt.legend();
plt.show()
def predict_label(model, dataloader):
prediction_list = []
labels = []
model.to(device)
model.eval()
for i, batch in enumerate(dataloader):
image, label = batch
image = image.to(device); label = label.to(device)
out = model(image)
ps = torch.exp(out)
_, top_class = torch.max(ps , 1)
preds = np.squeeze(top_class.cpu().numpy())
prediction_list.append(preds)
labels.append(label.cpu().numpy())
return np.squeeze(prediction_list), np.squeeze(labels)
def predict_plot(test_loader, model, target_label, n=20):
# obtain one batch of test images
dataiter = iter(test_loader)
images, labels = next(dataiter) # 使用next()函数替代.next()方法
images.numpy()
# move model inputs to cuda, if GPU available
train_on_gpu = torch.cuda.is_available()
if train_on_gpu:
images = images.cuda()
model.eval()
# get sample outputs
model.to(device)
output = model(images)
# convert output probabilities to predicted class
_, preds_tensor = torch.max(output, 1)
preds = np.squeeze(preds_tensor.cpu().numpy())
images = images.cpu()
# plot the images in the batch, along with predicted and true labels
n = min(n, len(images)) # 防止越界
cols = min(n, 10) # 每行最多10个
rows = (n + cols - 1) // cols
fig, axes = plt.subplots(rows, cols, figsize=(3*cols, 4*rows))
axes = axes.flatten()
for idx in range(n):
ax = axes[idx]
ax.imshow(images[idx].permute(1, 2, 0))
ax.set_title("{} ({})".format(target_label[preds[idx]], target_label[labels[idx]]),
color=("green" if preds[idx]==labels[idx].item() else "red"))
ax.set_xticks([])
ax.set_yticks([])
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
class Mineral_1(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 48, 11, stride=3, padding=0),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(3, 1), #out 70x70
nn.Conv2d(48, 128, 5, stride=1, padding=0),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(3, 1),#out 64x64
