Part I. Overview of Spring Framework
The Spring Framework is a lightweight solution and a potential one-stop-shop for building your enterprise-ready applications. However, Spring is modular, allowing you to use only those parts that you need, without having to bring in the rest. You can use the IoC container, with Struts on top, but you can also use only the Hibernate integration code or the JDBC abstraction layer. The Spring Framework supports declarative transaction management, remote access to your logic through RMI or web services, and various options for persisting your data. It offers a full-featuredMVC framework, and enables you to integrate AOP transparently into your software.
Spring is designed to be non-intrusive, meaning that your domain logic code generally has no dependencies on the framework itself. In your integration layer (such as the data access layer), some dependencies on the data access technology and the Spring libraries will exist. However, it should be easy to isolate these dependencies from the rest of your code base.
This document is a reference guide to Spring Framework features. If you have any requests, comments, or questions on this document, please post them on the user mailing list or on the support forums athttp://forum.springsource.org/.
Spring框架是轻量级解决方案和一站式构建企业级应用的潜能事物。然而,Spring是模块化的,允许你使用你需要的部分,而不必引入剩余的其他部分。你可以使用IoC容器,在之上使用Struts,但是你也可以只使用Hibernate整合代码或者JDBC抽象层。Spring框架支持声明式事物管理,RMI或者web services远程接口调用,多种数据持久选择。它提供全功能MVC框架,让你能透明地整合AOP到你的软件。
Spring被设计为非侵入示的,也就是说你的域逻辑代码一般不依赖与框架本身。在你的整合层(例如数据访问层),一些依赖与数据访问技术和Spring图书管将存在。然而,很容易将你其余的基础代码与这些依赖隔离。
这本文档是Spring框架特色的参考向导。如果你有任何要求,评论,或者问题关于这本文档,请发送相关信息到用户邮件列表地址发送邮件,或者在支持论坛 http://forum.springsource.org/。
1. Introduction to Spring Framework
Spring Framework is a Java platform that provides comprehensive infrastructure support for developing Java applications. Spring handles the infrastructure so you can focus on your application.
Spring enables you to build applications from “plain old Java objects” (POJOs) and to apply enterprise services non-invasively to POJOs. This capability applies to the Java SE programming model and to full and partial Java EE.
Examples of how you, as an application developer, can use the Spring platform advantage:
-
Make a Java method execute in a database transaction without having to deal with transaction APIs.
-
Make a local Java method a remote procedure without having to deal with remote APIs.
-
Make a local Java method a management operation without having to deal with JMX APIs.
-
Make a local Java method a message handler without having to deal with JMS APIs.
1.1 Dependency Injection and Inversion of Control
Although the Java platform provides a wealth of application development functionality, it lacks the means to organize the basic building blocks into a coherent whole, leaving that task to architects and developers. True, you can use design patterns such as Factory, Abstract Factory,Builder,Decorator, andService Locator to compose the various classes and object instances that make up an application. However, these patterns are simply that: best practices given a name, with a description of what the pattern does, where to apply it, the problems it addresses, and so forth. Patterns are formalized best practices thatyou must implement yourself in your application.
The Spring Framework Inversion of Control (IoC) component addresses this concern by providing a formalized means of composing disparate components into a fully working application ready for use. The Spring Framework codifies formalized design patterns as first-class objects that you can integrate into your own application(s). Numerous organizations and institutions use the Spring Framework in this manner to engineer robust,maintainable applications.
