
#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
if(n>=10)
{
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(1)<<n*2.0<<endl;
}
else
{
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(1)<<n*2.2<<endl;
}
return 0;
}

#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
if(n>0)
{
cout<<"是正数"<<endl;
}
else
{
cout<<"不是正数"<<endl;
}
return 0;
}

#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int t ;
cin>>t;
if(t>=20 && t<=30)
{
cout<<"OK";
}
else
{
cout<<"no";
}
return 0;
}

#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
if(n <= 10 && n >= 10)
{
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(1)<<n*2.5<<endl;
}
else
{
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(1)<<n*2.5+1.5<<endl;
}
return 0;
}

#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int t;
cin>>t;
if(2000<=n && n<=10000)
{
cout<<"ok"<<endl;
}
else
{
cout<<"no"<<endl;
}
return 0;
}

#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
if(n>=1.3)
{
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(1)<<n*60<<endl;
}
else
{
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(1)<<n*120<<endl;
}
return 0;
}

#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
int j;
int y;
cin>>n;
cin>>j;
cin>>y;
if(n+j>y && j+y>n)
{
cout<<"yes"<<endl;
}
else
{
cout<<"no"<<endl;
}
return 0;
}

#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int m;
int n;
cin>>m;
cin>>n;
if(m*m>m*n)
{
cout<<m*m-m*n<<endl;
}
else
{
cout<<m*n<<endl;
}
return 0;
}

#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
int x;
cin>>n;
cin>>x;
if(n <= 10 && x <= 100 && x>=100)
{
cout<<n/x<<endl;
}
else
{
cout<<n/x+1<<endl;
}
return 0;
}

#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int A;
int B;
cin>>A;
cin>>B;
if(A > B && A < B)
{
cout<<"A>B"<<endl;
}
else
{
cout<<"A<B"<<endl;
}
return 0;
}

#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
if(n%30 == 0)
{
cout<<n/30<<endl;
}
else
{
cout<<n/30+1<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
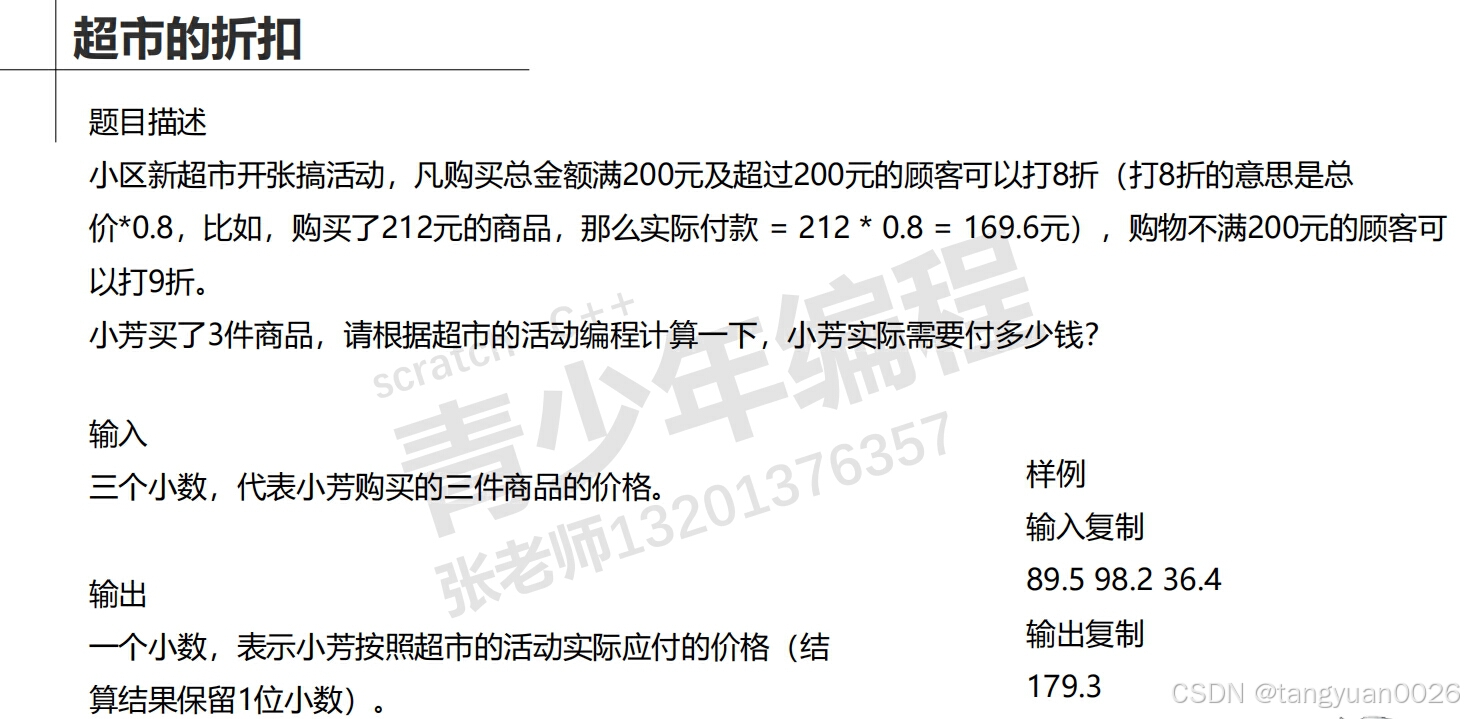
#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
if(n>=200)
{
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(1)<<n*0.8<<endl;
}
else
{
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(1)<<n*0.9<<endl;
}
return 0;
}