nn.Conv2d(128, 128, 4, stride=1, padding=0),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(4, 3),#out 20x20
nn.Conv2d(128, 64, 3, stride=1, padding=0),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(3, 3),#out 20x20
nn.Flatten(),
nn.Linear(64*6*6, 512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(p=0.3),
nn.Linear(512, 3),
nn.LogSoftmax(dim=1),
)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.net(x)
return out
if __name__ == '__main__':
freeze_support()
# # Load Data and Get Insight
root_folder = r'G:\python learn\py.test\岩性识别\input\minet'
#root_folder = '../岩性识别/input/minet'
#七类矿物测试如下:
# target_label = ['biotite', 'bornite', 'chrysocolla', 'malachite',
# 'muscovite', 'pyrite', 'quartz']
# 四类矿物测试如下:bornite(斑铜矿)malachite(孔雀石)pyrite(黄铁矿)quartz(石英)chalcopyrite(黄铜矿) gold(金矿)
target_label = ['bornite','chalcopyrite', 'gold']
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
#load data and tranform it into tensor
dataset = ImageFolder(root_folder, transform=transforms.ToTensor())
print('Data size: ',len(dataset))
#transform format to augmetation dataset beacuse our dataset only has 956 images
#I reload the data and do multiple transformation and resize it
data_transform = transforms.Compose([transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
transforms.RandomRotation(30),
transforms.RandomVerticalFlip(p=0.5),
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(p=0.5),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean = [0.485, 0.456, 0.406],std = [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])]) #imagenet mean and std
load_data = ImageFolder(root_folder, transform=data_transform)
# split data to get the same distributiom
idx_label = {}
for i in range(len(dataset)):
_, label = dataset[i]