Spring框架介绍Spring框架是一个JAVA平台,提供广泛的基础机构来支持JAVA应用开发。Spring处理这些基础架构所以你可以把精力放在你的应用上。
Spring让你能够使用POJOs建立应用,提供企业服务对POJOs非侵害。这种能力完全适用于Java Se程序模型和部分Java EE。
作为应用开发者,下面列子告诉你如何能使用 Spring平台的优越性。
实现一个数据库事物方法不需要处理事物APIs
实现一个本地方法远程调用程序不需要处理远程APIs
实现一个本地管理操作方法不需要处理JMX
实现一个本地消息处理器方法不需要处理JMS APIs
1.1依赖注入和控制反转
Java应用一个松散的术语运行在全范围从受限的applet到n层服务段企业应用,典型的由对象协作形成适当的应用。因此应用里的对象互相有依赖。
尽管Java平台提供大量的应用开发功能,它缺少方法组织最基础的代码块,把这个任务留给了设计者和开发者。事实上,你能使用设计模式例如工厂方法模式,抽象工厂模式,建造者模式,装饰模式等去组成各种各样的类和对象实例来组织应用。然而,这些模式非常简单:最佳实践命名,根据功能描述,哪里应用它等等。模式拘泥于最近实践,你必须实现你自己的最佳实践在你的应用里。
Spring框架的控制反转模式组件解决了这个问题提供一个形式化方式组织不同组件在整个工作应用等待使用。Spring框架编码把设计模式形式话作为初始类对象你可以整合你自己的应用。大量的组织和机构正在使用Sping框架用此方式设计健壮的,可扩展的应用。
The Spring Framework consists of features organized into about 20 modules. These modules are grouped into Core Container, Data Access/Integration, Web, AOP (Aspect Oriented Programming), Instrumentation, and Test, as shown in the following diagram.
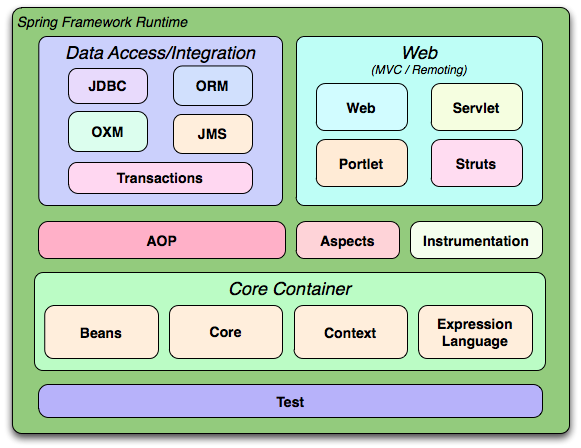
Overview of the Spring Framework
1.2.1 Core Container
The Core Container consists of the Core, Beans, Context, and Expression Language modules.
The Core and Beans modules provide the fundamental parts of the framework, including the IoC and Dependency Injection features. TheBeanFactory is a sophisticated implementation of the factory pattern. It removes the need for programmatic singletons and allows you to decouple the configuration and specification of dependencies from your actual program logic.
The Context module builds on the solid base provided by theCore and Beans modules: it is a means to access objects in a framework-style manner that is similar to a JNDI registry. The Context module inherits its features from the Beans module and adds support for internationalization (using, for example, resource bundles), event-propagation, resource-loading, and the transparent creation of contexts by, for example, a servlet container. The Context module also supports Java EE features such as EJB, JMX ,and basic remoting. TheApplicationContext interface is the focal point of the Context module.
The Expression Language module provides a powerful expression language for querying and manipulating an object graph at runtime. It is an extension of the unified expression language (unified EL) as specified in the JSP 2.1 specification. The language supports setting and getting property values, property assignment, method invocation, accessing the context of arrays, collections and indexers, logical and arithmetic operators, named variables, and retrieval of objects by name from Spring's IoC container. It also supports list projection and selection as well as common list aggregations.
