java中抛出异常有三种方式:
- 系统自动抛出的异常
- throws
- throw
1.系统自动抛出
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
student p1 = new student();
System.out.println(p1.getName ().equals ("1"));
}
}
这段代码会自动抛出空指针异常
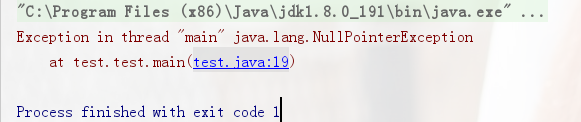
2.throw
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 12;
if ( a== 12){
throw new NullPointerException ("a为12");
}
}
直接在需要的地方使用关键字throw 抛出异常

3.throws
public class test {
//因为test()方法会抛出FileNotFoundException,main方法是调用者
//则需要使用try...catch进行捕获或者抛给JVM
//抛出时要遵循父类声明抛出“大于”子类声明抛出的原则
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
test();
}
public static void test() throws FileNotFoundException
{
//因为FileInputStream构造器会抛出FileNotFoundException
//所以需要使用try...catch块进行处理或使用throws抛给调用者
FileInputStream f = new FileInputStream ("a.txt");
}
}
使用throws关键字在方法上声明这个方法可能会抛出某种类型的异常,处理的话可以丢给jvm或者由程序员自己处理.
总结
- throw和throws出现的位置不一样
throw出现在函数体(方法内部),throws出现在函数头; - 含义不一样
throws表示出现异常的一种可能性,并不一定会发生这些异常;throw则是抛出了异常,执行throw则一定抛出了某种异常对象;
3.使用方法
两个关键字最好一起使用,也就是先声明异常,在进行抛出;





















 223
223

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








