CLH队列
在AQS类文件的开头,作者添加了很长一段注释,向开发者解释CLH队列,以及AQS对CLH队列的使用。AQS里面的CLH队列是CLH同步锁的一种变形。其主要从两方面进行了改造:节点的结构与节点等待机制。在结构上,AQS类引入了头结点和尾节点,他们分别指向队列的头和尾,尝试获取锁、入队列、释放锁等实现都与头尾节点相关: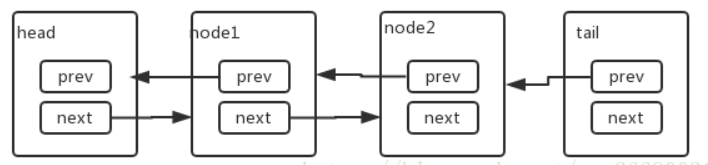
To enqueue into a CLH lock, you atomically splice it in as new tail. To dequeue, you just set the head field.即要加入CLH锁,可以自动将其作为新尾部进行拼接。 要出队,您只需设置头字段。
Node
CLH队列由Node对象组成,Node是AQS中的内部类。
static final class Node {
//用于标识共享锁
static final Node SHARED = new Node();
//用于标识独占锁
static final Node EXCLUSIVE = null;
/**
* 因为超时或者中断,节点会被设置为取消状态,被取消的节点时不会参与到竞争中的,他会一直保持取 消状态不会转变为其他状态;
*/
static final int CANCELLED = 1;
/**
* 当前节点释放锁的时候,需要唤醒下一个节点
*/
static final int SIGNAL = -1;
/**
* 节点在等待队列中,节点线程等待Condition唤醒
*/
static final int CONDITION = -2;
/**
* 表示下一次共享式同步状态获取将会无条件地传播下去
*/
static final int PROPAGATE = -3;
/**
* 等待状态
*/
volatile int waitStatus;
/**
* 前驱节点
*/
volatile Node prev;
/**
* 后继节点
*/
volatile Node next;
/**
* 节点线程
*/
volatile Thread thread;
Node nextWaiter;
/**
* Returns true if node is waiting in shared mode.
*/
final boolean isShared() {
return nextWaiter == SHARED;
}
Node() { // Used to establish initial head or SHARED marker
}
Node(Thread thread, Node mode) { // Used by addWaiter
this.nextWaiter = mode;
this.thread = thread;
}
Node(Thread thread, int waitStatus) { // Used by Condition
this.waitStatus = waitStatus;
this.thread = thread;
}
......
}CLH队列执行
1.线程调用acquire方法获取锁,如果获取失败则会进入CLH队列
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}2.addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE)方法会将当前线程封装成Node节点,追加在队尾。
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
// 获取原队尾
Node pred = tail;
if (pred != null) {
node.prev = pred;
//用cas更新 ,pred是原来队尾,作为预期值,node作为新值
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {
pred.next = node;
return node;
}
}
//前面cas更新失败后,再enq方法中循环用cas更新直到成功
enq(node);
return node;
}enq方法:
private Node enq(final Node node) {
for (;;) {
Node t = tail;
if (t == null) {
//使用cas初始化head节点
if (compareAndSetHead(new Node()))
tail = head;
} else {
//将当前节点放在clh队列尾部
node.prev = t;
