阅读 【快速入门教程 | NumPy】时有些地方疑惑。
记录下来以供参考。
1.ndim shape size
- ndarray.ndim - 数组的轴(维度)的个数。在Python世界中,维度的数量被称为rank。
- ndarray.shape - 数组的维度。这是一个整数的元组,表示每个维度中数组的大小。对于有 n 行和 m 列的矩阵,
shape将是(n,m)。因此,shape元组的长度就是rank或维度的个数ndim。 - ndarray.size - 数组元素的总数。这等于
shape的元素的乘积。 - ndarray.dtype - 一个描述数组中元素类型的对象。可以使用标准的Python类型创建或指定dtype。另外NumPy提供它自己的类型。例如numpy.int32、numpy.int16和numpy.float64。
- ndarray.itemsize - 数组中每个元素的字节大小。例如,元素为
float64类型的数组的itemsize为8(=64/8),而complex32类型的数组的itemsize为4(=32/8)。它等于ndarray.dtype.itemsize。 - ndarray.data - 该缓冲区包含数组的实际元素。通常,我们不需要使用此属性,因为我们将使用索引访问数组中的元素。
import numpy as np
print("=情况1========================================")
n = np.array([1,2,3,4])
print("data:",n)
print("Shape:",n.shape)
print("ndim:",n.ndim)
print("size:",n.size)
print("dtype:",n.dtype)
print("itemsize:",n.itemsize)
print("=情况2========================================")
n = np.array([[1,2,3,4],[1,2,3,4]])
print("data:",n)
print("Shape:",n.shape)
print("ndim:",n.ndim)
print("size:",n.size)
print("dtype:",n.dtype)
print("itemsize:",n.itemsize)
print("=情况3========================================")
n = np.array([[1,2,3,4],[1,2,3,4],[1,2,3,4]])
print("data:",n)
print("Shape:",n.shape)
print("ndim:",n.ndim)
print("size:",n.size)
print("dtype:",n.dtype)
print("itemsize:",n.itemsize)=情况1========================================
data: [1 2 3 4]
Shape: (4,)
ndim: 1
size: 4
dtype: int32
itemsize: 4
=情况2========================================
data: [[1 2 3 4]
[1 2 3 4]]
Shape: (2, 4)
ndim: 2
size: 8
dtype: int32
itemsize: 4
=情况3========================================
data: [[1 2 3 4]
[1 2 3 4]
[1 2 3 4]]
Shape: (3, 4)
ndim: 2
size: 12
dtype: int32
itemsize: 4
总结:
ndim :返回数组的行数和列数,如果是一维数组,则行数=1维数组的列数。
行数=数组左侧[的个数列数=里面1维数组的列数。特俗情况,如果所有1维数组列数的不一致,则创建会报错
shape :左侧 “[” 的个数
size : 存储元素总数
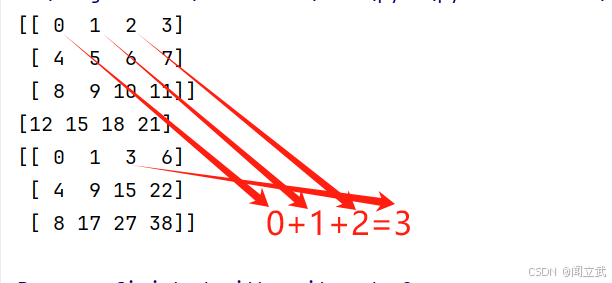
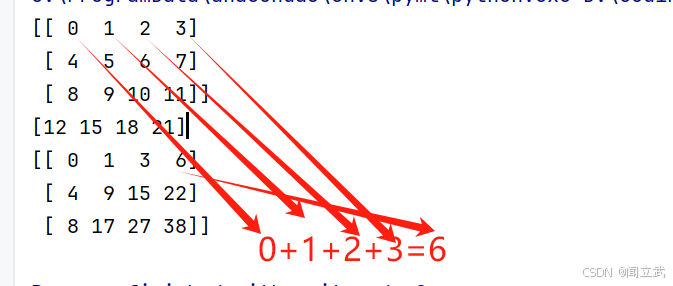
2. cumsum
沿着轴,依次相加,将计算的结果放到当前行中。
b = np.arange(12).reshape(3,4)
print(b)
# 列数据求和
print(b.sum(axis=0))
#行数据操作
print(b.cumsum(axis=1))[[ 0 1 2 3]
[ 4 5 6 7]
[ 8 9 10 11]]
[12 15 18 21]
[[ 0 1 3 6]
[ 4 9 15 22]
[ 8 17 27 38]]

3.其他
exp:指数函数
sqrt:开平方
**:幂函数
b = np.arange(10)
print(b)
print(b**2)
print(b**3)
[0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9]
[ 0 1 4 9 16 25 36 49 64 81]
[ 0 1 8 27 64 125 216 343 512 729]
4.fromfunction
np用于从一个函数对象创建数组。它允许用户根据指定的函数规则来生成数组的元素值,而无需使用显式循环。
import numpy as np
def f(x, y):
return 10 * x + y
result = np.fromfunction(f, (3,4), dtype=int)
print(result)[[ 0 1 2 3]
[10 11 12 13]
[20 21 22 23]]
解析:
1步创建位置数组
【 0,0 0,1 0,2 0,3
1,0 1,1 1,2 1,3
2,0 2,1 2,2 2,3
】
之后根据坐标,传入规则函数计算:
【
10*0+0 10*0+1 10*0+2 10*0+3
10*1+0 10*1*1 10*1*2 10*1+3
10*2+0 10*2*1 10*2*2 10*2+3
】
最好得出结果:
[[ 0 1 2 3]
[10 11 12 13]
[20 21 22 23]]
























 1299
1299

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