1.2模型
Spring框架有20个特色模型组成,这些模块按组分为:核心容器,数据访问/整合,
Web,AOP,Instrumentation,和测试,如下图表所示
1.2.1 核心容器
核心容器包括核心、Beans,背景,和表述语言模块。
核心和Beans模块提供框架的基础部分,包括控制反转和依赖注入特色。BeanFactory是一个
工厂模式的精妙实现。它删除了程序必须的单列模式允许你从你实际逻辑程序解耦
背景模块建立在坚实的基础上为核心容器。它是一种从框架访问对象的方式,类似与JNDI注
册。背景模块继承Beans模块的特色同时增加了国际化支持,事件传播,资源载入,在上下文
透明创建,例如servlet容器。上下文容器也支持JavaEE特色,例如EJB,JMX和基础远程调用
。ApplicationContex接口是上下文模块的焦点。
表达语言模块提供了超强的表达语言查询和处理对象图标在运行时。它是作为JSP2.1规格统一表述语言的扩展。语言支持存取属性值,属性任务,方法,访问上下文队列,集合和索引,逻辑和数学算法,可变名称,根据名称从Spring IoC容器收回的对象。它也支持列表项目和选择和普通列表集合一样。
The Data Access/Integration layer consists of the JDBC, ORM, OXM, JMS and Transaction modules.
The JDBC module provides a JDBC-abstraction layer that removes the need to do tedious JDBC coding and parsing of database-vendor specific error codes.
The ORM module provides integration layers for popular object-relational mapping APIs, includingJPA,JDO,Hibernate, and iBatis. Using the ORM package you can use all of these O/R-mapping frameworks in combination with all of the other features Spring offers, such as the simple declarative transaction management feature mentioned previously.
The OXM module provides an abstraction layer that supports Object/XML mapping implementations for JAXB, Castor, XMLBeans, JiBX and XStream.
The Java Messaging Service (JMS) module contains features for producing and consuming messages.
The Transaction module supports programmatic and declarative transaction management for classes that implement special interfaces and forall your POJOs (plain old Java objects).
The Web layer consists of the Web, Web-Servlet, Web-Struts, and Web-Portlet modules.
Spring's Web module provides basic web-oriented integration features such as multipart file-upload functionality and the initialization of the IoC container using servlet listeners and a web-oriented application context. It also contains the web-related parts of Spring's remoting support.
The Web-Servlet module contains Spring's model-view-controller (MVC) implementation for web applications. Spring's MVC framework provides a clean separation between domain model code and web forms, and integrates with all the other features of the Spring Framework.
The Web-Struts module contains the support classes for integrating a classic Struts web tier within a Spring application. Note that this support is now deprecated as of Spring 3.0. Consider migrating your application to Struts 2.0 and its Spring integration or to a Spring MVC solution.
The Web-Portlet module provides the MVC implementation to be used in a portlet environment and mirrors the functionality of Web-Servlet module.
Spring's AOP module provides an AOP Alliance-compliant aspect-oriented programming implementation allowing you to define, for example, method-interceptors and pointcuts to cleanly decouple code that implements functionality that should be separated. Using source-level metadata functionality, you can also incorporate behavioral information into your code, in a manner similar to that of .NET attributes.
The separate Aspects module provides integration with AspectJ.
The Instrumentation module provides class instrumentation support and classloader implementations to be used in certain application servers.
The Test module supports the testing of Spring components with JUnit or TestNG. It provides consistent loading of Spring ApplicationContexts and caching of those contexts. It also provides mock objects that you can use to test your code in isolation.
