优点: 1、抽象和实现的分离。 2、优秀的扩展能力。 3、实现细节对客户透明。
缺点:桥接模式的引入会增加系统的理解与设计难度,由于聚合关联关系建立在抽象层,要求开发者针对抽象进行设计与编程。
使用场景:
1、如果一个系统需要在构件的抽象化角色和具体化角色之间增加更多的灵活性,避免在两个层次之间建立静态的继承联系,通过桥接模式可以使它们在抽象层建立一个关联关系。
2、对于那些不希望使用继承或因为多层次继承导致系统类的个数急剧增加的系统,桥接模式尤为适用。
3、一个类存在两个独立变化的维度,且这两个维度都需要进行扩展。
注意事项:对于两个独立变化的维度,使用桥接模式再适合不过了。
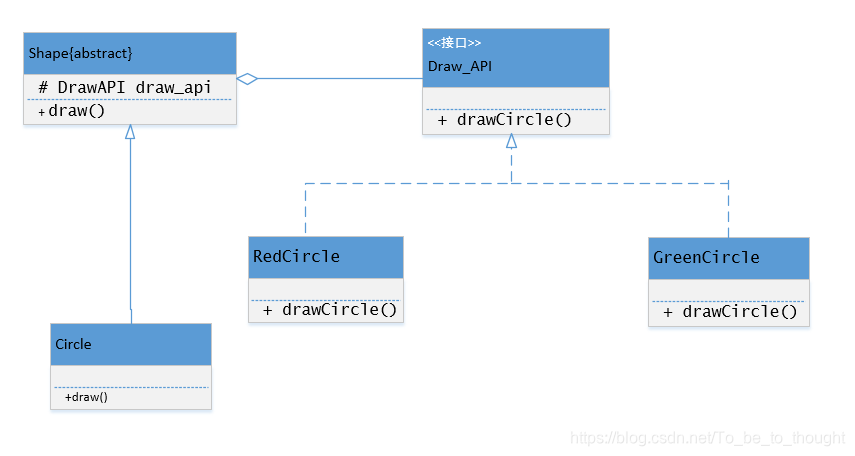
绘图API的接口
package DesignPattern.BridgePattern;
public interface DrawAPI {
public void drawCircle(int radius, int x, int y);
}
具体实现绘图API的类
package DesignPattern.BridgePattern;
public class RedCircle implements DrawAPI {
@Override
public void drawCircle(int radius, int x, int y) {
System.out.println("Drawing Circle[ color: red, radius: "
+ radius +", x: " +x+", "+ y +"]");
}
}
package DesignPattern.BridgePattern;
public class GreenCircle implements DrawAPI{
@Override
public void drawCircle(int radius, int x, int y) {
System.out.println("Drawing Circle[ color: green, radius: "
+ radius +", x: " +x+", "+ y +"]");
}
}
实体抽象类
package DesignPattern.BridgePattern;
public abstract class Shape {
protected DrawAPI draw_api;
public Shape(DrawAPI api){
this.draw_api=api;
}
public abstract void draw();
}
实体
package DesignPattern.BridgePattern;
public class Circle extends Shape {
private int x, y, radius;
public Circle(int x, int y, int radius, DrawAPI drawAPI) {
super(drawAPI);
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.radius = radius;
}
public void draw() {
draw_api.drawCircle(radius,x,y);
}
}
客户端测试程序
package DesignPattern.BridgePattern;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Shape redCircle = new Circle(100,100, 10, new RedCircle());
Shape greenCircle = new Circle(100,100, 10, new GreenCircle());
redCircle.draw();
greenCircle.draw();
}
}





 本文深入探讨了桥接模式的优点和缺点,包括抽象和实现的分离、扩展能力和实现细节的透明性,同时也指出了该模式可能增加的设计复杂度。文章通过实例讲解了桥接模式的应用场景,特别是当系统需要在抽象化角色和具体化角色之间增加灵活性,或在两个独立变化的维度上进行扩展时。通过具体的代码示例,展示了如何在绘图API中应用桥接模式,实现颜色和形状的独立变化。
本文深入探讨了桥接模式的优点和缺点,包括抽象和实现的分离、扩展能力和实现细节的透明性,同时也指出了该模式可能增加的设计复杂度。文章通过实例讲解了桥接模式的应用场景,特别是当系统需要在抽象化角色和具体化角色之间增加灵活性,或在两个独立变化的维度上进行扩展时。通过具体的代码示例,展示了如何在绘图API中应用桥接模式,实现颜色和形状的独立变化。
















 2526
2526

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








