简单使用
String key = "key-lock";
RLock lock = redisson.getLock(key);
lock.lock();
try {
// TODO
} catch (Exception e){
log.error(e.getMessage(), e);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
String key = "key-tryLock";
long maxWaitTime = 3_000;
RLock lock = redisson.getLock(key);
if (lock.tryLock(maxWaitTime, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)){
try {
// TODO
} catch (Exception e){
log.error(e.getMessage(), e);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
} else {
log.debug("redis锁竞争失败");
}
流程图
多个线程节点锁竞争的正常流程如下图:

多个线程节点锁竞争,并出现节点下线的异常流程如下图:

源码解析
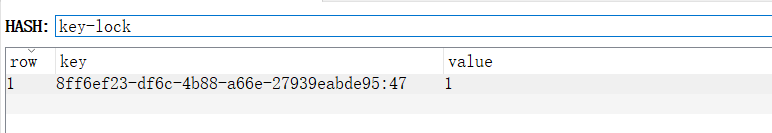
RedissonLock是可重入锁,使用redis的hash结构作为锁的标识存储,锁的名称作为hash的key,UUID + 线程ID作为hash的field,锁被重入的次数作为hash的value。如图所示:
private void lock(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, boolean interruptibly) throws InterruptedException {
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
// 尝试获取锁,锁获取成功则ttl为null;获取失败则返回锁的剩余过期时间
Long ttl = tryAcquire(leaseTime, unit, threadId);
if (ttl == null) {
return;
}
// 锁被其他线程占用而索取失败,使用线程通知而非自旋的方式等待锁
// 使用redis的发布订阅pub/sub功能来等待锁的释放通知
RFuture<RedissonLockEntry> future = subscribe(threadId);
commandExecutor.syncSubscription(future);
try {
while (true) {
ttl = tryAcquire(leaseTime, unit, threadId);
// 尝试获取锁,锁获取成功则ttl为null;获取失败则返回锁的剩余过期时间
if (ttl == null) {
break;
}
if (ttl >= 0) {
// 使用LockSupport.parkNanos方法线程休眠
try {
getEntry(threadId).getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
if (interruptibly) {
throw e;
}
getEntry(threadId).getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
} else {
if (interruptibly) {
getEntry(threadId).getLatch().acquire();
} else {
getEntry(threadId).getLatch().acquireUninterruptibly();
}
}
}
} finally {
// 退出锁竞争(锁获取成功或者放弃获取锁),则取消锁的释放订阅
unsubscribe(future, threadId);
}
}
public boolean tryLock(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
long time = unit.toMillis(waitTime);
long current = System.currentTimeMillis();
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
Long ttl = tryAcquire(leaseTime, unit, threadId);
if (ttl == null) {
return true;
}
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - current;
if (time <= 0) {
acquireFailed(threadId);
return false;
}
current = System.currentTimeMillis();
RFuture<RedissonLockEntry> subscribeFuture = subscribe(threadId);
if (!await(subscribeFuture, time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) {
if (!subscribeFuture.cancel(false)) {
subscribeFuture.onComplete((res, e) -> {
if (e == null) {
unsubscribe(subscribeFuture, threadId);
}
});
}
acquireFailed(threadId);
return false;
}
try {
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - current;
if (time <= 0) {
acquireFailed(threadId);
return false;
}
while (true) {
long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
ttl = tryAcquire(leaseTime, unit, threadId);
// lock acquired
if (ttl == null) {
return true;
}
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - currentTime;
if (time <= 0) {
acquireFailed(threadId);
return false;
}
currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (ttl >= 0 && ttl < time) {
getEntry(threadId).getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} else {
getEntry(threadId).getLatch().tryAcquire(time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - currentTime;
if (time <= 0) {
acquireFailed(threadId);
return false;
}
}
} finally {
unsubscribe(subscribeFuture, threadId);
}
}
RedissonLock实现的是可重入锁,通过redis的hash结构实现,而非加单的set nx ex。为了实现原子性的复杂的加锁逻辑,而通过lua脚本实现。获取锁会有如下三种状态:
- 锁未被任何线程占用,则锁获取成功,返回null
- 锁被当前线程占用,则锁获取成功并进行锁的重入,对锁的重入计数+1,返回null
- 锁被其他线程占用,则锁获取失败,返回该锁的自动过期时间ttl
<T> RFuture<T> tryLockInnerAsync(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId, RedisStrictCommand<T> command) {
internalLockLeaseTime = unit.toMillis(leaseTime);
return commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync(getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, command,
"if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then " +
"redis.call('hset', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +
"end; " +
