应该背景:计划写一个公共方法,用以截取前端请求的参数正确性,解放后端开发频繁查询代码的压力。此处用的是around切面的方式。首先,获取注解的方式有一种是直接上切点,如下:
//定义切点Pointcut
@Pointcut("execution(* com.biierg.pg.controller.*Controller.*(..))")
public void excudeService() {
}
@Around("excudeService()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {.............
}
另外一种方式如下:
//定义切点Pointcut
@Pointcut("execution(* com.biierg.pg.controller.*Controller.*(..)) && @annotation(io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParams)")
public void excudeService() {
}
@Around("excudeService() && @annotation(apiImplicitParams)")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp,ApiImplicitParams apiImplicitParams){.............
}
@annotion 还可以多添加几个,但是缺点就是只能获取到方法上面的注解,无法得到方法参数的注解,我理解为:切点只切到方法,就不会往里走,所以拿不到方法参数的注解(纯属个人猜测~_~,如果不正确,欢迎下方留言)。
下面进去正题,下面只讨论怎么去到参数值,至于效率问题自己斟酌即可。
1.按照上面第二种方式,可以直接拿出传递的变量,取值即可。但如果是复合注解,还需要遍历一下,比如RequestMapping,可以如下取值:
requestMapping.value();
requestMapping.name()
只可获取到方法上的注解,参数注解我还不没有得到。
2、第二种方式就是通过ProceedingJoinPoint pjp 获取,如下:
Signature sig = pjp.getSignature();
MethodSignature msig = null;
if (!(sig instanceof MethodSignature)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("该注解只能用于方法");
}
msig = (MethodSignature) sig;
Object target = pjp.getTarget();
//getDeclaredMethod() 包括自身所有方法,private\protected\public ;
//getMethod() 包括从基类继承,接口实现的所有public方法
Method currentMethod = target.getClass().getDeclaredMethod(msig.getName(), msig.getParameterTypes());
通过上面的方式获得当前方法currentMethod,然后在往下查找注解,下面代码中可以找到提取方法:
private Map getParamMap(Method method) throws NoSuchFieldException, SecurityException, IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Map<String,Param> mapParams= new HashMap<String,Param>();
ApiImplicitParams aip=method.getAnnotation(ApiImplicitParams.class);
InvocationHandler ih=Proxy.getInvocationHandler(aip);
Field field=ih.getClass().getDeclaredField("memberValues");
//private final 需要打开权限
field.setAccessible(true);
Map memberValues=(Map) field.get(ih);
ApiImplicitParam[] value = (ApiImplicitParam[]) memberValues.get("value");
for(ApiImplicitParam param:value) {
Param pa=new Param();
InvocationHandler ihp= Proxy.getInvocationHandler(param);
Field fieldP=ihp.getClass().getDeclaredField("memberValues");
fieldP.setAccessible(true);
Map map=(Map)fieldP.get(ihp);
String name=(String) map.get("name");
String type=(String) map.get("dataType");
boolean required= (boolean) map.get("required");pa.setName(name);
pa.setType(type);
pa.setRequired(required);
mapParams.put(pa.getName(),pa);
