练习题
题目:用户在键盘依次输入若干个数字,每输入一个数字都需要按回车键确认,最后在键盘输入一个非数字字符串结束整个输入操作过程。程序将计算出这些数的和以及平均值。用来读写外设字符的,它们都是字节流。如果编程人员愿意,可以用基于字符的流来包装它们
package com.yan2;
import java.io.IOException;
/*
* 题目:用户在键盘依次输入若干个数字,每输入一个数字都需要按回车键确认,
* 最后在键盘输入一个非数字字符串结束整个输入操作过程。
* 程序将计算出这些数的和以及平均值。
*/
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
int sum = 0;
int count = 0;
while (true) {
String ss = readData();
if ("quit".equals(ss))
break;
if (ss != null && ss.trim().length() > 0) {
int kk = Integer.parseInt(ss);
sum += kk;
count++;
}
}
System.out.println("数字和为 " + sum + " ,平均值为 " + (1. * sum / count));
// int kk = System.in.read();
// System.out.println(kk);
//
// System.out.println((int) '\r');// 换行符
// System.out.println((int) '1');
}
public static String readData() throws IOException {
byte[] res = new byte[10];
int len = 0;
while (true) {
// 具体的键盘录入和应用编码无关,这里是按照一个InputSteam进行使用
int kk = System.in.read();
if (kk == '\r' || kk == '\n') {
break;
}
res[len++] = (byte) kk;
}
return new String(res, 0, len);
}
}
//IllegalArgumentException extends RuntimeException 不合法的参数异常
//NumberFormatException extends IllegalArgumentException 数字格式化异常
//RuntimeException extends Exception 运行时异常
//
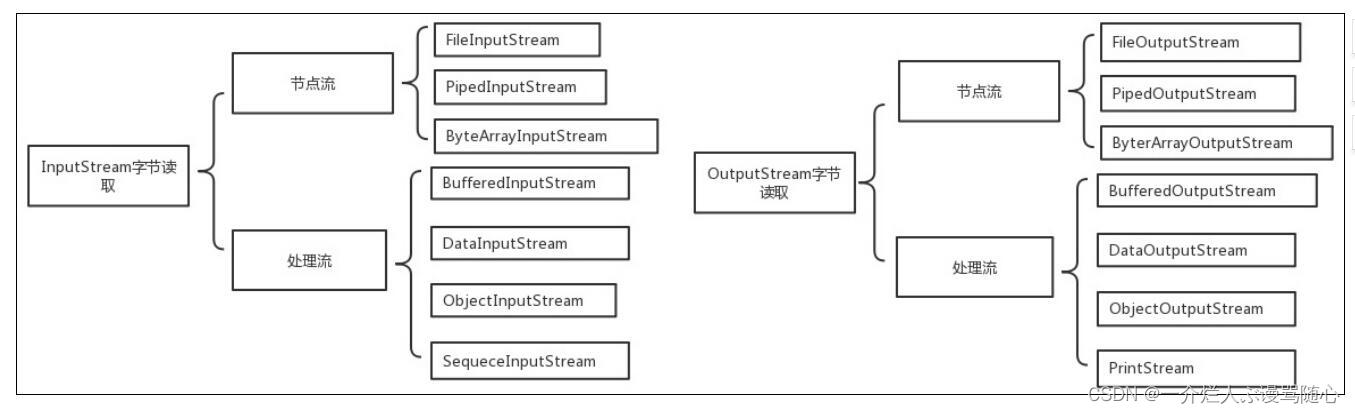
- FileInputStream、FileOutputStream 顺序读取文件
- PipedInputStream、PipedOutputStream 管道
- ByteArrayInputStream、ByteArrayOutputStream 内存读写
- FilterInputStream、FilterOutputStream 过滤流(有多线程同步)
- DataInputStream、DataOutputStream 对数据类型读写,有多线程同步
- BufferedInputStream、BufferedOutputStream 缓冲类型读写
1、使用字节流进行文件的单字节复制
- FileInputStream是InputStream的子类,FileInputStream属于节点流,用于按字节读取文件内容
- FileOutputStream是OutputStream的子类,FileOutputStream属于节点流,用于按字节输
- 出数据到文件中
//FileInputStream中read方法的定义
/** 从指定的输入流中按字节读取数据,如果读到流的末尾则返回-1,否则返回读取到的数据。如果文件不存 在则异常FileNotFoundException【IOException的子类】 */
public int read() throws IOException {
return read0();
}
//FileOutputStream中write方法的定义
//属性,用于表示是否进行文件的追加操作而不是覆盖操作
private final boolean append;
//构造器方法的定义,其中name是文件名称,默认采用覆盖操作
public FileOutputStream(String name) throws FileNotFoundException {
this(name != null ? new File(name) : null, false);
}//按照字节执行写出int数据,自动会去除多余的字节。如果文件不存在则自动创建新文件,如果 文件已经存在则按照append的值决定采用的是追加操作还是覆盖操作
public void write(int b) throws IOException {
write(b, append);
}
