java远程调用是一个很老的技术了,一提到远程调用或许很多小伙伴都会想到 Java RMI (Remote Method Invocation),这个是jdk自带的功能,但是现实中使用的很少,一般都是自己实现远程调用,如阿里开源的Dubbo框架就是一个比较优秀的框架。
研究远程调用框架的目的并不是自己写一个框架,而是掌握远程调用的基本原理,下面我就通过自己实现的代码来讲解他的原理。
首先我们要明白远程调用的流程,以及网络中发生的什么。
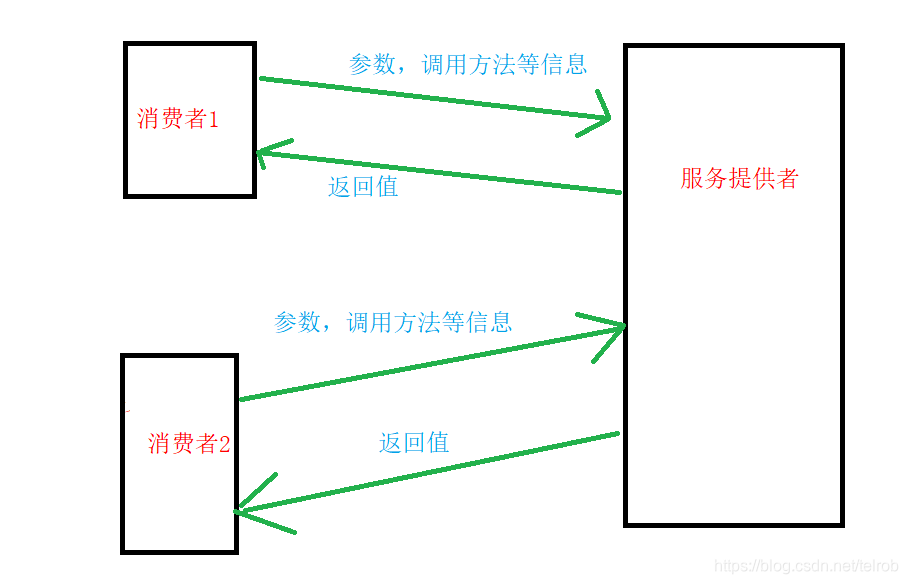
这里只是画了一张简单的调用图,里面其实涉及到java的一些基础知识。
当消费者调用某个接口之前系统会为配置文件中的接口都添加动态代理,当调用方法的时候就会到代理的invoke方法中,此时我们可以拿到调用接口的名称,调用方法,调用方法参数类型,参数值,这些信息,然后通过Hessian将这些信息序列号成byte数组,通过网络传输到服务提供者那边,然后服务提供者会将处理结果返回,在通过Hessian反序列化成对象。
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
//这里会调用对应的方法
//对参数进行序列化
ByteArrayOutputStream resultOut=new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[]paramData=null;
byte[]paramType=null;
if(args!=null) {
ByteArrayOutputStream byteout=new ByteArrayOutputStream();
HessianOutput out=new HessianOutput(byteout);
out.writeObject(args);
paramData=byteout.toByteArray();
byteout.close();
out.close();
Class<?>[]param=method.getParameterTypes();
ByteArrayOutputStream typeout=new ByteArrayOutputStream();
HessianOutput tout=new HessianOutput(typeout);
tout.writeObject(param);
paramType=typeout.toByteArray();
typeout.close();
tout.close();
}
byte[]beanNameData=beanName.getBytes();
byte[]methodNameData=method.getName().getBytes();
resultOut.write(int2byte(beanNameData.length));
resultOut.write(int2byte(methodNameData.length));
if(paramData!=null) {
resultOut.write(int2byte(paramType.length));
resultOut.write(int2byte(paramData.length));
}else {
resultOut.write(int2byte(0));
resultOut.write(int2byte(0));
}
resultOut.write(beanNameData);
resultOut.write(methodNameData);
if(paramData!=null) {
resultOut.write(paramType);
resultOut.write(paramData);
}
byte[]resultData=resultOut.toByteArray();
resultOut.close();
byte[]returnObject=sendPack.sendData(resultData);
ByteArrayInputStream bino=new ByteArrayInputStream(returnObject);
HessianInput hin=new HessianInput(bino);
Object retObj=hin.readObject();
hin.close();
bino.close();
return retObj;
}当服务提供者接收到调用信息后通过Hessian反序列化获取调用类名,方法名,参数类型,参数值,然后在bean列表中找到对应的bean通过反射调用方法,然后将返回结果序列化为字节数组返回给消费者。
public ParseBin(byte[]data) throws IOException {
ByteArrayInputStream in=new ByteArrayInputStream(data);
byte[]temp=new byte[4];