#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int aw;
int jy;
cin>>aw;
cin>>jy;
if(aw > jy && aw < jy)
{
cout<<aw<<endl;
}
else
{
cout<<jy<<endl;
}
return 0;
}

#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int dg;
int zq;
cin>>dg;
cin>>zq;
if(dg >= zq && dg <= zq)
{
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(1)<<dg<<endl;
}
else
{
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(1)<<zq<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
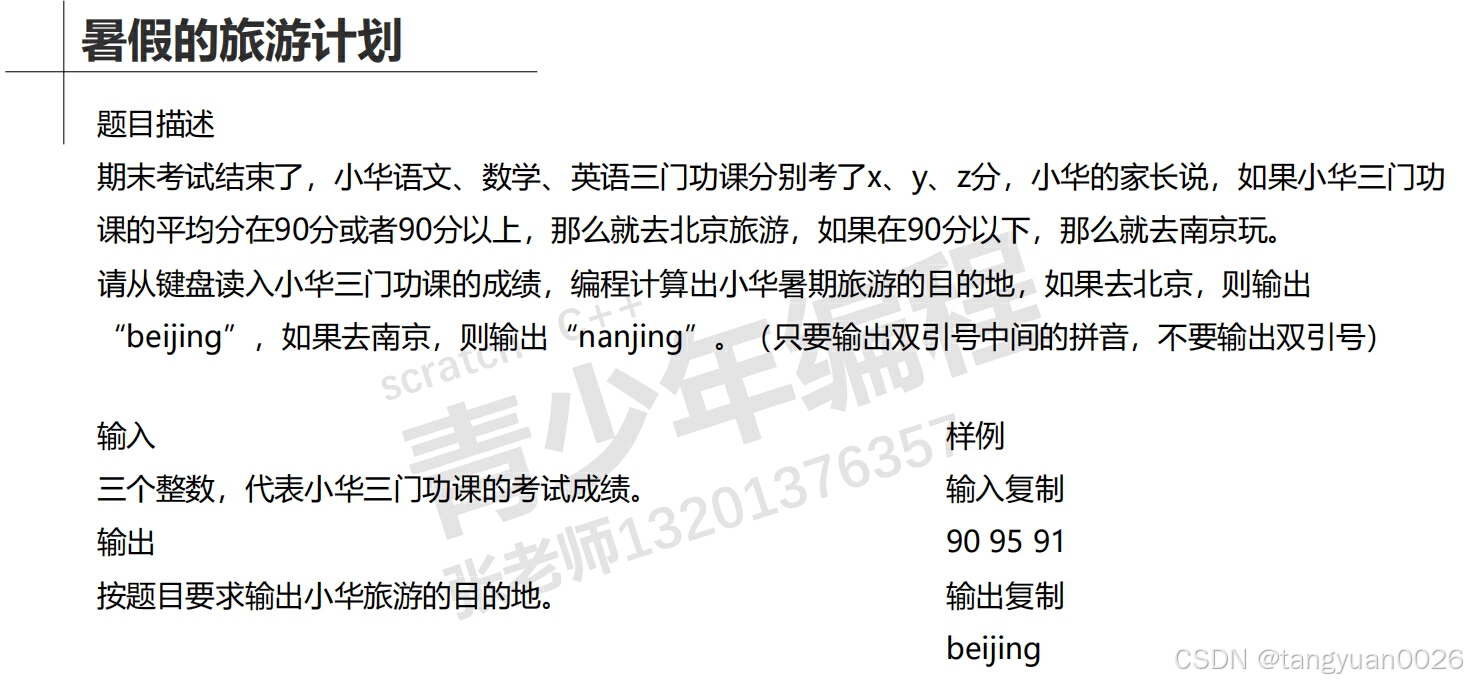
'
#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
if(x y z >= 90 x y z <= 90 )
{
cout<<"beijing"<<endl;
}
else
{
cout<<"nanjing"<<endl;
}
return 0;
}