if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {
t.next = node;
return t;
}
}
}
}假如有两个线程,第一个执行中,第二个在lch队列里面,在return node处,此时debug:
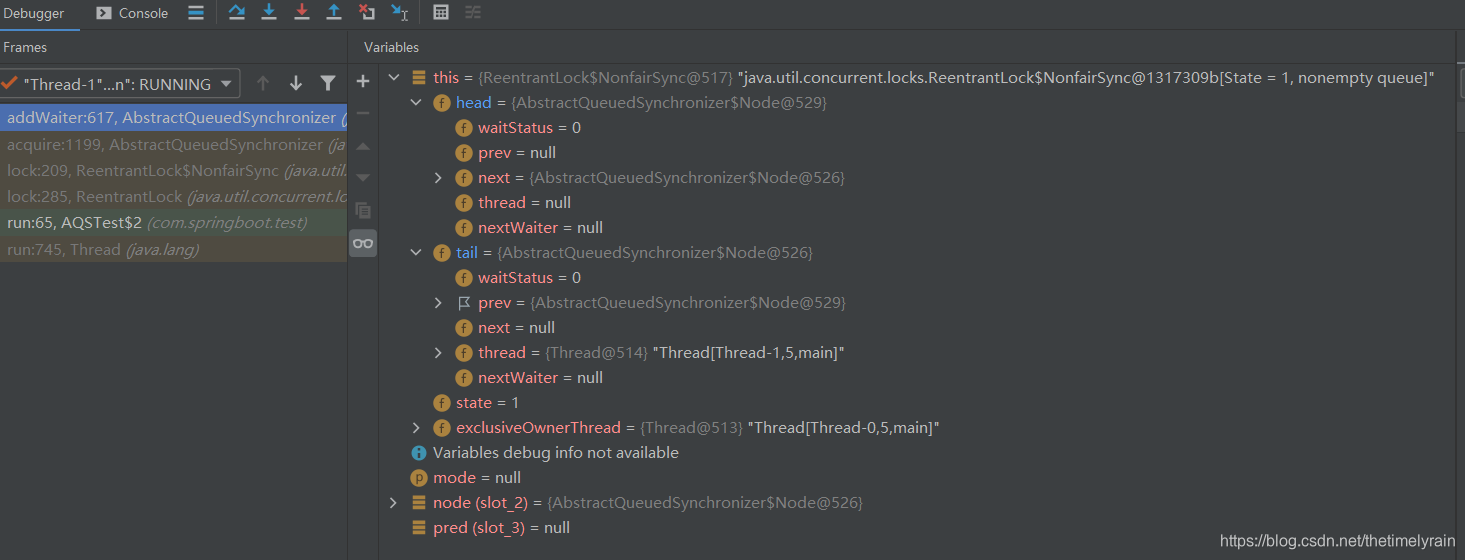
接下来是acquireQueued方法,他会使线程自旋阻塞,直到获取到锁。
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
//1. 拿到当前节点的前置节点
final Node p = node.predecessor();
//2. 如果当前节点的前置节点是头节点的话,就再次尝试获取锁
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
//成功获取锁后,将节点设置为头节点
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
/**
更改当前节点前置节点的waitStatus,只有前置节点的waitStatus=Node.SIGNAL,当前节点才有可能被唤醒。如果前置节点的waitStatus>0(即取消),则跳过取更前面的节点。
*/
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
//通过Unsafe.park来阻塞线程
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {
//在此阻塞,收到unlock()方法的unPark()方法会被唤醒
LockSupport.park(this);
return Thread.interrupted();
}线程释放锁,从前面可以知道,获取到锁的线程会设置为CLH队列的头部。这里如果tryRelease返回true,且head的waitStatus!=0。就会更新head的waitStatus为0并且 唤醒线程head.next节点的线程。
public final boolean release(int arg) {
//判断是否可以释放锁。
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;
}
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {
int ws = node.waitStatus;
//waitStatus不是取消状态,就设置成0
if (ws < 0)
compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);
//获取下个waitStatus不为取消的Node
Node s = node.next;
if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {
s = null;
for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)
if (t.waitStatus <= 0)
s = t;
}
//LockSupport.unpark是调用了Unsafe.unpark,唤醒线程。
if (s != null)
LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);
}总结:
其实aqs的核心原理无非三点:1.自旋 2.Lock.park()和unpark() 3.cas,顺着这三个关键点和加锁以及解锁过程就可以理清
参考文章:
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/qq_26680031/article/details/82348053
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/java_lyvee/article/details/98966684





 本文详细解析了AQS框架中的CLH队列工作原理,包括节点结构、等待机制及核心方法实现,如enqueue、dequeue等。通过具体代码示例展示了线程如何加入并退出CLH队列。
本文详细解析了AQS框架中的CLH队列工作原理,包括节点结构、等待机制及核心方法实现,如enqueue、dequeue等。通过具体代码示例展示了线程如何加入并退出CLH队列。
















 1393
1393

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