private native void write(int b, boolean append) throws IOException; // 由VM采用对等类的方式提供实现
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try (InputStream is = new FileInputStream("c:/面向对象文档.txt");
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("test.txt");) {
int kk;
while ((kk = is.read()) != -1) {
os.write(kk);
}
}
}
}
2、读取A.java文件并在控制台上显示
- 如何使用控制台输出: System.out字节流
- 分析:使用字节流从A.java中一个字节一个字节的读取内容,然后再使用System.out.print方法输出即可
- 注意:读取操作返回的int的取值范围为0-255,则表示这里不会有符号位,所以is.read()==-1不是只适合于文本文件
File ff = new File("T1.java");
if (ff.exists()) {// 如果文件存在则进行拷贝操作,否则提示文件不存在
InputStream is = new FileInputStream(ff);
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("t1.bak");
while (true) {
int kk = is.read();// 返回值应该是0-255,如果返回-1表示流已经结束
if (kk < 0)break;
os.write(kk);
}
is.close(); os.close();
} else
System.out.println("T1.java文件不存在");
InputStream基本输入类
InputStream类是基本的输入类。它定义了所有输入流所需的方法。
- public abstract int read() throws IOException读取一个字节并以整数的形式返回,0-255。如果返回-1已到输入流的末尾。
- public int read(byte b[]) throws IOException读取一系列字节并存储到一个数组,返回实际读取的字节数。如果已经读到输入流的末尾则返回-1
- public void close() throws IOException 关闭输入流并释放资源
- public int read(byte b[],int offset,int length) throws IOException功能为从输入流中读数据。这一 方法有几种重载形式,可以读一个字节或一组字节。当遇到文件尾时,返回-1。最后一种形式中的offset是指把结果放在b[]中从第offset个字节开始的空间,length为长度
- public long skip (long n) throws IOEnception 从输入流跳过几个字节。返回值为实际跳过的字节数
OutputStream基本输出类
三个重载形式都是用来向输出流写数据的
- public abstract void write(int b)向输入流写入一个字节数据,该字节为参数的低8位。
- public void write(byte b[],int offset,int length)将一个字节类型的数组中的从指定位置offset开始的length个字节写入到输出流
- public void close( ) 关闭输出流,释放资源
- public void write(byte b[])将一个字节类型的数组中的数据写入到输出流
- public void flush() 清除缓冲区,将缓冲区内尚未写出的数据全部输出
需求:使用字节流将一个文件进行拷贝
- 每次读写一个字节效率太低,所以使用字节数组。同时编码中需要考虑如果文件存在则进行拷贝操作,否则提示文件不存在
- 要点1:从文件中读取数据放入到buffer字节数组中,如果文件中的内容大于byte[],则最多读取1024个字节;如果文件中数据不足,则实际有多少则读取多少;写入buffer数组默认是从0开始写入,最终返回实际读取的字节数。如果读取到流末尾则返回-1
- 要点2:不能直接写出数组,否则会有多余内容产生。可以使用write(byte[],int,int)保证只写出读取到的内容
- 要点3:注意try/finally结构,JDK1.7中提供Closeable接口支持自动关闭,从而简化try/finally写法
package com.yan5;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.Reader;
import java.io.Writer;
/*
* 练习:编写一个程序,把指定目录下的所有的带.java文件都拷贝到另一个目录中
* ,拷贝成功后,把后缀名是.java的改成.txt
*
*
* 例如src下多个文件位于src的子目录中,如果文件名称重复,则需要改名称,在名称后面添加(n)