}
return mapParams;
}
这是方法上的注解,方法的参数注解通过method.getParameterAnnotations()获得,然后如上代码遍历即可。但是需要注意的是此时获得的是一个二维数组,也就是有几个参数就有几个一维数组在该二维数组里面。如果某参数没有注解,此时一维数组为空。
3.通过handlerMappings获得注解
既然mvc可以拿到handler,那么我们也可以参照DispatcherServlet去拿到类以及方法,然后再去取相应的注解。首先我们要取到requeste,
RequestAttributes ra = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
ServletRequestAttributes sra = (ServletRequestAttributes) ra;
HttpServletRequest request = sra.getRequest();
第二步,通过request拿到ApplicationContext
ServletContext sc = request.getServletContext();
ApplicationContext context = WebApplicationContextUtils.getRequiredWebApplicationContext(sc);
第三步,构造handlerMappings
Map<String, HandlerMapping> matchingBeans =
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false);
if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
this.handlerMappings = new ArrayList<>(matchingBeans.values());
}
第四步,通过handlerMappings 取拿注解
for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) {
HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
if(!HandlerMethod.class.isInstance(handler.getHandler())) {
continue;
}
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = (HandlerMethod) handler.getHandler();
for(MethodParameter param:handlerMethod.getMethodParameters()) {
Param parameter=new Param();
Annotation[] annotatedElement = param.getParameterAnnotations();
//查询注解中的required=true
for(Annotation annotation:annotatedElement) {
if(RequestParam.class.isInstance(annotation)) {
RequestParam requestParam = (RequestParam) annotation;
//parameter.setRequired(requestParam.required());
if(requestParam.required()) {
paramRequiredList.add(param.getParameterName());
}
}
}
map.put(parameter.getName(),parameter);
}
break;
}
}
上面代码中进行类别判断,是因为handlerMappings中存在六个不通的HandlerMapping,其实是spring容器中对应的六种不同的bean,如下:
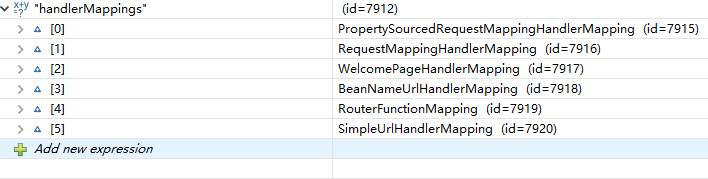
我这里需要的是第二个RequestMappingHandlerMapping,这里每个都是一个map,里面存储这url和handler的对应关系。
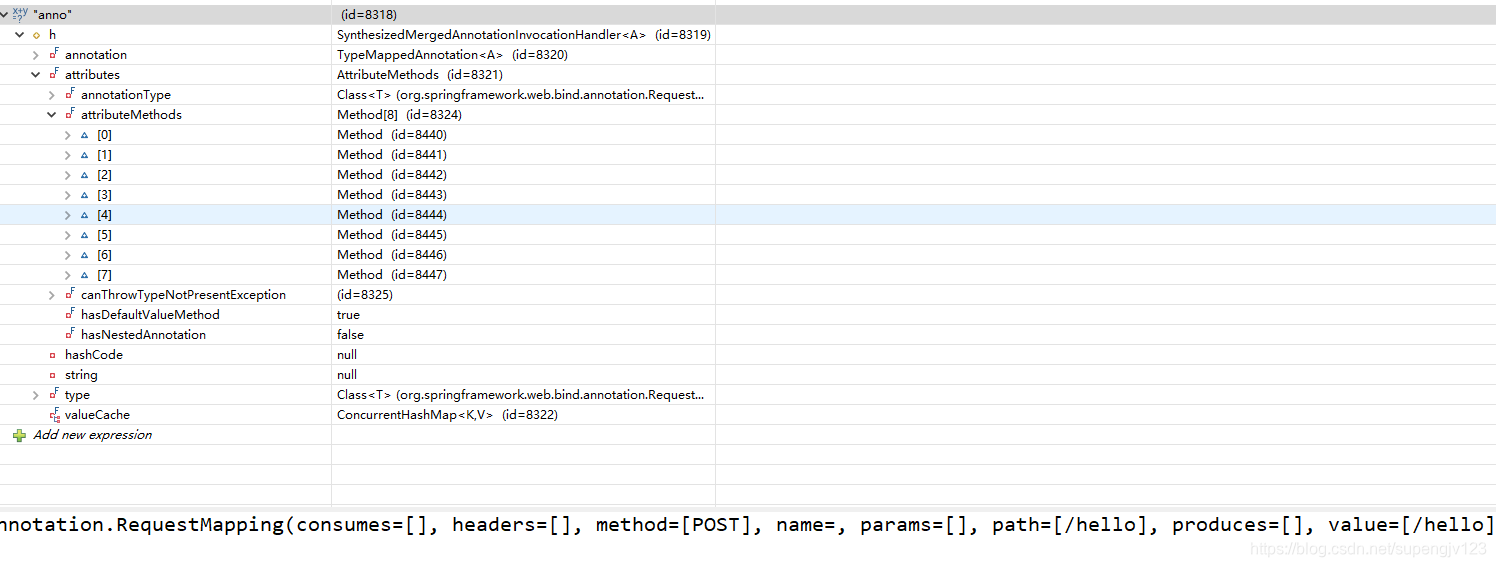
方法上的注解可以通过RequestMapping anno = handlerMethod.getMethodAnnotation(RequestMapping.class)获取 ,相应值如anno.value(),anno.name()可以直接取到,anno结构如下
目前知道的三种方式已经讲述完毕,各有优略,欢迎大家补充留言,谢谢阅读!




 本文介绍了在AOP中如何获取方法及其参数的注解,包括直接使用切点表达式、通过 ProceedingJoinPoint 和 MethodSignature,以及通过handlerMappings获取注解的方式。详细解析了每种方式的实现过程,并指出不同方式的适用场景。
本文介绍了在AOP中如何获取方法及其参数的注解,包括直接使用切点表达式、通过 ProceedingJoinPoint 和 MethodSignature,以及通过handlerMappings获取注解的方式。详细解析了每种方式的实现过程,并指出不同方式的适用场景。
















 861
861

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