idx_label[i] = label
#split for data validation
x_train, x_val, y_train, y_val = train_test_split(list(idx_label.keys()), list(idx_label.values()),
stratify = list(idx_label.values()), test_size=0.05)
#exclude validation index from dataset
idx_label_2 = {}
for idx, label in idx_label.items():
if idx not in x_val:
idx_label_2[idx] = label
#split data train and test after exlude x_val
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(list(idx_label_2.keys()), list(idx_label_2.values()),
stratify = list(idx_label_2.values()), test_size=0.05)
plot_dist(x_train, dataset)
plot_dist(x_val, dataset)
plot_dist(x_test, dataset)
#load into dataloader for each data after split it
batch_size = 128
#using subset to get data from indexes with the same distribution label
train_set = SubsetRandomSampler(x_train)
val_set = SubsetRandomSampler(x_val)
test_set = SubsetRandomSampler(x_test)
#dataloader
train_loader = DataLoader(load_data, batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=False, num_workers=4, sampler= train_set)
val_loader = DataLoader(load_data, batch_size=batch_size,
num_workers=4, sampler=val_set)
test_loader = DataLoader(load_data, batch_size=batch_size,
num_workers=4, sampler=test_set)
# # Build Model自定义模型训练
# model_1 = Mineral_1()
# model_1.to(device)
#
# criterion = nn.NLLLoss()
# optimizer = optim.Adam(model_1.parameters(), lr=0.0001)
# epoch = 5
# history_mineral = fit(epoch, model_1, train_loader, val_loader, criterion, optimizer)
#
# #save mode
# save_model(model_1, optimizer, 'mineral_seq_own.pt')
#
# plot_loss(history_mineral, epoch)
# plot_accuracy(history_mineral, epoch)
# Pre-trained mode vgg模型训练
# 使用新的weights参数替代已弃用的pretrained参数
try:
# 新版本PyTorch的写法
modelVGG = models.vgg16(weights=models.VGG16_Weights.IMAGENET1K_V1)
except AttributeError:
# 兼容旧版本PyTorch
modelVGG = models.vgg16(pretrained=True)
# Freeze parameters so we don't backprop through them
for param in modelVGG.parameters():
param.requires_grad = False
#vgg16
modelVGG.classifier = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(in_features=25088, out_features=4096),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
nn.Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=1000),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
nn.Linear(in_features=1000, out_features=500),
nn.Linear(500, 3),
nn.LogSoftmax(dim=1))
modelVGG.to(device);
modelVGG.train()
criterion = nn.NLLLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(modelVGG.classifier.parameters(), lr=0.0001)
epoch = 10
history_VGG = fit(epoch, modelVGG, train_loader, val_loader, criterion, optimizer)
#save_model(modelVGG, optimizer, 'mineral_vgg.pt')
torch.save(modelVGG.state_dict(), 'mineral_vgg_state_dict.pt')
plot_loss(history_VGG, epoch)
plot_accuracy(history_VGG, epoch)
# # Prediction and Evaluation自定义模型评估
# model_mineral = load_model_with_custom_classes('mineral_seq_own.pt', custom_classes=[Mineral_1], inference=True)
# y_predict, y_true = predict_label(model_mineral, test_loader)
#
# print(classification_report(y_true, y_predict))
# sns.heatmap(confusion_matrix(y_true, y_predict), annot=True)
# plt.ylabel('True label'); plt.xlabel('Predicted Label')
# plt.yticks(np.arange(0.5, len(target_label)), labels=target_label, rotation=0);
# plt.xticks(np.arange(0.5, len(target_label)), labels=target_label, rotation=45)
# plt.title('My Model Prediction Over Test Set')
# plt.show()
#预训练模型vgg评估
model_vgg = load_model('mineral_vgg.pt', inference=True)
y_predict_vgg, y_true_vgg = predict_label(model_vgg, test_loader)
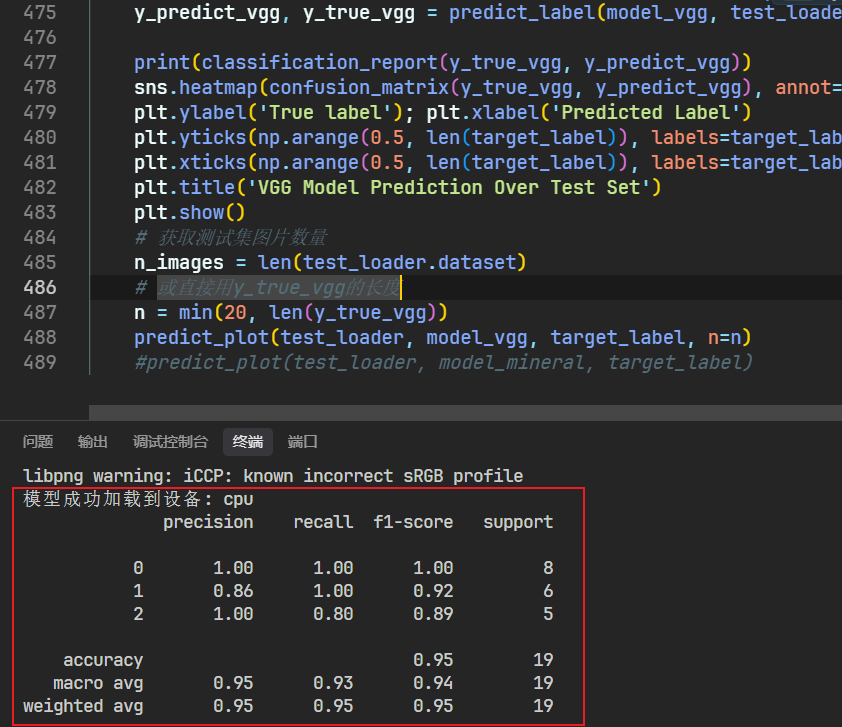
print(classification_report(y_true_vgg, y_predict_vgg))