1.2.2数据访问/整合
数据访问/整合层包括JDBC,ORM,OXM,JMX和事物模块。
JDBC模块提供JDBC抽象层移除了乏味的JDBC代码和分析数据库提供商特殊的错误代码
ORM模块为普通对象关系映射接口提供整合层,包括JPA,JDO,Hibernate,和iBatis。使用
ORM包你可以使用所有的O/R-mapping框架与Spring提供的其他特色框架结合,例如前面提到
的简单声明事物管理。
OXM模块提供抽象层支持对象到XML映射为MAXB,Castor,XMLBeans,JiBX和XSteam提供实现
Java消息服务模块包含生成和消费消息特征。
事物 模块支持程序和类声明事物管理为所有普通JAVA类实现特殊接口
1.2.3Web
Web层由Web,Web-Servlet,Web-Struts,和Web-Porlet模块组成。
Spring Web模块提供面向Web的基础整合特征,例如多文件上传功能,使用servlet监听和面
向Web的背景应用IoC容器初始化。它也包括Spring远程支持的web-related部分。
Web-Servlet模块包括Spring为web应用做的MVC实现。Spring的MVC框架提供清晰的分离从本
地域代码到Web表单,与其他Spring特色框架结合。
Web-Struts模块包括支持类为实现传统的Struts web层在Spring应用里。注意这个支持现在
在Spring3.0不赞成使用。考虑迁移你的应用到Struts2.0和Spring整合或者使用SpringMVC解
决。
Web-porlet模块提供MVC实现在portlet环境下使用,是Web-Servlet模块的镜像功能。
1.2.4 AOP和仪表
AOP模块提供AOP面向方面的程序设计实现允许你声明,例如,方法拦截和切入点为清楚的解
耦代码实现必须分离的功能。使用资源元数据功能,你还可以吸收信息行为到你的代码,用
同样的方式为.net属性。
分离方面模块提供整合AspectJ。
仪表模块提供类仪表支持类加载实现经常在应用服务器使用。
1.2.5测试
测试模块支持Spring组件为Junit或TestNG测试。它提供一致的Spring应用背景和那些背景缓存。它也支持模拟对象你可以测试你的代码在隔离状态下。
The building blocks described previously make Spring a logical choice in many scenarios, from applets to full-fledged enterprise applications that use Spring's transaction management functionality and web framework integration.
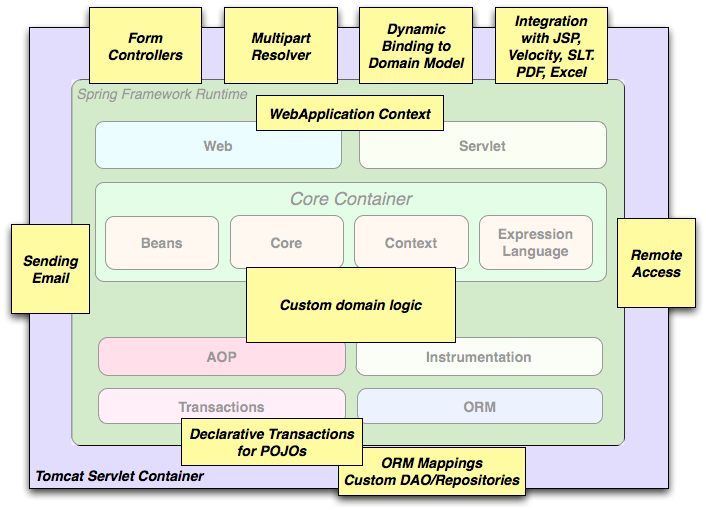
Typical full-fledged Spring web application
Spring's declarative transaction management features make the web application fully transactional, just as it would be if you used EJB container-managed transactions. All your custom business logic can be implemented with simple POJOs and managed by Spring's IoC container. Additional services include support for sending email and validation that is independent of the web layer, which lets you choose where to execute validation rules. Spring's ORM support is integrated with JPA, Hibernate, JDO and iBatis; for example, when using Hibernate, you can continue to use your existing mapping files and standard HibernateSessionFactory configuration. Form controllers seamlessly integrate the web-layer with the domain model, removing the need forActionForms or other classes that transform HTTP parameters to values for your domain model.