in.read(temp, 0, 4);
int classNameLen=bytes2int(temp);
in.read(temp, 0, 4);
int methodNameLen=bytes2int(temp);
in.read(temp, 0, 4);
int paramTypeLen=bytes2int(temp);
in.read(temp, 0, 4);
int paramDataLen=bytes2int(temp);
byte[]classNameData=new byte[classNameLen];
in.read(classNameData, 0, classNameLen);
className=new String(classNameData);
byte[]methodNameData=new byte[methodNameLen];
in.read(methodNameData, 0, methodNameLen);
methodName=new String(methodNameData);
if(paramTypeLen>0) {
byte[]paramTypeData=new byte[paramTypeLen];
in.read(paramTypeData, 0, paramTypeLen);
ByteArrayInputStream hbin=new ByteArrayInputStream(paramTypeData);
HessianInput Hessian2Input=new HessianInput(hbin);
paramType=(Class<?>[]) Hessian2Input.readObject();
Hessian2Input.close();
hbin.close();
}
if(paramDataLen>0) {
byte[]paramDataData=new byte[paramDataLen];
in.read(paramDataData, 0, paramDataLen);
ByteArrayInputStream hbin=new ByteArrayInputStream(paramDataData);
HessianInput Hessian2Input=new HessianInput(hbin);
param= (Object[]) Hessian2Input.readObject();
Hessian2Input.close();
hbin.close();
}
in.close();
}public static byte[] invoke(ClassPathXmlContext ctx,ParseBin parse) throws Exception {
Object obj=ctx.getBean(parse.getClassName());
if(obj!=null) {
Method method=obj.getClass().getDeclaredMethod(parse.getMethodName(), parse.getParamType());
Object data=method.invoke(obj, parse.getParam());
ByteArrayOutputStream byteout=new ByteArrayOutputStream();
HessianOutput hout=new HessianOutput(byteout);
hout.writeObject(data);
byte[]result=byteout.toByteArray();
hout.close();
byteout.close();
return result;
}
return null;
}至此就完成了一次调用过程。由于只是探讨远程调用的基本原理所以有很多问题都没有考虑周全,其实远程调用框架还有很多事情要考虑,如通过注册中心来获取服务信息,可以达到动态添加删除服务和负载均衡的目的,设置请求超时来提高服务的可用性等。项目参考代码 https://github.com/zhangruizhi123/mdubbo





 本文介绍Java远程调用技术,提到JDK自带的Java RMI使用少,常用阿里Dubbo框架。通过代码讲解远程调用原理,包括消费者添加动态代理、序列化信息传输,服务提供者反序列化、反射调用方法并返回结果,还提及远程调用框架需考虑注册中心、请求超时等问题。
本文介绍Java远程调用技术,提到JDK自带的Java RMI使用少,常用阿里Dubbo框架。通过代码讲解远程调用原理,包括消费者添加动态代理、序列化信息传输,服务提供者反序列化、反射调用方法并返回结果,还提及远程调用框架需考虑注册中心、请求超时等问题。
















 752
752

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