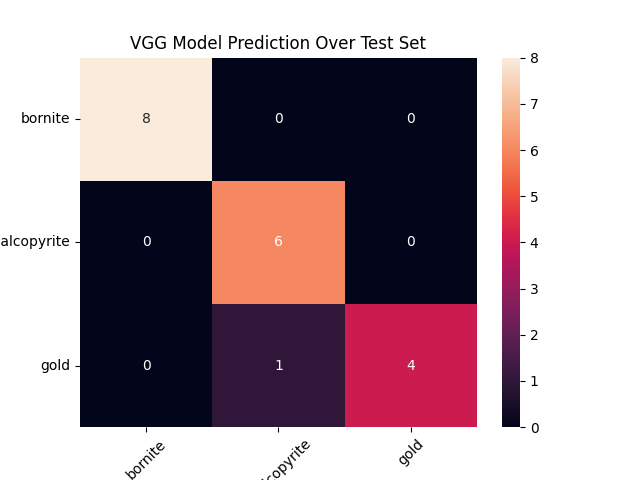
sns.heatmap(confusion_matrix(y_true_vgg, y_predict_vgg), annot=True)
plt.ylabel('True label'); plt.xlabel('Predicted Label')
plt.yticks(np.arange(0.5, len(target_label)), labels=target_label, rotation=0);
plt.xticks(np.arange(0.5, len(target_label)), labels=target_label, rotation=45)
plt.title('VGG Model Prediction Over Test Set')
plt.show()
# 获取测试集图片数量
n_images = len(test_loader.dataset)
# 或直接用y_true_vgg的长度
n = min(20, len(y_true_vgg))
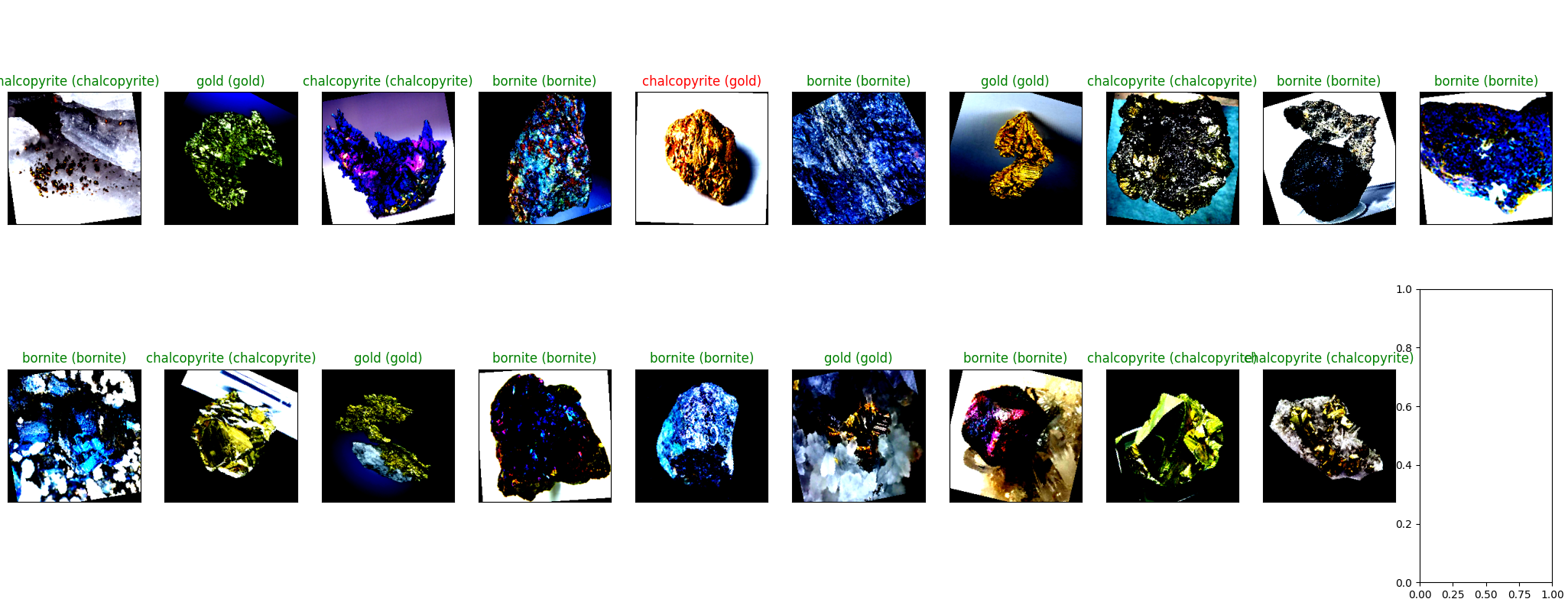
predict_plot(test_loader, model_vgg, target_label, n=n)
#predict_plot(test_loader, model_mineral, target_label)然后接下来是一些根据我的数据输出的结果:
终端评估输出:
热力图:
预测标签展示:
3.3 前后端协同调用
这里用的是Python下的flask服务来实现的,主要的过程就是把前面那个训练好的模型参数保存,然后加载训练好的权重参数,完成模型初始化与设备适配;接着通过Flask接口接收前端上传的图像文件,解码为RGB格式后,统一调整尺寸至224×224并按ImageNet标准归一化,实现图像预处理; 然后将预处理后的张量输入模型执行前向传播,通过卷积层提取特征并经全连接层映射至类别空间,再通过标签映射转换为具体矿物名称;最后将预测结果封装为JSON格式返回。这里也是直接上代码:
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify
from flask_cors import CORS
import torch
from torchvision import models, transforms
import torch.nn as nn
from PIL import Image
import io
MODEL_PATH = r"G:\python learn\py.test\岩性识别\mineral_vgg_state_dict.pt"
target_label = ['bornite', 'chalcopyrite', 'gold']
def get_model():
model = models.vgg16(weights=None)
model.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(in_features=25088, out_features=4096),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
nn.Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=1000),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
nn.Linear(in_features=1000, out_features=500),
nn.Linear(500, 3),
nn.LogSoftmax(dim=1)
)
return model
def load_model(weight_path, device='cpu'):
model = get_model()
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(weight_path, map_location=device))