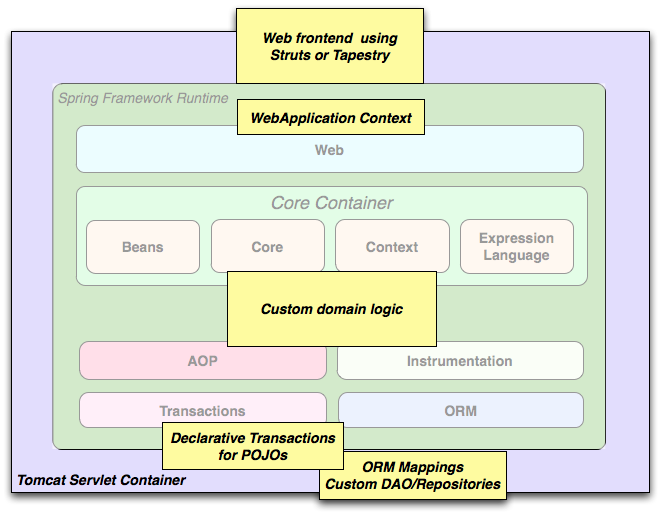
Spring middle-tier using a third-party web framework
Sometimes circumstances do not allow you to completely switch to a different framework. The Spring Framework doesnot force you to use everything within it; it is not anall-or-nothing solution. Existing front-ends built with WebWork, Struts, Tapestry, or other UI frameworks can be integrated with a Spring-based middle-tier, which allows you to use Spring transaction features. You simply need to wire up your business logic using an ApplicationContext and use aWebApplicationContext to integrate your web layer.
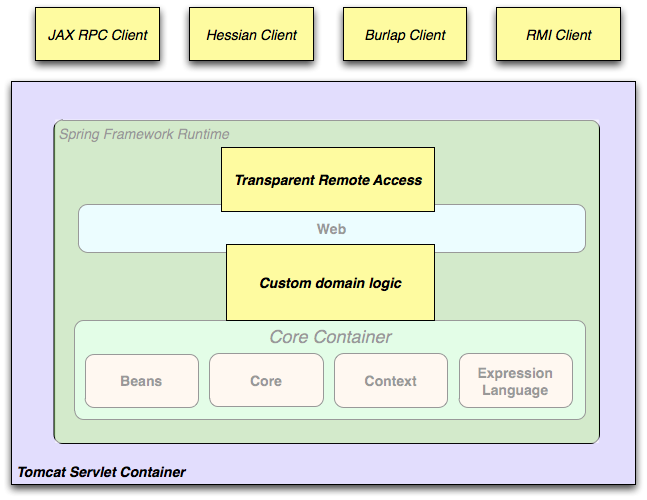
Remoting usage scenario
When you need to access existing code through web services, you can use Spring'sHessian-, Burlap-, Rmi- or JaxRpcProxyFactory classes. Enabling remote access to existing applications is not difficult.
1.3使用场景
之前描述的建筑块使得Spring在很多场景有一个逻辑选择在,从小程序到使用Spring的事物管理功能和web框架整合成熟的企业应用。
典型的成熟Spring web应用
Spring的声明事物管理功能使web应用成为完全交互的,正如它可以是如果你使用EJB容器广利事物。所有你的客户业务逻辑可以被Spring的IoC容器用简单的POJOs实现和管理。其他服务包括发送邮件,验证它在web层是独立的,让你可以选择在哪里执行你的验证规则。Spring的ORM支持与JPA,Hibernate,JDO和iBatis的整合;例如,当你使用Hibernate,你可以继续使用已经存在的映射文件和标准的Hibernate SessionFactory配置。表达控制无缝整合web层和域代码,移除必须的ActionForms或者其他为你的域模型改变HTTP参数到值的对象。
Spring中间层使用第三方web框架。
有些时候环境不允许你完全替换不同的框架。Spring框架不会强迫你使用里面的任何事;它不是要么全有要么全无的解决方案。存在的前端有WebWork,Struts,Tapestry,或者其他UI框架可以被整合到Spring基础中间层,允许你使用Spring的事物功能。你只需要写你的业务逻辑代码使用ApplicationContext和使用WebApplicationContext去整合你的web层。
远程调用场景
当你需要通过web服务访问现有代码,你可以使用Spring的Hessian-,Burlap-,Rmi-或者JaxRpcProxyFactory类。能够远程访问已存在应用不是很难。
EJBs - Wrapping existing POJOs
The Spring Framework also provides an access and abstraction layer for Enterprise JavaBeans, enabling you to reuse your existing POJOs and wrap them in stateless session beans for use in scalable, fail-safe web applications that might need declarative security.