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " +
"redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +
"end; " +
"return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);",
Collections.<Object>singletonList(getName()), internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
}
当锁因为被其他线程占用而 使用redis的发布订阅pub/sub功能,通过监听锁的释放通知(在其他线程通过RedissonLock释放锁时,会通过发布订阅pub/sub功能发起通知),等待锁被其他线程释放。通过如此的线程唤醒而非自旋的操作,提高了锁的效率。
public RFuture<E> subscribe(String entryName, String channelName) {
AtomicReference<Runnable> listenerHolder = new AtomicReference<Runnable>();
AsyncSemaphore semaphore = service.getSemaphore(new ChannelName(channelName));
RPromise<E> newPromise = new RedissonPromise<E>() {
@Override
public boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning) {
return semaphore.remove(listenerHolder.get());
}
};
Runnable listener = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
E entry = entries.get(entryName);
if (entry != null) {
entry.aquire();
semaphore.release();
entry.getPromise().onComplete(new TransferListener<E>(newPromise));
return;
}
E value = createEntry(newPromise);
value.aquire();
E oldValue = entries.putIfAbsent(entryName, value);
if (oldValue != null) {
oldValue.aquire();
semaphore.release();
oldValue.getPromise().onComplete(new TransferListener<E>(newPromise));
return;
}
RedisPubSubListener<Object> listener = createListener(channelName, value);
service.subscribe(LongCodec.INSTANCE, channelName, semaphore, listener);
}
};
semaphore.acquire(listener);
listenerHolder.set(listener);
return newPromise;
}
由于是可重入锁则需要在释放锁的时候做订阅通知,因此释放锁的操作同样是lua脚本实现。锁的释放会有如下三个状态:
- 等待释放的锁不存在或者不是当前线程持有,返回null
- 等待释放的锁被当前线程持有,且该锁当前被重入多次,则锁的重入计数-1,返回0
- 等待释放的锁被当前线程持有,且该锁当前未被重入,则锁的删除并发布该锁释放的订阅通知,返回1
protected RFuture<Boolean> unlockInnerAsync(long threadId) {
return commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync(getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN,
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[3]) == 0) then " +
"return nil;" +
"end; " +
"local counter = redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[3], -1); " +
"if (counter > 0) then " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]); " +
"return 0; " +
"else " +
"redis.call('del', KEYS[1]); " +
"redis.call('publish', KEYS[2], ARGV[1]); " +
"return 1; "+
"end; " +
"return nil;",
Arrays.<Object>asList(getName(), getChannelName()), LockPubSub.UNLOCK_MESSAGE, internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
}
Watchdog
RedissonLock为了避免应用获取锁后宕机,因为没人来释放锁而导致死锁情况的出现,默认每次锁的占用只有30秒的时间(org.redisson.config.Config#lockWatchdogTimeout = 30 * 1000)。于是便有了Watchdog设计,由独立的线程定时给未释放的锁续期,默认锁有效期的三分之一的时长即每10秒给锁自动续期。
private void renewExpiration() {
ExpirationEntry ee = EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.get(getEntryName());
if (ee == null) {
return;
}
// 默认10秒钟后执行锁续期任务
Timeout task = commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().newTimeout(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run(Timeout timeout) throws Exception {
ExpirationEntry ent = EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.get(getEntryName());
if (ent == null) {
return;
}
Long threadId = ent.getFirstThreadId();
if (threadId == null) {
return;
}
RFuture<Boolean> future = renewExpirationAsync(threadId);
future.onComplete((res, e) -> {
if (e != null) {
log.error("Can't update lock " + getName() + " expiration", e);
return;
}
// 如果锁续期成功,则10秒钟后再次续期
if (res) {
renewExpiration();
}
});
}
}, internalLockLeaseTime / 3, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
ee.setTimeout(task);
}
protected RFuture<Boolean> renewExpirationAsync(long threadId) {
return commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync(getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN,
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return 1; " +
"end; " +
"return 0;",
Collections.<Object>singletonList(getName()),
internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
}
























 3075
3075

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