*/
public class Test4 {
private static String target = "d:/abcd";
public static void main(String[] args) {
copyFile(new File("src"));
}
private static void copy(File source) {
System.out.println("拷贝文件" + source.getAbsolutePath());
File f1 = new File(target);
if (!f1.exists()) {
f1.mkdirs();
}
int cc = 0;
String fileName = source.getName();
String sourceName = fileName;
File f2 = null;
while (true) {
f2 = new File(f1, fileName);
if (!f2.exists()) {
break;
} else {
fileName = sourceName.substring(0, sourceName.lastIndexOf("."));
fileName = fileName + "(" + (cc++) + ").java";
}
}
try (Reader r = new FileReader(source); Writer w = new FileWriter(f2);) {
char[] arr = new char[8192];
int len = 0;
while ((len = r.read(arr)) > 0) {
w.write(arr, 0, len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void copyFile(File file) {
if (file.exists()) {
if (file.isDirectory()) {
File[] fs = file.listFiles();
if (fs != null && fs.length > 0) {
for (File tmp : fs) {
copyFile(tmp);
}
}
} else if (file.isFile()) {
String fn = file.getName();// 获取文件的简称
if (fn != null && fn.endsWith(".java")) {
copy(file);
}
}
}
}
}
字符流
在顶层有Reader和Writer两个抽象类。Reader和Writer中定义了read()和write()方法,它们被派生流类重载
Reader抽象类的定义
public abstract class Reader implements Readable, Closeable {
//BIO,读取一个有效的字符,返回值为0到65535的整数,如果到达流的末尾则返回-1
public int read() throws IOException
//BIO,读取字符存储到char数组中,返回读取的字符个数,流结束则返回-1
public int read(char cbuf[]) throws IOException
//关闭流,同时释放资源
abstract public void close() throws IOException;
Writer抽象类的定义
public abstract class Writer implements Appendable, Closeable, Flushable {
//写出一个字符到字符流,要写的字符包含在给定整数值的16个低位;16个高位被忽略。
public void write(int c) throws IOException
//将字符数组中的指定部分内容压入到字符流,从off开始共len个字符
abstract public void write(char cbuf[], int off, int len) throws IOException;
//关闭流,同时释放资源
abstract public void close() throws IOException;
相关的子类
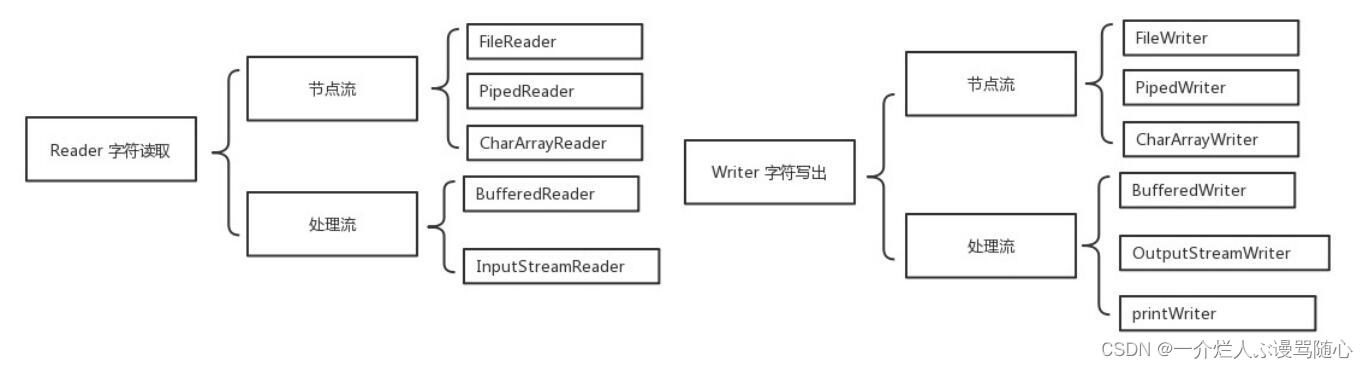
- InputStreamReader、OutputStreamWriter桥接流,用于自动实现字节流和字符流的转换
- FileReader、FileWriter文件流,用于实现针对文本文件的读写操作
- CharArrayReader、CharArrayWriter内存流,用于实现针对char数组的读写操作
- PipedReader、PipedWriter管道流,用于线程之间的通讯
- FilterReader、FilterWriter过滤流的父类
- BufferedReader、BufferedWriter缓存流,用于在流中添加缓冲区
- StringReader、StringWriter内存流,用于实现针对字符串的读写操作