Dependency management and dependency injection are different things. To get those nice features of Spring into your application (like dependency injection) you need to assemble all the libraries needed (jar files) and get them onto your classpath at runtime, and possibly at compile time. These dependencies are not virtual components that are injected, but physical resources in a file system (typically). The process of dependency management involves locating those resources, storing them and adding them to classpaths. Dependencies can be direct (e.g. my application depends on Spring at runtime), or indirect (e.g. my application depends on commons-dbcp which depends on commons-pool). The indirect dependencies are also known as "transitive" and it is those dependencies that are hardest to identify and manage.
If you are going to use Spring you need to get a copy of the jar libraries that comprise the pieces of Spring that you need. To make this easier Spring is packaged as a set of modules that separate the dependencies as much as possible, so for example if you don't want to write a web application you don't need the spring-web modules. To refer to Spring library modules in this guide we use a shorthand naming convention spring-* or spring-*.jar, where "*" represents the short name for the module (e.g. spring-core, spring-webmvc, spring-jms, etc.). The actual jar file name that you use may be in this form (see below) or it may not, and normally it also has a version number in the file name (e.g. spring-core-3.0.0.RELEASE.jar).
In general, Spring publishes its artifacts to four different places:
-
On the community download site http://www.springsource.org/downloads/community. Here you find all the Spring jars bundled together into a zip file for easy download. The names of the jars here since version 3.0 are in the form
org.springframework.*-<version>.jar. -
Maven Central, which is the default repository that Maven queries, and does not require any special configuration to use. Many of the common libraries that Spring depends on also are available from Maven Central and a large section of the Spring community uses Maven for dependency management, so this is convenient for them. The names of the jars here are in the form
spring-*-<version>.jarand the Maven groupId isorg.springframework.
EJBs 包装已存在POJOs
Spring框架也为企业级JavaBeans提供抽象访问,让你能重用你已存在的POJOs包装它们为无
状态会话beans可扩展使用,安全web应用可能需要申明式保护。
1.3.1依赖管理和命名规范
依赖管理和依赖注入是不同的事情。为获取那些Spring的特色功能(例如依赖注入)你需要
收集所有的依赖包放入到你的类路径在运行时,还可能在编译时。那些依赖不是实际注入的
组件,而是实际的文件系统资源包。依赖管理的过程包括找出那些资源,保存,添加到类路
径。依赖有直接的和间接的。间接的依赖关系也被称为“及物”,它是非常难管理和识别的
。
如果你要使用Spring你需要拷贝相关jar包包括你需要的Spring套件。为了使这些变得容易
Spring被打包为一套尽可能分离依赖关系的模块,例如你不需要编写web应用你就不需要
spring-web模块包。为了把Spring资源包提到这个向导我们使用简单名称规则spring-*或者
spring-*.jar,*代表模块短名称。你使用的实际jar文件名称或许在下面表达或者不在,一
般的它也有版本好在名称里。
总体而言,Spring在四个不同的地方发布它的包文件
1在社区下载站点http://www.springsource.org/downloads/community。这里你可以找到所
有的Spring jars文件绑定到一起压缩为一个zip文件方便下载。jars包的名称这里从3.0版本
在表单里
2Maven中心库,默认Maven查询仓库,不需要任何特别的配置就可以使用。Spring依赖的很多
普通的资源包也是可用的从Maven中心库,很大一部分Spring社区都在使用Maven管理依赖,
所以对他们来说这是非常方便的。这里jars的名称这里表示为spring-*-<>





 Spring框架是一个轻量级的Java平台,提供全面的基础架构支持,帮助开发者专注于应用程序逻辑而非基础设施细节。该框架支持依赖注入、声明式事务管理等功能,并提供丰富的模块如Web、AOP等。
Spring框架是一个轻量级的Java平台,提供全面的基础架构支持,帮助开发者专注于应用程序逻辑而非基础设施细节。该框架支持依赖注入、声明式事务管理等功能,并提供丰富的模块如Web、AOP等。
















 5122
5122

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