model.eval()
model.to(device)
return model
transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean = [0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std = [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
])
def predict_single(model, img_bytes, device='cpu'):
img = Image.open(io.BytesIO(img_bytes)).convert('RGB')
img = transform(img).unsqueeze(0).to(device)
with torch.no_grad():
output = model(img)
_, pred = torch.max(output, 1)
return target_label[pred.item()]
# Flask服务
app = Flask(__name__)
CORS(app)
device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
model = load_model(MODEL_PATH, device)
@app.route('/recognize', methods=['POST'])
def recognize():
if 'file' not in request.files:
return jsonify({'error': 'No file uploaded'}), 400
file = request.files['file']
img_bytes = file.read()
try:
result = predict_single(model, img_bytes, device)
return jsonify({'result': result})
except Exception as e:
return jsonify({'error': str(e)}), 500
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=5000)运行之后的结果:
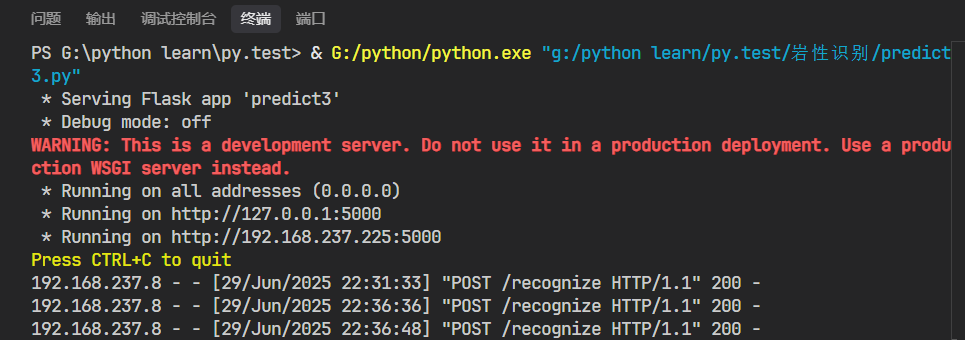
前端只要访问这个端口,把图片上传就好了,这里要确保前端设备和后端是在同一个热点下运行,后期大家如果可以改进的话可以处理这个问题,包括把它放到云服务器上以及一个并发处理。
然后下面就是整个前后端流程描述如下:
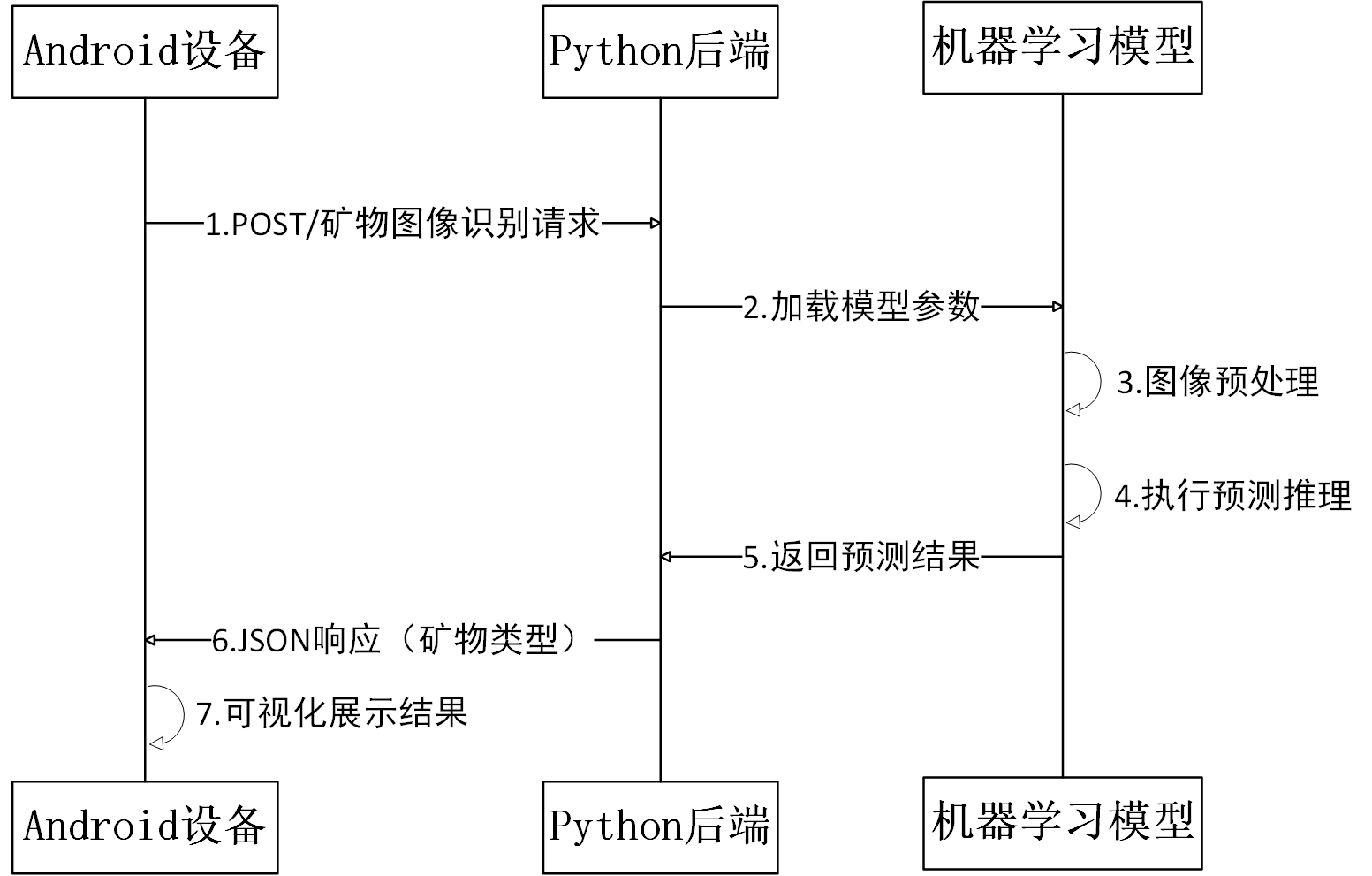
构建了端到端的矿物图像识别系统,通过迁移学习与自定义分类器适配,实现了对bornite、chalcopyrite、gold三类矿物的高效识别。在19个测试样本的场景下达到95%的整体准确率。API服务采用Flask框架搭建,支持图像上传、预处理、实时推理及JSON结果返回,具备跨平台调用能力(如Android设备集成)。系统通过设备感知(CPU/GPU自动切换)与模型轻量化部署,在保证95%准确率的同时,单图像推理耗时控制在合理范围内。
4、总结
这里前端的调用我就没有放了,因为是集成到另外一位同学的APP上的,他的整个项目架构比较复杂,大概的流程就是在里面增加一个button然后发送请求到后端,传输图片,然后接收后端的一个识别结果输出就行了,这个前端也不定限制在android大家也可以在pc端或者web写好自己的网络服务请求调用后端就好了。以上便是整个项目的内容,主要供大家的学习使用,原理大家就自己去学习就好了哈哈哈哈哈,当然本质目的还是想记录一个这个作业,所不定能帮到以后得学弟学妹(汇报PPT也有),毕竟整个上机过程确实很抽象。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。




















 511
511