字符流Reader
- int read()读取一个字符并以整数的形式返回0-65535,如果返回-1则已到输入流末尾
- int read(char[] cbuf)读取一系列字符并存储到一个数组中,返回实际读取的字符数,如果读到输入流末尾则返回-1
- void close()关闭输入流并释放内存资源
- int read(char[] cbuf, int off, int len) 读取len个字符并存储到一个数组中,从off位置开始,返回实际读取的字符数,如果读取到输入流末尾则返回-1
- long skip(long n)跳过n个字符不读,返回实际跳过的字节数
字符流Writer
- void write(int c) 将字符(int数组的低8位)压入到字符流中
- void write(char[] cbuf, int off, int len)将字符数组中的指定部分内容压入到字符流中,从off开始共len个字符
- void write(String str) 将字符串中的内容压入到字符流中
- void close() 关闭流并释放所占用的资源
- void write(String str, int off, int len) 将字符串中的指定部分内容压入到字符流中,从下标off开始共len个字符
- void flush()刷新缓冲区,将缓冲区中的数据全部送出到目标地,然后清空缓冲区
- void write(char[] cbuf) 将字符数组中的所有数据压入到字符流中
一般来说:一次读写一个字符效率太低,可以引入char[]数组提高执行效率
使用字符流实现文件的拷贝
package com.yan5;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.Reader;
import java.io.Writer;
/*
* 练习:编写一个程序,把指定目录下的所有的带.java文件都拷贝到另一个目录中
* ,拷贝成功后,把后缀名是.java的改成.txt
*
*
* 例如src下多个文件位于src的子目录中,如果文件名称重复,则需要改名称,在名称后面添加(n)
*/
public class Test4 {
private static String target = "d:/abcd";
public static void main(String[] args) {
copyFile(new File("src"));
}
private static void copy(File source) {
System.out.println("拷贝文件" + source.getAbsolutePath());
File f1 = new File(target);
if (!f1.exists()) {
f1.mkdirs();
}
int cc = 0;
String fileName = source.getName();
String sourceName = fileName;
File f2 = null;
while (true) {
f2 = new File(f1, fileName);
if (!f2.exists()) {
break;
} else {
fileName = sourceName.substring(0, sourceName.lastIndexOf("."));
fileName = fileName + "(" + (cc++) + ").java";
}
}
try (Reader r = new FileReader(source); Writer w = new FileWriter(f2);) {
char[] arr = new char[8192];
int len = 0;
while ((len = r.read(arr)) > 0) {
w.write(arr, 0, len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void copyFile(File file) {
if (file.exists()) {
if (file.isDirectory()) {
File[] fs = file.listFiles();
if (fs != null && fs.length > 0) {
for (File tmp : fs) {
copyFile(tmp);
}
}
} else if (file.isFile()) {
String fn = file.getName();// 获取文件的简称
if (fn != null && fn.endsWith(".java")) {
copy(file);
}
}
}
}
}




 本文介绍了如何使用Java编程处理用户通过键盘输入的一系列数字,计算总和与平均值,并利用字节流进行文件操作,如单字节复制和字符流文件拷贝。
本文介绍了如何使用Java编程处理用户通过键盘输入的一系列数字,计算总和与平均值,并利用字节流进行文件操作,如单字节复制和字符流文件拷贝。
















 348
348