#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
int g = n%10;
int b = n/100%10;
if(g == b)
{
cout<<"yes"<<endl;
}
else
{
cout<<"no"<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
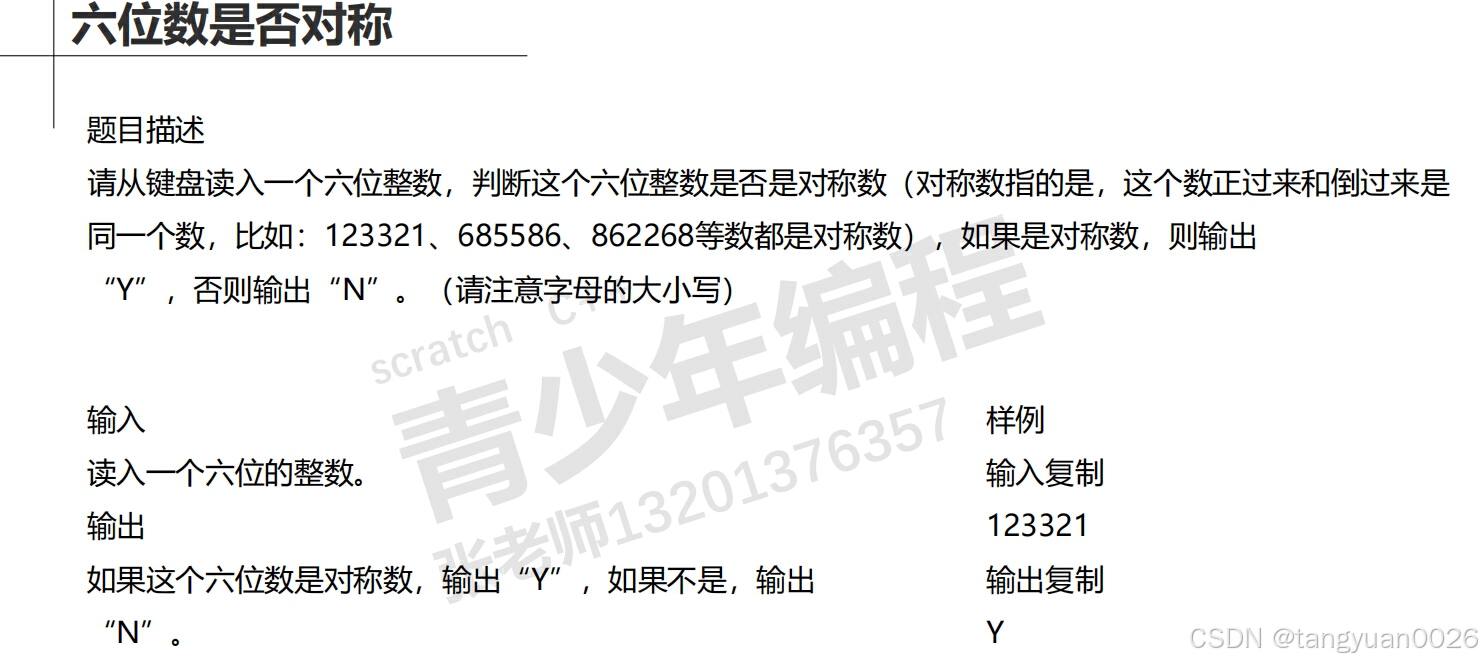
#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
int h = n%10;
int z = n/10%10;
int q = n/100%10;
int w = n/1000%10;
int b = n/10000%10;
int y = n/100000
if(h == z == q == w == b == y)
{
cout<<"yes"<<endl;
}
else
{
cout<<"no"<<endl;
}
return 0;
}

#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
if(n<=10 && n>=10)
{
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(1)<<n*1.5<<endl;
}
else
{
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(1)<<n*1.2<<endl;
}
return 0;
}

#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int s,q,w,j,y,z;
cin>>s,q,w,j,y,z;
if(s == q == w == j == y == z)
{
cout<<s,q,w<<endl;
}
else
{
cout<<j,y,z<<endl;
}
return 0;
}




















 1810
1810

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








